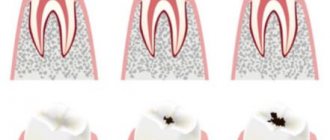
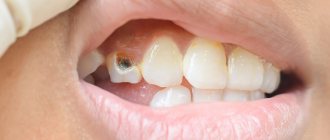
Reasons for appearance
There are many reasons for the development of the disease, but the most common is a violation of the dental treatment protocol. If during his work the master did not completely dry the cavity freed from caries, installed the light-curing filling incorrectly, poorly cleaned the affected areas, or chose the wrong composition of the filling material, the patient may later encounter the appearance of hidden caries.
Also, such a problem can be caused by loosening or too much shrinkage of the filling. Because of this, small chips and cracks may appear on the surface of the tooth, where pathogenic bacteria and food particles can enter. This pathology does not manifest itself in any way at first; it can only be detected when visible signs appear on the enamel: spots, dark areas, depressions.
If a person notices the appearance of severe pain even after eliminating the irritants, this may indicate that caries has affected the pulp chamber. Pulpitis is an inflammatory process affecting nerve fibers. In this case, it is not always possible to save the tooth; sometimes experts recommend installing an implant in its place.
Prevention measures
To prevent hidden caries from appearing, you must adhere to the following rules:
- Brush your teeth at least twice a day, paying attention to cleaning hard-to-reach surfaces like the space between your teeth. It is advisable to choose the right toothbrush and toothpaste.
- Drink water that contains fluoride. If there is not enough of this element in the water, the tooth enamel will gradually deteriorate. Drinking water must be fluoridated or seafood must be included in the diet. They also use special rinses.
- Do not eat food that has a high or low temperature; it can cause microcracks to appear on the enamel, into which microorganisms that cause caries can penetrate.
- Visit your dentist twice a year for a physical examination. In this case, dental diseases can be detected in time and treated without any special consequences. When plaque appears on your teeth, you need to have your teeth professionally cleaned and prevent bacteria from spreading.
Types of internal caries
Today it is customary to distinguish several types of hidden caries depending on its location. Contact is the one that appears in the spaces between the teeth, that is, on the inner edges. It is impossible to notice the problem at the initial stage; it makes itself felt only after some time, when the tooth is already quite badly damaged. As a result, severe pain appears that cannot be eliminated even with potent medications.
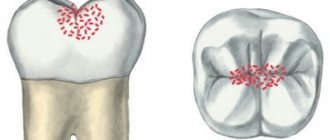
Fissure caries is a bacterial infection of fissures - small grooves on the chewing side of the teeth. When the first dark areas appear in this area, you should immediately seek advice from a specialist. If caries has not affected the deep layers of tissue, then it is very easy to treat. As a preventative measure, fissure sealing can be performed.
The most complex type of hidden caries is root caries. It is difficult to treat because it is usually diagnosed too late. Often the patient is tormented by concomitant diseases: periodontitis, pulpitis, etc. Secondary caries also occurs in dental practice. It appears in place of a previously installed filling. The cause may be both medical errors and neglect of oral hygiene.
Symptoms and course of the disease
Hidden caries does not appear in the initial stages of the disease and becomes noticeable only after serious damage to the dental tissue. There is no pain, dental lesions are not visible in the mirror. Now, if a filling falls out, this is already an important symptom, meaning that caries is developing. The enamel becomes spotted.
If caries has progressed far, the tooth begins to hurt severely due to temperature changes, from sweet or salty foods. At the same time, the tooth itself does not hurt, only from various causes. When the irritant disappears, the pain immediately goes away. If pain begins to appear on its own, it means that caries has already turned into pulpitis, and the tooth tissue has begun to become inflamed.
If you press on the affected area (chewing food), it also responds with pain. The reason for this is that food penetrates the hole and compresses the vessels and nerves of the pulp. If the remaining food is removed from the affected area, the pain will go away.
Detection and treatment
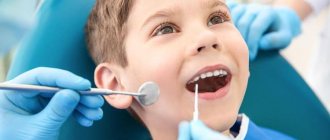
As mentioned earlier, identifying the presence of internal caries at home is quite problematic. It is often diagnosed during the next preventive examination in the dental chair or during the correction of anomalies not related to caries. If a person has complaints and suspicions of tooth decay from the inside, he may be prescribed one of the examination methods. Doctors often use x-rays, as well as fluorescent illumination. These verification technologies are the most informative and accessible.
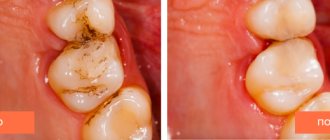
The patient may also be referred for a hardware examination, which involves the use of a laser beam. Treatment of hidden carious lesions is carried out in several successive stages. If there is a filling in the tooth, it must be removed. After this, the affected areas of enamel and dentin are drilled out, treated with an antiseptic and thoroughly dried. After this, the doctor installs the filling, polishes it and restores the normal shape of the tooth.
If caries has affected the pulp, the tooth is almost always depulped and the canals are sealed. A permanent filling is not installed immediately; at first, they are limited to a temporary structure. If a large tooth crown is often destroyed, prosthetics or implantation are recommended. In this case, the risk of re-development of caries will be minimal.
Diagnosis of hidden caries
Modern diagnostic techniques make it possible to identify a cavity in a tooth affected by caries at any stage of its development. Another thing is that the doctor uses these techniques when there is a suspicion of caries. And these suspicions are precisely difficult to identify - the tooth does not hurt, and the patient is not worried. So often caries remains unnoticed and actively grows. Hidden caries can coexist with ordinary caries, the damage from which is quite noticeable. If there is a lot of tooth decay, an experienced dentist will definitely check for hidden lesions. Diagnostics can be carried out using various methods:
- Laser is very reliable. A special device “Diagnodent” directs a laser beam at the tooth and analyzes the resulting reflection from the tooth being examined.
- X-ray detects lesions in hard-to-reach places, but not in the early stages of development.
- Visual examination with a mirror is the primary method of diagnosis. If the doctor begins to suspect something after the examination, he prefers to use other techniques.
- Transillumination, when the tooth is illuminated with bright light. A photopolymerization lamp can be used for this.
Complications and consequences of internal caries
The soft tissues surrounding the tooth may also become inflamed. Sometimes the patient notes a general deterioration of the condition against the background of progressive carious lesions. His body temperature may rise, problems with the digestive system, bad breath, etc. may appear. Due to the negative effects of bacteria, flux and suppuration, cysts, and ulcers may appear.
Due to pain in the tooth, it becomes impossible to chew food normally, and a reaction to the slightest irritants appears. If the disease is not treated in time, periodontitis and periodontitis develop, which can result in tooth loss. This, in turn, is a serious stress and requires a long recovery.
Unfortunately, not all patients' caries disappears without a trace; some may encounter unpleasant complications both in the first days after treatment and several months after it. The most common phenomenon is an allergy to the materials used in the work. Sometimes infectious lesions are diagnosed, the cause of which may be the unscrupulous work of the doctor or failure to comply with the rules of personal hygiene.
previous post
White caries
next entry
Possibility of complications
Complications after caries are varied:
- allergy to a developing infection;
- development of inflammation of the gums and facial tissues;
- an infected tooth affects the condition of the body;
- the appearance of flux is possible;
- A jaw cyst may develop.
Painful sensations do not allow high-quality chewing of food, which harms the stomach and intestines. Damage to a tooth can lead to its removal, and this is a serious stress received by the body. Complications can be very serious diseases - pulpitis and periodontitis. With pulpitis, pain appears when biting; this disease can manifest itself even after treatment of caries if the affected tissue is removed poorly. An even more serious complication is periodontitis, which affects nerve bundles and ligaments. Left untreated, it can become a chronic disease.
Stages of development of caries between teeth
The stages of formation of carious lesions in the interdental space do not differ from the classical ones. In the photo below you can see what caries looks like between teeth:
First stage
The first stage of development of the carious process is called initial or caries in the “spot” stage
. It is characterized by a change in the normal color of the enamel with the formation of specific chalky spots that are practically invisible. The structure of the enamel is not yet damaged. There are no symptoms, so the problem is rarely detected at this stage.
Second stage
Superficial brown
c is the next stage, in which only the enamel is affected. There are no specific symptoms, but tooth sensitivity may increase. At this and the previous stages, caries between teeth can be cured without drilling.
Third stage
The next stage in the development of the carious process is middle caries.
. It is characterized by damage not only to the enamel, but also to the upper layers of dentin. Increased tooth sensitivity may be accompanied by periodic pain, aggravated by mechanical and chemical irritants.
Fourth stage
Deep caries
– this is the last stage of the development of infection, in which bacteria penetrate not only into the dentin, but also reach the neurovascular bundle of the tooth (pulp). In this case, an incessant aching pain occurs. Pulpitis forms.
What is dental caries?
This pathology can be called, without exaggeration, “dental enemy of humanity No. 1.” This disease affects 93% of the world's population. It was found even in people who lived 5-6 thousand years ago, and today caries in adults is the cause of tooth loss in almost 90% of cases. Moreover, it leads not only to the formation of the well-known “holes”. Subsequently, when the pathological process begins to spread to the surrounding areas, this causes the appearance of periodontitis, and then complete destruction of the tooth, which requires the irreversible removal of its remains and root.
How does cervical caries develop?
The beginning of cervical caries is the accumulation of plaque near the neck of the tooth.
Against the background of increased acidity and lack of oxygen, as well as under the action of enzymes secreted by bacteria, the enamel softens, opening the gates of infection.
The basal form of caries develops in 4 stages:
- in the first, known as the white spot stage, a dull white spot appears on the tooth at the level of the gum margin;
- at the second stage, a superficial carious lesion develops, which looks like darkening of the enamel;
- on the third, the carious cavity deepens through the enamel into the thickness of the dentin;
- at the fourth stage, deep caries develops, and a “hollow” forms in place of the spot.
The final stage of the disease is a fracture of the tooth in the neck area, pulpitis, accompanied by acute pain, and sometimes an abscess in the gum.
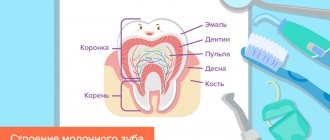
Our teeth are like stones
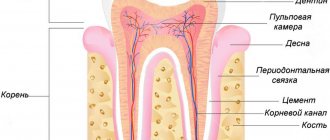
Tooth enamel is the outer protective shell of the tooth, which is 97% composed of hydroxyapatite crystals (Fig. 4) - Ca10(PO4)6(OH)2 - and foundation proteins: amelogenins and emellines, on which during the development of enamel (amelogenesis ) and hydroxyapatite crystals are strung [2], [3], [6], [7].
Figure 4. This is what the “closest relative” of our enamel looks like - hydroxyapatite. It’s good for him, because he doesn’t know anything about caries!
"Wikipedia"
Hydroxyapatite, although the hardest part of man, is still very sensitive to acids. Acids “stuck” in dental plaque, especially in the area of fissures (Fig. 5) - folds of enamel - begin to destroy the mineral, leading to demineralization of dental tissue, in other words, to softening. The mineral decomposes, forming calcium salts with other acids [3].
Ca10(PO4)6(OH)2 + acid → 10Ca2++ 6HPO42– + 2H2O
Notably, hydroxyapatite can remain dissolved for up to two hours after ingestion. In addition to carbohydrates, the main role here is played by fruit acids. That is why after eating fruit you feel a feeling of cleanliness of the enamel. Over time, saliva neutralizes the effects of acids due to its buffering properties [2]. The more often high-carbohydrate foods are consumed, the more constant the acidification process in the oral cavity becomes. Thus, tooth decay does not depend on the amount of sugar you take, but on the frequency of its consumption: do not eat a bag of sweets during the day, but eat a large dessert once a day.
Figure 5. Enamel folds - fissures - are the favorite place for the “seeds” of caries. It is here that demineralization processes occur especially actively.
drawing by Anastasia Prokhorova
Causes of interdental caries
The causes of caries between adjacent teeth are the same as for classic caries. Interdental spaces are the main place for the accumulation of food debris and the formation of plaque, in which pathogenic bacteria multiply, which have a negative effect on the enamel.
The reasons for the formation of caries between two teeth vary from person to person. This may include genetic predisposition, lack of proper oral hygiene, chronic infections in the oral cavity, excessive consumption of sweets, and so on. Regardless of the cause of the disease, timely professional treatment of interdental caries is necessary to avoid unpleasant complications, including the loss of both affected teeth.