Ear pain - mild or intense, shooting or aching - is a symptom that can indicate both a disease of the hearing organ and pathological processes occurring in nearby organs and tissues. According to statistics, otitis media is the most common cause of ear pain. However, the diversity of its forms and many other diseases with similar symptoms require accurate diagnosis and different treatment approaches. To establish the true causes of ear pain, it is necessary to be examined by an otolaryngologist, and sometimes by a neurologist, dentist, and even a cardiologist.
At CELT you can consult an otorhinolaryngologist.
- Initial consultation – 3,000
- Repeated consultation – 2,000
Make an appointment
Otitis externa
Most often, inflammation of the outer ear is bacterial in nature.
The causes of infection may be:
- trauma to the external auditory canal, for example, from a sharp or blunt object, or from a hearing aid;
- skin defects due to eczema, psoriasis, diabetes and other diseases;
- too thorough removal of earwax, which creates an acidic environment that prevents the growth of microbes;
- frequent entry of water into the outer ear (“swimmer’s disease”).
Symptoms of external otitis:
- acute ear pain, aggravated by pressing on the tragus or pulling the earlobe;
- possible itching and a feeling of “stuffiness” in the ear;
- discharge of a purulent or bloody nature, sometimes having an unpleasant odor;
- examination reveals swelling and hyperemia of the external auditory canal;
- possible hearing loss;
- enlargement and tenderness of the lymph nodes in the neck and behind the ear on the affected side.
The course of the disease may be complicated by a perforation of the eardrum, which cannot be determined without a visit to an ENT specialist.
External otitis of fungal origin is a common phenomenon, usually occurring in patients with low immune status or due to long-term use of antibacterial drops. It is characterized by severe itching, the formation of crusts, profuse thick discharge and the absence of a therapeutic effect from the use of antibiotics.
Separately, it is worth noting the localization of a boil on the skin of the external auditory canal or inflammation of the atheroma. The clinical picture is similar to otitis externa, but upon examination there is a more localized focus of inflammation with an opening from which pus and blood can be discharged.
What is prohibited for otitis media
- Under no circumstances should foreign bodies be introduced into the ear (geranium leaves, ear phyto-candles). This will make diagnosis difficult and may lead to a worsening of the condition (for example, leaves that have not been removed begin to rot and become a source of infection).
- If the pain is severe, do not apply a heating pad to your ear or apply warm compresses. This is dangerous if purulent inflammation has begun in the ear. Compresses can only help at stages 1-2 of the disease.
- You should not put melted oil in your ear: if there is a perforation, the oil will end up in the tympanic cavity.
- You should not put camphor oil or camphor alcohol into your ear - it can burn the walls of the ear canal and irritate the eardrum, which will increase ear pain.
At MedicCity you will be denied professional help for otitis media and other ENT diseases. Our otolaryngologists will conduct a comprehensive examination of the patient and prescribe a treatment regimen, depending on the cause and stage of the disease. However, the success of treatment depends no less on the patient himself: the sooner he consults a doctor, the more effective the result will be and the lower the likelihood of complications. It is also important to follow preventive measures. So, in the cold season, to prevent otitis media, it is important to wear a hat, protect your ears from drafts, and of course, boost your immunity!
Otitis media
The middle ear communicates with the nasopharynx through the Eustachian tube, through which infection can penetrate from the upper respiratory tract due to acute respiratory viral infections, influenza, sore throat, rhinitis, sinusitis and other diseases. Children are especially often affected because their Eustachian tube is short and wide, which makes it easier for infection to enter. The process can be one- or two-way.
Symptoms of acute otitis media:
- pain in the ear from moderate to severe, pulsating in nature (pain does not depend on pulling the lobe or pressing on the ear canal);
- increased body temperature;
- possible noise in the ear, dizziness, decreased hearing acuity;
- the presence of discharge (mucous, purulent, bloody) indicates a perforation of the eardrum.
With an aggressive course of the inflammatory process and the absence of adequate therapy, otitis media is fraught with such serious complications as meningitis, sepsis, intracranial abscess formation, and deafness.
Treatment of otitis media
If you have otitis media, treatment can only be prescribed by an otolaryngologist. Treatment of otitis media depends on the stage of the disease and the patient’s condition.
In acute eustachitis, treatment of otitis media is aimed at restoring the functions of the auditory tube. Sanitation of the paranasal sinuses, nose and nasopharynx is carried out in order to eliminate infection - rhinitis, sinuitis, etc.).
Vasoconstrictor nasal drops (otrivin, nazivin, etc.) are prescribed; in case of excessive mucous discharge from the nose, drugs with an astringent effect (collargol, protargol) are prescribed. Catheterization of the auditory tube is carried out using aqueous solutions of corticosteroids, and pneumomassage of the eardrums.
In the stage of acute catarrhal otitis media, catheterization of the auditory tube is carried out with the introduction of aqueous solutions of corticosteroids and antibiotics (penicillins, cephalosporins) into the cavity of the middle ear. Local anesthesia is prescribed (otipax drops, Anauran, Otinum). An intra-ear endaural microcompress according to Tsytovich is carried out: a cotton or gauze turunda soaked in a drug with an analgesic and dehydrating effect is inserted into the external auditory canal. Painkillers with an antipyretic effect (nurofen, solpadeine, etc.) are also prescribed. If there is no effect from symptomatic therapy, antibiotic therapy is prescribed within 48-72 hours.
Purulent otitis in the pre-perforated acute stage requires the same set of procedures as in the second stage, but supplemented with the following measures:
- prescription of penicillin antibiotics (amoxicillin, etc.), cephalosporins or macrolides;
- paracentesis (incision of the eardrum) when the eardrum appears to bulge.
It is important to prevent complications of the disease at this stage. After spontaneous opening of the eardrum or paracentesis, the disease progresses to the next stage.
The post-perforation stage of acute purulent otitis media involves the following treatment regimen:
- started antibacterial therapy continues;
- catheterization of the auditory tube is performed with the introduction of corticosteroids and antibiotics;
- a thorough toilet of the external auditory canal is carried out daily - cleaning it from purulent contents;
- transtympanic infusion of drops with an antibacterial and anti-edematous effect is prescribed (alcohol-based drops (otipax, 3% boric acid solution) are not used in this case).
In the scarring stage of AOM, spontaneous restoration of the integrity of the membrane occurs, and all functions of the ear are completely restored. However, this period requires mandatory observation by an otolaryngologist: there is a danger of chronic inflammation in the middle ear, its transition to a purulent form, or the development of an adhesive scar process in the tympanic cavity. It is also possible to develop mastoiditis.
1 Audiometry in MedicCity
2 Audiometry in MedicCity
3 Audiometry in MedicCity
In case of acute otitis media, timely contact with an otorhinolaryngologist is very important. The only measure to prevent complications is correct and timely diagnostic and treatment measures for otitis media. Sometimes the consequences of acute otitis media are adhesions in the tympanic cavity (adhesive otitis media), dry perforation in the eardrum (dry perforated otitis media), purulent perforation (chronic suppurative otitis media), etc. In addition, AOM can lead to such complications as such as mastoiditis, labyrinthitis, petrositis, meningitis, sepsis, venous sinus thrombosis, brain abscess and other life-threatening diseases of the patient.
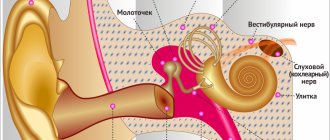
Inflammation of the inner ear (labyrinthitis)
The labyrinth is an organ of hearing and balance, is richly innervated and includes auditory and kinetic receptors, so its inflammation causes:
- severe ear pain and headaches;
- a sharp decrease in hearing, the appearance of noise, crackling, squeaking in the ear;
- dizziness, nausea, loss of orientation in space, horizontal nystagmus.
Labyrinthitis occurs as a result of the penetration of infection in various ways from different parts and cavities of the body:
- from the middle ear with untreated or advanced otitis media;
- with infected meninges during meningitis;
- with blood for diseases such as syphilis, tuberculosis, herpes;
- damage to the temporal region, the organ of hearing with disruption of the integrity of cells and blood vessels.
The disease requires immediate medical attention.
Diagnostic methods
For headaches that affect the ear area, it is important to undergo a timely examination and determine the cause of the alarming symptoms. At the initial examination, only visible disorders are determined, including inflammatory processes, fever and other signs. However, to get a complete picture, additional examinations will be needed:
- clinical and biochemical blood tests - these data will indicate infectious processes, pathologies of the hematopoietic system, as well as disruption of the functioning of internal organs;
- bacterial culture if purulent inflammation is suspected - will allow you to identify the pathogen and select an antibiotic to which the bacteria are sensitive;
- Dopplerography - ultrasound diagnostics of blood flow in the vessels of the neck and head, prescribed to detect areas of ischemia;
- MRI or CT scan of the head – often used when tumors in the brain are suspected;
- consultations with specialized specialists – dentist, otolaryngologist, neurologist.
The Clinical Brain Institute has precise, high-quality modern equipment, which makes it easy to make the correct diagnosis in a short time. Here you can take blood tests and other biological fluids, and undergo an examination of the brain and cervical spine. Qualified specialists will help you decipher test data and identify any pathologies in the early stages.
Eustachite
Eustachitis is an inflammation of the canal connecting the middle ear to the nasopharynx. The degree of pain varies. Characteristic features are:
- feeling of stuffiness in the ear;
- noise and crackling in the ear, the patient hears his voice as too loud with a weakened perception of extraneous sounds;
- sensation of water pouring into the ear.
In the absence of timely treatment, eustachitis becomes chronic, causing chronic exudative otitis media.
Treatment for headaches behind the ear
The course of treatment includes various techniques that will eliminate the cause of the headache and all manifestations of the disease. A regimen can only be selected after examination and a final diagnosis; taking medications at home is not recommended. The following treatments may be needed:
- symptomatic drug therapy - includes painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs, vitamins, remedies against cold and flu symptoms;
- antibacterial therapy - antibiotics are prescribed for bacterial diseases, as well as to prevent complications of viral infections;
- dental treatment – necessary for caries, diseases of teeth and gums;
- surgical intervention is prescribed to remove tumors in the ear canals, as well as when conservative treatment of mastoiditis is insufficiently effective.
At the Clinical Brain Institute, doctors will select the most effective treatment regimen. In most cases, taking medications as scheduled is sufficient, but additional procedures or surgery may also be required. The patient should listen to the opinion of specialists with many years of experience and strictly follow all recommendations.
Ear pain of non-infectious origin
Ear tumors
Neoplasms are most often localized in the outer and middle sections; tumors of the labyrinth are an extremely rare phenomenon. Malignant formations of the outer ear are accompanied by severe pain: the pain is burning and radiates to the temple. Possible bleeding; When the ear canal is obstructed, conductive hearing loss develops. If the middle section is affected, the symptoms are similar to otitis media; a high degree of hearing loss and intense pain, increasing in the evening, should alert you. When the process spreads, symptoms of damage to neighboring structures arise: loss of orientation in space, paresis of the facial nerve, trigeminal neuralgia.
Ear injuries
- Mechanical injuries. The auricle most often suffers with the formation of lacerations and damage to cartilage. Blunt trauma to the ear usually results in a hematoma. As a result of trauma to the ear canal, the ear hurts greatly, there is a feeling of stuffiness, and bleeding is possible. Such symptoms are an indication to consult a doctor, since rupture of the eardrum and fractures of the skull bones are possible.
- Barotrauma is caused by a difference in pressure in the external environment and the cavity of the middle ear, for example, during a sharp loud sound (explosion), take-off/landing of an airplane, deep-sea immersion (diving), climbing a mountain. As a result, the eardrum is pulled inward, which is accompanied by pain, noise or ringing, and congestion in the ears. The opposite situation is also possible, when a decrease in atmospheric pressure causes the membrane to bulge outward. As a rule, unpleasant sensations go away on their own, however, if sharp pain is noted, it makes sense to check the integrity of the tympanic membrane when examined by a doctor.
- Entry of a foreign body in the form of small objects or insects causes swelling of the skin of the ear canal, itching, pain, and sometimes hearing loss. Attempting to remove a foreign object yourself can damage the eardrum.
- With burns and frostbite of the ears, **pain // of varying intensity is observed, depending on the degree of damage.
- Conventionally, ear injuries include the formation of wax plugs, which irritate the skin of the ear canal, causing discomfort and tinnitus. Removal should be carried out by an otolaryngologist.
Ear pain in a healthy person
Unpleasant sensations in the organ of hearing can occur in a completely healthy person, and there are many reasons for this (we will look at some in more detail):
- sensitivity to strong wind and cold (Due to a long stay in the wind, a hematoma may form in the ear - it will go away on its own in a few days. No additional measures need to be taken in this situation.);
- water getting into the ear;
- presence of sulfur plug;
- mechanical injuries (if, in addition to pain, bleeding from the ear begins, consult a doctor immediately);
- acoustic injuries (occur due to exposure to loud sounds on the organ of hearing, for example, at a rock concert, in a noisy industry, or during prolonged use of headphones. As a rule, the pain goes away when moving away from the source of noise. If, due to the nature of the work, it is impossible to eliminate the source of noise, You definitely need to use special earplugs.);
- barotrauma (manifested by changes in atmospheric pressure; most often occur during air travel or diving. When your ears are blocked on an airplane, you need to yawn more often, swallow, or simply chew something to eliminate the condition of “stuffiness”);
- foreign body.
Ear pain due to diseases of other organs
- Mastoiditis - inflammation of the mastoid process - causes intense throbbing pain in the ear, swelling of the tissue behind the auricle, hearing loss, and hyperthermia.
- With arthrosis and arthritis of the temporomandibular joint, the patient is bothered by shooting pains in the ear, which intensify when chewing, a crunching sound in the temple area, and over time, hearing impairment and malocclusion are possible.
- Mumps is an inflammation of the salivary gland located in front of the auricle, accompanied by acute pain in the ear, aggravated by swallowing and chewing, and swelling of the tissues.
- Inflammation of the parotid lymph nodes (lymphadenitis) develops when infection penetrates into them from diseased teeth or from other foci of inflammation.
- Inflammatory diseases of the nasopharynx and sinuses, malignant processes in the larynx and oral cavity are often accompanied by pain in the ear when swallowing.
- Caries, pulpitis. Since the organ of hearing, like the teeth, is innervated by the branches of the trigeminal nerve, damage to the teeth and jaw may be accompanied by pain in the ear area.
- An atypical form of heart attack, when the patient’s only subjective complaint is pain in the ear.
Causes of pain
Painful sensations in the ear area and the right side of the head can occur due to inflammatory processes, as well as when the blood circulation in this area is impaired. The process can spread from the organ of hearing to part of the head and vice versa. When the first complaints appear, it is necessary to undergo an examination and determine their cause.
Otitis
Ear inflammation (otitis) can occur in adults and children. It occurs as a complication of viral diseases (ARVI, influenza), injuries, hypothermia or inflammation of the sinuses. At the first stage, the patient is bothered by constant pain in the ear, which spreads to the entire surface of the head. However, otitis media can progress and develop in several stages:
- aseptic inflammation, which causes aching pain;
- addition of a bacterial infection;
- development of purulent inflammation - accompanied by acute pain and hearing impairment;
- probable complications in the form of purulent melting of the eardrum, as well as the spread of infection to the inner ear and lining of the brain.
Otitis media is often chronic and appears annually. After an examination, an otolaryngologist will help you choose the most effective treatment regimen. It is important to pay attention to the first symptoms in time, since the chronic course of the inflammatory process can provoke partial or complete hearing loss.
Diseases of the external ear
The outer ear is the peripheral part of the hearing organ, which is separated from the middle part by the eardrum. Pathological processes in this area often manifest as acute pain in the right ear and head. With timely treatment, they resolve without complications, but in the absence of intervention they can spread to the middle and inner ear.
- Furunculosis, eczema, fungal skin infections - these processes are accompanied by inflammation and pain. The skin of the auricle turns red and peels, and ulcers (boils) may form on it. Treatment consists of external use of anti-inflammatory and antifungal drugs.
- Diseases that lead to the formation of cerumen plug - it forms deep in the ear canal, so it is impossible to remove it yourself. The cause may be anatomical features of the structure of the hearing organ or excessive formation of sulfur.
- Injuries, falls and bruises are another cause of inflammation of the outer ear. In young children, the process can be triggered by foreign objects entering the ear canal.
When diagnosing, it is important to assess the condition of the eardrum. Inflammatory processes can spread to it and even cause its perforation. Injuries that cause damage are also dangerous.
Inner ear diseases
Inflammation of the inner ear is the cause of acute pain in the right side of the head and in the ear. The organ has a complex structure and is responsible not only for hearing, but also for balance. It is presented in the form of channels and labyrinths filled with liquids. This is where bacteria multiply, causing inflammation.
Diseases of the inner ear require immediate treatment; in most cases, antibiotic therapy is used for this. The tympanic cavity is a comfortable environment for the growth of bacteria, and they can cause purulent inflammation. This leads to hearing loss, constant headaches, and the development of complications, including acute meningitis - inflammation of the membranes of the brain.
Change in blood pressure
An increase or decrease in blood pressure is a common reason why the right ear and the right side of the head hurt. Hypertension (high blood pressure) occurs due to insufficient elasticity of blood vessels, nervous tension and other factors. It manifests itself with characteristic symptoms:
- pressing headache that spreads to the back of the head, temple, and may affect the ear;
- deterioration of hearing and vision, the appearance of tinnitus;
- redness of the skin and mucous membranes, the appearance of small capillary hemorrhages.
With a decrease in pressure (hypotension), an increase in heart rate, weakness, and impaired coordination of movements are observed. The skin and mucous membranes may become pale. Insufficient oxygen supply to the brain is dangerous, as it can provoke a stroke or transistor ischemic attacks.
Stroke
Acute cerebrovascular accident is a stroke. It occurs when there is a sudden stop in the flow of oxygen-rich blood to certain areas of the brain. There are ischemic (manifested by blockage, compression of a vessel, low blood pressure) and hemorrhagic (the result of damage to an artery and hemorrhage in the brain) stroke. The first type is more common and is manifested by the following symptoms:
- sudden headache, often one-sided, which may affect the ear;
- impaired coordination of movements;
- weakening of the facial muscles on the injured side;
- discomfort and pain behind the sternum;
- impaired diction, the appearance of memory lapses;
- loss of consciousness.
The main reason why strokes occur is the lack of early diagnosis. Doctors at the Clinical Brain Institute recommend undergoing regular scheduled examinations to identify cardiovascular diseases in the early stages. Monitoring blood pressure, proper nutrition and dosed exercise, as well as systematically taking medications as needed are the basis for preventing stroke at any age.
Pain in the ear and right side of the head due to neuralgia
If your head hurts and radiates to your right ear, this may be a sign of neuralgia. This is not a separate disease, but a type of pain that occurs when a nerve is inflamed or damaged. The trigeminal nerve is most often affected, which gives off branches to the muscles of the face, the organ of hearing, the upper and lower jaws.
Neuritis is an inflammatory process that develops in nerve fibers. It is accompanied by acute throbbing pain, which can be one-sided, affecting part of the head, ear and half of the face. It intensifies with sharp sounds, bright lighting and other irritants, as well as with chewing and turning the head. Treatment consists of taking painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs. If they are ineffective, a nerve block is indicated - injections along its course with anesthetics and hormonal anti-inflammatory drugs.
Diseases of the cervical spine
The cervical spine contains arteries that carry blood from the heart to the brain, analyzer organs, muscles and facial skin. Their mechanical pinching leads to impaired sensitivity in certain areas and chronic headaches. Normally, the vessels are located in the canals formed by the processes of the vertebrae, and blood moves freely through them. However, there are a number of diseases that lead to poor circulation, pain in the head and ear:
- osteochondrosis is a pathology of intervertebral discs, in which they become fragile and cannot absorb movement, and the distance between adjacent vertebrae decreases;
- spondylosis - fusion of two or more adjacent vertebrae as a result of injury, inflammatory or dystrophic changes, destruction of cartilage;
- curvature of the spine, most often cervical scoliosis;
- chondrocalcinosis - deposition of salts in the periarticular tissues, which leads to decreased joint mobility;
- intervertebral protrusions and hernias - protrusion of intervertebral discs, their gradual erasure until the outer fibrous membrane ruptures;
- vertebral displacement.
Spinal diseases often manifest as headaches. It can be one-sided, since the load on the spinal column becomes uneven, and mechanical compression of the vessels and nerves occurs.
Inflammation of the lymph nodes
Lymphadenitis is inflammation of the lymph nodes. Pain in the right ear and right side of the head can be caused by damage to the parotid lymph nodes. It is acute, pulsating, and may be accompanied by fever. The disease occurs as a complication of a viral infection of the upper respiratory tract; a bacterial or fungal pathogen can also be diagnosed.
With lymphadenitis, redness of the skin behind the ears and the appearance of a hard lump may be observed. The local temperature is increased and pulsation is felt. Treatment consists of taking antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs, and painkillers.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis and treatment of pathologies associated with this symptom is carried out by an ENT doctor (otorhinolaryngologist) or an audiologist (a narrower specialty in otorhinolaryngology). During the appointment, the specialist talks with the patient, examines him, conducts the necessary examination, and establishes a diagnosis.
The multidisciplinary CELT clinic employs experienced, highly qualified otolaryngologists. Rich clinical experience helps them make the correct diagnosis in the most difficult cases.
Diagnosis and treatment of ear pain in Moscow
At the appointment, the doctor talks with the patient, collects anamnesis and conducts an examination using an otoscope, assesses the condition of the outer ear, ear canal and eardrum. He examines the pharynx, larynx, oral cavity and nasal passages. Sometimes the patient is referred for audiometry. If the cause of the pain is injury, you will also need to do an X-ray or CT scan.
Ear treatment in Moscow is offered by many medical institutions: from district clinics to multidisciplinary medical centers. The final cost of ear treatment in Moscow depends on the type of medical institution and its pricing policy. "ENT Clinic of Doctor Zaitsev" specializes in diseases of the hearing organs. Treatment of ear diseases is our specialty. We use the most modern equipment from famous world manufacturers. Our doctors' many years of experience allow us to successfully diagnose hearing pathologies and offer the most effective treatment. Prices for our services have not changed for more than three years.
If ear pain and other unpleasant symptoms appear, do not tolerate it and do not self-medicate. Please call, make an appointment and come. We will be happy to help you!
Our doctors
Debryansky Vladimir Alekseevich
Doctor - otorhinolaryngologist, doctor of the highest category
34 years of experience
Make an appointment
Zharova Galina Gennadievna
Doctor - otorhinolaryngologist, member of the European Society of Rhinologists, doctor of the highest category
40 years of experience
Make an appointment
Gogolev Vasily Gennadievich
Doctor - otorhinolaryngologist
20 years of experience
Make an appointment
Prevention methods
Doctors have a number of recommendations that will help prevent headaches behind the ears. They are easy to follow at home:
- observe a regime of rest and physical activity, regularly carry out moderate exercise;
- pay attention to proper brushing of teeth and oral hygiene;
- observe bed rest in case of viral diseases, avoid contact with other people;
- carry out ear hygiene, while cleaning the ears carefully so as not to damage the eardrum;
- avoid hypothermia in the neck and head;
- Seek medical help promptly if headaches occur regularly or occur with high intensity.
The Clinical Brain Institute specializes in the diagnosis and treatment of diseases that manifest themselves as headaches in the ear area. Here you can undergo a full examination and get advice from specialists of a narrow and broad profile. For long-term treatment, a course of procedures and round-the-clock supervision by doctors, it is possible to stay in a hospital. During outpatient treatment, it is important to follow all recommendations and promptly contact for re-examination.
Treatment
Treatment of inflammatory ear diseases includes:
- antibacterial, antiviral agents of local and general action;
- antipyretics, analgesics;
- physiotherapy;
- in some cases - surgical intervention.
Treatment must be based on accurate diagnosis, which is impossible outside a specialized clinic. The high professionalism of CELT specialists allows us to identify various diseases of the hearing organ and choose the most effective means of solving the problem.
Make an appointment through the application or by calling +7 +7 We work every day:
- Monday—Friday: 8.00—20.00
- Saturday: 8.00–18.00
- Sunday is a day off
The nearest metro and MCC stations to the clinic:
- Highway of Enthusiasts or Perovo
- Partisan
- Enthusiast Highway
Driving directions
Water getting into the ear canal
Normally, water that enters the auricle due to the anatomical features of the structure of the hearing organ flows out of it independently. If for some reason she did not succeed, she needs to be “helped.” There are a couple of simple ways to do this.
Make an appointment right now!
Call us by phone or use the feedback form
Sign up
Method one: tilt your head to one side; bring your hand to the shell of your ear, press it hard, and then release it. The hand will act here as a pump - excess liquid will flow out.
The second method is probably known to everyone since childhood. We tilt our heads to the side and perform jumps on one leg: if the liquid has flowed into the right ear, then on the right, if into the left, on the left, respectively.
Method three. Dry your ear with a towel, take a deep breath and close both nostrils. Without unclenching your fingers, try to exhale, but without opening your mouth! If this manipulation is performed correctly, the excess liquid will be pushed out with the help of air. Method four: you can simply lie on your side, depending on which side the water poured in, and hold there for a short time, periodically making swallowing movements: the water will flow out on its own. If none of the methods brings results, and the fluid inside continues to cause discomfort, you need to seek help from an otolaryngologist.
Jaw pain near the ear: what causes the discomfort and how to cope with it
Jaw pain is an unpleasant symptom that causes significant discomfort. The problem requires immediate medical attention. When examining and making a diagnosis, he takes into account the location of the problem area. If your jaw hurts near your ear, this may indicate problems with the temporomandibular joint, which provides mobility to the lower jaw and its connection to the skull. Soreness in this area often indicates a number of other diseases. A specialist will help determine the cause.