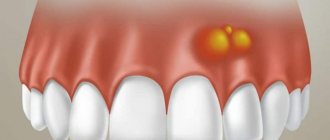
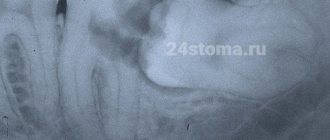
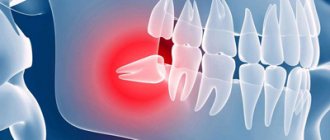
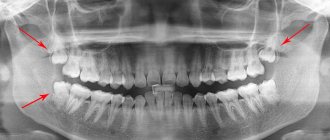
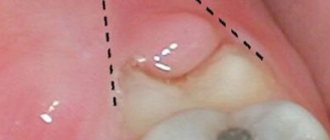
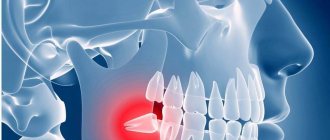
Purulent inflammation can affect the mucous membrane above the root eight that has not fully erupted. Timely removal of the wisdom tooth hood helps prevent the development of pericorontitis, a rather serious disease in dentistry. It is almost impossible to constantly clean this cavity above the molar; it accumulates plaque and food debris, which leads to the active activity of bacteria and the appearance of suppuration (abscess), which is life-threatening. This inflamed focus with pus is located very close to the brain area. Symptoms of the disease:
- Inflammation, redness and swelling in the gum mucosa above the wisdom tooth;
- An unerupted molar is pressed down by a swollen fold of mucous membrane, the process is aggravated by the appearance of pus;
- The swelling spreads to the cheek, causing asymmetrical facial expressions;
- The appearance of pain and tension in the affected area;
- Discharge of pus from under the mucous hood;
- Difficulty chewing food;
- Increased body temperature;
- Bad breath due to suppuration.
If surgical treatment is not carried out, the process will affect deeper and deeper tissues. Pericorontitis can be treated surgically. The radical method involves removing the wisdom tooth. This type of operation is carried out in the presence of appropriate indications, severe destruction of the figure eight or an abnormal location. A more gentle method involves removing the hood of the wisdom tooth with excision of the entire fold of mucous membrane hanging over the root eight. Patients are hospitalized when phlegmon appears. In other cases, the operation is performed on an outpatient basis.
Indications for gum excision
Indications for wisdom tooth removal under the hood
relate:
- The presence of swelling in the cheeks and gums.
- Painful sensations.
- The appearance of lymph nodes.
- Pain when swallowing.
- Increased body temperature.
- Discomfortable sensations when opening the mouth.
Such symptoms should never be ignored. If the patient has indications for wisdom tooth hood removal,
you need to consult a doctor.
Such symptoms should never be ignored. Further spread of the inflammatory process threatens inpatient surgical treatment. Therefore, it is necessary to urgently consult a doctor and remove the tooth hood.
Treatment of inflammation of the hood over a wisdom tooth at home
Treatment at home can be effective only at the initial stage of the disease, before symptoms such as swelling, pus discharge, pain when swallowing and opening the mouth occur. The progression of the inflammatory process can be stopped using antibiotics in combination with treating the hood with chlorhexidine 0.05% and applying Cholisal gel. To do this, you need to: rinse your mouth with a solution of chlorhexidine 0.05 for 1 minute, then dry the gums with a sterile cloth or bandage. Apply a little gel to your finger and rub into the gums in a circular motion. After that, take a little more gel and apply it to the hood. At the end of the procedure, close your mouth, do not eat food for 3 hours, and swallow saliva. During the disease with pericoronitis, under no circumstances should you use warm compresses and warm rinses. This will lead to the rapid proliferation of pathogenic bacteria. You should not apply painkillers to a sore tooth, as they will not relieve the pain and can severely damage the mucous membrane. Such measures will only bring temporary relief and prolong the inflammatory process. It is better not to postpone a visit to the doctor in order to prevent serious complications. Particular attention should be paid to oral hygiene during tooth growth. If any inflammation occurs, contact your dentist immediately.
We cannot diagnose ourselves on our own, much less prescribe the necessary course of treatment. The sooner a qualified specialist determines the cause of inflammation, the less likely you will encounter complications!
Progress of the procedure
Removing a wisdom tooth hood is not particularly difficult for either the doctor or the patient. The procedure takes a short period of time and causes virtually no inconvenience to the patient. After it is carried out, the tissue heals quickly, and the cavity around the tooth disappears.
Sequence of actions when removing the hood:
- an injection with an anesthetic is given at the excision site;
- cut out part of the tissue that hangs over the wisdom tooth;
- treat the excision site with an antiseptic;
- medicine is applied.
After the wisdom tooth hood is removed, the patient can go home. A control appointment is usually scheduled after 2–3 days.
In some cases, a situation arises that, despite excision, the hood is formed again, and this process can last quite a long time, repeating from time to time. Then the doctor will most likely recommend removing the wisdom tooth.
Diagnosis of pericoronitis
Pain in the teeth, the main symptom of pericoronitis, does not directly indicate the disease. This symptom is considered common to dozens of other dental diseases. Only a doctor can make a diagnosis in person.
When examining a patient, the dentist will ask about the nature of the pain, its frequency and duration. This will be followed by a mandatory examination of the oral cavity, perhaps the doctor will use instruments: somewhere he will knock on the teeth, somewhere he will apply a little pressure. If the picture seen remains unclear to the specialist, he will send the person for an x-ray. However, in the vast majority of cases, the doctor immediately determines pericoronitis in the patient, and additional research is carried out when the disease is adjacent to other dental pathologies.
What to do after the procedure
The healing process will largely depend on how the patient takes care of the oral cavity and teeth in the days following the removal of the hood.
- During the first hours after the procedure, it is not recommended to eat or drink.
- Within 24 hours after removal, solid foods should be excluded from the diet. Until the wound heals completely, you need to chew food on the other side of the mouth.
- You need to take care of your oral cavity very carefully, use rinsing, and be extremely careful when brushing your teeth so as not to injure the site of the hood excision.
- In addition to medications prescribed by the doctor, cold is indicated on the side where the hood was.
- To prevent the development of the inflammatory process, overheating (hot food, bath) should be avoided.
Stages of the procedure in Clarimed dentistry
Removal of the hood is carried out according to the following algorithm:
- Examination of the patient, determining the causes of the problem and the degree of development of the disease, collecting the necessary tests.
- Based on the collected medical history, an anesthetic is selected and anesthesia is administered. Clarimed dentistry uses only modern, certified and safe drugs that reliably protect the patient from pain and discomfort during the operation.
- The dentist uses a scalpel to cut through the mucous membrane and free the molar crown. Excess tissue is removed and the area is treated with an antiseptic.
- In case of critical damage to the wisdom tooth or its abnormal growth, the molar is removed by extraction in whole or in parts. The resulting hole is disinfected, bone shavings are placed in it, and the mucous membrane is sutured.
- A drug is applied to the wound to speed up healing. In case of serious intervention, a drainage is installed to remove the ichor. The patient is given the necessary consultations and is sent home.
After the intervention, it is recommended not to eat for 3 hours, not to smoke or drink alcohol. It is not recommended to visit the sauna, take a hot bath or go to the gym on this day (strong physical activity can lead to renewed bleeding).
Causes of inflammation of the gingival hood
- Anatomical features of the structure of bone tissue. In some cases, thickened periosteal tissue is diagnosed, which, when erupting, can contribute to the formation of a hood above the gum.
- Failure to comply with oral hygiene rules. The pathogenic environment multiplies very quickly in the gum pockets and leads to inflammatory processes.
- Soft tissue injury. Damage can occur due to ingestion of hard foods or an incorrectly selected toothbrush.
Among the predisposing factors are close proximity of dental units, bite pathology, curvature of the root element of the dentition, diagnosis of chronic oral infection, stressful situations, and lack of vitamins. As follows from the clinical picture, a hood on the gum most often occurs at the location of the wisdom tooth. At the end of the dentition there is simply no room left for the figure eight, which leads to difficulties in teething.
How is the operation performed?
The operation is performed under infiltrative or conduction anesthesia. The doctor performs preliminary irrigation of the gum tissue and pericoronal space to remove mucus, saliva, epithelial particles, and pieces of food. After this, he excises the hypertrophied mucosa. The mucous membrane can be removed with a scalpel, scissors, laser device, or through cryodestruction. A turunda of gauze is left in the wound, which is treated with an iodoform solution.
If the patient also has periostitis, the doctor additionally cuts the base of the pterygoid fold located at the bottom of the jaw. The doctor inserts a drain into the incision to sanitize the infection. The pain disappears 2-3 days after the procedure. The gum tissue heals completely within 7-10 days.
If the wisdom tooth is positioned correctly, it is left in place. If the cutting is incorrect, there is not enough space for the tooth in the row of alveoli, or there is significant destruction of the bone in the neck area, the doctor will prescribe an operation to remove the object of treatment from the dentition.
Final provisions
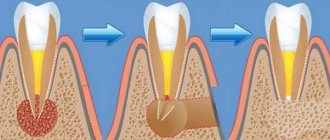
When a doctor diagnoses pericoronitis, it means that the gums around the erupting teeth - permanent or baby - have become inflamed, and the tooth is probably not growing properly. The abnormality creates a pocket called a hood between the new tooth and the soft tissue. The cavity quickly fills with a substrate consisting of plaque and bacteria, and decay begins. The main symptom is pain at the site of the growing tooth; in addition, other signs are present.
Pericoronitis is treated by removing the inflamed soft tissue (hood), or extracting the tooth (in extreme cases). Home methods, rinses, lotions will not help, they can only do harm if you rely on them completely and do not visit the hospital.
Treatment of pericoronitis can be quick - in the early stages, and long and painful - in advanced stages. A person can prevent the development of pathology while complying with hygiene standards. And it is worth remembering that modern dentistry is a very rapidly developing branch of medicine. Trust the professionals to help you maintain your health.
Treatment of pericoronitis of the wisdom tooth in the lower jaw
Treatment of dental caries using the Icon method without preparation
Dental treatment without a drill, placing a filling without drilling in Moscow
Repeated endodontic treatment of tooth canals for pulp inflammation
Dental treatment without pain in Moscow
Dental treatment during pregnancy 2nd trimester
Treatment of tooth enamel erosion, causes, photos, price
Rehabilitation after tooth extraction from the socket includes
- Rinsing the wound surface with disinfecting solutions according to the rules prescribed by the doctor, always preserving the blood clot;
- Sometimes - taking a course of antibiotics;
- Taking painkillers to eliminate pain after volumetric intervention in living tissue. If the patient’s pain threshold is low, assistance cannot be avoided, because both the jaw bones and injured soft tissues will hurt. After a few days, the sensations become tolerable. Full recovery will take several weeks.
Physiotherapeutic treatment
Physiotherapy methods are also used to speed up the healing process:
- UHF therapy - one of the indications for the procedure is the presence of an inflammatory (including purulent) process in the tissues before and after opening the pathological focus. Ultrahigh-frequency therapy has anti-inflammatory, analgesic and resolving effects. The average course of treatment is 5 sessions.
- Microwave therapy is used to treat socket pain and complications of pericoronitis (periostitis and osteomyelitis). Course – 5-7 procedures.
- Irradiation of tissues with low-intensity laser radiation - laser radiation of this type has a local immunomodulatory and analgesic effect, relieves inflammation, and accelerates wound healing. Minimum course – 5 sessions.