Functions of the sky and structural features
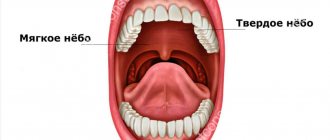
The palate is a vault that separates the oral cavity from the nasopharynx. The structure of the palate consists of two sections - hard and soft. This organ performs an important function - it prevents food from entering the nasopharynx from the oral cavity.
In addition, receptors on the surface of the palate are associated with the larynx and take part in articulation and influence the timbre of the voice and the pitch of sounds. Thus, the inflammatory process of the upper palate disrupts all the functions of this important organ, and therefore requires mandatory treatment.
How is differential diagnosis performed?
As mentioned above, if the doctor has doubts about the cause of the symptoms, the patient will have to undergo a differential diagnosis. It is necessary to make a correct diagnosis, excluding all other pathologies with similar symptoms. As part of such a survey, the following activities may be required:
- visual examination and medical history,
- x-ray examination,
- general blood tests and allergy tests,
- consultation of specialized specialists,
- full examination of the body, including ultrasound and CT.
For diagnosis, it is necessary to undergo tests.
But such in-depth diagnostics are not needed in all cases. If the clinical picture is obvious, the doctor will not require additional procedures. However, it is very important to establish an accurate diagnosis, because the further course of treatment will directly depend on it.
Why does inflammation occur?
The muscular structure of the palate is covered on top with a mucous membrane, which is subject to the development of an inflammatory process. Inflammation often occurs under the influence of such factors:
- burn of the mucous membrane as a result of consuming excessively hot food and drinks;
- damage to the palate due to dental diseases - periodontitis, stomatitis, caries, pulpitis;
- disruption of the oral environment due to the action of metals - when wearing braces or installing crowns;
- smoking;
- allergic reactions to medications;
- neurological diseases affecting the joints of the upper or lower jaw;
- osteomyelitis - an infectious lesion of the bone tissue of the jaw;
- malignant neoplasms;
- infectious diseases of the upper respiratory tract - sore throat, tonsillitis, pharyngitis, rhinitis.
The development of the inflammatory process of the palate may be facilitated by some of these causes in their entirety or separately from each other.
Diagnosis of cancer of the soft and hard palate
The resulting cancerous tumor of the palate is difficult to determine independently in the early stages. If the pathological process has affected large areas of the soft or hard palate, a preliminary diagnosis can be made after a visual examination of the oral cavity.
To confirm the diagnosis, oncologists at the Yusupov Hospital perform the following diagnostic procedures:
- X-ray – finds pathological changes in bone tissues adjacent to the oral cavity;
- Biopsy – taking a piece of tissue for histological examination (analysis is necessary to identify altered tumor cells and its type);
- Blood tests - signs of anemia;
- Radioisotope examination - allows you to examine the structure of the neoplasm.
Ultrasound examination is carried out to detect cancer metastases in distant organs. Patients of the Yusupov Hospital can undergo complex diagnostic procedures in partner clinics and receive advice from leading dental oncologists in Moscow.
Signs and symptoms of inflammation of the palate
Depending on the causes of inflammation in the oral cavity, a person may experience the following unpleasant symptoms:
- A feeling of acute pain that makes it difficult to eat. Soon the pain increases, sometimes even swallowing becomes impossible.
- If the inflammation is caused by the action of a fungus, a white coating and erosion forms on the surface of the palate. The process is accompanied by an unpleasant putrid odor from the mouth.
- When the cause of inflammation is an infectious lesion - sore throat or tonsillitis, the palate becomes red and swollen.
- In case of acute inflammation, an increase in body temperature and fever is possible.
- If the cause is dental disease, the patient will be bothered by toothache.
- With cancer, the patient complains of aching pain in the palate.
Diseases
Pain in the palate is caused mainly by inflammatory processes.
Causes of inflammation
- Mechanical damage. Injury can occur from cuts from sharp edges of chipped teeth, improperly fitted dentures, or chewing hard food.
- Caries, pulpitis or osteomyelitis cause pain from cold or hot food or chewing it.
- An incision in the gum and removal of the dental nerve sometimes lead to disruption of the temporomandibular joint, which causes pain.
- Inflammation of the tonsil or trigeminal nerve.
- Stomatitis as a consequence of damage to the mucous membrane.
If the reasons described above are not corrected in a timely manner, the inflammatory processes will progress, which will only worsen the situation.
How is inflammation of the palate treated?
How to treat inflammation on the roof of the mouth, a specialist will tell you after determining the diagnosis. The following therapy methods can be used:
- If the cause of inflammation is minor damage to the mucous membrane, rinsing with decoctions of medicinal herbs is usually sufficient. Decoctions and infusions based on calendula, sage and chamomile have an antiseptic and healing effect. The herbal decoction for rinsing should be used warm.
- When the palate is affected by a fungus, patients are prescribed topical agents. The most effective are the solution and gel “Chlorhexidine”, “Rotokan” or “Stomatofit”.
- In case of severe pain symptoms, regardless of the cause of inflammation, drugs of combined action are prescribed. “Cholisal-gel” and “Kalgel” have proven themselves well.
- If a purulent inflammatory process is detected in the oral cavity, the patient is prescribed antibiotics. The minimum course of treatment is usually 7 days, but there are also stronger drugs that only need to be taken for 3 days. Along with local agents, antibacterial drugs for internal use - Sumamed, Flemoxin Solutab - can be prescribed.
- The inflammatory process of the palate is easily treatable. The earlier therapy is carried out, the less likely it is to develop complications.
Anatomy
The anterior part is called the hard palate, it occupies two-thirds of the total volume, the posterior part, the soft palate, forms the remaining third.
The color of the soft palate is red with a pink tint, the color of the hard palate is pink and pale.
The hard palate is a bone formation that separates two cavities of the skull - the nasal and oral. For the oral cavity, the hard palate is the roof, and for the nasal cavity it is the base. The palatine processes of the upper jaws form its anterior part, and the horizontal plates of the palatine bones form the posterior part. The most common is a pronounced dome-shaped shape. The degree of curvature changes with age. In infancy, the dome is almost flat, towards adulthood its steepness becomes greater, and in old age the bend decreases again.
The mucous membrane contains glycogen in large quantities, so it is not susceptible to keratinization, as indicated by the pink color of the tissue. However, where the surface is subject to the greatest friction with food, the superficial layers of the epithelium are in various stages of keratinization.
The mucous membrane performs a protective function; it prevents microorganisms from penetrating into tissues. Receptors located in the mucous membrane perceive temperature, pain, and tactile stimulation and participate in the formation of taste sensations.
Rudimentary transverse folds of the hard palate are located in its anterior third, they are best expressed in children, and are practically smoothed out in old age.
On both sides of the midline, closer to the posterior edge of the hard palate, there are palatine dimples. Dentists use these grooves to determine the placement of removable dentures.
Injections for local anesthesia are made into the tissue surrounding the nasopalatine nerves, which pass through the incisive canals. The location of the canals is the incisive fossa of the hard palate.
The soft palate looks like a fold of mucous membrane that separates the pharynx from the oral cavity. At rest, it hangs freely down almost vertically, and during eating it regularly rises in response to swallowing efforts and blocks the upper part of the pharynx. The fold consists mainly of ligaments of tendons and muscles. The fibrous plate in front is attached to the hard palate; it is covered with mucous membrane on both sides.
The small uvula of the soft palate prevents food bolus or liquid from entering the nasal canals; in addition, it is involved in the formation of sounds, for example, the sound r. The uvula of the palate is located above the root of the tongue and has its own muscle fibers.
The two arches, which form a continuation of the ends of the velum palatine, are named in accordance with the organ to which they are closer - the pharyngeal and lingual.
Muscles of the soft palate
- the uvula muscle, it raises and shortens the uvula;
- palatoglossus muscle, lowers the palate and narrows the pharynx;
- the velopharyngeal muscle lifts the larynx, pharynx and tongue, narrows the swallowing space, pulls the soft palate to the back wall of the pharynx;
- The levator muscle is involved in lifting the velum palatine and separating the mouth and nasal cavity;
- The tensor muscle stretches the palatine aponeurosis and the soft palate.
Due to the action of the muscles, when swallowing, the lower palate blocks the posterior openings of the nose and the entire upper area from the rest of the pharynx.
Prevention measures
Preventive measures come down to following simple rules:
- brush your teeth at least twice a day; - use mouth rinses every time after meals; - Avoid eating excessively hot food; — enrich the diet with vitamins and microelements to increase local immunity.
Elimination of stressful situations, a balanced diet, regular visits to the dentist and examination of the body - all these actions are reliable prevention of the development of inflammatory processes in the oral cavity.
How to treat inflammation of the palate depends on the causes of the development of the inflammatory process and its symptoms. To determine an accurate diagnosis, you should visit the dentist's office.
This article is for informational purposes only, please consult your doctor for details!
Treatment of palate cancer
The choice of treatment method for cancer of the hard and soft palate depends on the histological type and stage of the malignant tumor, the extent of the pathological process to nearby tissues. The main method of treating the disease is irradiation of a malignant neoplasm of the palate with X-rays. Radiation therapy can stop the development of cancer cells. If it is started at an early stage, complete destruction of the malignant neoplasm is possible. Radiation is performed before and after surgery.
Surgery for palate cancer involves removing the tumor and the soft tissue and bones located next to it. After surgery, a defect remains on the face, to eliminate which plastic surgery is performed. In advanced cases of cancer, surgery and radiation therapy sessions are performed.
For palate cancer, treatment is carried out with cytostatic drugs. They are administered as droppers or prescribed for oral administration. Chemotherapy for cancer of the soft and hard palate is effective in combination with radiation and surgery. The action of chemotherapeutic drugs is aimed at preventing and eliminating metastatic foci.
Timely diagnosis and selection of a well-designed treatment regimen allow doctors at the oncology clinic to achieve an almost complete cure for 80% of patients. If you experience unpleasant sensations in the oral cavity, contact oncologists and make an appointment by calling the Yusupov Hospital.
Causes of cleft palate formation in humans
Experts do not have a consensus on the question of why children are born with a cleft palate. The appearance of the defect is associated with the presence of one or more provoking factors:
- inferiority of the germ cells of the parents: age over 40 years, hereditary gene mutations;
- infections and chronic diseases of the mother: rubella, chicken pox, herpes, syphilis, chlamydia, etc.;
- chemical intoxication: alcohol, drugs, smoking, chemicals, etc.;
- physical impact: amniotic fluid pressure, body overheating, radiation, falls, blows to the stomach, etc.
Often the cause of cleft palate is a metabolic disorder in the early stages of pregnancy, when it is accompanied by a lack of vitamins and minerals, toxicosis, lack of oxygen, and the threat of miscarriage. Taking antibiotics, sleeping pills and sedatives, medications for thyroid diseases, tumors, and arthritis can provoke a cleft palate in newborns. Psychological factors increase the risk of developing a defect: stress, prolonged experiences, lack of rest.
Help from the project “Towards Life”
The scope of rehabilitation activities, the number of doctors involved in the treatment, and the cost of cleft palate surgery in well-known medical centers should not diminish your determination to improve your child’s health. After consultation with specialists, you can do a significant part of the work to restore functions (breathing exercises, exercises to develop the speech apparatus, preventive measures, etc.) with your baby yourself at home. Your persistence and patience are an important component of success in treatment.
There is also an answer to the question of where surgery for congenital cleft palate is performed free of charge - in Yaroslavl. With the support of charitable organizations (Rusfond, “Beautiful Children in a Beautiful World”), we offer medical care from the best specialists without payment. To receive free surgical treatment from our maxillofacial surgeons: Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor S.N. Bessonova and L.A. Eremeyshvili, you need to collect the necessary documents according to the list, send them for consideration and wait for the call for treatment.
You can make an appointment with a specialist by phone: 8 on weekdays from 9.00 to 19.00 Moscow time Or through the form on the website Sign up for a free consultation
Types and manifestations of anomalies
The defect in newborns is manifested by a complete cleft of the soft and hard palate, passing through, or a small crack only in the soft tissues. According to the degree of bifurcation, the defect is classified into:
- complete – with splitting of soft and hard tissues up to the incisive foramen;
- incomplete - with a cleft only in the soft palate or with partial cleft of the hard palate;
- through – one- or two-sided clefts of the hard and soft palate with the inclusion of the alveolar process;
- hidden - the gap cuts only the muscles while preserving the oral mucosa.
“Cleft palate” in newborns, in addition to a cosmetic defect, is accompanied by a number of symptoms indicating disorders of the vital functions of the body. From the moment the baby is born, disturbances in sucking and swallowing of food appear. Shallow breathing develops, leading to oxygen deficiency and a tendency to inflammation of the middle ear, which negatively affects hearing. With the active growth of the baby, disorders of the speech apparatus (pronunciation of sounds through the nose) and delayed development of all body structures are detected.
How to prevent diseases of the palate?
There are many reasons for pain in the palate. It is within human power to prevent burns, infections, and injuries.
To prevent pathologies associated with the palate, you need to take responsibility for your health
It is important to follow these rules:
- the temperature of the food should not be very high or low;
- Before eating vegetables and fruits, it is important to wash them thoroughly;
- visiting the dentist should be systematic - teeth treated on time will not cause problems with the palate;
- reduce the consumption of solid foods to avoid trauma to the mucous membranes;
- Oral hygiene should be done every morning and evening;
- taking multivitamins helps strengthen the immune system, which increases the resistance of mucous membranes to infections;
- parents should talk with children about the rules of oral hygiene, explain why certain objects should not be allowed to get into the mouth;
- It is necessary to exclude contact of dirty hands with the mouth, stop biting your nails, and make it a rule to wash your hands after every trip to the toilet.
Pain in the mouth is always a warning sign
Important ! Pain in the mouth is an alarming signal that requires immediate medical attention!
In order to prevent infection, it is important to change your toothbrush after treatment of dental diseases (stomatitis) or after dental prosthetics.
Stomatitis provokes increased salivation, so during the period of illness you should increase the amount of water consumption.
A child’s palate is inflamed – what to do?
Fungal infections are the most common cause of inflammation of the palate in children.
A child can injure the delicate mucous membrane of the palate by testing everything that comes his way. Such exploration of the world around us is a serious test for a baby’s mouth.
Important ! Gentle treatment is the key to the recovery of a small patient.
Can be used:
- rinsing with a weak salt solution;
- Furacilin solution;
- faint pink solution of potassium permanganate;
- Chlorhexidine solution.
Treatment of pain in the palate of a child should be especially careful
What drugs are used in different clinical cases
The choice of treatment must be justified by the cause of the problem. So, all the drugs that are prescribed if the palate is inflamed or if the gums also hurt can be divided into 3 large groups:
- antifungal: these include broad-spectrum antimycotics that effectively combat the development of candidiasis and trichomonas. They are usually prescribed for trauma to the mucous membrane, for stomatitis and thrush - “Levorin”, “Nystatin”, “Candide”,
- antibacterial: these include antibiotics that specifically prevent the proliferation of bacteria and pathogenic microorganisms. So, for example, “Metronidozole” and “Amoxicillin” can only be prescribed by a doctor, and their help is usually resorted to when there is a serious infection of tissues and an increase in temperature. But antibacterial rinsing solutions are used as maintenance therapy, and these include “Chlorhexidine”, “Stomatofit” and others,
- antiviral - as a rule, used in the early stages of the disease and for preventive purposes, they suppress the reproduction of viruses. Such drugs include “Acyclovir”, “Oxolin”, “Interferon”1.
Drugs can only be prescribed by a doctor.
Any of the above drugs, and especially antibiotics, can only be taken as prescribed by a doctor. Remember, if suspicious symptoms appear, it is better to consult a doctor immediately. The longer you delay visiting a specialist, the higher your chances will be of encountering very serious consequences and complications.