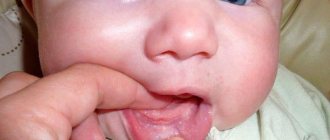
We are used to the fact that we need to go to the dentist if we have problems with our teeth or gums. What to do if you have inflammation of the tongue or glossitis? Dentists identify more than 10 types and subtypes of infection. The infection can be caused by both fungus and bacteria. Viral infection is less common. Inflammation can be caused by a lack of certain vitamins and minerals, or hormonal changes. There are many reasons for the disease, so it is important to identify what exactly caused the inflammatory process.
Causes of glossitis
- improper oral hygiene;
- bacterial infection;
- fungal infection;
- heavy metal poisoning;
- bad habits (smoking, alcoholism);
- congenital pathologies of the tongue (folded tongue);
- allergic reaction;
- tongue injury (often caused by malocclusion);
- oral infections;
- lack of iron in the body;
- burn of the mucous membrane (hot food or drinks);
- infectious diseases (AIDS, tuberculosis, scarlet fever, measles).
Under the influence of what factors do tongue diseases develop?
Tongue diseases can occur in humans due to many factors:
- Pathogenic fungi, viruses and bacteria that accumulate in dental plaque or enter the body through the “gate of infection” - the oral cavity.
- Injuries caused to teeth by careless chewing of food, spicy and hard foods, uncomfortable dentures, or a splintered tooth.
- Contact with food allergens.
- Vitamin deficiency or lack of elements necessary to maintain healthy tongue tissue.
- Dehydration due to illness or improper drinking regimen.
- Unhealthy lifestyle with bad habits.
- Metabolic disorders in the body.
- Blood supply defects.
- Nervous regulation disorder.
- Neoplasms.
- Congenital developmental anomalies.
- Accumulation of toxins and metabolic products in tissues due to kidney or liver dysfunction.
- Inflammatory diseases in the digestive and respiratory organs.
- Development of dysbacteriosis.
The most common types of glossitis
The most common occurrences in dental practice are:
- acute catarrhal glossitis;
- tongue abscess;
- desquamative glossitis.
Acute catarrhal glossitis is the most common type of inflammation. Inflammation can be caused by microbes or mechanical damage to the tongue. The predominant symptoms are pain, redness and swelling.
A tongue abscess is the appearance of an abscess in the tongue. The abscess can be superficial, under the mucous membrane, or maybe in the thickness of the tongue. Abscesses in the thickness of the tongue, in addition to pain in the tongue, can cause a disturbance in the general condition. A person develops a fever, a headache, and weakness. Most often occurs due to injury to the tongue.
Desquamative glossitis, also known as “geographic tongue,” most often appears in children. It appears in the form of various spots on the tongue, which look like a white coating, alternating with areas of pink mucous membrane. There are no changes other than appearance. Scientists have identified a clear reason for it. The main factors are believed to be bacteria, allergic reactions and hormonal imbalances.
Is my tongue my doctor? What diseases can be identified by the organ of taste?
The tongue is one of the most important organs in the body. It contains receptors that allow you to recognize all shades of taste of products entering the oral cavity.
As scientists noted back in ancient times, human language has a connection with various organs of the body. When diagnosing, they divided it into conventional parts: basal, middle and tip. And they believed that in case of pathology of a particular organ, the lesion would be observed strictly in one of these areas. AiF.ru looked into what diseases leave their mark on the language together with Professor, Doctor of Medical Sciences, head of the laboratory for the development of an interdisciplinary approach to the prevention of chronic non-infectious diseases of the Federal State Budgetary Institution "State Research Center for Preventive Medicine of the Ministry of Health of Russia", expert of the National Health League Mehman Mamedov .
Color spectrum
When examined by a doctor, you are often asked to show your tongue. And they do this not out of idle curiosity. After all, even by the color of the tongue it is quite possible to determine whether there is a particular disease. For example, the tongue of a healthy person should be pale pink: this is what is accepted as the norm. If there is a white coating on the tongue, we can talk about fungal infections of the body or disorders of the gastrointestinal tract. A gray tongue is usually the result of chronic pathologies. Bright red - will indicate infectious and inflammatory processes in the human body; if the red color has a shade of scarlet, doctors will suspect problems with the circulatory system. A burgundy tint is a clear sign of an acute infectious process. The tongue is part of the gastrointestinal tract, and is also connected with the respiratory system, because located in the oral cavity. With stomach and duodenal ulcers, problems with the gallbladder, liver and intestines, there may be changes in the color of the tongue. Each disease has its own manifestations - in some places it can be more contrasting, in others it can be lighter.
It also happens that the color of the tongue changes to blue and purple. In this case, they talk about problems with the lungs or severe kidney ailments. Yellowing of the tongue is not only a characteristic feature of a heavy smoker, but also a signal of problems with the gastrointestinal tract. If there is a lack of vitamins in the human body, the tongue may completely lose color.
It is worth considering that a shade that is too dark and saturated is a sign of problems that require immediate medical intervention, or even hospitalization.
Additional factors
However, not only color matters. If the tongue is too dry, the following diagnoses may be made: dehydration, intestinal obstruction, peritonitis. Often, dry tongue is observed with an increase in body temperature. If the situation approaches critical, the taste organ may even crack due to dryness. In this case, an additional threat is created: it is easily infected with bacteria, resulting in suppuration and severe inflammation.
The type of coating on the tongue is also of particular importance. So, if it is thin, it means that the disease is in the initial phase, and if it is frankly fatty and thick, then the problem most likely lies in pathologies of the gastrointestinal system: this usually happens if mucus has accumulated there and food stagnates. A spotted and purple coating indicates the development of blood stagnation. Malfunctions in the digestive system will cause the tongue to become slightly swollen and wet. In this case, it is recommended to be checked for gastritis, cholecystitis, ulcers and even appendicitis.
Doctors pay special attention to the place where plaque accumulates. So, if it is more adjacent to the root of the tongue, then problems are noted in the large intestine: most likely, many human waste products have accumulated there and cannot find a way out. Plaque in the middle indicates problems in the small or duodenal intestine or stomach. If the plaque is so thick and the tongue is so swollen that you can see teeth marks along the edge, you need to reconsider your diet: with a high degree of probability it can be said that the intestines cannot cope with the food that a person eats.
The presence of deep wrinkles and cracks located transversely should alert you and send you to a neurologist - as a rule, this problem manifests itself with a predisposition to vascular disorders of the brain.
The tongue can even indicate serious cardiac and vascular problems, which may occur without any symptoms for some time. For example, a tongue that is slightly shifted to the side or slightly bent will indicate a hemorrhagic stroke, cerebrovascular accidents, or problems with the functioning of the cerebellum.
An increase in the volume of the taste organ may be a consequence of problems with the thyroid gland, malfunction of the pituitary gland, or mental disorders.
Shaky and grainy
Sometimes a person may notice that his tongue... trembles. This condition indicates nervousness and problems with the central nervous system. In such a situation, doctors recommend changing the psychological environment, as well as working on your lifestyle. It is also worth checking with a doctor if your sense of taste begins to decrease. After all, it does not develop out of the blue: there must be a reason why a person no longer feels the tastes to which he is accustomed. Moreover, it is important to understand that there are certain zones and areas on the tongue that are responsible for the reaction to different tastes: spicy, salty, sweet, etc. If a malfunction is noted in any of the parts, this may indicate that the nervous system is suffering. or endocrine system. Loss of taste in the taste buds of the tongue manifests itself as a result of metabolic disorders in the human body, as well as malfunctions of the central system of various etiologies, the development of anemia and the presence of cancer.
Also, people often begin to notice that the tongue has become rougher: this is due to an increase in the size of the papillae on the surface of the organ. When swollen papillae are localized at the tip, it is worth being examined by a cardiologist. If the tongue becomes “spiky” around the edges, you need to check the liver. An affected middle part of the tongue indicates problems in the stomach and intestines. At the same time, you should not rejoice when the tongue becomes smooth and “mirror-like”. After all, this is also a pathology. This happens with anemia, exhaustion or severe pathologies of the stomach.
Symptoms of glossitis
- increased salivation;
- swelling and redness;
- pain and burning when eating;
- plaque on the tongue in the form of spots;
- bad breath;
- papillomas or warts on the tongue;
- speech disorder;
- foreign body sensation.
Prevention of glossitis - high-quality oral hygiene and no bad habits. It is important to undergo timely preventive examinations and also eat well. All these factors actively contribute to the development of the disease and bring a number of problems.
Surface type
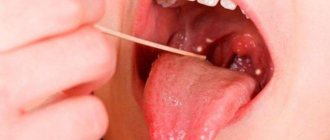
In general, the disease can affect different areas of the mucous membrane, but the superficial variety affects only its upper layer. Superficial glossitis of the tongue can be seen in the photo.
The photo shows superficial glossitis of the tongue
It all starts small - the catarrhal stage of the disease. First, the mucous membrane becomes swollen, and upon visual inspection it is noticeable that it is covered with a dense coating. If treatment is not started during this period or the pathology is not completely cured, then an ulcerative form develops - small painful aphthae appear on the mucous membrane, which can bleed.
What is glossitis of the tongue? This is a disease that, like many other dental pathologies, can occur in acute and chronic stages. It can have pronounced symptoms or a sluggish inflammatory process that will go unnoticed for a long time, undermining your health. That is why it is so important to undergo timely preventive examinations with a dentist and therapist.
Treatment of glossitis
A specialist must make an accurate diagnosis and identify the cause of the disease. If you suspect that you have glossitis , and all symptoms indicate this, contact your dental clinic. This is the only way to create the right treatment plan and provide timely assistance. Quite often in such cases, doctors prescribe antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs and rinsing the mouth with special antiseptic solutions. In advanced stages, glossitis is treated surgically. Deep abscesses must be opened in the maxillofacial department. Under no circumstances should you take medications without a doctor’s recommendation.
You can cure glossitis, caries or any other diseases of the oral cavity right in your sleep. Family Dentistry Center "Medexpert" provides dental treatment under medicinal sedation. Thanks to this approach, the patient falls into a healthy sleep, ceases to feel pain and discomfort, while the vital functions of the body remain unchanged. Sedation is widely used in pediatric dentistry and even helps fight dental phobia. Dental treatment can be comfortable and painless - tested for yourself.
Diagnostics
The cause of the symptom is determined by the dentist. If there are indications, patients are referred for consultation to a gastroenterologist, therapist, neurologist, and other specialists. The doctor determines when the pain first appeared, what symptoms were accompanied, and how the disease developed. To clarify the diagnosis, the following procedures are performed:
- Inspection
. During the physical examination, general changes are sometimes detected (for example, pale and dry skin with anemia). When examining the tongue, swelling, hyperemia, discoloration, the presence of erosions, ulcers, and infiltrates may be detected. With neuralgia, areas of pain indicate damage to one or another nerve. During a dental examination, carious teeth, defects in dentures and orthodontic structures may be detected. - Instrumental techniques
. To exclude xerostomia and assess the condition of the salivary glands, sialography and ultrasonography are recommended. If gastrointestinal pathologies that provoke glossalgia are suspected, esophagogastroduodenoscopy and a contrast study of the stomach are performed. For neuralgia, electromyography is indicative. - Lab tests
. Confirm the presence of pernicious or iron deficiency anemia. As part of the differential diagnosis, saliva is examined. In case of candidiasis and bacterial lesions, the discharge is inoculated onto nutrient media. For viral infections, PCR is performed.
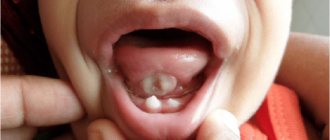
Interstitial or sclerosing
Glossitis, shown in this photo, occurs in adults due to the presence of such a serious disease as syphilis. Symptoms: the affected muscles are gradually replaced by fibrous connective scar tissue, the papillae are completely smoothed out, painful cracks and trophic ulcers appear. The organ acquires tuberosity, because foci of inflammation grow unevenly. Externally it resembles a quilted blanket. The patient's tongue movement is difficult, swallowing and chewing functions are impaired, and speech is altered. And if treatment is not carried out in a timely manner, then there is a risk of oncological progression of the disease in areas of inflammation.
Candidiasis glossitis occurs with syphilis
Comments
At what age do people usually get Günther Müller's glossitis?
Vladimir (01/30/2021 at 11:57 pm) Reply to comment
- This type of glossitis, in fact, like all others, can develop in patients of any age, but people who have chronic diseases, pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract, and smokers are always at risk.
Editorial staff of the portal UltraSmile.ru (02/05/2021 at 09:16) Reply to comment
It turns out that our tongue can say a lot about the body, it’s not for nothing that doctors always ask to see it, even if they just came for a medical examination. Can any age have these diseases or older people?
Maria (02/05/2021 at 07:32) Reply to comment
I wonder what is better to eat to avoid such serious problems? It seems to me that a lot depends on food. Against the backdrop of abundance, you begin to not understand what is useful and what is not.
Marina (02/05/2021 at 08:20) Reply to comment
I once had glossitis, about five years ago. Although I don’t smoke, don’t drink, I lead a healthy lifestyle. Before this I had a sore throat. What folk remedies do you recommend that are the most effective?
Irina Frolova (02/05/2021 at 09:40) Reply to comment
Hello. I developed glossitis due to candidiasis. The tastes are very dull. Everything seems to have been cured, but I don’t feel the same brightness from food. Please tell me, can something be done about this or is it forever?
Vera (03/04/2021 at 10:56 am) Reply to comment
Since childhood, all doctors have told me “geographical language.” It has some stains and a yellow-green coating. Is this a disease or not? It just doesn't bother me the way it feels. But it's not very easy to clean.
Vladimir (03/04/2021 at 11:38 am) Reply to comment
Write your comment Cancel reply
Treatment of the disease: what doctors usually prescribe
For Gunther-Miller glossitis, doctors prescribe complex treatment.
If Gunter's glossitis is not treated, in advanced cases this can lead to the disappearance of the papillae on the tongue and a reduction in the muscle organ itself, speech impairment, problems with breathing and adequate food intake. All this will significantly worsen the quality of life. In addition, advanced disease is fraught with phlegmon of the tongue and purulent melting of tissue, which does not exclude sepsis and even death.
Drugs that help eliminate symptoms of pathology
Local antiseptics “Furacilin”, “Chlorhexidine”, “Miramistin”, and chamomile decoction help to reduce swelling of the tongue and signs of inflammation, remove ulcers and prevent the appearance of new ones. To eliminate pain, it is usually recommended to use non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, for example, Nurofen.
"Chlorophyllipt" can also be used for rinsing
In order for wounds on the tongue to heal faster and delicate tissues to regenerate successfully, doctors prescribe retinol solution, vinylin, Solcoseryl, and rosehip oil to patients for local treatment of the affected areas.
During illness, you must follow a special diet. You should avoid spicy, hot and smoked foods. There is no need to season food with spices. It is better to give preference to boiled and stewed dishes with a soft or liquid consistency. Doctors also advise drinking more fluid in the form of plain water, herbal teas, berry infusions and fermented milk drinks.
Medicines to replenish vitamin deficiencies
Here we are not talking about classic vitamin and mineral complexes, which are presented in a wide range in pharmacies and are available to any person. If you suspect you have anemia or pellagra and simply buy such a drug, you will do little to improve the situation.
What is usually prescribed? For anemia, as a rule, injections with vitamin B12. Each age has its own dosage. They must be placed within 4 weeks, after which maintenance therapy is recommended every 6 months and follow-up for 2 years. Doctors note that some patients develop iron deficiency anemia during treatment with vitamin B12, which is subsequently eliminated with iron supplements2.
For anemia, vitamin B12 injections are prescribed
Sprue may require taking tetracycline drugs, as well as injections of vitamin B12 and folic acid. For pellagra, niacin or nicotinamide is prescribed in combination with B vitamins (thiamine, riboflavin) and vitamin C.
During treatment, as well as after it, the patient is not recommended to take actions that lead to increased consumption of B vitamins: physical and emotional overload, smoking, drinking alcohol.
Drug therapy
In order for a smooth tongue to regain its healthy appearance, doctors may prescribe, in addition to the measures listed above, the use of antibiotics, antidepressants, immunostimulants, sedatives and hormonal drugs. The liver of medications and further actions will be determined by what causes the pathology.
Notice
: Undefined variable: post_id in
/home/c/ch75405/public_html/wp-content/themes/UltraSmile/single-item.php
on line
45 Notice
: Undefined variable: full in
/home/c/ch75405/public_html/wp-content /themes/UltraSmile/single-item.php
on line
46
Rate this article:
( 3 ratings, average: 5.00 out of 5)
language
- Lyulakina E.G., Chizhov Yu.V. Oral diseases in elderly and senile people // Clinical gerontology, – 2011.
- Rumyantsev A.G., Maschan A.A. Federal and clinical guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of anemia caused by B12 deficiency, 2014.
Expert “Smooth Gunter's tongue can be a symptom of deficiency conditions that often occur against the background of bacterial and fungal lesions of the oral cavity, helminthiasis, unbalanced nutrition, HIV and syphilis, gastritis, cirrhosis of the liver, cardiovascular pathologies, systemic and genetic abnormalities (for example, syndrome Down, Sjögren's syndrome), blood diseases." Dentist-therapist Elena Vladimirovna Orlova
Consulting specialist
Varlamova Tatyana Vitalievna
Specialization: Dentist-therapist Experience: 6 years
The best way out is to avoid injury
Statistics show that most tongue injuries are mechanical in nature, which, in turn, is evidence of negligence. To avoid damage to the oral cavity, follow these simple rules:
- do not get lost in thoughts while eating;
- When eating, do not be distracted;
- do not talk with your mouth full of food;
- Chew your food thoroughly and slowly.
Often the cause of wounds is a malocclusion or unsuitable dentures. An improperly growing or filed tooth also poses a risk to the integrity of the oral cavity.
Be extremely careful and remember that it is better to prevent a traumatic situation from occurring than to suffer trying to cope with its consequences. If you observe suspicious symptoms, be sure to seek help from a dentist or ENT doctor.
History of pathology
With atrophy and smoothing of the filiform papillae, the surface of the tongue resembles polished. These are the first signs of glossitis - an inflammatory disease of the muscle organ. There are several types of pathology according to the factors of appearance and clinical manifestations: rhomboid, folded and desquamative.
If the tongue is smooth, it means that the patient has encountered non-infectious Günther-Miller glossitis. The pathology was named after the doctors who first described the clinical manifestations of the disease in their works. The syndrome was first mentioned in 1851.
Traditional medicine at the service of the people
Here is a selection of recipes for solutions, the use of which will help disinfect, heal wounds and reduce pain:
- A decoction of bedstraw helps to cope with tongue pain . Brew 1 tablespoon of dried herb with boiling water, leave for half an hour, strain the resulting mixture. The decoction is suitable for both rinsing and internal use.
- Sage tincture is an assistant in the fight against pain during the treatment of oral injuries. By brewing 2 tablespoons of the substance with half a liter of boiling water and letting the infusion “rest” for 30 minutes, you will get an excellent antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory medicinal drug. Rinse frequency: 5-11 times a day.
- Pour 1 tablespoon of chamomile 250 ml of boiling water and let it brew. Use the strained solution after meals and before bed to heal wounds and relieve inflammation.
- St. John's wort tincture is a panacea for pain caused by a tongue injury. Use 40% alcohol and dried herb in a ratio of 5 to 1, respectively. Add 30-40 drops to 250 ml of water and rinse your mouth.
- Finding potatoes in a cellar or drawer is not difficult, but peeling them is a matter of two minutes. Feel free to use sliced raw vegetables to relieve pain from burns.
Hairy black tongue
Such inflammation of the tongue, as in the photo, is a consequence of the proliferation and keratinization of the papillae. The main provocateurs for the development of the disease are mechanical and chemical damage, long-term use of antibiotics, and untreated oral candidiasis. The patient with this pathology does not experience the most pleasant sensations. Firstly, filiform papillae on the mucosa can grow up to 1-2 cm in height. Secondly, the affected areas become black, which looks aesthetically unattractive and forces you to always keep your mouth shut. Plus, physical discomfort also manifests itself: most often, patients complain of vomiting and a sore throat.
The photo shows hairy black glossitis