Impact of frenulum pathology
Problems with speaking
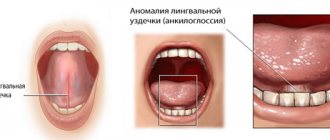
But sometimes a child has a congenital pathology - shortened frenulum .
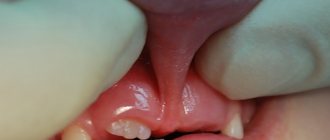
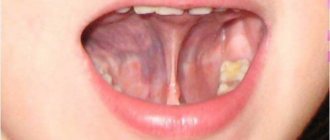
Such a diagnosis means that the frenulum is not attached in the middle of the tongue, but much closer, at the tip. Sometimes it lasts until the very tip, and the tongue even slightly bifurcates from its pressure. A serious pathology is diagnosed after the birth of a child by a neonatologist, and minor deviations in the length of the frenulum can be detected in preschool age, when the child begins to have problems pronouncing certain sounds.
Problems with breastfeeding
In infancy, a shortened frenulum can interfere with breastfeeding, as the baby cannot grasp the nipple comfortably, often loses it, and may even experience pain when sucking. This negatively affects the child’s weight gain and causes a lot of unpleasant moments for the whole family.
Indications and contraindications
Cutting the frenulum in children is resorted to in cases where:
- there are difficulties with breastfeeding;
- Speech defects and dental problems are observed.
Trimming the upper lip frenulum in children is recommended by dentists at the age of 6-8 years, when all four front incisors have fully erupted. But a short frenulum of the tongue can be operated on even in a newborn.
Among the contraindications:
- increased body temperature;
- decreased hemoglobin;
- purulent-inflammatory processes in the oral cavity.
If you have a polyvalent allergy to anesthetic drugs, surgery is contraindicated.
Tongue frenulum surgery
At what age should a tongue tie be operated on?
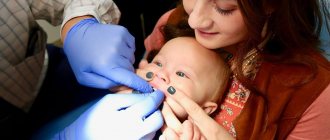
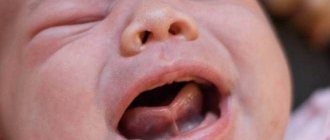
In infancy, the frenulum looks like a thin membrane and has no blood vessels or nerve endings. Plastic surgery is performed with one movement of a scalpel without anesthesia and subsequent treatment. After this simple procedure, the mother just needs to give the baby the breast; mother's milk will prevent any hygienic problems in the incision area. But this procedure may negatively affect future tongue movements due to the resulting scar. Therefore, if it is possible to avoid such a procedure, it is better to postpone the resolution of the issue to a later date.
For the mother, the main thing in this situation is to establish the process of breastfeeding.
With age, the membrane becomes stronger, blood vessels appear in it, and it is no longer possible to correct this as simply as in infancy. Usually, at a later age, a shortened frenulum is discovered during an appointment with a speech therapist, pediatrician or dentist. Signs of this phenomenon may include problems with speech, since the baby cannot make sounds that require touching the tip of the tongue to the palate or teeth. He begins to burr or lisp. Parents may also notice that the child has problems sticking his tongue out of the mouth.
Doctors recommend waiting until surgery
If a slightly shortened frenulum is detected, even at an early age, doctors recommend waiting until surgery. It can lengthen on its own as it grows.
Plastic surgery – frenuloplasty
But if this did not happen before primary school, a full-fledged plastic surgery called frenuloplasty is required. It is done under general or local anesthesia, depending on the perseverance and age of the child. The operation itself is extremely simple and does not take long, so if possible it is better to limit yourself to local anesthesia. The frenulum is cut at the tongue and moved a little further, and then sutured to functional size.
Postoperative period
The postoperative period at this age, unfortunately, requires special oral care, sometimes even taking antibiotics. The stitches are removed within a week. Once the incision and suture sites have completely healed, a long period of exercise with a speech therapist is required to ensure that the child develops proper language skills.
If a child is diagnosed with a shortened frenulum of the tongue, do not rush into action.
Early excision, although seemingly simpler, may cause speech problems later. Therefore, first, find a good pediatrician and consult to choose the optimal age of the small patient. And remember, such a problem can be solved in any case, it is only important to choose the method you need.
If you have any doubts about your child’s tongue frenulum, come to the A.Dent children’s clinic, here you will receive a comprehensive consultation and, if necessary, a course of treatment will be prescribed.
Treatment options
If the clinical indications for surgery are painful attachment to the breast and small weight gains, in infants the frenulum is dissected in its center. This simple operation is called frenotomy. How does it go? The parent holds the baby's head, the doctor lifts and fixes the tongue, and then begins the operation itself. A big advantage of frenotomy is that there is no need for anesthesia or sutures. After cutting the hyoid frenulum, the baby can be immediately applied to the breast.
Z-plasty is a more complex operation that requires local anesthesia and suturing. The choice of pain relief method depends on the child’s physical health, his age and emotional state. General anesthesia is usually used when working with children under 5 years of age with a labile psyche.
How to determine
How to recognize any frenulum deviations? What consequences can this pathology have for a child? - such questions are often asked to mothers at a doctor’s appointment.
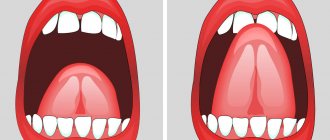
Identifying a short frenulum in a baby is not difficult even for a non-specialist; it can be seen immediately.
Parents just need to lift the baby’s lip a little and they will be able to see where the frenulum is woven. Compare with the level of the incisor neck. In a normal state, the bridle should be woven slightly above this level - approximately half a centimeter. If the reading is lower, this may directly indicate a short frenulum.
But the final diagnosis, of course, must be made by a doctor. If a pathology is detected, you should contact a medical facility. The consequences of a short frenulum can be found in the list below:
- sucking function is impaired. In most cases, the baby is not able to properly attach to the mother's nipple - to clasp it well and completely;
- changes external data, the face takes on a not entirely aesthetic appearance;
- Tremas are formed, diastemas are gaps located between the front teeth. The latter can be provoked by physiological reasons, for example, this is observed at the stage of development of baby teeth. During this period, the child’s body prepares the jaws for the natural process of replacing teeth with permanent ones. But there are gaps that are caused by pathological reasons - one of which is a short frenulum. In this case, both surgical and orthodontic treatment are recommended;
- be a provoking factor in the manifestation of bite pathology. This occurs as a result of the constant tension of the frenulum causing the incisors to protrude forward. A similar disorder usually occurs in children who already have permanent incisors. The pathology is treated, as in the previous case, with the help of a surgeon and an orthodontist;
- due to the pressure that is constantly exerted on the mucous membrane of the upper jaw, prerequisites are created for the development of inflammatory processes and dental diseases - gingivitis and periodontitis. As a result of the gums exposing the necks of the teeth, they acquire increased sensitivity, which opens the way for caries.
Short frenulum of the upper lip in a newborn: etiology and pathogenesis
The reason for the appearance of this feature in a newborn is a violation of the formation of the mucous membranes of the mouth and congenital anatomical anomalies of the oral cavity. The etiology of this defect is determined by various hereditary and external risk factors during the first trimester of pregnancy, when the embryo develops the facial skeleton and oral cavity.
Lip frenulums are thin triangular mucous bridges located vertically between the middle of the lip and the middle of the gum (alveolar process of the jaw). These movable thin bridges serve as limiters for lip mobility.
Most often, the pathogenesis of the defect is caused by the fact that the connection of the frenulum with the gum occurs below the base of the gingival papilla, that is, too close to the teeth. There are also various types of defects in the shape of the bridle itself - compaction, thickening, curvature of the shape, shortening of the free side. These defects lead to the fact that the upper lip becomes inactive, does not completely cover the upper row of teeth, and the patient experiences difficulty closing the lips.
First aid
The international classification of diseases ICD-10 classifies the short frenulum not as a disease, but as an anatomical feature of intrauterine development, and assigns code Q38.0 “Congenital anomalies of the lips.” A rupture of the child's upper lip frenulum requires parents to perform several assistance procedures before the ambulance arrives.
- Rinse the injury with cold or cool boiled water, and if possible, inspect where the tissue may have been torn.
- Stop the bleeding. Every home medicine cabinet contains a bottle of hydrogen peroxide, which can clog blood vessels and stop capillary bleeding. Soak a piece of bandage, a cotton pad or a cotton swab with peroxide and apply it to the damaged area. The child may be frightened by the rapid formation of foam; you should be patient, take him in your arms, and calm him down. Ice or frozen foods in the freezer will help cool the area of the tear, stopping the bleeding. Apply ice wrapped in a clean cloth on the outside of your mouth to avoid cold burns. If the red border of the lips is torn, the wound should be treated with brilliant green after stopping the bleeding.
- If the injury is minor or there is no opportunity to visit a doctor, the mother treats the wound with antiseptic drugs (furatsilin solution or oil chlorophyllipt, miramistin spray) and monitors oral hygiene. Care consists of frequent hand washing if the baby has the habit of holding them in the mouth, toys, and careful brushing of teeth. It is necessary to make an appointment with a doctor for a professional examination.
- If the injury is serious, the child has torn the mucous membrane, torn it off on one side or the other, you need to contact a doctor as soon as possible. If a visit to a medical facility is postponed, the child will experience pain when chewing, swallowing, talking, or smiling, which will lead to wound infection, speech defects, facial deformities, an ugly smile, and problems with chewing. Such injuries are sutured to avoid the complications described above.
Possible consequences
Often minor damage does not cause any unpleasant consequences. The same thing applies if the mucous membrane has been restored to its normal state. If medical correction has not been carried out, the tissues have grown together incorrectly, this can cause problems as a person grows and in his later adult life:
- problems with pronouncing certain sounds, especially if the injury occurred before the baby first spoke;
- susceptibility to infections of the oral cavity, if the tissues have grown together crookedly, there is no normal oral hygiene;
- Gastrointestinal problems can occur due to the fact that children do not chew food well after gum injuries.
Kids are active and curious, they require the attention and responsible attitude of adults. Childhood injuries happen everywhere; the frenulum can tear even from excessive efforts when brushing teeth or a minor bruise; only the doctor decides whether to stitch it up or not. Many speech therapists do not see a connection between such damage and poor diction. Parents should not be afraid of a protruding lip after surgery. A child can even tear the mucous membrane several times; the main thing is not to panic and maintain a reasonable approach to the treatment and prevention of injury.
Torn frenulum
It often happens when a child, injuring the upper lip, causes damage to the frenulum - it ruptures. In such a situation, you should immediately seek help from a doctor. Not only to treat the wound, but also to avoid complications when the frenulum heals on its own.
After all, without proper surgical treatment, there is no guarantee that the frenulum will heal correctly and not asymmetrically. In addition, a rough scar will appear, which will limit the mobility of the lip. And this, in turn, will lead to speech impediment. After such an injury, the child will need to be taught exercises that will promote the mobility of the organ responsible for articulation and allow the frenulum to be slightly lengthened.