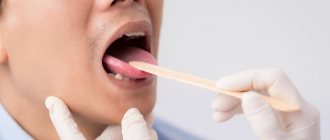
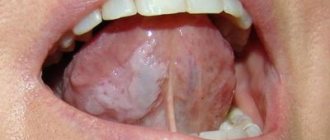
Plaque on the tongue itself is not a disease, it is a symptom that reflects what is happening in the body. There are types of plaque on the tongue that indicate a disorder in the functioning of internal organs. These types of plaque are called pathological.
Author:
- Sadykhov Rahim Agalarovich
ENT pathology expert
3.64 (Votes: 14)
Plaque on the tongue itself is not a disease, it is a symptom that reflects what is happening in the body. In this regard, the statement that language is a mirror of our health is quite true. A slight transparent or whitish coating is normal for a healthy adult. It is usually noticeable after sleep and can be easily cleaned with a toothbrush. However, there are other types of plaque that are not so harmless and indicate a disorder in the functioning of internal organs. These are pathological types.
Pathological plaque can be different: the color ranges from thick white to black, dense and sticky in consistency, and has a bad odor. The structure of the language itself may also change. This is the first signal about the onset of the disease, so if you notice uncharacteristic changes in the appearance of your tongue, consult a doctor for a correct diagnosis. Indeed, in this case it is necessary to identify the root cause of this unpleasant manifestation and quickly begin to treat the underlying disease.
What can cause pathological plaque?
The main reason is a malfunction of the internal organs. However, there are two other possibilities: smoking and improper oral hygiene. For active smokers, a yellowish coating is a constant companion, which may not indicate anything bad about health other than the presence of a bad habit. If you don't brush your mouth properly, your tongue will be completely ignored. It is wrong to brush your teeth alone. Bacteria accumulate on the surface of the tongue; they also need to be removed. To clean the tongue, many toothbrush manufacturers make a special brush on the other side. There are also scrapers for the surface of the tongue.
If a person does not smoke and maintains proper hygiene, but there is still plaque, then this may be an indicator of the following diseases:
- Diseases of the digestive system (the most common cause) are ulcers, gastritis, diseases of the gallbladder, pancreas, and liver. Usually in such cases the plaque is accompanied by a persistent unpleasant odor that does not go away even after cleaning.
- Diseases of the respiratory system - tuberculosis, bronchitis, asthma.
- Infectious diseases - influenza, sore throat, ARVI, acute respiratory infections.
- Reduced immunity.
- Diseases of teeth and gums.
- Changes in acid-base balance due to medications.
Provoking factors and causes
Various provoking factors cause changes in the color of the mucous membrane and the appearance of layers of plaque on the tongue. These include the following pathogens:
- bacterial microorganisms;
- fungal and viral infections;
- dysbacteriosis of endogenous microflora;
- endogenous and exogenous diseases of visceral organs;
- alcohol abuse, smoking;
- food and toxic poisoning.
In addition to the relationship with pathological changes in internal organs, plaque contributes to the development of secondary infections in the oral cavity and nasopharynx, since it is a breeding ground for anaerobic bacteria.
The reasons why different types of deposits appear lie in the condition of the internal organs and systems. A weakened body is more susceptible to the effects of pathogens and the subsequent appearance of interrelated symptom complexes. There are two main reasons for the formation of plaque in adults:
- tendency to diseases of a bacterial nature;
- damage to individual internal organs.
An additional reason is insufficient oral hygiene. In childhood, the formation of the protein layer is often associated with nutritional principles and hygiene.
What color is the pathological plaque?
By the color of the coating on the tongue, you can determine which organ malfunction caused it:
| White | A light whitish coating that can be easily cleaned with hygiene procedures is the norm for an adult. A cause for concern is if the white coating is dense or has a cheesy structure and is not cleaned. This may be a sign of a fungal infection. Other reasons include: monotonous diet, lack of vitamins, poor hygiene, smoking, intoxication, wearing dentures, taking medications. |
| Grey | Sometimes the tongue becomes covered with a gray coating when taking antibiotics for a long time. Also accompanies diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. |
| Yellow | Often indicates liver disease (in such cases a bitter taste is felt in the mouth). It can also occur with diseases of other organs of the digestive tract, with viral diseases, with an excess of bile in the body. |
| Green | This is a rare occurrence. Most often it is an indicator of liver problems. |
| Brown | Occurs with disorders of the digestive tract, alcoholism and smoking, and abuse of brown foods (chocolate, coffee, black tea). |
| Orange | It occurs mainly with gastritis, due to the fact that gastric juice enters the oral cavity in large quantities. |
| Blue | It may appear due to problems in the cardiovascular system, kidneys, due to a lack of folic acid, iron, Vit C, Vit B12. It can also appear due to mercury and heavy metal poisoning. |
| Black | Appears in cases of liver dysfunction, lead poisoning, acute infections, Crohn's disease, acidosis. |
Treatment of plaque on the tongue
Protein deposits that appear on the tongue make it possible to promptly identify the pathological process and begin treatment. Plaque is not a diagnostic tool, but helps facilitate diagnosis. When examining the oral cavity, the doctor pays attention to the location, color and consistency of the formed layer, therefore he builds a plan for the examination and further treatment measures taking into account these factors.
The treatment plan depends on the nature of the plaque and the factors that triggered its development. Physiological deposits do not require medical intervention, since they are not concomitant signs of certain pathologies. The condition can be controlled by preventive measures, which include careful oral hygiene and the exclusion of coloring products.
Types of therapeutic measures
Treatment of pathological plaque depends on the etiology and pathogenesis of the provoking disease. There are several types of treatment for protein deposits formed on the tongue due to diseases:
- Antibacterial therapy
. If plaque is of bacterial origin or diseases that provoke its appearance, a course of antibiotics or antimicrobial drugs is prescribed. - Dietary food
. For diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, hepatobiliary tract and urinary system, therapeutic nutrition must be included in the therapeutic plan. Diets minimize the harmful effects of certain food groups and promote rapid recovery of the body.
Depending on the nature and characteristics of the disease, symptomatic treatment is carried out. Therapeutic measures are aimed at stopping the underlying disease and restoring normal functional activity of organs.
In case of insufficient effectiveness of drug therapy, surgical operations are required. Surgical intervention in the presence of tumors, perforated ulcers, staghorn stones and other complex pathologies is aimed at quickly relieving symptoms. As a result of successful treatment, the condition of the mucous membrane of the tongue returns to normal.
Diagnostics
To establish a complete picture of the state of the body, the doctor determines the color of the tongue, its structure, position, motor functions, and possible other pathologies in the oral cavity. Among the laboratory and instrumental research methods aimed at clarifying the characteristics of plaque and the reasons for its appearance, the following may be prescribed:
- general and biochemical blood test;
- sowing on flora from the surface of the tongue;
- determination of antibodies to the bacterium Helicobacter pylori;
- Ultrasound of internal organs;
- fibrogastroduodenoscopy;
- scatological research.
If you are concerned about the condition of your tongue, plaque on it, pain, unpleasant odor, contact the ENT doctors of our clinic. High-precision equipment and the experience of our specialists allow us to quickly make correct diagnoses and prescribe treatment.
Features of the raid
Diagnostic measures aimed at identifying diseases by the color of the tongue should take into account the characteristics of plaque. There are two types of mucosal lesions:
- Physiological plaque
. This phenomenon is observed when the papillae are stained with food dyes (black tea, coffee, fruit and vegetable juices, confectionery). Physiological coloring quickly disappears when you avoid products containing coloring pigments. - Pathological plaque
. Appears as a result of functional disorders of visceral organs or infectious diseases of systemic organs and structural tissues of the nasopharynx.
When diagnosing, the physiological and pathological characteristics of plaque are differentiated by examining the quality of the latter. If a change in the surface of the mucous membrane is caused by coloring pigments, then such a manifestation does not pose a danger to the body and is of no value in establishing a diagnosis.
Prevention of tongue diseases
To reduce the risk of diseases of the tongue itself and other organs, you need to monitor your diet, daily routine, and have less contact with infectious patients. Caring for the tongue itself should be no less thorough than caring for your teeth.
Accumulating plaque, especially in sick people, is a place for mass reproduction of bacteria and fungi. If it is not removed in time, it will become a source of infectious pathogens that can penetrate any part of the body.
When cleaning the oral cavity, it is useful to use toothbrushes with a ribbed back surface to clean the tongue from plaque, or special spoons and scrapers. But they must be used carefully so as not to damage the taste buds and mucous membrane. After cleaning, it is advisable to use pharmaceutical rinsing solutions or prepare homemade herbal decoctions.
FAQ
Will I be able to correct my malocclusion if my tongue position remains incorrect?
Modern orthodontics has a wide range of methods for correcting malocclusion. At the same time, bite correction must be comprehensive. A prerequisite is the elimination of all causes and factors leading to the formation of malocclusion. This also applies to correcting the position of the tongue.
Will myogymnastics help correct the situation?
Yes. Exercises will help correct the position of the tongue. But sometimes exercise is not enough. Additionally, orthodontic treatment to correct the bite is required. In some cases, surgery is needed.
Should the tongue rest on the teeth?
No, it should be located behind the teeth.
Training to improve the situation
It is possible and necessary to correct the position of the tongue. Myofunctional therapy has been developed for this purpose. It is used for both therapeutic and preventive purposes. The advantages of this treatment are that it can be performed at any age and at any stage of orthodontic treatment. In addition, mewing does not require special skills or experience. Myofunctional orthodontics specialists will simply show you exercises that need to be performed regularly. The patient’s task is to perform the complex in strict accordance with the doctor’s recommendations.
Here are some common exercises that will help correct the position of your tongue:
- Place your lips behind your lower teeth, press your tongue to the roof of your mouth, and tighten your chin. Hold this position for 5 seconds, then relax your muscles. Repeat 10 times.
- Place your tongue behind your upper teeth, lengthen your chin and tense your lower jaw and hold for 10 seconds. Repeat 10 times.
- The tongue must be placed in the palatine cavity and tense. Stay in this position for 10 seconds, then relax. Repeat 10 times.
- The starting position is the same as in the previous exercise. Now try to swallow saliva without using the muscles of your cheeks and lips. Only the muscles of the tongue should work. This exercise will be difficult for you at first, but every time you do it you will notice progress. Repeat 10 times.
- The starting position is the same as the previous exercise. Tighten your tongue and smile. Then use your index fingers to press on the corners of your mouth, trying to hold back your smile. After 10 seconds you can relax. Repeat 10 times.
- Pull your tongue forward as far as possible, trying to reach your chin. Hold for 5 seconds. Repeat 15 times.
- Extend your tongue, trying to reach the tip of your nose. Hold for 5 seconds. Repeat 15 times.
Healthy tongue color
A healthy tongue is distinguished by a delicate pink color, and taste buds are evenly distributed over its entire area. The middle fold has clearly defined edges.
Due to the intake of certain foods, drugs and medicines, and all kinds of drinks, the color of the tongue can change. Some give such a reaction due to the specific substances contained in the composition, others simply contain a lot of coloring pigments, which color the tongue and the coating on it in the corresponding color.
There is also a slight dependence of the color of the tongue on the time of year. For example, in summer the tongue becomes redder, and in autumn and winter it becomes slightly yellow.
Introduction to linguistics
Diagnosis by language is best carried out in daylight or in the light of fluorescent lamps. Better - in the morning, immediately after waking up. Please note that the color of the tongue can be changed by foods, physical activity, stress, and nasopharyngeal diseases.
So, go to the mirror and stick your tongue out at him. Now carefully examine its appearance. Normally, this organ should be pale pink, with a smooth, velvety surface. At the tip of the tongue there are small papillae, in the middle part there are larger ones, and at the root there are whole clusters. There are approximately ten thousand of them in total. These are taste, heat and biochemical analyzers associated with various parts of the body.
The tip of the tongue is believed to reflect the condition of the heart and lungs. In the middle, on the very “body” of the organ, there is a projection of the stomach and spleen. The branches of the liver and gall bladder run along the lateral edges. By changes in the language, you can discern ailments that have already appeared, as well as guess about future problems. As a rule, warning signs in the tongue appear several days before other symptoms accompanying a particular illness.
By the way
It's sweeter to be a girl! Our perception of the taste of food depends not only on the state of the tongue, but also on many other factors, including the gender and age of the person. This is exactly the conclusion that Danish scientists came to. Experts conducted a large study involving almost 9,000 schoolchildren. All children received a set of samples of different foods, with the help of which experts had to find out how well boys and girls distinguished tastes of different intensities. It turned out that girls are better at distinguishing one or another taste than boys. Thus, the sensitivity threshold of boys to sour is 10%, and to sweet – 20% lower than that of girls. An important factor in the perception of taste is also the age of a person. Children's taste buds work better than adults'.
How to identify a disease by the color of your tongue
When making a diagnosis, they rely on a set of signs:
- tongue color in diseases;
- the form of this body;
- oral odor;
- plaque, its color and quantity;
- work of taste buds;
- degree of language functioning.
Another criterion is a change in certain areas of a given organ. But this criterion is very individual and rare. Scientists have hypothesized that the tongue is divided into sections, and each section is associated with a specific organ.
If you need to determine whether the body is healthy or there is some kind of disease, you should examine the tongue only early in the morning on an empty stomach, and rinse your mouth with water before examination. It is best to carry out the inspection in a well-lit room.
Swollen throat
If the tongue and throat are swollen at the same time, this condition is life-threatening for the patient. In the vast majority of cases, this condition occurs during anaphylactic shock (the most severe manifestation of allergies). Only an experienced doctor can remove a patient from a state of anaphylactic shock, therefore, at the first signs of swelling of the tongue and throat, you should immediately call an ambulance, especially if the patient has other dangerous symptoms - such as difficulty swallowing, bluish coloration of the lips and nails, swelling of the eyes and lips, small rashes, low blood pressure, nausea, shortness of breath or choking.
Identification marks
Ulcers, spots, lines on the tongue can also tell a lot to an experienced interpreter. Thus, a curved line running in the middle of the tongue “hints” at a deformation or curvature of the spine.
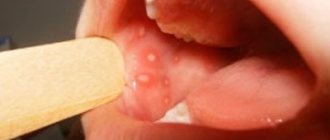
Enlargement or inflammation of the papillae on the entire surface of the tongue often occurs with gastritis with increased secretion of gastric juice. And, conversely, a smoothed surface of the tongue occurs with gastritis with low acidity, as well as with diseases of the liver and gall bladder. The imprint of teeth along the edges of the tongue indicates poor intestinal function and insufficient digestion of food. The so-called “geographical” language, in which continents and oceans seem to be imprinted, is a sign of food allergies. One crack in the tongue appears with gastritis, and numerous creases appear with fever, diarrhea, diabetes, and anemia.
Swollen after puncture
Many patients complain that their tongue is swollen after piercing. In most cases, this swelling is not pathological. The tongue was injured during the puncture process, and slight swelling is completely natural and natural. Therefore, it is necessary to strictly adhere to the recommendations of the specialist who performed the puncture, keep the oral cavity clean, and rinse your mouth with antibacterial drugs. However, if the swelling does not go away within 4-5 days, and purulent exudate forms at the puncture site, you should immediately consult a doctor, since various complications often arise with tongue piercing.
Normally, healing after a puncture occurs within two weeks. During this period, the tongue may swell, hurt, and the patient may experience a feeling of discomfort, burning, and soreness. In the future, all these unpleasant symptoms will disappear, and after two weeks the wound should heal without a trace, and the swelling should go away.