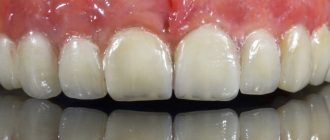
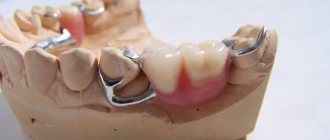
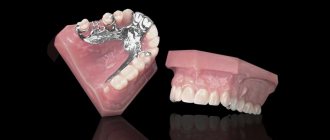
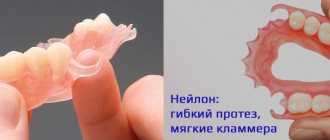
Clasp prosthetics is a good alternative to implantation and has a number of advantages over bridge prosthetics. The most popular type is clasp dentures with clasps; this is a more budget-friendly option than those fixed with attachments; it is quickly manufactured and does not require additional grinding of the teeth. They are also used as splinting prostheses.
Clasp dentures on a turnkey basis without additional payments!
Clasp prosthesis on hooks - 40,000 rubles! Clasp prosthesis with locks - 70,000 rubles!
What is a clasp denture with clasps?
“Bugel” (German: bugel)
translated as “arc”. It is the arched metal frame that is the basis of the orthopedic design. A base saddle is welded to it, imitating gums and crowns, artificial teeth. Fixation in the mouth occurs by attaching hooks to the supporting teeth. Hooks are otherwise called clasps. Therefore, clasp dentures with hooks and dentures with clasps are one and the same.
A metal arch and a convenient fastening method have made it possible to reduce the volume of the prosthesis; it is not as massive as a plate one. It takes up less space in the mouth and you quickly get used to it. On the lower jaw it does not interfere with the tongue, it will not move the product from its place, and on the upper jaw it does not block the palate like the same removable acrylic one, which does not cause a gag reflex and does not interfere with talking. Speech is clear and without defects.
Hooks are often made of metal. This provides better fixation, but over time the enamel in the areas of contact may undergo changes. Sometimes technicians combine materials using nylon and acrylic. The first is prone to stretching, which can interfere with the stable retention of the prosthesis, and plastics break easily. In practice, it occurs when the distant supports are made of metal clasps, and in the frontal area they are made of white or transparent material to make the smile area more attractive.
Types and structure of clasps
Clasp fasteners can be retaining (settle under load, transfer pressure to the oral mucosa), support (evenly distribute pressure under load during clenching, unclenching teeth, talking, eating on the supporting teeth and gums), support-retaining. The latest (combined) types of hooks have a complex design:
- body (fixed element located in the upper part of the tooth);
- shoulders (adjacent in front and behind to the supporting units);
- occlusal overlay (a protective barrier that prevents the clasp from immersing in soft tissue and transfers the load to the supporting teeth);
- process (connects the hook to the base of the prosthesis).
Classification of clasps:
- round, flat, ribbon, semicircular (in shape);
- single-, double-armed, double-armed, single-linked, ring-shaped (according to the girth of the tooth);
- holding, supporting, supporting-holding (by function);
- cast and bent (according to technology and materials of manufacture).
The main advantage of clasp structures is the ability to remove them at night and provide rest to the oral mucosa and supporting teeth. Hooks on clasp dentures must meet a number of requirements: securely fix the structure, distribute the chewing load along the axis of the teeth and oral mucosa. Clasps should not affect teeth at rest; in case of periodontitis, they also have a fixing function.
Indications for installation
Clasp dentures on hooks are used in the following cases:
- in the absence of several teeth in a row;
- included defects (loss in different places of the jaw);
- end defects (no outer teeth);
- periodontal diseases and tooth mobility from this. The arc prosthesis splints and keeps them stationary;
- increased wear of crowns. The denture covers them, protecting them from further abrasion.
Many patients choose an arched prosthesis because they want to move away from the insufficiently comfortable plate one.
Design
The standard design of a clasp includes three elements: a shoulder, a body and a process.
The shoulder is a special part that provides coverage of the dental crown, and is located between the gum line and the middle part. A prerequisite is a tight fit to the tooth surface in all areas, the identity of the anatomical structure and the strength of the element. The supporting part of the shoulder is two-thirds of its length, and is placed above the boundary line, eliminating lateral displacement of the prosthetic structure, and maintaining the basic rigidity parameters. The retaining element, which makes up the remaining third of the length, is located below the boundary line and fixes the prosthesis in a given position.
The process is a part used when using the method of rigidly connecting the clasp to the base of the system, which is placed under artificial crowns. In such designs, the connecting link is the body of the clasp, which is a spring element located on the chewing surface of the unit.
Models of the support-retaining type are characterized by the absence of a process, which is replaced by an occlusal pad and an anchor part.
Contraindications
To install an orthopedic structure, support teeth are required, to which hooks are attached. That is, if you are completely edentulous, the clasp cannot be used. You can use the implantation service. Artificial teeth will securely hold the clasp denture with clasps, while restoring natural metabolic processes in the bone, preventing tissue atrophy.
The supporting teeth must be healthy and strong. They take on the burden of holding and chewing.
If you are allergic to metal, an orthopedic dentist may suggest a metal-free clasp prosthesis. If you are sensitive to other materials of the product, you should consult an allergist and choose with your doctor the best option for prosthetics or implantation.
Manufacturing stages
The production of a clasp clasp prosthesis takes place in several stages. The stages are divided into laboratory and clinical. Here's what happens during the clinical stages:
- examination of the patient, preparation of his teeth for prosthetics,
- grinding of abutment teeth to install crowns,
- taking impressions of the jaws,
- selection of shade of artificial teeth,
- protecting treated teeth with temporary crowns,
- production of permanent crowns and arches,
- fixation of crowns,
- frame fitting,
- fabrication of the structure in the laboratory,
- delivery of the finished prosthesis.
Laboratory stages:
- making a model based on the obtained plaster impressions,
- production of wax bases with occlusive rollers,
- drawing the frame onto the plaster model,
- duplication of this model,
- frame modeling,
- frame casting, subsequent processing,
- fitting the frame to the model,
- fitting of a metal frame by a patient,
- modeling the wax base, installing teeth on the structure,
- checking the clasp denture in the patient’s oral cavity,
- replacing the wax part with a plastic part, grinding and polishing,
- fitting and application of the finished prosthesis.
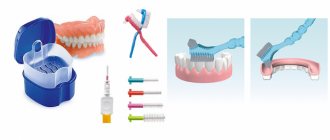
Caring for your prosthesis
In order for clasp dentures with hooks to maintain their original appearance for a long time, it is necessary to provide them with fairly simple care, which consists of simple steps:
- brush them twice a day with a brush and toothpaste without harsh abrasives;
- rinse your mouth after eating;
- have your dentures professionally cleaned once a year;
- come every six months for relocation to correct the correct chewing load and its uniform distribution;
- follow all doctor's recommendations;
- apply disinfectant antiseptic tablets, solution, where to place the prosthesis.
If part of the prosthesis or hooks breaks, immediately contact the dentist where the treatment and installation took place.
Advantages and disadvantages
For comparison, let’s take the clasp’s “classmates” - fixed bridges and removable plate prostheses. Clasp orthopedic structures, of course, are superior to plate ones in strength, but, like bridges, they are a temporary way to restore the dentition. Despite all the efforts of manufacturers, the clasp is not able to stop the loss of bone tissue, the inevitable decrease of which soon leads to changes in facial features and disturbances in the functioning of the dental system and internal organs. The obvious disadvantages of a removable clasp also include an aesthetic defect when installing a clasp prosthesis, when metal hooks attached to the teeth are visible, and a slow adaptation time to the design. In addition, any denture puts pressure on the gums and causes discomfort when chewing and hypoxia - a condition in which the gums do not have enough nutrition, which causes bone tissue to atrophy even faster. As for the service life of clasp dentures, compared to dental implants, it is quite short and is no more than 10 years. Subject to proper care and timely correction once a year.
Expert opinion
Roman Borisovich Alekperov
orthopedic dentist
Experience: 24 years
Advantages of clasps over attachments. When there is a need to restore the dentition, and the dental defects are scattered, the patient does not have enough financial resources, I recommend installing clasp dentures with clasps. You quickly get used to them, their production does not require much time, the chewing load is distributed on the teeth, and not on the gums, as is the case with lamellar ones. Yes, the aesthetics are insufficient because of the visible hooks, but you have teeth, you can eat, drink, and live a normal life.
How clasps are made
The structures in question are made in a dental laboratory, and first you need to choose one from all the varieties. Most often, such fixing elements are made from base metals. Any type of hook is bent with pliers, tongs or round nose pliers - it is given its original shape. Then the metal element is “implanted” into the base and the prosthesis is given to the patient to try on and, if necessary, the product is adjusted.
Important! Thorough polishing of the metal in the element that is adjacent directly to the tooth is required: the material should not injure the enamel or serve as a place for plaque accumulation. But the process, on the contrary, is covered with small notches, which ensure its reliable fixation with the acrylic base.
Clasps are an integral part of a removable denture, which has an extensive classification. The choice of a specific model is made by the dentist, because it is important to take into account not only the financial capabilities of the patient, but also the condition of the supporting teeth, gums and alveolar process.
Price
The average cost of a clasp denture with clasps is 35,000 rubles, when choosing a metal-free base (acrifri) - from 60,000 rubles. This includes the material, the work of the dental technician, fitting, and correction. The number of missing teeth in this type of prosthetics does not greatly increase the price. Whereas when fixing with locks, it is interconnected with the number of supporting teeth, and directly with the production of crowns on them.
Other jobs
How much does a clasp prosthesis cost?
The price of lower jaw prosthetics using a clasp design depends on the following factors:
- base and frame material;
- the number of teeth that need to be restored with a prosthesis;
- material for dental crowns.
The average price of a clasp prosthesis is from 32,000 rubles. The price, as a rule, already includes payment for the prosthesis itself, treatment planning, installation of the system, and check-ups with the dentist.
Clasp dentures are an inexpensive and accessible way to restore a smile with a long service life (more than 10 years).
Prices
| Service | Price |
| Consultation + treatment plan | |
| Clasp prosthesis | 47 700 ₽ |
| Quadrotti | from 57,100 ₽ |
| Splinting | 52 150 ₽ |
Expert of the article you are reading: Natalich Boris Anatolyevich Chief physician, CMN, doctor of the highest category, orthopedist, surgeon, implantologist, leading specialist of the NovaDent network
38 years
Clinical experience
Otradnoe
st. Khachaturyan, 7
+7 +7
Free consultation with this specialist
Features of clasp prosthetics on the upper and lower jaws
The differences between the upper and lower dentures lie in the location of the bridge and retainers. The arch model depends on the topography of the dentition defect, the shape of the palate, the relief of the alveolar process and other factors.
When restoring the upper jaw, the thickness of the bridge should be 0.9-1.2 mm and the width 4-10 mm. In this case, the arc should be located 0.5 mm from the mucosa. In most cases, the upper jaw prosthesis is fixed on the lateral incisors or molars.
The lower jaw prosthesis must be made with an arch that is unevenly spaced from the mucous membrane: at the upper edge it extends by 0.5-0.6 mm, at the lower edge - by at least 1 mm. In this case, the jumper should not come into contact with the underlying tissues and injure the frenulum. In most cases, the structure is attached to the lateral incisors.