The choice of the type of anesthesia for a child is made after a thorough history taking. Dentists should identify possible contraindications to the use of a particular method or pain medication. The risk group includes children with a tendency to allergic reactions.
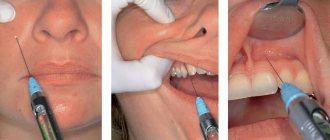
Most often, topical anesthesia is used as local anesthesia. An anesthetic is applied to the surface of the tissues adjacent to the diseased tooth, which blocks the receptors and terminal sections of nerve fibers in the periphery. Sensitivity is turned off in the surface layers and does not affect the deep ones.
Application anesthesia is also used in other cases:
- if the patient exhibits a pronounced gag reflex during tooth preparation;
- when it is necessary to obtain intraoral X-rays or impressions of the jaw;
- to relieve pain in the marginal periodontium;
- in case of difficult eruption of wisdom teeth - for the period of excision of the hood above them;
- during a biopsy;
- during dissection of the frenulum;
- when performing curettage of periodontal pockets;
- in the treatment of minor destruction of tooth enamel, etc.
When are dental procedures acceptable?
Some experts believe that during pregnancy it is better to refuse any health-related interventions, because this period is characterized by serious changes both in the endocrine system and in the entire body as a whole. Surgery can be a real test for the mother and significantly affect the health of the fetus.
In the first trimester of pregnancy, a woman should be attentive to herself, since during this period all the vital organs of the baby are formed. The health of the baby for the rest of his life depends on how correct the mother’s lifestyle is. That is why you should be careful when taking medications that have a strong effect, including anesthetic.
In later stages of pregnancy, care should be taken to ensure the safety of the fetus. In the last trimester, any severe stress can cause serious complications, including premature birth. Incorrectly selected anesthesia and fear of surgery can seriously harm the baby’s health.
In the second trimester, pregnancy is more stable. There are much fewer dangers to the baby’s health than at the beginning or end of pregnancy. That is why experts consider this period the most favorable for seeking dental care. For a period of 4-6 months, it is permissible to use certain medications during dental treatment. Most procedures will be well tolerated by the woman’s body and will not affect the development of the child.
In any case, before going to the dentist, you should consult with your doctor who is managing your pregnancy. He will tell you about all the dangers that can await a woman when using this or that drug. In addition, it is imperative to inform your dentist about your exact gestational age, who will select the appropriate treatment regimen depending on all the individual characteristics of the body.
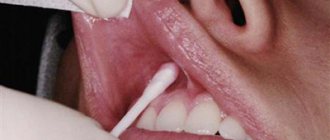
How is topical anesthesia performed?
The area of the mucous membrane is dried with a cotton swab. Then a small amount of anesthetic is carefully applied to it with a cotton swab or swab. The drug instantly penetrates 2-3 mm deep - the effect occurs within 30-40 seconds in the case of solutions and after 2 minutes if ointments or gel are used. The anesthesia lasts for 10-15 minutes.
As anesthetic agents in pediatric dentistry, those that meet certain requirements are used:
- soluble in water and isotonic solution;
- demonstrate high resistance to sterilization and stability in solutions;
- have a bactericidal effect and a pleasant taste, which is important for children;
- penetrate well through the epithelial layer;
- provide rapid pain relief;
- do not cause irritation;
- exhibit minimal toxicity upon absorption;
- give a minimum of adverse reactions.
General anesthesia in pediatric dentistry
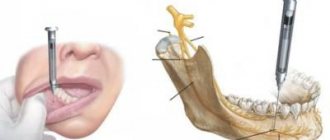
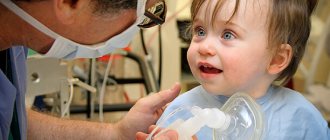
Sometimes in pediatric practice it is necessary to use general anesthesia. There must be serious reasons and indications for treating or removing teeth for children under anesthesia, because anesthesia is a deep depression of the nervous system, and this kind of exposure entails a risk of complications. A lot depends on the qualifications of the anesthesiologist: he must correctly calculate the dosage and take into account all the characteristics of the child’s body.
The anesthetic for general anesthesia is administered by inhalation. The child inhales the vapor of the substance and quickly falls asleep. This way, the doctor has the opportunity to carry out treatment in a calm environment, quickly and efficiently, while the little patient will not receive psychological trauma.
Indications for general anesthesia:
- A lot of work. It is difficult for a child to sit still, and if several teeth need to be treated in one session or a complex operation must be performed, then this mission becomes almost impossible.
- Allergy to drugs for local anesthesia. Articaine and other similar anesthetics may cause an allergic reaction. In this case, anesthesia may be the only solution.
- Ineffectiveness of local anesthesia. Sometimes the injection does not provide the required degree of pain relief due to the characteristics of the baby’s body. If the child remains highly sensitive, it is better to use anesthesia.
- Insurmountable fear of treatment. Severe dental phobia is an indication for general anesthesia if the child cannot be distracted from his worries with affectionate words, cartoons or toys.
- Some mental and neurological diseases (cerebral palsy, epilepsy, Down syndrome and the like).
What to do if your child has allergies?
Allergy to anesthesia in dentistry in children is a fairly common occurrence. The child's body is more susceptible to unusual reactions to new substances, which include anesthetics. Before visiting the dentist, it is necessary to undergo tests to understand whether local anesthesia is acceptable, and if an allergic reaction does occur, treatment is carried out under anesthesia.
What drugs are used for topical anesthesia?
In pediatric dentistry, solutions, emulsions, ointments, pastes, gels, aerosols are used, as well as special dispersed tablets, caramels and children's chewing gum. They contain highly concentrated anesthetics without vasoconstrictors. Most often, dentists use solutions, sprays and aerosols.
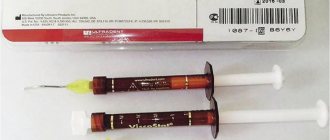
- "Babident" is intended for pain relief during the eruption of primary teeth in infants. Apply 1-2 drops of the solution with a cotton swab or finger to the mucous membrane of the gums 1-3 times a day.
- In pediatric dentistry, Perylene-Ultra solution is often used.
- The most popular gels and pastes are “Xylonor”, “Instilagel”, “Aroma paste carried”, Jen-Dental, Xyligel.
- The most commonly used ointments are 2-3% dicaine, 5% lidocaine, 2-3% falicaine, etc.
Non-injection anesthesia
Non-injection anesthesia involves the use of local agents that are in the form of an aerosol or gel. They are used for initial pain relief. In some cases where short-term dental treatment is required, non-injection sedation methods can be used as applications that are applied to a limited area of tissue.
Non-injection anesthesia in dentistry can be of the following types:
- electronarcosis;
- superficial or terminal anesthesia;
- refrigeration or freezing.
The specific type of anesthesia is selected by the dentist after a personal consultation, studying the patient's medical history, his general health and many other factors.
Particular attention when choosing an anesthesia option and a specific drug is required in the presence of chronic diseases affecting the cardiovascular system, kidneys, liver and respiratory organs. It is also important to minimize the risks of severe allergic reactions in people suffering from allergic pathologies (bronchial asthma, skin diseases).
Spray irrigation method
According to the results of clinical studies, the most pronounced analgesic effect in the treatment of caries of temporary teeth is provided by sprays and aerosols, for example Lignospam, Lidokain 10%, Legekain, etc. Anesthesia occurs after 30-40 seconds and lasts for 15 minutes. Due to their unpleasant taste, gels and aerosols are contraindicated in children under four years of age, as they increase salivation and can enter the respiratory tract and cause respiratory arrest.
Older children also complain of local symptoms after irrigation - numbness of the laryngeal tissue, sensation of a lump in the throat, hoarseness, which sometimes lead to breathing problems. Therefore, before using sprays and aerosols, the dentist must tell the patient how to behave correctly and make sure that he has accepted the information. This type of anesthesia can only be done while exhaling, but it is safer to apply the product to a cotton swab and apply it to the area, similar to liquid solutions.
"Freeze"
What is “freezing” and why does it “freeze”? Many of us are mistaken in thinking that it's all about temperature. The loss of sensation as a result of cooling is fundamentally different from anesthesia, which is carried out using an injection with an anesthetic. As such, toothache does not disappear anywhere, but the nerve impulse that transmits the signal about its occurrence to the brain is blocked by an anesthetic. Once in the tissue, the anesthetic deprives the nerve of the ability to conduct pain impulses, changing its electrical potential. The nerve acquires the ability to conduct impulses again after the anesthetic leaves the body, breaking down under the action of special enzymes. The effectiveness and duration of anesthesia directly depends on the correctly selected type of anesthetic, its dose and method of application.
I would also like to note that today anesthesia is carried out not only before the process of “tooth drilling”, but also for the anesthesia manipulation itself! To do this, the planned injection site is “frozen” using a special anesthetic gel, after which the introduction of the needle and the drug becomes absolutely painless.
Sedation or anesthesia?
Sedation and anesthesia are two different things. Sedation does not disconnect consciousness from the outside world. It is more like a state of light dozing. However, it is also a medical exposure to the body that should be avoided. It is quite possible to manage only with anesthesia. If you are very nervous, you can do a breathing practice that will help you calm down.
Anesthesia is a more serious manipulation. It has a number of side effects:
- dizziness, nausea;
- severe thirst after the end of the effect, but you can’t drink;
- weakness;
- chills or, conversely, high temperature.
In addition, after recovering from anesthesia, you need to remain in bed for some time and limit physical and thermal stress.
The worst thing that can happen during anesthesia is cardiac arrest. This happens with incorrect diagnosis and incorrect selection of the dosage of the drug. However, it is best to avoid additional procedures beyond local anesthesia.
What should I do to make the anesthesia wear off?
The anesthesia will go away faster if you do a massage.
In order to avoid undesirable consequences, you should ask your doctor in advance how to remove the frost after dental treatment.
The specialist should explain that in order for the painkiller to wear off as quickly as possible, you need to follow a few simple rules:
- A few hours before visiting the dentist, it is not recommended to eat heavy food or drink alcohol. Do not take any medicines unless they have been prescribed to you by your doctor.
- In order for the frost to go away faster after a simple dental procedure, it is recommended to drink something warm, as well as massage the numb area.
- After a serious intervention (pulp opening, drainage, etc.), you should not drink or touch this area. Stop drinking for an hour after the intervention, and do not eat food for four to five hours.
After dental treatment, you should not drink for several hours.
If the effect of the painkiller does not go away for a long time, then you need to visit a doctor as soon as possible. It is possible that a nerve was damaged during the intervention. In this case, physical therapy is performed, and a consultation with a neurologist may be required.
Anesthesia in pregnant and lactating women
During pregnancy, dentists do not recommend dental treatment; if possible, this should be postponed until later. However, there are situations in life when it is impossible to tolerate. The most successful period for such manipulations is the second trimester.
But what kind of pain relief should be used during this period? The composition should not contain adrenaline; the patient’s blood pressure should not be allowed to increase, otherwise the uterus will begin to contract.
Dental treatment for pregnant women is not recommended
Important! The drug must be non-toxic; if necessary, the procedure is carried out in a hospital.
There is no danger during lactation, and the doctor can safely use an anesthetic. This anesthesia acts locally, does not penetrate into the blood, and has no toxic effect on the body.
In order to still protect your child, you need to feed him before going to the dentist, and also express milk for the next feeding.
Freezing usually does not last longer than a few hours. If everything was done correctly and the doctor did not make a mistake, then the procedure goes well and the patient does not feel any discomfort.
Anesthesia for dental treatment
Many women are interested in the question: is it possible to freeze a tooth during pregnancy? The answer to this question is ambiguous. Some obstetricians and gynecologists have a negative attitude towards any type of painkillers. Other experts believe that pain should not be tolerated as it can cause serious stress and affect the health of the fetus.
In any case, you should trust your doctor. Local anesthesia is considered the safest in terms of influence on the intrauterine development of the child. Drugs must be of high quality and have all certificates confirming the safety of the drug. You should also pay attention to the expiration date of the anesthetic. If any suspicions arise, it is better to refuse the help of a doctor and go to another clinic.
Properly done freezing a tooth during pregnancy does not in any way affect the health of the fetus or the duration of its gestation. Modern drugs do not allow the active substances to penetrate the placenta to the baby. Therefore, you can not be afraid and feel free to treat your teeth.
Indications for the use of sedation and anesthesia
Sedation, as a mild sedative, is used in the following cases:
- small children
- severe fear of the procedure, dental phobia
- long and complicated operation
- strong gag reflex
As for anesthesia, it is not recommended in principle. It should only be used with the permission of a doctor in extreme cases. For example:
- several hour treatment
- panic attacks
- intolerance to local anesthetic components
It is worth mentioning separately about anesthesia for pregnant women. Pregnancy is a delicate situation in which you should carefully choose medications for treatment. Of course, general anesthesia and sedation are completely contraindicated during pregnancy. However, anesthetics based on ultracaine and primacaine are quite safe. They cannot penetrate the fetus and are used even during lactation.
What to do if the pain is severe?
In some cases, toothache can be so severe that it cannot be tolerated. Moreover, unpleasant sensations are a serious stress for the body, and this is unacceptable for a pregnant woman. If you do not have time to consult with your doctor, you can directly seek emergency dental care.
During the appointment, the dentist will definitely ask the expectant mother about the duration of pregnancy and the presence of individual drug intolerances. Depending on this, he will select the right treatment.