In what cases should you contact a dentist surgeon?
As planned
A visit to a dental surgeon is mandatory for children from 1 to 3 years old. During this time, it is necessary to carry out from one to several examinations by a specialist in this profile. The doctor should first examine the child at 1 year of age. By this age, approximately 8 baby teeth have already grown, the rest are in the process of erupting. The doctor checks them for the presence of caries, inflammatory diseases, assesses the sensitivity of the enamel, and checks their correct location. At this time, bite pathologies can be detected in time.
Routine examinations are also indicated for patients with neoplasms in the maxillofacial area, as well as for persons who have previously undergone surgery. In this case, the doctor observes the pathology for progression or degeneration when it comes to benign tumors, fistulas, keloid scars, etc.
Unscheduled
Unscheduled assistance from a dental surgeon may be needed in many cases. It is necessary for a number of diseases and medical problems. Here is a list of the main ones:
- Removal of teeth and administration of anesthesia . A dental surgeon can remove damaged and diseased teeth, as well as administer anesthesia (infiltration and conduction).
- Placement of dental implants . A dental surgeon can help with dental implants. He works on bone reconstruction in the areas where implants will be placed. If necessary or desired by the patient, the dental surgeon can also modify the gum tissue around the implants to create a more natural and attractive appearance.
- Treatment of facial injuries . Dental surgeons can treat small and complex lacerations on the face, restore broken jaws and facial bones, and nerve endings. Their expertise includes facial injuries that involve the tissues of the mouth, jaw, cheeks, nose, eye sockets and forehead.
- Assessment of pathological conditions . Oral surgeons treat patients with benign cysts and tumors of the mouth and face, malignant neoplasms, and severe infections of the mouth, salivary glands, jaws and neck.
- Elimination of pain syndrome . A dental surgeon can diagnose and treat facial pain that is caused by temporomandibular joint (TMJ) problems.
- Reconstructive and cosmetic surgery . A dental surgeon can correct problems with the jaw, facial bone and soft tissues of the face that have arisen as a result of injury or removal of tumors. Such corrective surgeries restore the shape and function of the maxillofacial area.
- Correction of birth defects . Oral surgeons also surgically correct congenital defects of the face and skull, such as cleft lip or cleft palate.
Work with children
The main feature of dental treatment for children is that the child’s dental system is in constant development and change. Surgery in the early stages of formation of the dentofacial apparatus can lead to malocclusion.
To choose the right treatment tactics, a pediatric dentist of any specialization must know which condition is normal for age and which is a developmental defect.
Peculiarities of the child's psyche, hypertrophied fear of the dental chair, requires the dental surgeon to know the psychology of children, the ability to relieve their feelings of fear and induce relaxation.
Factors of specialist competence
The specialty of a dental surgeon involves broad theoretical and practical knowledge in the diagnosis, treatment and prevention of major dental surgical diseases in people of all age groups.
A dental surgeon must have one of two types of education:
- higher education in the specialty “Dentistry” + residency in the specialty “Surgical Dentistry”;
- higher education in the specialty “General Dentistry” and “Dentistry” + retraining in the specialty “Surgical Dentistry”.
It is also important that a dental surgeon has not only professional, but also purely human qualities - attention and participation in his patient, empathy for his condition, sincerity in informing about the course of the disease and the expected consequences.
What diseases does the dentist treat?
Among the main diseases treated by a dental surgeon:
- periodontitis;
- diseases of the TMJ (temporomandibular joint);
- periostitis;
- osteomyelitis;
- tumors and cysts of the oral cavity;
- diseases of the salivary glands;
- sinusitis;
- abscesses;
- trigeminal nerve diseases;
- phlegmon and others.
A doctor of this profile also diagnoses some specific systemic diseases that manifest themselves in the oral cavity. Among them: syphilis, actinomycosis, scurvy, tuberculosis, etc. For such diseases, treatment is prescribed to the patient by another doctor (infectious disease specialist, virologist, pulmonologist).
Prospects for the profession
An aspiring practitioner begins as a dental intern in one of the private or public clinics. Then, gaining experience and knowledge, he begins to treat patients independently and takes control of other interns. Over time, the dentist becomes deputy chief physician. The peak of the career is the position of chief physician. In such a role, a specialist has a large area of responsibility, which requires strong skills and knowledge.
Another direction of development is scientific activity. Starting with graduate school, you can get your first scientific degree. Developing further, you can grow to the degree of Doctor of Science. The peak of a career in this case is opening your own educational institution or heading the department of dentistry in one of the existing ones.
One way or another, the path of a promising doctor begins with the successful completion of one of the programs of the Department of Dentistry at a specialized higher educational institution. However, obtaining a diploma is only the beginning of the educational process. To succeed in the profession, you need to regularly improve your qualifications and keep your finger on the pulse of the development of this medical industry.
Preparing for an appointment with a dentist surgeon
Before going to the dentist, you need to have a hearty snack - after surgical procedures, you should not eat food for several hours. On the eve of the visit, drinking alcohol is contraindicated - it can negatively affect the effect of anesthetics (painkillers will not work). Immediately before visiting a doctor, you need to perform thorough oral hygiene.
Patients who have encountered acute infectious diseases of the ENT organs, rashes in the oral cavity, or herpes on the lips should avoid visiting a specialist. Women are not recommended to undergo surgical procedures on menstruation days, since at this time the body is in a weakened state.
You must bring your medical history, reports from previous examinations, and all x-rays (if available) with you to your appointment.
How does an appointment with a dental surgeon take place?
Like any other specialist, a dental surgeon first of all listens to patients’ complaints and collects anamnesis. He must know everything related to the problem that worries the patient. Then it’s time for a visual inspection. The doctor examines the problem area, and he can use tools such as a dental mirror, spatula, probe and others.
Using light tapping, the doctor identifies the area that is causing pain. If we are talking about soft tissues, palpation is performed. The doctor pays attention to swelling, redness, altered areas of the skin and mucous membranes, as well as the patient’s appearance. How the examination will be carried out directly depends on the specific case.
Dental surgeon diagnostic methods
In surgical dentistry, instrumental and laboratory diagnostic methods are used. These include:
- taking anamnesis;
- visual and manual inspection;
- temperature diagnostics;
- X-ray examination (x-ray and orthopantomogram);
- electroodontic diagnostics;
- general blood test, etc.
If oncological processes are suspected, the patient is prescribed a biopsy and a series of cytological studies. With their help, you can determine the type of neoplasm, as well as confirm or refute its benignity.
If there are concomitant diseases that are not within the competence of the dental surgeon, the patient may need the help of other specialists. In particular:
- orthodontist;
- orthopedist;
- gastroenterologist;
- oncologist;
- infectious disease specialist;
- allergist, etc.
Dental surgeon treatment methods
Surgical dentistry provides a wide range of treatments, which include special methods of surgical influence on the tissues of the oral cavity. The specific choice of treatment method depends on the disease. This section of dentistry practices the following treatment methods:
- bone grafting;
- tooth extraction operations;
- aesthetic surgical operations;
- implantation;
- prosthetics;
- resection of soft tissues.
After surgery, anti-inflammatory, antihistamine, antiprotozoal and antibacterial drugs may be prescribed. If pain is present, anesthetics are indicated.
Cosmetic surgeries
© Francesco83 / Fotolia
In addition to operations performed for therapeutic purposes, the surgeon performs interventions for cosmetic restoration of the maxillofacial apparatus.
Gingivoplasty
This technique is aimed at eliminating defects in periodontal tissue associated with its uneven position. Gingivoplasty is necessary for high, uneven or low gum lines.
For correction, periodontal tissue from the problem area is used, separated into flaps, or a flap is transferred from the palate. The periodontal tissue is given the required shape using surgical sutures, which are removed after 10 days.
Vestibuloplasty
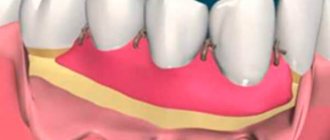
It is a technique designed to expand the vestibule of the oral cavity by moving facial muscles deeper into it. The procedure is carried out by cutting the mucous tissue that regulates the tension of the gums.
After weakening the muscles of the vestibule, the likelihood of developing periodontal diseases decreases, and speech therapy problems are eliminated.
The vestibuloplasty procedure is presented in the following video:
We will tell you what to do if your gums hurt for a long time after tooth extraction.
We talk here about complications after removal and treatment.
We will discuss the resection of the apex of the tooth root at the link https://www.vash-dentist.ru/hirurgiya/rezektsiya/verhushki-kornya-zuba-zachem-nuzhna-operatsiya-i-kak-ona-provoditsya.html.
Frenuloplasty
The main indication for frenuloplasty is shortening of the frenulum of the tongue or lips , exposing the neck of the teeth, or the formation of a speech therapy defect. The incision is made under local anesthesia, using a scalpel to excise the frenulum in the transverse direction.
Elimination of gum recession
When the volume of the gums decreases (recession), accompanied by exposure of the roots of the teeth, flap surgery is resorted to. A section of mucous membrane taken from the palate or another area of the oral cavity is applied to the gum, after which the tissue is secured with sutures.
After a week, the mucous membrane takes root and the sutures are removed.