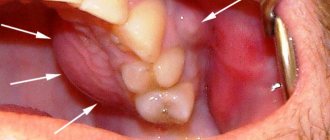
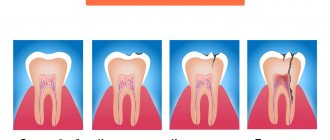
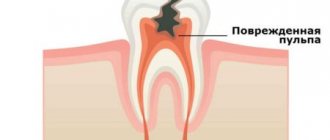
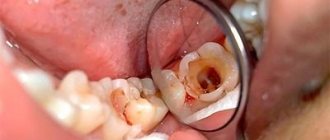
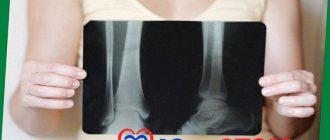
Chronic periodontitis: description and symptoms
Unlike acute periodontitis, chronic periodontitis is often practically asymptomatic, that is, it is not accompanied by severe swelling and severe pain. That is why many patients come to the doctor when conservative treatment of chronic periodontitis is impossible, and to eliminate complications they have to resort to more radical measures. Chronic periodontitis in the acute stage has much more pronounced symptoms.
Symptoms of chronic periodontitis
- pain
- soft tissue swelling
- tooth mobility
- enlarged lymph nodes
- weakness
- temperature increase
Exacerbation of chronic periodontitis is often associated with concomitant diseases, as well as hypothermia, decreased immunity and other factors.
Causes of chronic periodontitis
Chronic apical periodontitis (chronic apical periodontitis, chronic root periodontitis) is so named because the inflammatory process occurs in the area of the apex of the tooth root. This type of disease is often the next stage of the acute form, but it can also develop independently. Based on their origin, experts distinguish two types of chronic periodontitis.
✔
Infectious chronic periodontitis. Occurs as a result of the activity of pathogenic bacteria in the oral cavity. The presence of foci of infection contributes to the penetration of bacteria into periodontal tissue and the development of the disease.
✔
Non-infectious chronic periodontitis. It can be caused by trauma and mechanical damage to the teeth, including due to doctor errors during therapeutic treatment. Another reason may be an allergic reaction to medications (in particular, arsenic and anesthetics), as well as the toxic effects of pulp decay products.
How is this pathology treated?
The key to successful therapy is a thorough diagnosis of periodontitis, which is based on radiographic studies. Treatment of this disease takes place in several stages. In case of exacerbations of periodontitis, it is necessary to first relieve the pain reaction and eliminate inflammation. For this use:
- physiotherapeutic approaches;
- antibacterial therapy to destroy pathogenic microflora.
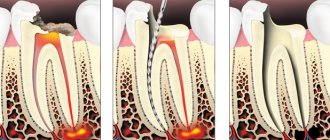
After this, the root canals of the tooth should be filled. First, to isolate the working area from saliva, SM-Dentistry specialists resort to using a rubber dam system. It ensures the sterility of all manipulations and also does not allow dental preparations to enter the patient’s oral cavity.
Then you need to remove all areas of dental tissue that are affected by caries. If the degree of destruction of the dental crown is too great, the possibility of its complete removal and subsequent replacement with an implant is considered. Next, the doctor cleans the tooth canal and at the same time tries to give it as even a shape as possible. This will make it easier to install the filling, and will also significantly reduce the risk of developing complications of periodontitis.
The next stage is temporary filling of the dental canal. The doctor places a drug with an antibacterial effect in it and seals it with a seal. The drug remains in the tooth canal for two weeks. During this time, it will penetrate the hard shell of the teeth and destroy pathogenic bacteria in the periodontium. After the infection has been eliminated and the inflammatory process has been suppressed, the temporary filling is replaced with a permanent one, or if the tooth is destroyed by more than 50%, it is recommended to restore the tooth with a crown. For its production, the SM-Dentistry clinic uses modern and high-strength composite materials, and the shape of the filling will correspond to the natural and familiar shape of the tooth for the patient. Quality control of treatment at all stages is carried out using computed radiography.
Diagnosis of chronic periodontitis
Unfortunately, without the necessary equipment, it is very difficult to identify chronic periodontitis. A visual examination performs a purely formal function, since even in the presence of symptoms (pain, swelling, etc.), it is necessary to determine the type and stage of periodontitis in order to draw up the most effective treatment plan. Today, diagnosis of the disease is carried out in several proven ways.
- X-ray examination. The most popular type of diagnostics. All types of chronic periodontitis can most often be detected on a regular targeted X-ray. In case of fistula formation, a narrow-profile X-ray examination - fistulography - is often prescribed.
- Radiovisiographic examination. A more modern and gentle x-ray examination, during which the image is transferred to a computer screen.
- Electroodontodiagnosis (EDD). Diagnosis of inflammatory processes in the dental pulp by monitoring its response to electric current.
- In the case of periodontitis, specialists use differential diagnosis to distinguish it from other dental diseases with similar symptoms.
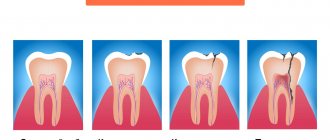
Chronic forms of periodontitis
Chronic fibrous periodontitis
Periodontal tissues are gradually replaced by connective tissue, and the inflammatory process is usually mild. One of the most common types of periodontitis, which is most often asymptomatic. With exacerbation, pain, enlarged lymph nodes and fever are possible. When diagnosed on an x-ray, you can notice an expansion of the periodontal fissure.
Treatment of chronic fibrous periodontitis is usually easier compared to other forms.
Chronic granulating periodontitis (chronic granular periodontitis)
In the apical region of the root, granulation tissue is formed, which actively replaces bone. In terms of symptoms, this is the most pronounced type of chronic periodontitis, which manifests itself in the form of pain, especially when pressing on a tooth or biting. During an exacerbation, the pain intensifies, and fistulas with purulent discharge may occur. On an x-ray, it is quite easy to notice dark, irregularly shaped areas: clear evidence of the development of granulating periodontitis. It is advisable to treat chronic granulating periodontitis quickly enough to avoid the spread of granulation tissue.
Chronic granulomatous periodontitis
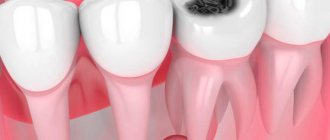
A type of periodontitis in which a purulent sac forms near the tip of the root, which, as it grows, first turns into a granuloma, and then into a cyst filled with dense epithelial tissue. The diameter of the cyst can exceed 1 centimeter. In the early stages it hardly manifests itself, but in later stages pain occurs, and the color of the tooth may also change. On x-ray it appears as a dark round spot. Treatment of chronic granulomatous periodontitis in some cases requires surgical intervention, since it is often not possible to get rid of the cyst using conservative methods.
Signs
Clinical manifestations of periodontal inflammation depend on the form of the disease.
In the acute course, the symptoms are pronounced, often accompanied by the formation of a painful abscess on the gum, gumboil (deeply located abscess with intense swelling of the soft tissues of the gums and face), increased body temperature, etc. Acute inflammation can occur in two forms:
- Serous periodontitis occurs without the formation of a purulent cavity. Accompanied by constant aching pain that does not intensify when touching a tooth or biting food.
- Purulent periodontitis is accompanied by the formation of an abscess. Accompanied by sharp, bursting or throbbing pain, the intensity of which may vary. Flux is noticeable on the gum near the diseased tooth, and the soft tissues of the face on the affected side swell. The mobility of the tooth is increased, the pain intensifies when biting and touching the tooth.
In the chronic form, periodontitis is not as severe as acute periodontitis. There are three forms of the disease:
- Fibrous , the symptoms of which are sluggish inflammation without the formation of an abscess and fistulas. Pain with this form rarely occurs. An external sign is a change in the color of the enamel to gray, a change in its transparency. Signs of inflammation are visible only on x-rays.
- Granulomatous , the symptoms of which are periodic formation of an abscess. As it “ripens,” a duct opens on the gum, from which purulent contents pour out. Such ducts can form permanent non-healing fistulas. On x-rays, this form of periodontitis looks like a lesion with a diameter of up to 5 mm at the root apex.
- Granulating , the symptoms of which are chronic toothache, aggravated by biting hard, hot or cold food with a sore tooth. The gums near the tooth are constantly swollen and hyperemic. The opening of the fistula can open both on the oral mucosa and on the skin of the face.
Symptoms of any form of periodontitis tend to subside when the purulent cavity is cleared of its contents.
It is important to know! The main difference between periodontitis and pulpitis is the nature of the pain. With pulpitis, it is acute, painful, reminiscent of electric discharges, intensifying when the diseased tooth comes into contact with solid food particles, hot or cold air.
Treatment of chronic periodontitis on teeth
Despite the fact that acute and chronic periodontitis are similar in many ways, treatment of chronic forms of periodontitis is usually more difficult and takes longer than the acute form. Treatment of acute chronic periodontitis is most often carried out using conservative methods and may require endodontic intervention: opening the tooth cavity to drain purulent exudate, filling the canals. Antiseptic drugs and antibiotics are also actively used. In the case of chronic periodontitis, the treatment method depends on the stage of the disease and the presence/absence of complications. Based on this, a conservative or surgical treatment plan is drawn up.
Treatment methods for chronic periodontitis
✔
Conservative treatment of chronic periodontitis. It implies a whole range of measures to eliminate the source of the disease. First of all, the tooth canals are cleaned, antiseptic medications are administered, and anti-inflammatory drugs and antibiotics are taken if necessary. After sanitation, the canals are filled with medicinal filling paste, after which it is necessary to wait for the restoration of periodontal tissue for 1 to 3 months. After this period is completed, a permanent filling is performed. In the treatment process, techniques such as electrophoresis, laser and UHF therapy are often used.
✔
Surgical treatment of chronic periodontitis. Surgical methods for treating chronic periodontitis one way or another involve invasive intervention in periodontal tissue. Typically, this technique is used in advanced stages of periodontitis and when complications develop (cysts, fistulas, etc.). Modern dentistry has a number of surgical techniques that allow you to save part of a root or tooth. These include: tooth root resection (removal of part of the root along with a pathological formation), cystectomy (operation to remove cysts and granulomas), and hemisection (removal of the crown part of a multi-rooted tooth along with the root). Despite the fact that chronic periodontitis of permanent teeth is most often tried to be cured with the help of tooth-preserving manipulations, in the most severe cases complete tooth extraction is indicated.
Traumatic periodontitis – Prices
| Services | Price |
| Placing a chemical polymerization filling | 2000 rub. |
| Machining 1 Ni-Ti channel with rotary tools | 1500 rub. |
| Drug treatment of 1 channel | 700 rub. |
| Unsealing of 1 channel, sealed with cement along the entire length | 5000 rub. |
| Unsealing of 1 channel, sealed with cement to 1/3 of the length | 3000 rub. |
| Unsealing of 1 channel, sealed with cement for 2/3 of the length | 4000 rub. |
Make an appointment
Traumatic periodontitis: before and after photos
Repeated treatment of chronic periodontitis
Sometimes specialists have to re-treat chronic periodontitis. This is usually due to the fact that previous treatment was ineffective. This could be poor cleaning and filling of canals, defects during surgical procedures, non-compliance by the patient with rehabilitation rules, as well as an initially incorrectly selected treatment plan. Secondary treatment almost always takes longer and is more difficult. In this case, it is still possible to do without tooth extraction or carry out repeated conservative treatment, however, quite often the patient comes with already developed complications that require surgical intervention.
Chronic periodontitis: treatment at home
Any form of periodontitis cannot be cured at home: this should only be done by a professional doctor. The only option is antibiotic therapy, which in the vast majority of cases is prescribed as an addition to complex treatment. The same applies to traditional medicine. In medical practice, there have been cases when a cyst or granuloma resolved without any intervention, but this should not be attributed to miraculous natural decoctions and tinctures. Much more important are preventive measures that will help improve oral health and avoid problems with teeth and gums. In this case, some traditional medicine can really help, but the main measures to prevent periodontitis are good hygiene, proper nutrition and regular visits to the dentist.
Prevention
Traumatic periodontitis is easier to prevent than to endure pain and risk serious complications. It is necessary to avoid any dental injuries and contact a dentist at the first sign of overload due to improper installation of a filling or orthopedic structure. Those who like to bite thread with their teeth, open bottles, crack nuts, bite a pencil, etc. These habits should be abandoned, especially if the teeth are pulpless. Without a nerve, teeth become more fragile than living ones, and even a small load is enough for chipping to occur at the gum level and traumatic periodontitis developing.
Still have questions?