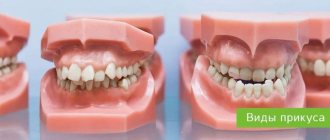
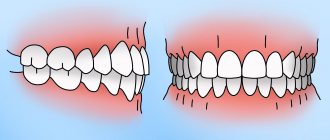
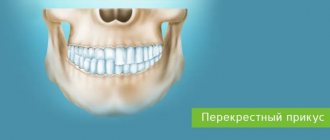
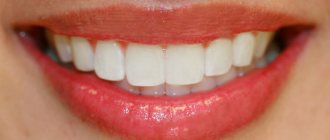
Bite is the way the dentition interacts when the upper and lower jaws are completely closed. An incorrect bite almost always leads to the fact that the enamel, and behind it the bone tissue of the incisors, canines, and molars, quickly wears out and is destroyed. This is why the correct bite of a person’s teeth is so important.
If you have any problems with your teeth, they can be corrected. But this will take a lot of time, because the teeth cannot just be moved, they need to be moved gradually. While studying the problem, doctors came up with many ways to combat malocclusion.
What is orthognathy
Translated from Greek, “gnathos” means jaw, and “ortho” means straight or regular.
In dentistry, orthognathic is a physiologically correct bite. Its main feature is a slight overlap (up to 1/3 of the crown height) of the lower teeth with the upper ones. This occlusion is considered the most advantageous from an anatomical and physiological point of view (which we will talk about later). Other characteristics of correct occlusion include straight teeth and tight grip of the incisors (there are no gaps between them).
Diagnostic techniques
To know how to effectively correct malocclusion, you need to make an accurate diagnosis. To determine the manifestations of pathology, additional measures are taken:
- X-ray pictures. West Dental has the Pax-i3D CBCT, which can perform OPTG, CT, and TRG. The ratio of the sizes of the jaws, teeth and bone volume, and the condition of the TMJ are determined.
- 3D scanner. The patient is shown a picture of changes in facial and dental signs of occlusion before and after orthodontic intervention.
- Photo protocol. A collection of photographs of the jaw relationship before, during and after treatment or jaw surgery allows you to trust the doctor. The results are visible at all visits.
Orthognathic bite: how to determine
The surest way to determine the type of occlusion is to consult a dentist for an examination. Orthognathic bite has the following features, which can be determined independently:
- The upper teeth overlap the lower teeth by 1/3 (or less) of the crown height. This is the basis of a physiological bite. It is important to note that if the closure is direct (when the edges of the upper teeth directly meet the edges of the lower teeth), then this is a type of pathological bite, although such a smile looks very aesthetically pleasing. With such closure, the teeth quickly wear out and are destroyed.
- One upper tooth meets the two lower ones.
- Middle line. Many people mistakenly believe that the middle of the upper jaw should coincide with the middle of the lower jaw. In fact, it is important that the midlines of the upper jaw and face coincide.
- You do not feel any functional impairment. The processes of chewing and swallowing are not accompanied by discomfort and pain. If clicking or crunching is felt, this indicates dysfunction of the temporomandibular joint (TMJ). This symptom is often observed with pathological bites.
- Correct facial proportions. This is an indirect characteristic for physiological occlusion. There are cases when pathological closure of teeth does not affect the symmetry of the face. There are also opposite cases when those with a correct bite have an asymmetrical face. An individual approach and correct diagnosis by a doctor are important here.
What does an orthognathic bite look like?
Orthognathia: benefits
- Uniform load on teeth . This protects hard tissues from premature destruction.
- No speech impediment . With pathological occlusions, a violation of diction is often observed, since some sounds are difficult for a person to hear.
- No strain on the digestive organs . With an incorrect bite, a person chews food poorly. Relatively large pieces of food enter the stomach, which impairs digestion.
- Effective oral hygiene . The correct shape of teeth is the key to good hygiene. In this case, the risk of developing caries, periodontitis and other dental diseases is significantly reduced.
- Successful dental treatment . People with malocclusion experience difficulties with prosthetics, implantation and other types of dental treatment. Often, before the main treatment, the doctor prescribes bite correction.
- Aesthetic benefits . In most cases, an orthognathic bite provides a beautiful smile and facial symmetry.
How does a correct bite develop?
You need to monitor your bite from early childhood. Pay attention to the position of the tongue, the position of the teeth and the development of the child’s jaw. Let's consider the main stages of bite formation in children of different ages.
- 0-6 months . During this period, the foundation for the closure of the dentition is laid. If the child is fed correctly (so that the masticatory muscles experience the proper level of load), then the dental arches and jaws develop harmoniously (if there are no hereditary or congenital anomalies of the dental system).
- 6 months . The first milk teeth appear, the tongue rests on the roof of the mouth.
- Up to 3 years . Closer to 3 years of age, baby teeth are formed. At this age, the child’s dentofacial arches are fully functioning, he is able to chew food normally and speak.
- 4 years . From this age, the milk bite gradually loses its position.
- 6 years . Permanent teeth appear in place of the lost milk teeth. An overlap of the lower teeth with the upper teeth is formed (no more than 1/3 of the height of the crown). If the child had gaps between the teeth in the primary dentition (tremas or diastemas), then by the time the permanent dentition is formed, these defects disappear.
- 15 years . In adolescents, the formation of dentition ends. The overlap of the upper teeth with the lower ones should remain at 1/3 of the height of the crown.
Treatment methods
The first thing that needs to be done is preparation from a dentist-therapist in the form of sanitation of the oral cavity. Before installing orthodontic structures, it is important to treat carious and gingival pathological processes and remove tartar using an ultrasonic tip.
Next, surgical preparation may be necessary - extraction of units, removal of excess soft tissue structures, plastic surgery of the labial frenulum. Removal of destroyed or supernumerary units may be required. It happens that further treatment tactics force the extraction of healthy teeth that interfere with the orthodontic process.
What to do if specialists discover an incorrect bite? - be sure to treat. Treatment is divided into 2 periods - active and retention.
Taking into account all the nuances of the clinical situation, at the active stage it is possible to use various correction options:
Aligners (transparent aligners).
Transparent soft silicone or polyurethane plates, individually manufactured according to a 3D print. They are worn constantly, removing them only for meals and hygiene. They are not visible in the mouth and do not cause discomfort. It is necessary to meet with an orthodontist once every few months to control the movement of units and receive a new batch of aligners, which are independently changed every 2 weeks. Aligners achieve effective results in cases of crowded units, narrow or wide dentition, or correction of previous treatment with braces.
Trainers
Silicone massive mouth guards with sides for wearing at night, and during the day for no more than a few hours. Suitable for treating children under 12 years of age, and at older ages they are used for correction or prevention.
Removable plate-devices.
They are used during the period of primary occlusion to reduce the period of further treatment with braces and improve sound pronunciation. The best results are achieved when interacting with a speech therapist.
Braces
Prescribed for the correction of various bite pathologies. Specialized buttons are attached to the coronal surface of the units with medical glue and connected with an arc. Thanks to the shape memory arch, the alignment of the dental units occurs.
Braces are classified according to:
- Places of attachment - vestibular (external) and lingual (internal).
- The method of attachment to the arch is ligature and self-ligating.
- Materials: plastic, metal, ceramics, titanium, sapphire, silicone.
The cost of a braces system varies depending on its type and the material used. They also need careful home care - special brushes, brushes, pastes, floss.
With age, restrictions on the use of certain systems and materials appear. The older the patient, the longer (more than a year) and more difficult it will be to change the location of the units due to the intractability of the bone tissue. Therefore, you should start correcting your bite as early as possible.
In the final retention period (preservation of the result), the patient has a retainer attached to the inner surface from canine to canine, and it is recommended to wear night guards. This period continues throughout the life of the teeth.
Surgery
Radical orthodontic surgery is considered when there is severe maxillofacial deformity, and all of the above correction methods will not be effective. An incision is made in the gum tissue and the jaw bones are shifted to an anatomical position. It is also possible to use implantation to restore missing units; implants add a fulcrum for the correction of individual areas. To speed up the treatment time, the orthodontist may additionally need mini-implants, which can be unscrewed after their work. They will allow in some cases to avoid surgical intervention and move an entire group of teeth.
Orthopedics
At the end of orthodontic treatment, to achieve the best aesthetic result, it is recommended to perform prosthetic treatment of the frontal group of units with veneers or crowns. This way, the optimal size of the crown parts of the teeth is achieved, suitable for facial characteristics.
The importance of physiological occlusion
Physiological occlusion is important for health for the following reasons:
- the bone tissue of the skull elements develops harmoniously;
- uniform load on teeth and joints;
- no negative effects on the digestive or respiratory system;
- correct facial proportions, lack of psychological discomfort in this regard;
- beautiful smile;
- good oral hygiene.
Anatomy and physiology of the dental system
When it comes to occlusion, not only the location of the teeth is important, but also the functions of the remaining elements of the dental system. These are the upper and lower jaws, jaw joints and muscles that ensure the process of chewing and swallowing.
The greatest load on the teeth occurs when chewing. It is important that at this moment the load is evenly distributed on the surface of the teeth. This way hard tissues will retain their strength and structure longer. Otherwise, the teeth will quickly wear out. This threatens with caries, wedge-shaped defect, gum disease and final tooth destruction.
Under the physiological norm, the position of the jaws should be parallel. The lower jaw resembles a parabolic arch, and the upper jaw is a semi-oval. The coordinated functioning of the jaw joints is also important - without discomfort, clicks and crunches.
Pathological consequences
The non-anatomical position of the units leads to the occurrence of an inflammatory process in the gum tissue, making it difficult to carry out a complete cleaning of the oral cavity. Also, the rate of abrasion of tooth enamel increases, causing carious damage to develop. In case of serious violations, headaches, crunching of the TMJ when chewing and muscle tension in the shoulder girdle will occur. Also, chewing a food bolus may be impaired due to the lack of interdental contacts, which will lead to the occurrence of diseases of the internal organs and gastrointestinal tract. Respiratory, swallowing and speech functions may also be impaired. Pathological conditions of the ENT organs develop very often.
What are the problems with orthognathic occlusion?
Orthognathia does not guarantee the absence of dental problems. Even with a physiologically correct bite, various defects are possible. These include:
- crowded teeth;
- diastema and trema - gaps between teeth;
- edentia (absence of one or more teeth);
- speech defect;
- other violations.
Important. Under no circumstances should you neglect such defects in your primary bite. Many parents believe that baby teeth are not that important because they will soon fall out. This is a big misconception, since the health of permanent teeth largely depends on the condition of baby teeth. Therefore, if you want your orthognathic bite to be preserved in the future, then take care of your teeth from early childhood.
Correct bite: how to maintain
Pathological bites are formed due to hereditary or external factors. If we cannot influence genes, then we can change our lifestyle. To avoid malocclusion, we recommend adhering to the following rules:
- Wean your child off bad habits - thumb sucking, cheek biting, excessive use of the pacifier.
- Provide normal nutrition - introduce solid food in a timely manner so that the jaw experiences normal load.
- Treat respiratory diseases. The child should breathe through his nose. Mouth breathing is one of the risk factors for the formation of a pathological bite.
- Treat dental diseases in a timely manner.
- Visit your dentist regularly for preventative checkups.
- Use an orthopedic pillow while sleeping.
Prevention
Adults need to regularly take their child to a consultation appointment with a pediatric dentist and orthodontist once every six months. Treatment of pathological foci in mammary units should be carried out in a timely manner. For harmonious sleep, you need to buy your child a suitable pillow.
After 3 years, you need to monitor the grinding of your child’s teeth, which is a natural process. If this does not happen, then grinding is necessary, otherwise the NP will not take its natural anatomical position. Also, in this age interval, interdental spaces appear, which is normal. Jaws grow, and emerging molars need a lot of space. If there are no gaps, then a malocclusion may occur, so you need to contact a specialist to monitor the situation.
Doctors at the branches of family dentistry West Dental in Yanino-1 and Vsevolozhsk offer effective correction of bite pathology using modern treatment techniques, at a reasonable price. An understanding of the prevention and treatment of dental pathology is formed. To make an appointment with our specialists, you can fill out the online form on the website or by calling the administrators.
FAQ
Why is correct bite important?
Correct bite means a reduced risk of not only dental, but also other diseases. With pathological occlusion, the load on the teeth is uneven, which leads to accelerated wear of some teeth.
In addition, malocclusion is an additional burden on the digestive system and respiratory organs. Finally, there is psychological discomfort due to facial disproportion.
Can the bite be incorrect if the teeth are straight?
Yes. The straight bite mentioned above can be formed with straight teeth. Therefore, the ideal shape of the teeth can also be observed in pathological occlusions that require orthodontic correction. In addition to straight teeth, straight teeth can also be observed in deep, distal or open bites.
Correct jaw anatomy - what is it?
The main sign of a physiologically correct jaw is its shape. The lower jaw resembles a parabola, while the upper jaw resembles a semi-oval. This is how the teeth are located on the corresponding jaws.
Both jaws should be symmetrical along an imaginary vertical line that runs between the central upper teeth.
What is the correct tongue position?
The entire tongue (both tip and back) should touch the roof of the mouth.
How to recognize an abnormal bite?
Above we looked at the criteria for correct bite. Therefore, deviations from these signs can be considered incorrect occlusion. At the same time, you cannot make diagnoses yourself. Consult a doctor who will accurately determine the type of bite. Let us remind you that among pathological bites the following are distinguished:
- distal – the upper teeth hang excessively over the lower teeth;
- mesial – the lower jaw protrudes strongly forward;
- deep – the upper teeth overlap the lower teeth by more than half;
- open – the presence of a sagittal gap between the teeth;
- cross – displacement of one jaw relative to the other (displacement towards the teeth, molars and premolars);
- straight - the closure of the lower edges of the upper and lower teeth during occlusion.
Diagnostics
Determination of the bite shape in orthodontics is based on several anatomical indicators that are assessed during diagnosis and serve as the basis for the use of a standard classification. Characteristics are divided into three groups:
- Within the jaw arch - correctness of curvature, contact between antagonists, coverage of the lower row with the upper, the location of the crowns and their height as they move away from the central area.
- In relation to incisors and canines - the degree of overlap, the normative value for which is the third part, as well as the location of the midlines, ideally located on the same straight line.
- In relation to masticatory units, indicators of the anteroposterior and velobuccal directions, including the ratio of planes and the position of the cusps in the transverse grooves.
It is worth noting that all of these signs are assessed with tightly closed jaws.