Pharmacological properties of the drug Mepivacaine
Local anesthetic of medium duration of action of the amide group. Causes a reversible block of nerve conduction by reducing the permeability of neuron membranes to sodium ions. Compared with lidocaine, mepivacaine causes less vasodilation and has a more rapid onset and longer duration of action. Systemic absorption of mepivacaine depends on the dose, concentration, route of administration, degree of tissue vascularization, and degree of vasodilation. When anesthetizing the teeth of the upper and lower jaw, the effect develops after 0.5–2 and 1–4 minutes, respectively. Dental pulp anesthesia lasts for 10–17 minutes; soft tissue anesthesia in adults lasts 60–100 minutes. When administered epidurally, the effect of mepivacaine develops after 7-15 minutes, the duration of action is 115-150 minutes. Distributed in all tissues, maximum concentrations are created in well-perfused organs, including the liver, lungs, heart and brain. Mepivacaine undergoes rapid metabolism in the liver and is inactivated by hydroxylation and N-demethylation. Three inactive metabolites are known: two phenolic derivatives, which are excreted as glucuronic conjugates, and 2′,6′-pipcolocylide. Approximately 50% of pepivacaine is excreted in the bile as metabolites and undergoes enterohepatic recirculation followed by renal excretion. Only 5–10% is excreted unchanged in urine. A certain amount of the drug is metabolized in the lungs. The metabolism of mepivacaine in newborns is limited; the drug is excreted in unchanged form. The half-life is 1.9–3.2 hours in adults and 8.7–9 hours in newborns. Penetrates the placenta through passive diffusion.
Anesthesia in dentistry
The best drugs for local anesthesia in dentistry
As we said, most often in dental clinics drugs based on articaine are used, in particular Ultracaine or Ubistezin. Now, taking into account the information presented, it is time to dwell in more detail on the advantages of such anesthetics.
Artikain
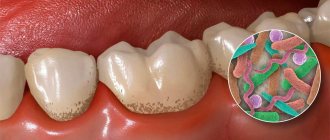
Modern local anesthesia in dentistry is unthinkable without articaine. It is this anesthetic that has a minimal ratio of toxicity and analgesic activity. In other words, among the most effective remedies, it is the least toxic.
Articaine is actively used for infiltration and conduction anesthesia. It is also used for intraosseous anesthesia before dental operations. But the surface anesthetic effect of articaine is not typical, which is why it is not suitable for applications.
The advantage of articaine is its high effectiveness against inflammation. (The inflammatory process reduces the effect of many drugs). This feature allows the use of Ultracain or Ubistezin in the treatment of purulent-inflammatory diseases of teeth and periodontium.
Due to its low toxicity, articaine is the best remedy for pediatric dentistry, the elderly, and patients with diseases of the hepatobiliary and urinary systems. Can be used while breastfeeding. Articaine practically does not penetrate into breast milk, and if it is found in it, it is in extremely low concentrations that have no clinical significance.
Can articaine be used during pregnancy? Studies have shown that although articaine crosses the placental barrier, it does not have a toxic or mutagenic effect on the fetus. Articaine can be used during pregnancy.
Lack of articaine in the average duration of action. It is quickly absorbed into the blood, quickly destroyed and excreted in the urine. This is partly due to the fact that articaine, like many local anesthetics, dilates blood vessels. For this reason, articaine is often used together with vasoconstrictors, which are already included in the drug. For example:
- Ultracain DS Forte, Ubistezin Forte contain adrenaline in a concentration of 1:100,000 (average concentration).
- Ultracain DS, Ubistezin contain adrenaline in a concentration of 1:200,000 (low concentration).
What if the patient belongs to a risk group and cannot be injected with an anesthetic with adrenaline? In this case, you need to use Ultracaine D - a drug with articaine without a vasoconstrictor component.
During pregnancy, it is recommended to use articaine in combination with adrenaline in low concentrations (Ubistezin, Ultracaine DS). Some experts believe that it is better not to use vasoconstrictors at all when treating pregnant women. Which option is better? The choice must be made taking into account individual characteristics. A woman should consult with specialists, including a gynecologist who monitors the pregnancy.
Lidocaine
Lidocaine is another popular and widely used drug, despite the fact that it is 2 times more toxic than procaine. The advantage of lidocaine is its average duration of action and more pronounced effect (it is 4 times stronger than procaine). The problem is that lidocaine dilates blood vessels, which requires the simultaneous use of high doses of a vasoconstrictor drug. For this reason, lidocaine is rarely used for conduction or infiltration, but is often used for superficial anesthesia.
Can lidocaine be used during pregnancy? We have already mentioned one drawback - the drug requires the use of adrenaline in high concentrations. The second disadvantage of lidocaine is that it is toxic, crosses the placenta and accumulates in the fetal liver. Considering the above, local anesthesia with lidocaine is contraindicated for pregnant women.
Mepivacaine
A unique drug, because it is the only anesthetic for local anesthesia with a vasoconstrictor effect. This feature allows the use of mepivacaine without a vasoconstrictor, which makes it the best tool for providing anesthetic benefits to patients at risk (diabetes, thyroid disease, hypertension and other cardiovascular diseases).
Mepivacaine is actively used for infiltration and conduction anesthesia. It is contraindicated during pregnancy because it penetrates the placental barrier and narrows the uterine arteries, which can lead to fetal hypoxia.
Anesthesia in pediatric dentistry
The problem of anesthesia in pediatric dentistry is quite acute, since it is psychologically and physically difficult for young patients to withstand a long treatment procedure. On the one hand, they are frightened by the noise of dental instruments, on the other hand, it is simply difficult for them to sit still for 40-60 minutes. In this regard, instead of local anesthesia, the dentist may recommend anesthesia.
Anesthesia in pediatric dentistry is carried out using a modern drug - Sevoran. Unlike the previously popular ZAX (nitrous oxide-oxygen mixture), Sevoran combines not only high efficiency (sufficient depth and duration of medicated sleep), but also maximum safety and a very “clean” recovery from anesthesia. After waking up, the child feels great; headaches, nausea or dizziness are extremely rare.
You can learn more about the methods of providing anesthesia in pediatric and adult dentistry at a consultation with a medical dentist.
Make an appointment
Use of the drug Mepivacaine
Infiltration anesthesia: For adults, up to 40 ml of 1% solution (400 mg) or 80 ml of 0.5% solution (400 mg) in divided doses over 90 minutes. For blockade of cervical nerves, brachial plexus, intercostal nerves: Adults - 5–40 ml of 1% solution (50–400 mg) or 5–20 ml of 2% solution (100–400 mg). Paracervical blockade: Adults up to 10 ml of 1% solution on each side. Inject slowly with an interval of 5 minutes between injections on the other side. Peripheral nerve block: Adults 1–5 ml of 1–2% solution (10–100 mg) or 1.8 ml of 3% solution (54 mg). Infiltration anesthesia in dentistry: Adults - 1.8 ml of 3% solution (54 mg). Infiltration is performed slowly with frequent aspiration. In adults, 9 ml (270 mg) of 3% solution is usually sufficient to anesthetize the entire oral cavity. The total dose should not exceed 400 mg. Children: 1.8 ml of 3% solution (54 mg). Infiltration is performed slowly with frequent aspiration. The maximum dose should not exceed 9 ml (270 mg) of 3% solution. Epidural or caudal anesthesia: Adults - 15–30 ml of 1% solution (150–300 mg), 10–25 ml of 1.5% solution (150–375 mg) or 10–20 ml of 2% solution (200–400 mg). Maximum doses: Adults: 400 mg as a single dose for regional administration; the maximum daily dose is 1000 mg. Children: 5–6 mg/kg. For children under 3 years of age or weighing less than 13.6 kg, mepivacaine solutions are used in concentrations up to 2%.
For whom is mepivacaine contraindicated?
When breastfeeding, dental treatment of a woman with Mepivacaine anesthesia is completely prohibited. Also prohibited are children under 4 years of age and weighing less than 20 kilograms, patients with low blood pressure, severe heart and liver diseases. Here the dentist will select another drug, for example, Articaine.
The anesthetic should also be used with caution in the following patient groups:
- in children,
- in pregnant women,
- in elderly people over 65 years of age, a minimum dose of Mepivacaine is used,
- in persons with liver or kidney disease,
- in the presence of diabetes mellitus,
- with pronounced inflammation of the gums,
The product should be used with caution in children
Drug interactions Mepivacaine
Local anesthetics (especially when prescribed in large doses) may have an antagonistic effect on neuromuscular transmission compared to cholinesterase inhibitors. The use of local anesthetics with ganglion blockers may increase the risk of arterial hypotension and bradycardia. Patients taking MAO inhibitors concomitantly with local anesthetics have an increased risk of developing arterial hypotension. Local anesthetics may have an additive hypotensive effect in patients taking antihypertensive agents and organic nitrates.
List of pharmacies where you can buy Mepivacaine:
- Moscow
- Saint Petersburg
Indications for use of anesthetic
According to the instructions for use, Mepivacaine is indicated for the following types of anesthesia:
- infiltration: “freezing” injection into the gum, tooth ligament or periosteum,
- intraligamentary: a subtype of infiltration, when injections are placed into the ligaments of the tooth, i.e. between the root and the walls of the bone socket,
- conduction: the anesthetic is injected near large nerves,
- regional (intraosseous),
- intrapulpal: an auxiliary technique, the essence of which is that the injection is placed directly into the dental nerve - the pulp.
The injection of the substance goes directly into the bone tissue of the alveolar process.
That is, Mepivacaine is suitable for such dental interventions as:
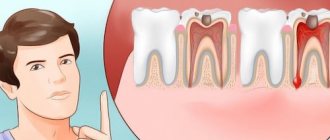
- treatment of medium and deep caries,
- treatment of pulpitis and periodontitis,
- tooth root resection,
- tooth extraction,
- preparing teeth for prosthetics,
- plastic surgery of gums and frenulums,
- bone tissue augmentation,
- sinus lift (raising the bottom of the maxillary sinus),
- implantation,
- curettage of deep periodontal pockets associated with gingival exfoliation.
The drug is used for tooth extraction.
Good to know! The drug is considered one of the safest to date. It can be used in older patients (but there are some peculiarities), in people with allergies to other anesthetics, with high blood pressure and mild pathologies of the cardiovascular system. Since adrenaline (epinephrine) is not included in its composition.
Features of anesthesia for pregnant women
During pregnancy, drugs that have minimal effects on blood vessels are used for pain relief. They also cannot cross the placenta and affect the baby.
Lidocaine is contraindicated during pregnancy. It can cause a sharp decrease in blood pressure, cramps and weakness.
Today, the best anesthesia option for pregnant women remains drugs based on anticain:
- Ultracaine.
- Altrifryn.
- Ubistezin.
- Alfacaine.
The listed drugs do not constrict blood vessels, which would be harmful for the expectant mother. They also have a local effect, so they do not affect the baby.
What are the alternatives - analogues
Analogues of the anesthetic drug "Mepivacaine" are "Mepivacaine-Binergia" (Russia), "Mepivastezin" (Israel), "Scandonest" (France), "Scandinibsa" (Spain), "Isocaine" (Canada). It is important to understand that analogues may have different contraindications and special instructions for use. Therefore, you need to be careful here.
“I am allergic to freezing injections, or rather, they have a very weak effect. I even once had to remove a tooth that was almost alive. Not much pleasant((But the problem was solved unexpectedly. I went to treat caries, and the dentist suggested not using lidocaine, but some kind of French remedy. He said that if it didn’t work, he wouldn’t take money for the injection. No joke, but this injection really helped Now I only go there for treatment.”
Elena A., review from the woman.ru forum
Read more about restrictions during pregnancy and lactation
As noted above, Mepivacaine is contraindicated during lactation (i.e., breastfeeding). If the clinic simply does not have any other anesthetics, then treatment can be carried out in an emergency. However, the woman will have to skip 2-3 feedings (at least 10 hours must pass after the injection) - the child will be temporarily transferred to an artificial formula, and her own milk will be expressed and poured out. Because the substance passes into breast milk and may harm the baby. The anesthetic is allowed for pregnant women, but it is used with caution - especially if the expectant mother has kidney problems or swelling in the legs or face. To avoid complications, it is better to give preference to a less toxic product.
What you need to know additionally
Special instructions for the use of Mepivacaine are as follows:
- the anesthetic drug is used only in a clinical setting by a professional dentist,
- in case of inflammation of the gums or bones, the anesthetic effect is slightly lower,
- intravenous administration is prohibited,
- You can eat only when the effect of the anesthetic wears off: since loss of sensation can cause you to bite your tongue, cheek or lip,
- slight confusion is possible: therefore, driving after treatment is not recommended. As well as working with dangerous mechanisms, caustic chemicals, and climbing to heights.
What adverse reactions may there be?
Mepivacaine is considered a fairly safe anesthetic in dentistry (if we compare it with earlier, outdated ones). And side effects are extremely rare. The instructions for use indicate that in rare cases the following ailments are possible:
- headache, dizziness, tinnitus,
- anxiety, restlessness, feeling of euphoria,
- drowsiness,
- labored breathing,
- decreased vision,
- nausea, vomiting,
- increased or slow heartbeat,
- swelling of the throat, anaphylactic shock: in this case, the dentist’s office always has a first aid kit equipped with an anti-shock kit.
Side effects may include headache and dizziness.
Do not confuse side effects with normal consequences. After all, loss of tissue sensitivity can occur over a fairly wide area. For example, it is completely normal if after an injection your cheek, tongue, lip become numb, or the pronunciation of sounds is impaired. In a few hours all these manifestations will disappear.
Features of dental treatment at different stages
0-12 weeks. The 1st trimester of pregnancy is very important for the fetus. It is during this period that the baby’s vital organs and placenta are formed. Therefore, the fetus is essentially not protected yet. Serious treatment cannot be carried out at this stage. But the doctor may prescribe topical medications to relieve the inflammatory process. These may be Cholisal, Chlorhexidine, Miramistin.
13-24 weeks. At this time, the placenta has already formed and protects the baby. Therefore, dental treatment and other procedures can be performed.
From the 25th week until birth. At this time, the female body is weakened, and the uterus is very sensitive to the effects of drugs. In addition, a visit to the dentist is often stressful for an expectant mother. Therefore, it is better to wait for treatment procedures until the feeding period. However, this does not apply to cases of acute toothache.