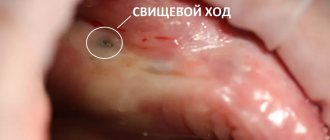
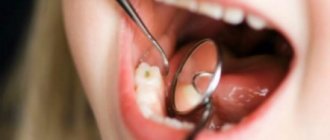
Periostitis is a purulent inflammation of the periosteum, the tissue covering the bone of the upper or lower jaw. Over time, the inflammation spreads to other tissues of the oral cavity , and a painful and unpleasant abscess can grow on the gum.
Periostitis is of two types: acute and chronic . the acute one , it goes on very quickly. Inflammation is manifested by asymmetric swelling of the cheek on the side of the diseased tooth and enlargement of the lymph nodes, and an increase in temperature is observed. Chronic periostitis can pass without obvious symptoms, while negatively affecting the condition of the child’s teeth, destroying them from the inside. The chronic form often occurs due to untreated acute periodontitis, pulpitis or due to injury.
Why is periostitis dangerous?
It is impossible to delay the treatment of periostitis , as this can lead to very dangerous consequences:
• acute purulent periostitis – it is manifested by swelling and hardening of the gums, tooth mobility, and increased body temperature. The child's appetite and sleep deteriorate. In this situation, the baby urgently needs medical attention and hospitalization;
• and dentia - the inflammatory process can quickly spread into the bone tissue, damage the rudiments of permanent teeth and destroy them. In the future, because of this, a tooth will not be able to grow .
• f legmon – inflammation of the tissues located under the skin, accompanied by severe swelling, thickening and suppuration. If not treated in time, it can cause blood poisoning.
Causes and risk factors
The mucous membrane of the child's oral cavity is often injured. The appearance of ulcers can be caused by temperature effects (hot food and drinks), biting the inner surface of the cheeks or lips; damage by sharp edges of the filling, braces or the tooth’s own tissues in case of chipped enamel. Normally, the immune response allows the pathological process to be quickly eliminated, the mucous membrane heals, and bacteria do not have time to cause severe inflammation and ulceration.
Weakened children's immunity cannot cope with this task, which leads to the development of aphthous stomatitis. A small number of opportunistic bacteria that populate the oral cavity begin to actively multiply. Often the disease occurs against the background or as a result of a severe infection: influenza, ARVI, acute tonsillitis, infectious mononucleosis, etc.
Main risk factors:
- food allergies, allergic reactions to hygiene products, such as toothpaste;
- deficiency of vitamins and microelements due to a strict diet or impaired digestion of food;
- hereditary predisposition;
- foci of infection in the oral cavity: caries, chronic periodontitis, periodontitis, gingivitis;
- frequent respiratory diseases;
- severe systemic diseases: pathologies of the endocrine system, blood vessels, metabolic disorders, etc.
Ask a Question
Signs of periostitis in a child:
• aching or nagging pain in a tooth or gum. Moreover, painful sensations intensify with any touch (including during meals);
• redness and swelling of the gums;
• when a lump appears above or below a tooth;
• o tech cheeks;
• enlargement of the lymph nodes (usually on the side where the source of inflammation is located);
• bad breath ;
• elevated temperature . It may not be present, but even if the temperature is normal and other symptoms are present, the child must be taken to the doctor;
• capriciousness and lethargy of the child.
Causes of swelling on the cheek
Many people believe that only teeth can provoke swelling of the cheeks. In fact, the reasons may be different.
Dental diseases
Factors related to oral health can provoke the problem. Among them:
- Eruption of impacted wisdom teeth, especially if the patient is over 25 years old. If the growth is abnormal, it is recommended to remove the “eight”.
- Stomatitis affecting the cheek, gums, tongue. The disease is most often diagnosed in children, but it can also occur in adults. An advanced disease provokes swelling. The cheek hurts from the inside, in the corner of the mouth.
- Gum disease, in which pathogenic bacteria accumulate in dental plaque, causing inflammation. Thus, gingivitis is accompanied by bleeding gums, swelling, and bad breath. If the disease is neglected, it will develop into periodontitis, a more serious problem.
Complications in the form of swelling of the cheek can develop after endodontic treatment. If during the procedure the canals are not washed and cleaned well enough, inflammation develops in the pulp chamber. The pathogenic process spreads to the bone, gum and cheek. This is how purulent periostitis develops, which is popularly called “flux”. If the disease is not treated in time, phlegmon and sepsis may develop, which pose a health hazard.
During the recovery period after tooth extraction, swelling of the cheek may also be observed. More often the symptom appears if the intervention was performed on the lower jaw. This problem often arises after implantation. This is the body's reaction to traumatic actions. It goes away in a few days. Otherwise, you need to consult a dentist, who must confirm or rule out the presence of a complication. It can develop due to infection getting into the wound, which threatens the manifestation of peri-implantitis.
Infectious, colds and other diseases
Cheek swelling is one of the symptoms of such diseases:
- Parotitis. When the disease occurs, the salivary glands become inflamed, which explains why soft tissues swell.
- Lymphadenitis. It occurs as an independent disease or as a complication of other ailments, such as diseases of the ENT organs. With lymphadenitis, the cervical, parotid and submandibular lymph nodes become enlarged, and the cheek becomes inflamed.
- Otitis, sinusitis, sinusitis. The inflammatory process can spread to the cheek, under the eye, and the area near the nose.
Pathological processes in gingival tissues often provoke inflammation of the salivary ducts and glands. It can also be an independent disease. It is caused by stones in the ducts, cysts, tumors.
The mucous membrane also swells with inflammation of the trigeminal nerve. In this case, other symptoms appear: numbness, pain radiating to the ear, “lumbago”. Swelling is a common occurrence in diseases of internal organs. Excess fluid due to malfunction of one or another organ accumulates in soft tissues, including the facial area.
Other causative factors
Swelling can also appear as a result of injury. This symptom accompanies soft tissue bruises, joint dislocations, and jaw fractures, which can be caused by a blow or fall. Children are more often susceptible to injury due to their excessive physical activity. Swelling can occur due to an allergic reaction, when the body shows immunity to a certain product. Other reasons:
- severe burn (both thermal and chemical);
- insect bites, which also cause redness and induration;
- poor oral hygiene.
Cheek swelling can occur in pregnant women. The fact is that during this period hormonal changes occur in the body. As a result, the gums swell, which is reflected on the cheek.
Causes of periostitis:
• of thorough oral care Small children do not yet know how to properly take care of their teeth, so plaque and food debris accumulate in the gum pockets, which can cause inflammation;
• injury to the gums . Children, especially toddlers, love to put almost everything in their mouths. Foreign objects can not only injure the gums, but also introduce harmful microbes into the wounds;
• to caries and its complications . Baby teeth are more vulnerable, so any defect can cause infection;
• angina , tonsillitis . _
Which doctor should I contact?
If you have a swelling of the cheek, you should first consult a dentist.
If the cause of the swelling is not dental, your doctor will refer you to other specialists:
- see a therapist for bacterial and viral infections;
- see a neurologist for neurological diseases;
- to an ENT specialist for inflammation of the ear and salivary gland;
- see a nephrologist for kidney pathologies;
- see a traumatologist or maxillofacial surgeon for trauma to the lower jaw.
Read also: Mental disorder
Treatment of periostitis
The main thing to remember is that you cannot try to treat periostitis on your own . There are several actions that absolutely cannot be performed while waiting for a doctor’s appointment, so as not to aggravate the disease:
• apply hot compresses , rinse with soda or drink hot drinks and decoctions. Heat will only increase swelling;
• give painkillers , and even more so antibiotics;
• try to cut the abscess yourself .
Allergic stomatitis
Allergic damage to the mucous membrane most often occurs in the form of contact stomatitis and chronic aphthous form of the disease1.
Allergens can include medications, food products, varnishes and paints that coat toys, toothpastes, mouth rinses, chewing gum, and dental metals included in braces1,2.
With allergic stomatitis in children, erosions and ulcers may appear in the mouth, but more often the matter is limited to redness and swelling of the mucous membrane1.
Treatment is avoiding contact with the allergen, rinsing or irrigating the mouth with antiseptic solutions to prevent infection. If necessary, doctors recommend taking antihistamines1,2.
Chronic recurrent aphthous stomatitis often occurs in schoolchildren and adolescents due to allergies2. In addition, its development can be provoked by diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, upper respiratory tract infections, disorders of the nervous system, and hypovitaminosis1,2.
With aphthous stomatitis in children, itching and burning first appear in the oral cavity. The mucous membrane at the site of the lesion becomes red and swollen, then an aphtha forms on it - a round or oval erosion 0.5-1 cm in diameter rising above the surrounding tissues with a red rim along the periphery and a bottom covered with a grayish-white coating. Aphthae are extremely painful, and if many of them form, they cause significant distress to the child1,2.
How many days does aphthous stomatitis last in children? With a mild course of the disease, the elements of inflammation persist for up to 5-7 days, then they heal without scar formation2 and do not appear for quite a long time. However, in severe cases, aphthae can occur constantly, and then many elements of inflammation can be found on the mucosa at different stages of development1,2.
To treat aphthous stomatitis, doctors use:
- antihistamines;
- immunomodulatory drugs;
- vitamins;
- probiotics2.
As a local therapy, it is recommended to treat the mucous membrane with drugs with analgesic, antiseptic, proteolytic (protein-breaking), anti-inflammatory and regenerating effects2.
Up to contents
Complications of flux
Complications with these localizations of phlegmon can be much more severe than with superficially located purulent foci with clear local manifestations. It is especially important to emphasize the danger of developing phlegmon of the floor of the mouth, taking into account the probable anaerobic component of the microflora.
Therefore, if there are complaints about difficulty swallowing, an increase in the volume of the tongue, its pushing towards the hard palate, a forced position of the head, you should urgently seek help from a dentist in order to avoid the development of the most common complication with this localization of phlegmon - anterior mediastinitis.
What to do?
First of all, you need to make an appointment with a dentist and conduct an X-ray examination, as a result of which you can determine the true cause of the tumor, make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe an individual treatment plan. Most patients are prescribed antibiotics or antiseptic drugs. Do not forget that treatment with traditional methods, which promise a quick recovery and supposedly relieve symptoms in a couple of hours, is not acceptable, since it can cause even more harm and lead to irreversible consequences. As a last resort, to relieve pain and reduce swelling, you can rinse your mouth with warm and clean water, but under no circumstances drink hot drinks or massage the sore spot.
In especially severe and advanced cases, surgical intervention will be required: a dental surgeon in Minsk makes an incision in the gum, removes pus, and, if necessary, removes the diseased tooth. All operations are performed under anesthesia, but sedation will be more effective in this case, allowing treatment to be carried out while you sleep. While the patient sleeps peacefully, without feeling discomfort or pain, all procedures are carried out as accurately and quickly as possible. It is safe for the body and is often used even in pediatric dentistry.
undergo dental treatment under anesthesia using drug sedation at the Minsk Family Dentistry Center. High-level specialists, modern equipment that meets European quality standards, affordable prices and an individual approach to each patient - we guarantee high-quality treatment without pain and complications. But you can only maintain the beauty and health of your teeth through joint efforts, so don’t forget about prevention: regular teeth cleaning, dental checkups at least once every six months, as well as timely treatment of oral diseases - together we can create the perfect smile!