Chief editor of the site:
Snitkovsky Arkady Alexandrovich
Chief physician of the professorial dentistry “22 Century”, dentist, orthopedic dentist
Author of the article:
Scientific team of dentistry “22 Century”
Dentists, candidates and doctors of medical sciences, professors
Turning under the crown has a corresponding medical term - preparation. Since the dentition is in close contact with each other in the bite (occlusion), the installation of any orthopedic structure requires certain preparation. It consists of grinding away hard tissues - enamel and dentin, in order to create space for a future structure, without affecting neighboring teeth. In this way, a stump is formed on which the prosthesis will be installed. This is the essence of preparation.
What is tooth preparation
Preparation (turning) is one of the stages in orthopedic treatment, which involves grinding down hard tissues to level their surface.
Previously, this procedure was extremely painful and quite lengthy. Modern instruments and advanced local anesthetics have significantly reduced the time of manipulation and made them absolutely painless.
Is it possible to do without turning?
Many patients are concerned about the question: is it possible to do without the preparation process and install a crown or prosthesis on a tooth in an intact state? Unfortunately, despite all the advances in dentistry, it is impossible to skip this stage of treatment.
In order for the crown to be securely fixed on the tooth, they must fit together as accurately as possible. But the natural tooth shape is not ideal; the side walls of the teeth have a convex shape, which excludes the possibility of creating a crown. During the grinding process, part of the enamel is ground down, as a result of which the tooth receives the correct geometric shape, onto which an orthodontic structure can easily be placed. In addition, any crown has its own thickness, which must be taken into account so that it does not interfere with the oral cavity and does not cause discomfort when talking and eating.
During preparation, the dentist removes all tissues affected by caries from the surface of the teeth. This is necessary so that complications do not develop after prosthetics - secondary caries and destruction of the supporting tooth.
How to grind correctly
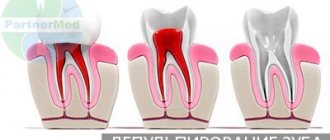
If pulpless (“dead”) teeth are being prepared, there is no need for anesthesia, except in cases where the use of a special thread is required to move the gums back. If the grinding procedure is carried out on vital (“living”) teeth, then in order not to hurt the patient, anesthesia is required.
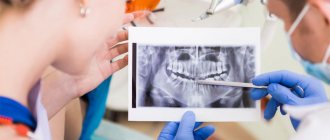
When preparing, it is imperative to take into account the anatomical features of various teeth and possible reactions of soft tissues. It is advisable to conduct an X-ray examination of the patient before the procedure in order to have an idea of the structure and places where the opening of the dental cavity is most likely.
If your teeth and gums hurt after grinding: reasons and what to do
The turning procedure itself does not cause any pain when adequate anesthesia is used. But after the effect of the painkiller wears off, unpleasant and even painful sensations may occur both in the tooth itself and in the surrounding gum.
Possible reasons:
- If the preparation is performed on a vital tooth, then it is possible that too thin a layer of dense tissue is left above the pulp containing nerves and blood vessels and the ground tooth thus reacts not only to the intake of sour or cold food, but also to touch. In such cases, installation of a temporary crown or additional cementation of the thinned area is indicated.
- To carry out shoulder grinding, the doctor needs a good overview of the working area, especially if the manipulations are carried out deeper than the gingival margin. To do this, gum retention is carried out - moving its edge back using a special thread. This manipulation can cause compression of the soft tissues, swelling and pain. Normally, such sensations go away on their own within 1-2 days.
- If enough time has passed after grinding, then the occurrence of pain in the tooth may indicate the development of pulpitis or periodontitis. This symptom is dangerous and requires urgent attention to a specialist.
Can a tooth crown be inexpensive?
The cost of a dental crown per tooth will directly depend on the type of material used, the method of its manufacture, the category of the clinic and its location, as well as the qualifications of the orthopedic doctor. For example, in Moscow, prices for metal crowns can vary from 3,000 to 16,000 rubles, for metal-ceramic crowns - from 7,000 to 40,000 rubles, and the average cost of a ceramic crown is about 21,000 rubles. You can find out in more detail how much a particular dental crown will cost for one tooth during an in-person consultation at a dental clinic.
Restoration of dental crowns
Dentures, like natural teeth, require care - careful oral hygiene and restoration of dental crowns. Service life and repair requirements depend on the material. Structures made of ceramics and metal-ceramics are susceptible to the formation of defects. Zirconium dioxide is more durable and cannot be broken or scratched. A zirconium prosthesis lasts about twenty years and does not require repair. As a rule, indications for restoration of the tooth crown are chips, cracks and discoloration of the structure. The procedure should only be carried out by a specialist; experiments at home often lead to breakage of the prosthesis or damage to healthy teeth.
Preparation methods: ultrasonic, laser, tunnel, chemical
There are several methods that allow you to prepare teeth; let’s look at each of them in more detail.
Ultrasonic preparation
The principle of operation of devices of this type is that the grinding of teeth occurs due to high-frequency vibration of the instruments under the influence of ultrasound.
Advantages:
- working tips exert minimal pressure on tooth tissue;
- during operation, a small amount of heat is released and no significant heating of enamel and dentin occurs;
- the procedure is painless;
- Ultrasound does not cause microcracks and chips on the walls of the pin;
- there is no negative effect on pulp tissue.
Laser preparation
Pulsed lasers are used for grinding teeth, the effect of which is that under the laser beam, water in the dental tissues is greatly heated. This leads to microscopic damage to the integrity of the enamel or dentin, pieces of which are immediately cooled and removed using a special water-air mixture.
Advantages:
- Laser equipment operates silently.
- High safety of the procedure, since there are no elements rotating at high speed.
- Low heating of dental tissues.
- Turning speed.
- Complete absence of pain.
- The edges of the pin have no chips or cracks.
- Since the procedure is non-contact, the possibility of infection is minimized.
»
Tunnel preparation
Today, turbine dental units are used for grinding teeth, with the ability to adjust the operating speed, and diamond or metal tips. The result of the work directly depends on the quality of the equipment, since worn-out tools cause significant overheating of the tissue, which significantly increases the risk of destruction.
When grinding teeth using the tunnel method, they try to leave as much of their own dental tissue as possible. The main advantage of the technique is the ability to clearly control the size of the removed tissue layer and clearly predict the result.
Flaws:
- possible heating of the enamel and resulting pain with insufficient anesthesia;
- If the technique is violated, soft tissue injury may occur;
- When using low-quality instruments, there is a high risk of microchips and cracks in hard dental tissues.
Air abrasive preparation
When using this method, instead of a rotating drill and drill, an air mixture with abrasive powder is used, which is supplied under fairly high pressure. When contacted with enamel or dentin, this combination causes minor destruction and removal of tooth dust.
Advantages of the technique:
- simplicity and high speed of all manipulations;
- no heating of tissues and no pain;
- the absence of vibration has a positive effect on pulp tissue during the preparation of vital teeth;
- maintaining the maximum amount of dental volume.
Chemical preparation
The chemical treatment method involves the use of active substances (most often acids) that soften enamel and dentin, followed by removal of damaged tissue. The disadvantage of the procedure is the need for prolonged exposure to reagents (sometimes up to half an hour).
Advantages of the chemical method:
- no thermal damage to teeth;
- there is no need for pain relief;
- there are no small chips or microcracks in the enamel;
- psychological comfort for the patient due to the lack of sound of a working drill.
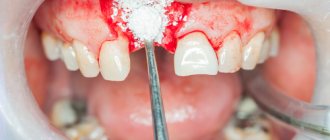
Types of ledges during preparation
Preparation of teeth with a ledge is a prerequisite for reliable fixation of the prosthetic structure in the oral cavity.
The most common methods of grinding teeth with a ledge:
- Knife -edge . The most commonly used type. Its width is only 0.3-0.4 mm. This is the best option for preparing inclined teeth and for solid metal crowns.
- Rounded grooved ledge ( Chamfer) . With a width of 0.8-1.2 mm, it allows maximum preservation of dental tissue. It is a classic option for metal-ceramic prosthetics.
- Shoulder ledge . The most uneconomical type with a width of 2 mm, requiring depulpation. However, it has the highest aesthetic characteristics and allows the crowns to be secured most firmly.
Grinding teeth without a shoulder is a serious mistake by the dentist, since the prosthetic crown will not be able to fit tightly to the tooth surface. And this will greatly complicate the care of dentures and increase the risk of developing caries.
Features of caring for metal ceramics
Everyday hygiene measures do not differ from normal procedures - it is important to brush your teeth twice a day, and also rinse your mouth, if possible, after eating.
Cleaning the teeth should be carried out as follows: using sweeping movements, you need to go over all the teeth in the direction from the gums to the cutting edge. You should not ignore the use of dental floss, or better yet, an irrigator.
You can clean metal ceramics in the same way as regular teeth - a toothbrush should be purchased in accordance with the doctor’s recommendations (the degree of stiffness of the bristles is determined by individual characteristics), the toothpaste can also be selected based on your needs.
Remember that it is better to protect metal-ceramic structures from mechanical damage. It is not recommended to bite into hard foods - this can result in cracks and chips, and subsequent breakage of the prosthesis.
Features of preparation in children
Preparation of primary primary teeth in children is a serious problem in dentistry. Young patients are the most difficult group among dental office visitors due to the high prevalence of phobia of the sound and sight of a rotating drill. In addition, baby teeth have a number of anatomical features that do not allow “adult” manipulations.
Therefore, doctors are looking for alternative methods for preparing teeth for caries in childhood.
The most promising method in this case is considered to be chemical preparation, which does not cause negative sensations even in the smallest children, but at the same time allows for sufficient quality treatment of the carious cavity.
Features of the procedure in childhood
When working with baby teeth, dentists try to avoid unnecessary procedures that may pose a certain threat to the condition of the child’s thin enamel. In addition, any additional manipulation using a noisy drill usually results in serious stress for the child.
As a rule, experts offer alternative and more gentle treatment methods that do not require preliminary preparation. In this case, pediatric dentistry is focused on protecting the not yet fully formed enamel from any type of injury. However, there are situations when turning for a crown is indispensable. Most often, preference is given to the chemical method, as it is less painful. Usually it is enough to remove only the tissue affected by caries.
Preparation for veneers
Veneers are partial microprostheses, the main function of which is to improve the aesthetic appearance of the vestibular part of the front teeth. The main material used for their manufacture is ceramics. Enamel preparation plays a significant role when installing such prostheses, since the density and reliability of fixation of the elements directly depends on its quality.
The preparation of teeth for ceramic veneers occurs in a certain sequence:
- processing of the vestibular surface;
- turning the side surfaces;
- preparation of the cutting edge and palatal surface (if necessary).
«
When processing the vestibular surface, the thickness of the layer that needs to be removed is initially determined. Then grooves are created on the prepared part, serving as a guide for the doctor, along which the entire volume of hard tissue is ground. A ledge is formed at the gum level (the grooved one is most often used). In the process of processing the lateral surfaces, 2 options are possible: with the preservation of interdental contact points and with the extension of the preparation boundaries to the lingual side. In the first case, the overall integrity and stability of the dentition is maintained. With the second option, aesthetic indicators are significantly improved.
Depending on the veneer model and the required conditions for its installation, the cutting edge can be ground off or left unchanged. If there is a need to remove tissue from the lingual surface, then the preparation boundary should in no case coincide with the line of contact with the antagonist teeth.
Installation process
Now let's talk about how cermets are installed.
- First of all, you need to undergo a diagnosis.
- Dental preparation procedure. Contrary to popular belief, installing metal ceramics on a living tooth is quite possible. However, in most cases there is a need to depulpate the tooth.
- After this, the orthopedic doctor will be able to take impressions of the ground teeth necessary for the manufacture of individual structures.
- Fixation of the prosthesis.
Many patients are interested in how teeth are ground for metal-plastic - dentures with a metal frame and a plastic coating on top. The preparation technique is the same as when installing metal-ceramic structures, but the tooth undergoes much more significant grinding due to the massiveness of the metal-plastic structures.
If you decide to install dentures, choose trusted dentists here.
Preparation for inlays: principles and rules
Inlays are partial dentures and are used to replace large defects in dental tissue.
Depending on the form, there are the following types of tabs:
- Inlay (inlay) - minimally invasive, since they do not affect the tubercles of the tooth;
- Onlay (onley) - serve to replace the internal slopes of the dental tubercles;
- Overlay - cover the entire volume of at least one tubercle;
- Pinlay (pinlay) - cover all dental cusps and have a special pin in their design - pin;
- stump inlays are a metal pin used in cases of severe destruction of tooth tissue and serving as a support for the crown.
Depending on the materials used, the inlays can be ceramic, metal or reinforced composite.
The main feature of preparing teeth for inlays is the need to create parallel side walls near the cavity for proper insertion of the finished structure, as well as to create sufficient depth for reliable fixation of the element.
Basic principles of turning for inlays:
- The prepared cavity must have an optimal shape for the smooth insertion and removal of the prosthesis. In this case, it is necessary to strive for maximum parallelism of the vertical walls. We allow only a slight angle of their deviation.
- The angle of transition of the cavity walls to the bottom should approach a straight line. The relationship of all walls should contribute to the uniform distribution of chewing pressure and maximum stability of the inlay.
- When forming the day, it is necessary to take into account that a minimum layer of tissue should remain above the pulp to ensure its protection from external factors. In adults, this value is 0.6 mm, and in children and adolescents - 1.4 mm.
- When forming complex cavities, additional fixation points should be formed to allow the inlay to be firmly fixed.
- When forming a cavity for metal inlays, it is necessary to create a bevel at the level of the enamel with a width of at least 0.5 mm and at an angle of 45°, which will ensure more accurate marginal contact of the prosthesis and tooth tissue.
- In the manufacture of metal-free structures, the presence of a bevel is contraindicated due to the fragility of materials with a small thickness.
Preparation (turning) for various types of crowns
A dental crown is a kind of “cap” that is placed on a healthy or damaged tooth. The main task of such a design is to restore the functions of the entire dentition.
The following types of crowns exist:
- Metal - made only of metal: sewn;
- stamped;
- metal-ceramic - consist of a metal frame lined with ceramic mass.
- porcelain;
Features of crown preparation:
- Grinding for solid metal crowns begins from the side surfaces, which eliminates damage to adjacent teeth, after which up to 0.3 mm of hard tissue is evenly removed.
- Preparation for metal-ceramics involves preliminary depulpation of the tooth, followed by the removal of 2 mm of tissue on each side. It is mandatory to create a ledge, the width of which depends on the model of the prosthesis. The walls of the stump must have a pronounced roughness for reliable fixation of the elements.
- The correct preparation technique for a porcelain crown involves giving the stump a conical or cylindrical shape. A rounded ledge is formed, which is immersed into the gum up to 1 mm (on the palatal surface it can be left at the border with the gum).
- Preparation for a zirconia crown should be carried out with a clearly visible margin, forming a rounded or shoulder shoulder. When treating anterior teeth, the thickness of the tissue removed should not exceed 0.3 mm, and for the chewing group - 0.6 mm.
Preparation for a prosthesis
All dentures are divided into 2 groups:
- Removable: plate plastic (acrylic) or metal;
- clasp dentures;
- nylon.
- bridge-like;
When installing dentures, tooth preparation takes place only in the case of fixed prosthetics with bridge structures. All other options (removable and implant prosthetics) do not require the removal of part of the enamel or dentin tissue.
When grinding teeth for a bridge, the basics and rules of technique are very similar to those when preparing for metal-ceramic crowns.
Is turning always required?
It all depends on the type of prosthesis that needs to be installed subsequently. For example, when installing veneers or lumineers, grinding will be minimal. When installing removable dentures on hooks, where the teeth remaining in the mouth act as a support, such a procedure will not be required. But if the quality of fixation of removable dentures needs to be improved with the help of clasps or telescopic crowns, then preparation of the “supports” is still carried out.
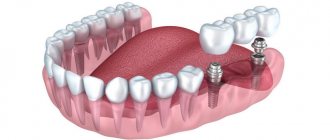
In the case of fixing a crown or bridge, doctors will be able to grind only those supporting units that have an apex remaining. And if it is destroyed at the root, then there will be nothing to prepare - in this case, the base is first built up using a pin or stump insert. If you choose implantation in case of missing teeth, then there is no need to grind adjacent units (as when installing a bridge) - the crown will be installed on the implant, which in no way will interfere with the neighboring teeth and will not rest on them.
Preparation during splinting
Splinting is the optimal method for preventing and treating tooth loosening due to periodontal disease, since this technique guarantees reliable long-term fixation.
Types of tires:
- Pin splints are fixed on the teeth using pin structures that are immersed vertically into hard dental tissues.
- Beam splints are metal structures with crowns at the ends, which are located in grooves on the lingual surface of the teeth.
- Inlay splints are polymer tapes that are attached to the inside of the teeth.
Tooth preparation during splinting is carried out depending on the type of structure, while trying to preserve the volume of hard tissue as much as possible. Often there is a need for depulpation.