The bite is the relationship between the teeth of the upper and lower jaws when they are closed. Depending on the nature of the closure, the types of bite are distinguished. It can be right and wrong. Doctors also talk about physiological and pathological occlusion. For example, if the jaw is too forward, so that individual teeth protrude and stick out, then correction is necessary.
An orthodontist deals with bite problems in children and adults. You can determine a malocclusion yourself. In front of the mirror, you can notice that the closure of the teeth is not ideal. In addition to aesthetic defects, malocclusion is also fraught with disturbances in facial expressions and speech. Facial asymmetry is often observed, which causes psychological problems to arise.
What is correct (physiological) bite
Physiological types of occlusion are characterized by the correct closure (occlusion) of the teeth. There should be no gaps, gaps or bony protrusions between the teeth. Correct occlusion is established only when all teeth are located along the center line.
Correct types of occlusion do not involve disturbances in chewing function. The upper jaw is shaped like a semi-oval, and the lower jaw resembles a parabola.
A physiological bite gives a person the following advantages:
- aesthetic smile;
- correct articulation and clear speech;
- correct primary processing of food (chewing).
Varieties and characteristics
When talking about what types of dental occlusion there are in adults in dentistry, there are two basic categories. In the first case, we are talking about correct occlusion, characterized by a harmonious relationship, natural facial contours, proportional shapes and symmetry of the midline and the junction of the frontal incisors. Such an anatomical structure not only ensures the aesthetics of a smile, but also allows you to fully realize the main tasks of the jaw region, which include food processing, as well as respiratory and speech functions. In turn, incorrect development is accompanied by more or less pronounced anomalies, often causing both physical and psychological discomfort to patients.
Physiological types of occlusion
Not only defective, but also natural conditions are subject to orthodontic classification. The ratio is divided into three varieties, the membership of which is determined by the indications of visual and hardware diagnostics.
Orthognathic
It is considered a reference because it provides optimal conditions necessary for the implementation of functional tasks. It is characterized by the overlap of the lower row with the upper by about a third of the height of the incisors, close contact when closing, as well as the absence of spaces and interdental gaps.
Biprognathic
A bite, the distinctive feature of which is the presence of a slight vestibular inclination, with a vector oriented towards the vestibule of the oral cavity. In this case, the frontal units retain points of contact, and the canines of the maxillary region are covered with antagonists for several millimeters.
Straight
It is diagnosed in cases when the cutting edges of the anterior incisors, which form the visible area of the smile, contact each other when closing, while the occlusion of the chewing molars remains correct. Eliminates the presence of empty areas, trema and diastemas, as well as signs of crowding.
The meaning of correct bite
The human body is a complex biological system in which each element affects the overall condition. Correct occlusal closure not only ensures the implementation of basic functionality, but also eliminates side effects such as joint pathologies, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, as well as heart and blood vessels. The asymmetrical position of the jaws leads to incorrect redistribution of the load, which ultimately forces the muscles to readjust, causing a change in posture, causing pain and dizziness.
When is the tooth relationship considered incorrect?
Factors indicating abnormal development include:
- Lack of contact between antagonists.
- Diction defects.
- Problems with chewing food.
- Distortion of facial features.
- Deformation of the jaws.
- The occurrence of pain syndrome.
The presence of even one of these signs is considered sufficient grounds for diagnosis. Practice shows that the earlier deviations are detected, the easier it is for the patient to eliminate them. Dental specialists use modern methods and technologies to determine the specifics of existing bite defects and draw up an optimal treatment plan that takes into account individual indications and recommendations.
Correct bite: how to understand
To evaluate your bite, you need to see a dentist. The doctor will do this quickly and accurately. If you want to do this yourself, you should know that a correct bite satisfies the following requirements:
- When the upper jaw contacts the lower jaw, an ideal contact is formed between the opposing teeth (upper and lower).
- The central front teeth (incisors) are positioned symmetrically. That is, they are equidistant from an imaginary line running down the center of the face.
- The dentition should be smooth, without gaps or crevices.
- It is considered normal if, when closed, the upper teeth cover the lower teeth by about a third.
Important! The criteria described above, which can be used to determine the bite, are for informational purposes only. Only a doctor determines the types of bite and makes a diagnosis.
Correct bite: types
There is no ideal physiological bite. There are only types of occlusion that are close to perfect and do not require orthodontic or surgical intervention. Let's consider the main physiological types of occlusion.
Orthognathic occlusion
Orthognathic is considered the most correct bite, and is found in 90% of people with physiological occlusion. Orthognathic bite can be determined at home. Permanent teeth should fit tightly together. In this case, the upper incisors slightly cover the lower ones.
Straight bite
In a straight bite, the upper and lower jaws are the same size. At the same time, both the incisors and chewing teeth close. Individuals with a straight bite can boast a very beautiful smile.
However, such a closure is not without its drawbacks. Direct bite is dangerous due to premature destruction of hard dental tissues. This is due to the increased load on the teeth when closing. In this case, the enamel wears off faster, cracks and chips form.
Biprognathic bite
Biprognathic types of occlusion occur in children and adolescents who have the habit of thumb sucking. Also, these types of closure can develop in a baby if it is too late to wean him off the pacifier.
With this type of bite, the incisors bend slightly forward. At the same time, they come into contact, and for this reason such a bite is considered physiological.
Progenic bite
This is a normal option provided that the teeth develop normally. A feature of a progenic bite is that the lower front teeth are slightly pushed forward.
Consequences
What complications can arise if a child’s malocclusion is not corrected? Possible consequences:
- tooth abrasion, premature wear, increased risk of caries;
- difficulty chewing causes gastrointestinal problems;
- mucosal injuries, gum inflammation, periodontal disease;
- increased load on the temporomandibular joint, pain, inflammation;
- breathing problems, ENT diseases;
- pinched nerves in the cervical spine;
- aesthetic facial defects, asymmetry;
- psychological problems;
- violation of diction.
Thus, malocclusion in children is dangerous for the development of diseases. It directly affects the emotional state of the individual, self-esteem, and self-confidence. If the bite is not corrected in time, physiological, psychological and aesthetic problems may develop.
Malocclusion: causes
Malocclusions are formed for a number of reasons, including:
- Hereditary factors . One of the leading causes of abnormal bite is genetics. The size and shape of the jaw are determined by genes received from the mother and father. Pathologies such as too narrow a jaw, cleft bite, misaligned dentition and other disorders are often dictated by hereditary factors.
- Nutrition . Malocclusion is considered one of the problems of modern civilization. In particular, we are talking about a situation where the lower jaw is underdeveloped. This is due to the abundance of liquid nutrition in childhood, which is why the lower jaw does not work fully.
- Mother's illnesses during pregnancy . Some abnormal types of bite occur due to maternal illness, especially in the first trimester of pregnancy.
- Wrong selection of pacifiers . An incorrect bite can develop if the nipples are not selected correctly. It is important that the baby makes an effort to obtain milk. Otherwise, underdevelopment of the lower jaw occurs.
- Bad habits in childhood . For example, thumb sucking and excessive use of pacifiers. Sleeping position also affects your bite. Often a malocclusion is formed when the head is thrown back.
- Diseases of the ENT organs . It is important to treat ear, nose and throat pathologies in a timely manner. With such diseases, the child is often forced to breathe through the mouth. Therefore, diseases such as sinusitis, rhinitis, adenoids and deformation of the nasal septum require adequate and competent treatment.
- Physical development disorder . In particular, we are talking about diseases affecting the growth and development of bones.
What factors influence malocclusion? Is there any way to avoid the problem?
Typically, the bite develops in people between infancy and about 17 years of age. It may be incorrect due to the following reasons:
- genetic predisposition;
- bad childhood habits: pacifier sucking, bottle feeding, finger sucking;
- problems with the spine that have not been corrected;
- chronic ENT diseases (for example, adenoiditis);
- calcium deficiency, as a result of which bone tissue is not formed correctly.
It is important! If a child breathes predominantly through his mouth during sleep, play, or in a calm state, this is one of the signals of problems, which may include an incorrect bite. The faster occlusion pathologies are corrected, the less likely it is that not only dental problems will occur, but also ENT diseases.
How to determine a pathological bite
Pathological types of bite are determined by the doctor. If you suspect a problem in yourself or your child, you should contact the dentist. Here are some features of pathological bites that you need to pay attention to:
- The teeth do not close tightly. Gaps and gaps form between the upper and lower teeth.
- There is partial or complete lack of contact between opposing teeth (incisors and/or chewing molars) (there is a short gap in the horizontal plane).
- The upper jaw is noticeably smaller than the lower jaw or vice versa.
- Dental crowding or occlusion, where teeth overlap each other.
- The presence of a diastema - a noticeable gap between the incisors.
- Change in appearance. For example, the lower jaw is shortened and the lips are turned inward.
- Exposure of tooth roots and other defects of hard dental tissues. For example, an indirect sign of malocclusion is poor enamel and wear of the cutting edges.
How to recognize that your child has an incorrect bite?
An abnormal bite can be corrected in adulthood, but the sooner it is noticed, the faster and easier the correction procedure will be.
Firstly, it can be visible to the naked eye. Secondly, an orthodontist can report its presence if the child comes to him for consultations regularly.
In addition, children at risk are those who:
- one of the parents has an incorrect bite;
- incorrect posture;
- if they suck on anatomically incorrect nipples.
The presence of diseases of the ENT organs is also a reason for closer attention to the baby’s bite. Another cause may be injuries to the head and, in particular, the face.
Malocclusion in a child can be recognized by:
- displacement of teeth to the sides;
- the presence of cracks, gaps between teeth;
- uneven placement of teeth in a row;
- displacement of teeth forward or backward;
- violation of the joining of the jaws when the teeth close together.
Malocclusion: types
Like physiological types of occlusion, pathological ones also come in different types. Below is a classification of malocclusions.
Distal bite
This is a type of malocclusion in which the upper jaw is highly developed compared to the lower jaw. For this reason, the upper teeth move noticeably forward.
Mesial bite
In this case, the lower jaw protrudes noticeably forward compared to the upper jaw. Sometimes there is a retraction of the upper lip. Often, with mesial occlusion, the functioning of the temporomandibular joint is impaired.
Crossbite
It is observed when the jaw shifts to the right or left. In this case, 1-2 teeth are in the wrong position.
Deep bite
In this case, the upper teeth cover the lower teeth by more than half. With a deep bite, a speech defect is observed, and the oral mucosa is also injured.
Open bite
There is a large gap between the dentition during occlusion. This is due to the fact that some teeth cannot close when closed. Open bites often occur when a child sucks a finger or a pacifier for a long time.
What is dental occlusion?
Today, not everyone can boast of healthy teeth from birth. This is due to various factors, and also to the fact that almost 7 out of 10 people have an incorrect bite from birth. With age, bite problems worsen, and if left untreated, teeth and gums suffer.
The bite is their position when the jaws are closed or during central dental occlusion. A bite is considered correct when the upper row overlaps the lower row by about one third, with the chewing units clearly touching each other.
Correction of malocclusion of the jaws is carried out by an orthodontist, who, based on a comprehensive diagnosis, recommends a certain type of treatment. In most cases, it is enough for the patient to place a braces system or aligners on the dentition; in complicated clinical cases, jaw surgery is performed to correct the bite.
Clinical case with malocclusion: the patient regularly takes care of his oral cavity, eats right, takes vitamins, but the teeth are susceptible to caries, wear out, and the gums also suffer from this. The orthodontist performed an orthopantomogram of the jaw and determined the cause of the problems - malocclusion, which leads to dental diseases. Having treated the bite, caries practically does not appear, and the general condition of the gums has improved.
Bite in the absence of teeth
If the patient has no teeth left, then there is no guarantee that prosthetics will be able to achieve an anatomically correct jaw. In this case, much depends on the initial positions (what the bite was like before losing teeth). If the upper and lower jaws are positioned relative to each other within normal limits, then the bite can be straightened with minor corrections. If the patient had problems with the jaw bones, then a deeper correction is required.
In the absence of teeth, the bite is determined using wax rollers. This creates an imitation of the dentition, which allows for standard changes. For this purpose, special plates and a curved, arc ruler are used. After all measurements and preparatory procedures have been carried out, a plaster and then a regular prosthesis is initially created in the dental laboratory.
Important: bite after wisdom tooth removal . Wisdom teeth were important for ancient people, but now there is no need for them. If wisdom teeth do not cause problems for a person, then doctors recommend not touching them. However, in cases where an adult wants to correct an incorrect bite, wisdom teeth can help with this. Thus, correction of the bite in adults is possible after the removal of wisdom teeth. The space formed after their removal allows the dentition to take an anatomically correct position.
Malocclusion: consequences
Malocclusion is a problem that should not be underestimated. Over time, malocclusion can lead to the following consequences:
- Premature tooth loss . This is due to two factors. Firstly, an incorrect bite increases the load on the teeth. This threatens the appearance of cracks and chips. In addition, an abnormal bite increases the risk of developing periodontal disease. This leads to accelerated tooth decay.
- Damage to the gums . With an incorrect bite, gum health deteriorates. They become sensitive to temperature, chemical and physical factors. In some cases, this leads to the formation of ulcers on the gums.
- Pathologies of the temporomandibular joints . The most common symptoms are a clicking sound when chewing, which should not normally be present. Then pain occurs, and the function of the joint deteriorates even more.
- Diseases of the digestive system . Well-chewed food is one of the conditions for normal functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. If the bite is broken, then relatively large pieces of food enter the stomach. Due to poor initial processing of food in the oral cavity, over time a person develops eating disorders.
- Psychological problems . Pathological types of bite often worsen a person’s appearance. This is how low self-esteem is formed. A person becomes overly modest, fearful and unsure of himself. Sometimes, in order to improve the situation, in addition to dental treatment, the help of a psychologist is also required.
Treatment of malocclusion
Today, malocclusions are treated using various techniques. Most often, the curvature can be corrected with orthodontic methods, but in some cases surgical correction is necessary. Let's look at the most effective ways.
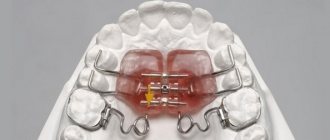
Orthodontic plates
These are removable hard plates that allow you to maintain the correct alignment of your teeth. Such structures consist of a plastic base and metal elements that hold the plate in the oral cavity.
Orthodontic plates are often used in pediatric dentistry. These products help develop the habit of breathing through the nose and also stop thumb sucking. In this case, the correct bite is formed due to the work of the muscular system. Depending on the tasks assigned, different types of plates are used. These are standard plates, plates with a visor, a flap or a bead. The plates are made from hypoallergenic materials. Those with baby teeth usually have soft plates installed. For permanent teeth, hard ones can be used.
Trainers
Another way to even out an uneven bite is to use trainers. These orthodontic structures are a two-jaw mouthguard made of silicone or polyurethane. Changing the bite with trainers occurs due to muscle work.
It is noteworthy that the result of such treatment persists even after the end of the course, because muscle memory is preserved. Trainers are successfully used for the following problems:
- open and deep bite types;
- mouth breathing;
- speech defects;
- crowded teeth;
- bad childhood habits (for example, thumb sucking);
- incorrect position of the lower jaw.
Treatment with trainers is carried out in 2 stages:
- First stage . It lasts 6 months and involves wearing soft trainers. This is necessary in order to activate the work of the chewing and facial muscles.
- Second phase . Soft trainers need to be replaced with hard ones. Such trainers directly affect the position of the dentition.
Advantages of trainers:
- affordable price;
- absence of unpleasant sensations;
- the ability to remove the structure while eating or talking.
Aligners
These are dense transparent trays for straightening teeth. Aligners are made individually for each patient. As a rule, this is a series of designs, each of which is worn for a certain period of time, and then replaced by a new one. This is a kind of cascade correction method. The disadvantage of this treatment is the relatively high price.
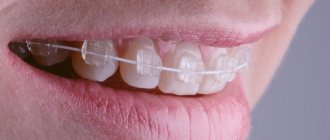
Braces
One of the most effective orthodontic methods of bite correction is braces. These are special locks connected in an arc. For more successful treatment, braces are also equipped with special elastic bands (or pulls). With the help of elastic bands, it is possible to increase the pressure on the dentition that needs to be corrected.
Incorrect types of bite are treated with braces in several stages:
- Preparatory . At this stage, diagnostic measures and selection of a treatment regimen are carried out. Professional teeth cleaning, plaque and tartar removal are carried out. If the patient has any dental diseases, they are treated before installing braces. Then the braces are made.
- Installation . The patient gets braces. Vestibular braces are installed on the outside, and lingual braces on the inside. Fastening is carried out on an adhesive basis, so it is painless. It should be borne in mind that during the first week there may be pain, which can be relieved with painkillers.
- Retention . After the braces are removed, the patient needs to wear retainers for a while. This is necessary to consolidate the result. The duration of wearing retainers is determined by the doctor.
Contraindications to orthodontic treatment
In some cases, orthodontic treatment for malocclusion cannot be carried out.
Contraindications:
- mental illness;
- pathologies of the central nervous system;
- malignant tumors;
- severe diseases of internal organs.
There are also relative contraindications, in which orthodontic treatment is possible subject to certain conditions.
Relative contraindications:
- Periodontitis with mobility of teeth 2 degrees.
- Poor oral hygiene. If a teenager does not take care of dental hygiene, then wearing orthodontic structures (for example, braces) is contraindicated. This is due to the fact that in this case the teeth are quickly destroyed.
Surgery
Surgery is resorted to in cases where it is a malocclusion of the 3rd degree of complexity. In such cases, orthodontic techniques are ineffective. Such operations usually last several hours. After 2-3 weeks you can return to your normal life. A month later, the patient begins jaw development techniques (to be discussed with the doctor). In some cases, after surgery, the patient is prescribed braces.
Laser bite correction
A laser for correcting occlusion is used at different stages of correction. For example, after correcting a bite, teeth tend to move. For this reason, bone tissue experiences heavy loads, causing microtrauma and inflammation to occur. Laser therapy helps eliminate inflammation and promotes rapid healing.
Attention! The laser is not used as an independent method of bite correction. It is used as an auxiliary method for treating associated complications and processes.
Stages of bite formation in children
The process of developing a child’s bite can be divided into several important stages.
Each of them is characterized by changes in the structure of the jaw and has factors that influence the formation of pathology. Stages of bite development in children:
- Elementary.
From birth to six months of the child. The first teeth begin to erupt towards the end of the period. The cause of pathology at this stage is a genetic predisposition or improper latching of the nipple during breastfeeding. - The process of formation of the bite of primary teeth.
Lasts until the age of three; as a rule, by the end of the period, all 20 baby teeth are in their position. At this age, the presence of gaps between the teeth is acceptable, but twisting, too close a fit, and growth in an uncharacteristic plane are considered as deviations from the norm. In addition to the above reasons, the most common factor in the development of pathology is bad habits: thumb sucking, pacifiers, toys or eating disorders. The child's diet should include a sufficient amount of solid food. - Preparation for the development of permanent dentition.
The stage continues until the appearance of the first permanent teeth. With proper oral care, no external changes are observed during this period. Bad habits can cause malocclusion. It is necessary to ensure that the child does not chew hard objects: pencils, thick books, furniture, since baby teeth are very soft and easily deformed. - Changing the temporary bite to a permanent one.
The most critical stage. It is during this period that serious pathologies begin to manifest themselves as unpleasant changes: torsion, improper growth of teeth, discrepancy between the size of the jaw and the volume of bone units, etc. On average, this period lasts up to 12 years. Factors in the development of anomalies are physiological characteristics or untimely replacement of teeth. - Formation of a permanent bite.
The teeth complete their growth and occupy a certain position in the jaw.
You can start correcting your bite from the early stages. There are several hardware and manual methods for this. Treatment with braces begins after a permanent bite has formed.
FAQ
Is it possible to correct an overbite without braces?
Yes, you can, but under certain conditions determined by the doctor. Malocclusions can be treated using orthodontic plates, trainers or aligners.
Is it possible to correct an overbite at home?
It is impossible to correct a crooked bite at home. There are exercises to strengthen the muscular system, but they are ineffective and are used only in addition to the main therapy.
How long do you need to wear braces for an overbite?
Depends on the degree of damage and the age of the patient. The minimum wearing period is 6 months. In some cases, braces are worn for up to 3 years.
Is it possible to get veneers if you have an incorrect bite?
It is possible, but only with minor deviations from the norm. Otherwise, orthodontic treatment is initially carried out, and only after that is it permissible to install veneers.
How much does it cost to correct a bite?
It all depends on the amount of work. First of all, you need to undergo a diagnosis. Mild degrees of malocclusion respond well to treatment with removable orthodontic structures. In such cases the price will be low.