During pregnancy, the processes of destruction of her teeth are activated in a woman’s body, and problems with their treatment often arise. Why does this all happen and how to deal with this problem?
During pregnancy, hormonal changes begin in a woman's body, which are aimed at the full development of the fetus. However, such adjustments do not always go unnoticed for a woman and she develops some problems, for example with her teeth.
Naturally, not all women’s teeth begin to decay. This applies to those pregnant women who have previously completely and efficiently treated all their problem teeth and other diseases that appear in the oral cavity. But life makes its own adjustments to pregnancy: very often women do not treat their teeth enough, which, of course, will then have a very negative impact on the integrity of the teeth.
Causes of dental deterioration
Affected masticatory organs are incompatible with pregnancy, since actively progressing caries begins to destroy the mother’s teeth, poisoning her body and the fetus. Low defenses of the body lead to deep caries, pulpitis, and periodontitis. If a tooth is broken, the body may be deficient in calcium. Teeth may crumble, since in the 2nd trimester the need for this element increases due to the formation of the baby’s skeletal system. It takes a lot of mineral to build hard tissue. If there is not enough of it in the mother’s blood, it will be washed out of her bones, incisors, fangs, and molars.
A few respond to this by demineralizing the enamel. This increases sensitivity. The thin enamel layer will be vulnerable, and the chewing organs may become loose. Old fillings can fall out because bacteria easily penetrates under them. What to do, how to stay healthy? If teeth crumble during pregnancy, this fact cannot be ignored. You need to visit a dentist who will develop a suitable therapeutic program. Main causes of problems:
- Hormonal changes, changes in the number of progesterone and estrogen;
- Suppression of the immune system when dental plaque thickens;
- Increased vulnerability of the oral mucosa leads to bleeding gums, and traumatism leads to inflammation and infection;
- “Aggressive” microorganisms are activated;
- The amount and composition of saliva changes, it becomes more acidic, which reduces the protection function;
How to prevent tooth decay in children and adults?
To strengthen the enamel and prevent tooth decay, it is necessary to follow the following measures:
- Take care of your oral hygiene at home, rinse your mouth after eating something sweet or sour.
- Twice a year, undergo an examination and comprehensive hygiene with a dentist, who will clean and strengthen your teeth with calcium and fluoride.
- Eat mostly healthy foods rich in vitamins and minerals.
- Take multivitamins and nutritional supplements prescribed by your doctor.
- Give up bad habits: biting nails and improvised objects, as well as smoking.
- Drink clean drinking water with normal mineral content.
How to prepare for pregnancy to save your teeth
Among the many causes of pathology of the gums and chewing organs of women in labor, there is a lack of sanitization of the oral cavity on the eve of pregnancy. That is, the expectant mother ignored professional hygienic cleaning when she planned to bear the child. Many did not treat existing dental diseases at all before pregnancy. Therefore, such women first of all develop problems in the oral cavity. Of course, therapy can and should be done while the baby is pregnant. But in order to minimize the risks of damage to the fetus, it is better to eliminate all problems on the eve of pregnancy.
Today, dental treatment during pregnancy is possible with anesthesia. The doctor selects a gentle drug that does not harm the embryo. But, surgical operations could have been avoided if the expectant mother had diagnosed the oral cavity and completed a therapeutic course before pregnancy. Sometimes it happens that dentists even recommend removing wisdom teeth in advance, so as not to carry out such serious manipulations after conceiving a child. Therefore, it is better to put the oral cavity in order before pregnancy, even at the stage of planning conception.
It is necessary to visit the dentist at least 2 times during pregnancy. Dentists often recommend that women take dental vitamins during pregnancy. Such courses will help eliminate mineral deficiency. If a woman has not prepared for pregnancy, the antenatal clinic will offer her not only the necessary tests, but also a visit to the dentist.
Why do teeth hurt during pregnancy?
Very often, the cause of toothache lies in the exacerbation of existing diseases - caries, periodontitis, gingivitis, pulpitis. A cutting wisdom tooth or tartar can also cause pain.
However, sometimes toothache is directly related to pregnancy.
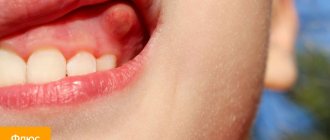
There is such a thing as gingivitis in pregnant women - rapidly developing gum disease against the background of toxicosis and changes in hormonal balance, in which inflammation occurs more intensely than usual.
Another reason why pregnant women’s teeth literally begin to “crumble” is the formation of bones in the fetus and their active growth. If there is a deficiency of calcium, vitamins D3 and K in the body of a pregnant woman, the fetus has nothing to “build” a skeleton from, so it begins to “pull” the substances it needs from the mother’s body. And the depots of calcium and phosphorus are teeth and bones. Therefore, if the expectant mother’s diet does not have enough calcium, then the teeth will begin to decay very quickly.
Many pregnant women do not associate their toothache with calcium deficiency, since the expectant mother receives quite a lot of calcium - it is also found in milk, cheese, other dairy products, fish and even in some plants, for example, chia seeds. But in order for calcium to be absorbed, the body must have vitamins D3 and K, but a pregnant woman’s diet may not have enough of them, unless she takes specialized vitamin-mineral complexes. The fact is that the main sources of these vitamins are not very popular products. Thus, a person can get vitamin D3 from animal fats (fish oil, margarine), and their consumption during pregnancy is reduced so as not to gain excess weight. The main sources of vitamin K are spinach, cauliflower and nettle leaves, and its content in other vegetables and fruits is low. But vitamins D3 and K are consumed in huge quantities during pregnancy.
Also, early toxicosis of pregnant women greatly affects dental health: frequent vomiting oxidizes the environment of the oral cavity, provoking the development of diseases that already exist, but previously did not bother the woman, and pass without any special external manifestations. Nausea forces pregnant women to carefully choose food, often not paying attention to its nutritional value, only to the absence of irritating smells and tastes. Thus, the body may not receive vitamins, the lack of which provokes even more severe attacks of toxicosis.
But the reasons listed above do not mean at all that toothache is an obligatory companion for the expectant mother. Let's see what can be done to prevent toothache during pregnancy.
Oral care during pregnancy
The oral cavity during pregnancy and lactation requires increased care and careful care. Basic hygiene rules do not differ from typical standards. But when a woman does not properly care for her teeth, she has serious problems. Gums may bleed and teeth may break off. At an appointment with a dentist, they identify and draw up a therapeutic plan, which includes activities to teach proper care. Observations have shown that insufficient hygiene activates the processes of crown destruction. When toxicosis occurs, many people undergo formal teeth cleaning. In addition, to get rid of nausea, women in labor constantly eat something. In such a situation, pathogenic bacteria quickly multiply, hard tissues are destroyed, and not only caries develops, but also periodontitis and pulpitis.
Today, dentists offer pregnant women caries treatment using the Icon system. Infiltration is used when the tissue is affected by no more than 1/3 of the thickness of the dentin layer. Pregnant women tolerate this therapy well. It does not harm the embryo, since no anesthesia is used. Caries of several units can be removed in one session. The procedure is painless and lasts 20-30 minutes. Basic principles of proper oral care:
- Since the enamel becomes thin and vulnerable, use a brush with soft or medium bristles.
- The brush must be changed after 2 months.
- It is not recommended to use pastes that contain a lot of fluoride, so as not to harm the little one.
- It is better to use pastes with a high calcium content.
- You should brush your teeth twice a day and rinse your mouth after eating.
- Once every 6 months you need to have your teeth professionally cleaned using approved methods.
- Promptly carry out therapy of masticatory organs using gentle technologies.
At the time of pregnancy, treatment of caries, non-carious lesions, periodontitis, and tooth extraction for medical reasons is allowed. The principles of hygiene during pregnancy do not change. But the procedures must be performed carefully, taking into account the processes that occur in the body of the expectant mother.
What to do if the tooth is completely crumbled
The crown part of the tooth has completely crumbled, what should I do? You must make an appointment with a doctor at a dental clinic within two days. After the x-ray, it will be clear whether the root is preserved, what condition it is in, and whether removal is necessary. Then possible recovery options:
- prosthetics (stump inlays, pins, crowns and bridges);
- implantation (implantation of a titanium artificial root into bone tissue followed by installation of a crown).
In any case, modern techniques are sufficient to compensate for any loss of teeth.
Forms and stages of development of caries
The systematization of various forms of caries is based on several parameters:
- time of detection of pathology;
- specific histological features of the pathological process;
- location and depth of the lesion.
The clinical picture of the disease in pregnant women can be either primary , diagnosed for the first time, or secondary , as a consequence of continued destruction (destruction) of dental tissue with the formation of carious cavities in previously filled teeth.
According to the severity of damage to dental tissues, various types of caries are distinguished: enamel shell, hard dentin tissue, bone tissue, or caries with a suspended destructive process.
To manage pregnant patients, the tactics of topographic systematization of the destructive process are used. There are several stages of development.
Initial stage of caries
Superficial demineralization of the hard structure of teeth is focal in nature, manifesting itself in the form of spots. The formation of white spots characterizes an active destructive process, brown spots - slow destruction. In treatment, the use of minimally invasive techniques is permissible.
Superficial caries
The process of destruction of tooth tissue does not extend beyond the outer protective enamel shell and does not disrupt the structure of the enamel-dentin junction. At this stage of the disease development, the first clinical symptoms appear. Treatment consists of mechanical treatment of the damage.
Average caries
It is characterized by the formation of carious cavities without signs of deep damage to the hard tissues of the tooth, and a pronounced clinical course. The basis of treatment is the removal of damaged tissue.
Deep stage caries
The destructive carious process spreads to the internal tissues of dentin, accompanied by the development of intense pain. Lack of timely treatment threatens pulp damage with a high probability of developing complications in the form of periodontitis or pulpitis.
While carrying a child, women usually develop moderate-intensity caries, which is explained by a decrease in immune defense, a pronounced deficiency of essential minerals, and sometimes a lack of proper dental hygiene. Systemic and multiple formation of carious cavities is rarely diagnosed.
Can pregnant women have anesthesia?
There are a large number of clinical studies on the safety of local anesthetics in the treatment and extraction of teeth in pregnant women. In Table No. 1, you can see 5 local anesthetics that can be used in pregnant women according to the FDA (corresponding to safety categories B and C). First of all, these are well-known anesthetics such as, for example, Lidocaine or Ultracaine DS, etc. The table also shows the permitted concentrations of vasoconstrictors.
Table No. 1 –
*according to the FDA (Food and Drug Administration, USA)
It should be noted that the use of a vasoconstrictor (vasoconstrictor component) not only allows you to reduce the dose of the administered anesthetic and increase the duration of its action. The presence of a vasoconstrictor makes it possible to reduce the possible systemic toxic effects of the anesthetic. This occurs due to the fact that the vasoconstrictor slows down the entry of the anesthetic into the bloodstream from the injection site, and therefore allows for a reduction in peak concentrations of the anesthetic in the blood (24stoma.ru).
The safety of the use of vasoconstrictors in pregnant women has been shown in many clinical studies (for example, the study by Haas D. “An update on local anesthetics in dentistry”). It is known that vasoconstrictors do not affect uterine blood flow - provided their dosages and anesthesia technique are observed. It is optimal to use the vasoconstrictor epinephrine at a concentration of 1:200,000, and to minimize the systemic effect of epinephrine in pregnant women, it is important to perform an aspiration test during each injection, because it will guarantee the absence of intravascular administration.
Dental treatment during menstruation –
There are no special contraindications for dental treatment on such days. However, if your periods are accompanied by increased nervousness, severe weakness, as well as a severe psycho-emotional state, then it is better to postpone dental treatment to more favorable days. Surgical interventions should also be avoided during this period, because starting 2-3 days before the start of menstruation in women, blood clotting decreases, which can lead to bleeding (for example, after tooth extraction).
Blood clotting indicators are fully restored approximately 2 days after the end of menstruation.
Methods for diagnosing and treating caries in pregnant women
Diagnosis of the carious process in pregnant patients is not difficult. The main goal of diagnosis is the timely identification of destructive processes in the structure of dental tissues that require urgent treatment, and carrying out differential diagnostics to exclude non-carious pathologies.
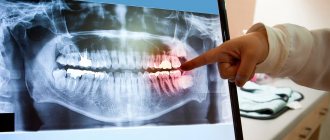
A feature of the diagnostic examination of pregnant patients is the exclusion of radiographic diagnostics in the first gestational trimester. The use of radiography in this period is justified only in cases of severe clinical signs (severe pain, purulent inflammation).
Diagnostic search for carious processes in pregnant women includes:
- visual examination using a dental probe and mirrors, a caries detector and thermal stimuli;
- electroodontodiagnostic examination (EDI) , which allows to assess the depth of damage to dental tissue;
- dental transillumination method , which allows identifying pathology at an early stage;
- laser diagnostics , revealing early signs of tooth decay in inaccessible places and signs of secondary caries.
Treatment of caries in pregnant women
A key feature when choosing treatment tactics for pregnant women is the limitations in the use of a number of techniques and medications traditionally used for tissue restoration.
Therapeutic treatment is selected individually for each specific case. The duration of pregnancy, the dynamics of pathological development, the severity of clinical signs and the presence of possible complications are taken into account.
Recommended methods for treating caries for pregnant women
- Remineralization. Used for caries at the stain stage. The lesion is saturated with fluoride and calcium-containing agents through medicinal applications and sessions of therapeutic electrophoresis. In addition to the procedures, it is recommended to use fluoride-containing dental hygiene products.
- Filling is the optimal method for restoring teeth with any severity of carious lesions.