About the prevention and treatment of common childhood dental diseases, the causes of candidiasis (thrush) and stomatitis. How can I help my child maintain oral hygiene? Note to parents.
Every parent, when visiting a pediatric dentist, wonders when can they start brushing their teeth? There are many opinions on this matter; some even argue that it is not necessary to clean dairy products. But this is a mistaken opinion. It is known that dental plaque contains pathogenic microorganisms that contribute to the occurrence of caries. It is necessary to accustom your child to brushing his teeth from the age of one. At first, the parent takes care of this himself, and later controls the process. By the age of one year, on average, a child has 8 to 12 teeth. If parents find it difficult to use a toothbrush, you can clean off plaque with gauze wrapped around your finger. This will reduce the trauma that can occur from a toothbrush, because... the child does not immediately begin to understand the meaning of this process. Later, you can start brushing with a soft-bristled toothbrush; you can find one in every pharmacy. There is a variety of choices, both in terms of external indicators and age.
Children's pastes are also varied. You can consult your dentist about your choice. When a child begins to brush his teeth on his own, parents should supervise this process, because children often do it in bad faith, for a short time. It is recommended to clean for up to 5 minutes, removing plaque from top to bottom.
Even despite hygiene, the child is not insured against such childhood diseases as candidiasis and stomatitis. Outwardly they are very similar, parents often confuse them. How to distinguish them and how to treat them?
Causes of candidal stomatitis
Normally, the yeast-like organism Candida is in the body of every person and does not harm him in any way. When certain conditions arise, fungi begin to actively multiply, which leads to inflammation of the oral mucosa. Such factors include:
- metabolic failures;
- diabetes;
- diseases of the endocrine system;
- hypovitaminosis;
- chronic pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract;
- long-term antibiotic therapy;
- pregnancy;
- use of birth control pills;
- bad habits (alcohol abuse, smoking), etc.
In addition to the mentioned endogenous (internal) causes of candidiasis, there are exogenous (external) causes. These are chemical and mechanical conditions that lead to disruption of the integrity of the skin and oral mucosa. These include: plaque and tartar, sharpened edges of teeth, uncomfortable dentures, chemical contamination, etc.
Stomatitis
Stomatitis in a child
There are several types of stomatitis, the most common are herpetic and aphthous . It differs from candidiasis in that it is accompanied by high fever. Bubbles and aphthae appear on the tongue, soft palate, and gums. The child stops eating due to severe pain. Most often, children in kindergartens suffer from stomatitis. They are constantly in contact and put toys in their mouths. If one child gets sick with viral stomatitis, the other is more likely to get infected from him. One of the reasons for refusing a pacifier is not only a violation in the formation of the bite, but also hygiene. Repeatedly, infection occurs from a child who brought a pacifier to kindergarten and lent it to his friends. Reduced immunity can provoke the disease; if relapses occur, laboratory tests are prescribed to rule out common diseases.
Treatment
Treatment for general symptoms of stomatitis is prescribed by a local pediatrician and locally by a pediatric dentist. It includes treating aphthae with sea buckthorn oil, some recommend an aqueous solution of blue, before eating they recommend painkillers gels, soda gargles, and spraying the throat with aerosols. As a rule, stomatitis disappears suddenly, just as it began, and good immunity copes with the disease.
Every parent faced with such problems panics.
These diseases are treated almost every day. This is not a reason to worry, because... everything is treated in a short time, and maintaining hygiene, monitoring the child’s behavior, weaning from bad habits completely eliminates these problems. Moscow metro station Zvezdnaya, Danube Avenue, 23
Signs of the disease
Symptoms of fungal stomatitis vary depending on the degree of inflammation, the characteristics of the patient’s body and his age.
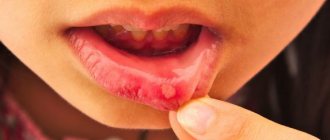
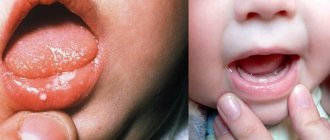
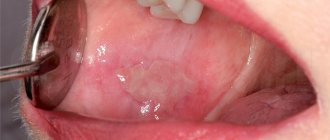
Signs of candidal stomatitis in young children are presented in the form of white cheesy plaques in the mouth. Parents often confuse them with leftover dairy foods. When plaque is removed, ulcers and erosions appear on the child’s mucous membrane and tongue. As the disease progresses, additional signs appear:
- the mucous membrane swells - it is difficult for the child to swallow;
- eating causes pain and discomfort;
- the patient loses appetite;
- When the infection penetrates the intestines, abdominal pain and digestive problems appear.
Symptoms of oral thrush in adults begin with a burning sensation in the larynx. Then a yellowish film appears on the mucous membrane and tongue, and when removed independently, blood is released. The patient complains of loss of taste, metallic taste. With chronic inflammation, the patient has a dry mouth and pain when swallowing.
Externally, fungal stomatitis in adults and children can manifest itself as glossitis (infection of the tongue) or as candidiasis.
Candidal stomatitis in children, symptoms and treatment
Candidal stomatitis, or fungal stomatitis, or thrush is the most common type of inflammation of the oral cavity in children. Although it is more common in young children, children of all age groups are not immune from the development of a cheesy coating with a rather unpleasant odor on the mucous membranes and tongue.
The causative agent of this type of inflammation is the Candida fungus, which is present in the microflora of the oral cavity, but some unfavorable factors can provoke its rapid proliferation and, as a result, candidiasis - inflammation of the mucous membrane.
Candidiasis is stomatitis on a child’s tongue and on the inside of the cheeks and lips, which is accompanied by severe pain and itching. Sometimes hyperemia (redness) and plaque spreads to the pharynx. Candida plaque is easily removed, revealing brightly colored erosions underneath. There is one popular misconception that if you take a bandage with powdered sugar (or honey) and remove the plaque, the thrush will go away. Yes, the plaque is removed, but the sharp microparticles of sugar injure the mucous membrane in new places and the microwounds immediately become infected with fungus. After some time, stomatitis returns in an even greater volume, since sweets serve as an excellent breeding ground for fungus, as well as various bacteria, so such self-medication can also result in infectious stomatitis in addition.
If your baby has inflammation in the mouth, immediately contact the experienced specialists of the Utkinzub clinic and they will determine the type of stomatitis and prescribe the appropriate treatment. And now we will tell you how to quickly cure stomatitis of fungal origin under the supervision of our doctors.
How to treat oral stomatitis
Treatment of candidiasis is carried out in two directions - local therapy and general treatment. It is known that all fungal diseases actively develop in an acidic environment, which means that in order to limit the spread, the pH in the mouth should be changed. You can alkalize the environment in the oral cavity using a soda solution or a 2% boric acid solution. Often, for children over 3 years old, lubrication with aniline dyes, in particular methylene blue, is used. of candidal stomatitis in infants has its own characteristics, which you can read about in the article “ Treatment of stomatitis in infants . You should rinse your mouth with alkaline solutions several times a day, or wipe the gums of the necks of your teeth, where harmful fungus is most often hidden in plaque. The doctor will prescribe a special solution for the treatment of Candide stomatitis, which destroys the fungus. The duration of use of the drug is strictly 10 days; you cannot stop treatment, even if there is no longer visible thrush, since the fungus may not be completely eliminated, and if it returns, it will be resistant to the drug and difficult to cure.
Older children can be prescribed Diflucan, but in a strictly individual dosage, determined by the doctor. The use of special antifungal ointments is also mandatory; vitamin complexes and immunomodulators will be prescribed to enhance immunity. After treatment, the teeth will be sanitized and the child will be taught the rules of oral hygiene. If thrush persistently returns, then other family members who can constantly infect the child should be examined. A sick child must be immediately isolated from other children, given a separate room, dishes and a towel, because candidal stomatitis is quite contagious. Complex forms of candidiasis are treated with antifungal medications, sometimes in the form of injections. The prognosis is good and a complete cure is possible.
Types and forms of pathology
In practice, acute and chronic oral candidiasis occurs. The first develops rapidly, the second is characterized by a sluggish course and vague symptoms, periodic relapses and inflammation.
Acute fungal candidal stomatitis can be pseudomembranous (white plaque is easily removed and reveals reddened areas) and atrophic (there is no plaque, the mucosal surface dries, turns red and becomes painful).
Chronic thrush can be hyperplastic (white or grayish cheesy plaques form on the soft tissues) and atrophic (the oral mucosa dries out, becomes thinner, the patient complains of pain and discomfort).
Symptoms of herpetic stomatitis
The disease has 4 stages, and each stage has its own symptoms:
- Incubation period. It has no obvious symptoms and cannot be noticed.
- Stage of vesicle (bubble) generation. First, redness appears on the mucous membrane, and then a bubble forms, which very soon bursts. At the same time, the temperature may rise, drowsiness and irritability may appear.
- After the vesicle bursts, damaged mucosa is exposed. At this stage, the child experiences pain and a lot of other unpleasant sensations in the affected area.
- The mucous membrane becomes marble-colored during the healing stage.
Symptoms also depend on the severity of the disease. Herpetic stomatitis in children can be expressed as either two blisters or massive damage to the mucous membrane, in which the child’s temperature rises quickly, vomiting or diarrhea occurs, nosebleeds, and even heart failure may begin.
How to treat fungal stomatitis?
In order not only to reduce inflammation of the mucous membrane, but also to prevent relapses, treatment of candidal (fungal) stomatitis in adults and children is carried out only in a comprehensive manner. Therapy involves taking several drugs at once:
- antimycotics – antifungal drugs for topical use;
- local antiseptic solutions for rinsing and irrigation (to prevent additional infection);
- antihistamines (recommended for the development of allergies to fungal activity);
- vitamin complexes (to eliminate deficiency of substances in the body).
To speed up recovery, the patient will have to follow a special diet. It is necessary to restore the mucous membranes of the oral cavity and pharynx.
Often sick patients are interested in how to treat candidal stomatitis at home, putting off going to the dentist. But it is impossible to cure candidiasis at home. Probably, it will only be possible to relieve the acute symptoms of the pathology, which will manifest itself again after a while. To prevent inflammation from becoming chronic, you should consult a doctor as soon as you notice the first symptoms of the disease.
Candidiasis (thrush)
Candida
enter the oral cavity . In children, thrush is often confused with stomatitis. It is most often transmitted from poorly washed, unsterile nipples, bottles, as well as from an infected mother, through the birth canal, with low immunity. Most children get sick before they are one year old. Parents complain about a white, curd-like coating.
Treatment
Infants are not prescribed serious medications for uncomplicated cases. The dentist recommends cleaning this plaque with a soda solution (1 teaspoon per glass of warm water). An ear stick, as an option. The same solution is used to treat nipples, bottles, toys, and mother's nipples during breastfeeding. In most cases, candidiasis quickly passes without leaving a trace. Prevention includes regular monitoring of the sterility of items used by the child.
Predisposing factors and risk groups
It is known that 50% of people are carriers of fungal microflora, and under normal conditions it can be in a kind of “dormant” or suppressed state in the form of chlamydospores, resistant to the external environment. This is why fungal microflora can be transmitted from person to person (i.e., it is contagious). However, under certain conditions, the fungus can begin to multiply rapidly, form colonies and lead to thrush in the mouth (candidal stomatitis). Moreover, under certain conditions, this disease can recur in both children and adults (chronic candidal stomatitis). There are many factors that predispose to this disease and form risk groups for candidal stomatitis in adults and children.
General decrease in immune defense. Can be caused by pregnancy, general diseases (diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, diabetes mellitus, tuberculosis, immunodeficiency states), long-term use of medications (especially antibiotics, corticosteroids, cytostics), dysbacteriosis, avitaminosis (lack of vitamins B, C, PP) , bad habits (alcohol, smoking).
Infants and elderly people. Children, up to about the seventh month of life, and the elderly, due to imperfect or reduced immune defense, are especially susceptible to this disease. Moreover, when diagnosed with chronic candidal stomatitis, a thorough immunological examination is necessary.
Local factors. For example, injuries to the oral mucosa (due to malocclusion of the dentition, chipped tooth enamel). Another common case is removable dentures, which, with insufficient hygiene, contribute to the proliferation of fungal microflora or injure the mucous membrane. Local factors include allergic reactions to dental materials, when allergic stomatitis initiates the appearance of fungal stomatitis.
Treatment of herpetic stomatitis
In severe cases of the disease, hospitalization of the child is required.
Treatment is carried out with acyclovir preparations, and the mucous membrane is treated in the first three stages with propolis and infusions of antiseptic herbs. At the last stage, the mucous membrane is helped to quickly return to normal by treating it with sea buckthorn oil and other oils. As an auxiliary treatment, a course of vitamins and, if necessary, antipyretic and local painkillers are given.
In addition to the two types of stomatitis described above, the disease can also be caused by allergic diseases, disruptions in the gastrointestinal tract and diseases such as scarlet fever, chickenpox and others. These types of stomatitis in children are treated with treatment of the underlying disease, and to speed up the process, symptomatic treatment is carried out (treatment of mucosal wounds and careful oral hygiene).
Doctors at A.Dent pediatric dentistry successfully combat the development of childhood diseases and claim that timely visits to the dentist prevent the occurrence of most diseases in children.
Therapy for different types of stomatitis
For different stomatitis, therapy is prescribed depending on the type of pathogen . These could be: bacteria, viruses, allergens. An analysis may be required to determine the causative agents of candidiasis, herpes, or bacterial culture.
To successfully treat stomatitis, you need to undergo an examination, follow all the pediatrician’s prescriptions and oral hygiene, and also drink plenty of chamomile or calendula tea.
Sometimes inexperienced young mothers do the wrong procedures or take medications on their own, which further aggravates the situation. In this case, before consulting a pediatrician or ENT specialist, you can only take painkillers and antiseptics.
Such drugs for stomatitis are prescribed containing benzocaine, chlorhexidine, lidocaine. If stomatitis is of viral etiology, the doctor will prescribe antiviral drugs. With bacterial stomatitis, symptoms depend on the type of microorganism. In cases of mild to moderate severity, antiseptics, painkillers and antibiotics will suffice.
You can use a spray containing lidocaine , however, for children under 2 years of age, this product only treats erosions and does not irrigate the oral cavity. After 4 years, children can dissolve Hexoral Tabs tablets. For all types of stomatitis, you can use the herbal mixture "Stomatofit", and do not forget to treat the oral cavity with a soda solution.
Hexoral Tabs tablets
With catarrhal stomatitis, the mucous membrane is not severely damaged; it occurs as a side infection of measles or scarlet fever. Rinsing with a solution of carrot, beet and cabbage juices with warm boiled water gives good results.
Traditional medicine recommends herbal infusions, Kalanchoe and aloe juices. Propolis tincture has pronounced antimicrobial properties.