05.12.2019
A huge number of people are afraid to visit dentists because dental treatment is usually accompanied by pain and other unpleasant sensations. There is even a special term - dentophobia - fear of dentists, which, according to some data, can describe 84% of patients. However, nowadays, anesthesia comes to the aid of dental phobes, facilitating a calm dental procedure.
But people are usually concerned about how long the freezing effect lasts and how to quickly recover from dental anesthesia, because it can interfere with eating or distort your smile.
Classification of anesthesia in dentistry
Anesthesia, or anesthesia, in dentistry has a certain classification. Various drugs and their types are used in individual cases, depending on the time required by the doctor for the operation, the patient’s condition, and the presence of severe fear or phobia. First of all, anesthesia is divided into two types:
- general anesthesia, or anesthesia;
- local anesthesia.
Anesthesia is usually used only in isolated cases of necessity, if the operation is expected to be very long. So, general anesthesia can last about six hours. Moreover, it has a number of advantages relative to local anesthesia:
- you can remove several teeth or perform several procedures in one go;
- Treatment under general anesthesia is completely painless;
- During anesthesia, the secretion of saliva is blocked, which is very beneficial to the doctor.
However, in most cases there is simply no need for anesthesia, so local anesthesia is used, which is often popularly called tooth freezing.
Features of local anesthesia
Local anesthesia is simple and in most cases can satisfy the need for pain relief, which is why it is especially popular among dentists. In turn, tooth freezing is divided into the following types:
Application anesthesia
It is carried out using gels or sprays that are applied to the gum or cheek. The effect can be observed approximately five minutes after application. However, topical anesthesia is used only in cases where it is necessary to get rid of tartar, remove a falling out or loose tooth, treat gums, or carry out another practically painless procedure, because the spray or gel freezes only the surface of the mucous membrane.
Moreover, topical anesthesia cannot be used for children under five years of age, as well as people with lung diseases.
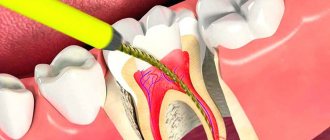
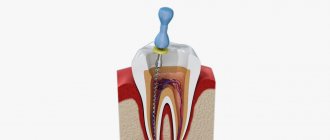
Infiltration anesthesia, or injection
This type of anesthesia is performed by injecting an anesthetic into the soft tissue located near the diseased tooth to freeze it. It affects the deep layers of tissue. The injection is administered near the location of the entrance of the nerve trunks leading to half of the jaw or its separate part. Usually, not only the cheek and the necessary gums are frozen, but also other organs of the oral cavity, since the exits of all nerves are located close to each other.
It is also important to understand that freezing the upper and lower jaws are somewhat different in their methodology and action due to differences in the structure of the skeleton. Considering that the lower jaw usually has greater loads relative to the upper jaw, evolutionarily it has developed that it has a more dense structure and its muscles are more developed.
Therefore, when injecting an anesthetic into the lower jaw, the needle is inserted deeper, which also affects the duration of the anesthetic.
Frequently asked questions from patients before agreeing to spinal anesthesia
How will I feel after the anesthesia is administered?
Answer. A couple of minutes after the injection of spinal anesthesia, heaviness in the lower extremities, slight numbness and warmth may be felt. After 15 minutes, the legs will be completely motionless.
How will I feel during the operation?
Answer. During a prolonged operation, a feeling of discomfort may occur due to the long static posture of the body. However, no pain will be felt. Also, discomfort during surgery can be caused by strong touches, stretching of the legs during the doctor's manipulations, or ambient noise. At the request of the patient, the anesthesiologist can put him into a state of light sleep for better comfort. At the same time, the specialist monitors his physical indicators: pulse, blood pressure, breathing and consciousness.
How will I feel after the surgery?
Duration of action of the anesthetic
A huge number of patients are usually interested in how quickly tooth frost will go away, but it is necessary to understand that the duration of action of the anesthetic depends not only on the type of anesthesia, the area of its application, dosage, the person’s age, metabolic rate and other individual parameters, but also on the painkiller used facilities. Thus, dental anesthetics can be divided into three groups according to the duration of their effect:
- short-acting (Novocaine) – up to twenty minutes;
- medium-acting (Prilocaine, Articaine, Trimecaine, Lidocaine) - from half an hour to an hour;
- long-acting (Bupivacaine) - the effect in some cases can last up to six hours, but usually a sensitivity-blocking dosage is used for two hours.
However, as mentioned above, there are a number of factors that influence the duration of action of the painkiller:
- the presence of inflammation at the site of drug administration;
- the presence of vasoconstrictors in the composition of the anesthetic - substances that narrow blood vessels;
- injection depth;
- site of drug administration;
- chronic diseases of the urinary system;
- individual parameters of the human body.
But in most cases, drugs when injected into the upper jaw last for the next two hours, and when injected into the lower jaw - up to four. However, again, this all depends on the freezing method and many other factors, so if the anesthesia persists for a longer period of time, there is no cause for concern.
Only if freezing remains relevant even after 24 hours should you consult your doctor.
Possible side effects of spinal anesthesia
First of all, it should be noted that the number of side effects with this type of anesthesia is much less than after general anesthesia. Therefore, the risk of complications is reduced to a minimum and is extremely rare.
Possible complications are associated with pathologies present in the patient’s body, as well as age and bad habits.
We should not forget that all manipulations in anesthesiology, up to the installation of a regular IV, carry a certain risk. However, by strictly adhering to all doctor’s prescriptions, a person in most cases manages to avoid negative consequences.
Possible complications after anesthesia include:
- headache. This negative consequence most often appears due to the fact that after anesthesia a person begins to actively move. Statistics show 1% of the total number of complications. This pain syndrome goes away on its own within a couple of days. However, during this period it would not be amiss to measure blood pressure and act based on the tonometer readings. The main rule in this case is compliance with bed rest in the postoperative period;
- decrease in blood pressure. This negative factor is caused by the introduction of an anesthetic. As a rule, it does not last long. To normalize blood pressure, special intravenous solutions are administered and it is recommended to drink more fluids. This condition occurs in 1% of patients;
- pain in the anesthesia puncture area. The discomfort goes away within 24 hours and does not require additional treatment. If the patient cannot tolerate the pain, then you can take a Paracetamol or Diclofenac tablet;
- delay in the process of urination. A common occurrence that does not require therapy and usually resolves on the second day after surgery;
- neurological complications. An extremely rare phenomenon characterized by loss of sensation, muscle weakness and tingling in the lower part of the body lasting up to two days. If this problem persists for more than three days, you should consult a doctor.
There is always a certain risk of complications after spinal anesthesia, but fortunately it is extremely small
Method for reducing the effect of anesthesia
Usually, even after an operation or a procedure requiring anesthesia, the painkiller continues to make itself felt: the lips remain numb, it is not possible to eat normally, the smile becomes distorted. Therefore, people are looking for a way to help the anesthetic stop working as quickly as possible.
In this case, dentists usually recommend applying warm compresses to the cheek. This will help dilate the blood vessels, which will ultimately increase the metabolic rate and remove the anesthetic from the body. However, this is contraindicated after tooth extraction or if inflammation remains. Thus, it is strictly forbidden to heat a tooth or cheek during gumboil. Therefore, it is highly recommended that you consult your dentist initially.
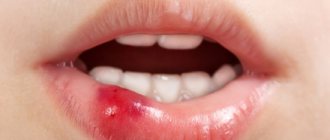
Why did gumboil appear after dental treatment?
Swelling of the gums indicates the occurrence of an inflammatory process, which caused the complication. If painful sensations are observed against the background of the tumor, the main reasons for this may be:
- Periodontal inflammation. The tumor is observed on both cheeks, but pronounced swelling occurs only on the infected side.
- Neglected teeth, improper placement of fillings. Before swelling occurs, pain occurs. After 2-3 days, a flux with pus may form.
- Incorrect development of wisdom teeth. A hood forms from the mucous membrane, in which food particles accumulate and become inflamed.
- Removal of a tooth. Due to mechanical damage to the tissue, swelling can be considered normal.
- Cyst. The inflammatory process lasts for 1.5-2 years and injures the periosteum. The pathology occurs against a background of severe pain.
Attention! Swelling of the cheek after dental treatment can develop due to infection in the socket, which not only causes discomfort and swelling, but can also lead to more serious consequences.
If there is no pain during swelling, the reasons for this are as follows:
- allergic reaction to anesthesia, dental materials (swelling sometimes affects the entire face);
- removal of the nerve: part of the nerve may remain in the canals; after installation of the filling, flux appears;
- dissection of the gums, extracted tooth (in these cases, swelling is normal);
- infectious inflammation of the lymph in children, accompanied by aches and fever;
- neurological diseases accompanied by swelling, congestion in the ears, sore throat, weakness.
Important! In the case of severe pathologies of internal organs, the drainage of fluid is often disrupted; as a result, it accumulates in the nose, cheeks, neck, cheekbones and near the eyes.
Anesthesia during pregnancy
Typically, dentists recommend treating teeth and gums while planning pregnancy, because anesthetics can indirectly affect the intrauterine development of the fetus. However, if necessary, it is better to go to the doctor in the second trimester of pregnancy, but if there is an urgent need for treatment, then it can be performed at any stage.
The most modern painkillers, which do not contain adrenaline, are used for pregnant women to avoid the possibility of increased blood pressure and contractions of the uterus. Usually, drugs with minimal toxic effects on the body are also used.
In some cases, pregnant women are transferred to a hospital for treatment.
Thus, all necessary procedures can be carried out under the strict supervision of the attending physician to avoid any complications.
Tooth freezing while breastfeeding
Some mothers are afraid to visit dentists while breastfeeding, thinking that anesthetics through milk can have a negative effect on their children. However, there is practically no reason for this.
Neither the anesthetic itself nor the accompanying possible toxic substances are reflected in the milk, because they act only on a certain area of the jaw and are not introduced into the blood.
But in order to further reduce the likelihood of negative effects of drugs on babies, dentists recommend feeding them before visiting the doctor, and also preparing in advance the required amount of milk for the next feeding of the baby. Thus, the toxic substance will not have the opportunity to enter the child’s body.
Category Miscellaneous Published by Mister dentist