Hyperesthesia or increased sensitivity of teeth is pain that occurs in response to temperature, chemical, and tactile stimuli. Characteristics:
- The pain is short-term but constantly recurring
- It is not associated with oral or dental diseases
Hyperesthesia is caused by thinning of the enamel. The underlying dentin is no longer protected and responds to irritation. Another reason could be receding gums. In this case, the root is exposed and reacts.
In Russia, 62% of the population
[1]. The problem mainly occurs between the ages of 30 and 60 years.
Dental hypersthesia
Dental hyperesthesia is an increase in the reaction of enamel to chemical and temperature provoking factors. Also, painful sensations can occur with acidic foods - fruits and berries. Discomfort is possible when chewing food and hygienic cleaning with a regular brush.
Dental hyperesthesia according to ICD-10, this condition is assigned code K03.8. It is important to understand that in most cases, increased sensitivity of the hard tissues of dental units is not an isolated pathological process. It occurs as a response to concomitant diseases.
In the branches of West Dental family dentistry in Vsevolozhsk and Yanino-1, our specialists, dental therapists, will help solve this problem. They will select the necessary measures for the prevention and treatment of this disease. In this article we will talk in detail about what dental hyperesthesia is and its varieties. You will learn how to prevent its occurrence and fight it.
What to do if you have tooth sensitivity
When unpleasant sensations appear, the first reaction of a modern person is to look for advice on the Internet. Among the recommendations, the first place is occupied by the use of folk remedies. A decoction of chamomile, calendula or sage has a soothing and anti-inflammatory effect. Propolis has the same effect, but it should not be chewed on an empty stomach. Tea tree oil and saline solution disinfect the oral cavity.
The problem is that home remedies do not eliminate the cause, but only mask it. Treatment of dental hyperesthesia should be comprehensive. First you need to determine the factors that led to its development. If it is caries, it is necessary to treat carious cavities. In the case of periodontal diseases, the work begins with stabilizing the process. Common diseases require treatment from a specialist. Often, eliminating the root cause is enough. In any case, the decision on how to treat tooth sensitivity should be made by the doctor.
Causes
Hypersensitivity of hard tissue structures of teeth can develop for certain reasons:
- Mechanical trauma to enamel - when cleaning at home, using an excessively abrasive paste or a brush with hard bristles, applying a lot of force to the enamel.
- Multiple acid exposure - juices, carbonated drinks, fruits and berries.
- The presence of pathological conditions in the oral cavity that violate the integrity of the structure of enamel prisms: carious process, wedge-shaped defect, erosion.
- Gum recession is the exposure of the cervical area of the teeth due to bite pathology, inflammation of the gum tissue, and vitamin deficiency.
- Exposure to radiation - increased occupational hazard, radiation exposure.
Hyperesthesia of tooth enamel may be a temporary phenomenon. Thus, it appears in the first 2 days after professional cleaning due to the removal of hard deposits or office lightening of the enamel.
There are factors that provoke symptoms - heavy smoking; dry mucous membranes due to endocrine pathologies; gagging; gastrointestinal diseases.
Algorithm of actions for hyperesthesia
- Adjust your diet. Avoid completely or significantly reduce the consumption of foods and drinks containing acids and sugar. Especially fruit and berry juices, wine, candies. Eat more green vegetables, fiber-rich foods, and whole grains.
- Change your toothpaste. Never use bleach. Choose from those labeled "Sensitive".
- Check if you are practicing proper oral hygiene. If it's wrong, correct it.
- Make an appointment with your dentist to find out the type of tooth sensitivity, find out the cause and get treatment.
- Visit the dentist twice a year, even if nothing hurts.
Manifestations
Dental hyperesthesia (according to ICD-10 K03.8) is manifested by a brief pain reaction when interacting with irritants. Unpleasant sensations usually do not exceed a few seconds in duration and appear with some regularity under the influence of a disturbing factor.
The severity of the pain varies - from inconvenience to difficulties with cleaning and standard meals. Such symptoms reduce the quality of life and can force you to change your usual diet and lifestyle.
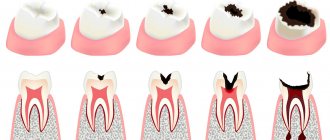
Some of the most severe symptoms occur with improperly formed enamel; carious process at the neck of the coronal part; severe abrasion of chewing surfaces.
High enamel reactivity can occur in one unit or all of them in the oral cavity. With a single lesion, one unit reacts, and with a developing erosive pathological process, the entire row will be affected.
How does hyperesthesia manifest (symptoms)
The main sign of dental hypersensitivity is intense but short-term pain (15-35 seconds) when exposed to temperature (cold, hot), chemical (sour, sweet, spicy), mechanical (percussion, brushing) factors. Increased reactivity is observed in one, several segments, or in all units of the series. A dental examination may reveal:
- atrophy of soft tissues in the cervical region;
- wedge-shaped defects on crowns;
- caries at different stages of development (from white spot to deep);
- cracks, chips of enamel;
- dental hypoplasia;
- enamel erosion;
- fluorosis, etc.
Classification
Clinical studies have resulted in the most complete structuring of dental hyperesthesia (ICD K03.8), based on which the doctor will determine the causes of the pathology and will be able to differentiate it from other diseases. And most importantly, the specialist will be able to make a true diagnosis and formulate the correct treatment tactics. The classification allows us to systematize the factors influencing the occurrence of the disease.
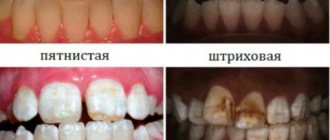
By location:
- Limited - a limited number of units are affected (1-3). Teeth ground for orthopedic structures, or affected by cervical caries.
- Generalized - most of the dentition is affected, sometimes the entire tooth row. The reasons are erosion, gum recession, high abrasion.
By origin:
- due to a decrease in the volume of solid tissue structures.
- volumes of hard tissues do not affect. Associated with periodontal diseases, pathologies of the endocrine, nervous and gastrointestinal systems. Visually, the integrity of the enamel is not compromised.
According to the severity of the pathology:
I—response to temperature;
II - pain when interacting with sweet, sour and bitter foods;
III - pain is caused by all irritants, as well as hygienic cleaning.
The strength of pain reactions depends on the characteristics of the body.
Provoking factors
Hyperesthesia does not appear immediately. There are several factors that you need to pay attention to in order to eliminate them in time. Don't wait for discomfort to appear. It is better to initially develop healthy habits that will help you maintain your health so that you never experience acute dental pain. Sensitivity increases when any of the factors listed below are present.
- Insufficient oral hygiene. Soft plaque is an accumulation of microbes that eat food microparticles stuck in crevices, releasing organic acids that dissolve enamel minerals. Externally, the dental unit looks intact, but the density of the enamel is significantly reduced. Its demineralization occurs. The first alarm bell is increased sensitivity, then caries develops.
- Consumption of certain foods. Juices, wine, sweet soda, fruits, candies, and other sweets contain phosphoric and other acids that negatively affect the strength of enamel.
- Constant use of aggressive whitening pastes containing abrasive and chemical components.
- Ultrasonic cleaning. Under a dense coating, the enamel becomes thinner and becomes loose. After professional cleaning, it is exposed, its sensitivity increases sharply. Usually, dentists, taking this point into account, use strengthening pastes at the end of the procedure for the preventive treatment of tooth sensitivity.
Complications
High reactivity of hard tissue structures of teeth can affect the general condition of a person. Diseases of the psyche and gastrointestinal tract may worsen. Soreness often disrupts the usual diet.
One of the most obvious and severe consequences of hypersensitivity is pulpitis - an inflammatory process that affects the neurovascular tissue inside the tooth. Constant exposure to irritants on the pulp can lead to aggravation of the process, as well as a deterioration in the general condition of the body. Treatment of such a complication is multi-stage and labor-intensive: the pulp is removed, endodontic treatment is carried out, and the coronal part is restored.
It happens that excessive sensitivity is only one symptom of pathology, for example, a harbinger of a wedge-shaped defect. Therefore, it is important to immediately make an appointment with a specialist with this problem in order to determine the provoking factors of the disease and avoid complications. Dentists at the West Dental clinic will help you with this and select fast and high-quality treatment.
Types of hypersensitivity
In 1981, Soviet dentists Yu. A. Fedorov and I. G. Lukomsky proposed a classification of dental hypersensitivity:
- According to the clinical course, they are distinguished:
- 1st degree of severity – the tooth reacts to temperature changes.
- 2nd degree of severity - the tooth reacts to temperature and chemical influences.
- 3rd degree of severity – sensitivity to mechanical stimuli is added.
- According to the area of distribution there are:
- Limited hyperesthesia, in which one or more teeth are sensitive.
- Generalized hyperesthesia - all teeth or most of them are sensitive.
- By nature of origin:
- With the loss of hard dental tissues (with caries, wedge-shaped defects, abrasion and erosion of enamel).
- Without loss of hard dental tissues (for periodontal diseases, functional disorders in the body).
Diagnostics
When examined by a specialist, it is important to conduct a thorough differential diagnosis in order to distinguish hypersensitivity from other diseases with similar symptoms:
- pulpitis;
- caries;
- cracked tooth or filling material.
In case of dental hyperesthesia, differential diagnosis consists of a visual and instrumental examination; an X-ray and electroodontodiagnosis (EDD) may be necessary.
A characteristic feature of high enamel reactivity is quickly subsiding acute pain. To identify it, a specialist needs to check the condition of the pulp using X-rays or using EDI. If a preliminary diagnosis of hypersensitivity is made, the doctor performs diagnostic tests to determine the degree of reaction of dental tissues to irritants. Afterwards, the specialist draws up an individual detailed plan for the treatment and prevention of dental hyperesthesia.
The mechanism of development of hyperesthesia
Tooth enamel is not sensitive; its purpose is to protect softer dental tissues from external influences. Enamel consists of 96% mineral substances, so it is extremely durable. Its main components are calcium and phosphorus compounds; the properties of enamel and its hardness depend on their quantitative ratio.
Under the enamel there is dentin, penetrated by dentinal canals - the main tissue of the tooth, which has some sensitivity to external irritants. When the physicochemical properties of enamel change, its permeability increases and the level of dentin protection decreases. The nervous structures of the dentinal tubules are connected to the pulp of the tooth - its nerve, therefore, when exposed to any irritant, increased sensitivity of the tooth appears.
The occurrence of hyperesthesia is explained by the hydrodynamic theory: when intratubular pressure changes, the speed of movement of dental fluid in the dentinal canals changes, which causes irritation of the nerve endings and pain. In practice, this happens like this: due to thinning or damage to the enamel, the dentin is exposed, the dentinal tubules open and dental fluid comes out of them; As a result, the intracanalicular pressure changes, which, when exposed to external stimuli, causes sharp pain in the tooth. The reaction to cold is most acute; when exposed to hot stimuli, there is no significant change in the speed of movement of the dental fluid.
Sometimes tooth hypersensitivity occurs without damage to the enamel, which is explained by existing pathologies of other organs. The strength of pain depends on the number of dentinal tubules in the tooth, the diameter of their lumen, which are individual characteristics of the body. The severity of pain is also affected by the patient’s pain sensitivity threshold: if it is reduced, then sensitivity increases.
Hypersthesia in children
Dental hyperesthesia in children, in most cases, is associated with non-carious lesions of the enamel:
- Thinning of enamel prisms, resulting from microcracks and defects;
- Bite pathology leading to abrasion of hard tissue structures;
- Traumatization of teeth;
- Treatment not carried out in a timely manner, leading to exposure of the root parts of baby teeth;
- Abuse of soda and sugar-containing products;
- Adolescence (10-14 years) during the eruption of several permanent teeth with still immature enamel.
At the appointment, the dentist will examine the child and diagnose the pathology. He will tell you in detail about preventive measures (remineralizing therapy, fluoride pastes) and treatment.
Tooth hypersensitivity after caries treatment
Hyperesthesia after medical intervention is associated with the use of phosphoric acid to treat the prepared cavity. This makes it possible to increase the adhesion of the filling material to the tooth tissues, but when it comes into contact with healthy enamel, the acid washes out calcium from it, so sensitivity increases. To avoid this phenomenon, the dentist treats the enamel after installing the filling with a special preparation.
Also, after caries treatment, tooth sensitivity to hot or cold temperatures may persist for several days due to the fact that when drying the prepared cavity before treating it with orthophosphoric acid, the surface was overdried, resulting in increased dentin sensitivity. After some time, the necessary moisture comes from the dental tissues into the surface layer of dentin, and the unpleasant sensations disappear.
If tooth hypersensitivity persists for a long time after treatment of caries, it is necessary to repeat the visit to the dentist to find out the reasons.
Treatment
The main therapy for hypersensitivity focuses on eliminating provoking causes and slowing down the flow of dentinal fluid in the tubules. This therapeutic regimen is performed:
- Clogging of micropores and cracks in the hard tissue structures of dental units with desensitizers - specialized means that reduce tissue reactivity.
- Narrowing micropores with mineralizing agents. Specialized gels containing fluorine and calcium. Restoring the mineral balance in the hard tissue structures of teeth helps to achieve high results. This technique is a fundamental part of preventive measures to combat caries and other pathological processes.
- Narrowing or complete blockage of tubules in dentin under a directed laser beam.
It is important to know that sensitivity formed due to loss of gingival and bone tissue, gum recession, will require major therapeutic and surgical interventions. It is necessary to perform comprehensive treatment of periodontal disease to restore a full life and diet.
If the symptoms are caused by pathological closing of the jaws, then orthodontic treatment is necessary. So, when the carious process develops, the doctor will remove the affected structures and further restore it with specialized material. If the process is complicated by pulpitis, endodontic treatment will be necessary - extirpation of the pulp bundle, mechanical and medicinal cleaning of the root canals with their further filling. Finally, restoration of the anatomy of the cusps and fissures of the chewing surface with filling material.
West Dental specialists have all the necessary knowledge, and the clinics have high-tech equipment to select and provide suitable therapy, taking into account all the symptoms of the process. Today, gels, pastes, and varnishes with fluorine and calcium are widely used. It is possible to use electrophoresis and vitamin therapy.
Doctors at West Dental branches will provide highly qualified assistance in treatment of any complexity. You can make an appointment for a consultation by phone or on the website.
How to reduce tooth sensitivity
Medical intervention depends on what is causing the increased sensitivity. The main thing is to remove not the symptoms, but the cause.
When treating, follow the rule: from simple to complex. In dentistry this is called “from reversible to irreversible methods.”
- Hygiene products
. Special rinses and toothpastes to reduce tooth sensitivity. These measures are sufficient for minor manifestations. They are good for reducing tooth sensitivity after whitening. - Professional measures
. Saturation of enamel with minerals, fluoridation, the use of dentin sealants and desensitizers and other drugs help combat hypersensitivity. - Laser therapy
. Dentin is able to absorb the energy of a laser beam, and its tubules become clogged. This allows for a decrease in sensitivity. - Physiotherapy
. The effectiveness of electrophoresis in reducing severe tooth sensitivity has been confirmed. - Endodontic treatment
. If other measures do not help, the tooth is depulped.
All these methods are used after or simultaneously with the elimination of the cause that caused hyperesthesia. An integrated approach helps to remove tooth sensitivity to cold, hot, as well as mechanical and chemical irritants.
Where can they help get rid of hyperesthesia?
The dental clinic “Academy Dent” is one of the few medical institutions in all of Moscow where doctors pay due attention to the problem under consideration and treat any diagnosis with attention, trying to differentiate it as accurately as possible and determine the only correct tactics for managing the patient. In addition, an individual plan of examinations and analyzes is developed, taking into account the characteristics of the person’s objective condition and his medical history. The service of the medical institution will please you no less - at the Dent Academy you will never see queues, and the staff will treat you as a VIP client, regardless of your receipt!
Summary
- If hypersensitivity occurs, avoid drinks and foods containing acids (fruits and fruit juices, wine, etc.).
- If you have previously used whitening toothpastes, stop using them, because... with a high probability, hypersensitivity is caused precisely by their use.
- Consult your dentist about the cause of sensitivity - it may be caused by caries or exposed tooth necks. Remember that caries in the form of a white spot is a reversible form of caries, and if you undergo remineralization therapy on time, you will not only get rid of increased sensitivity, but also prevent the destruction of this area of enamel.
- If there are dental deposits, they must be removed, followed by a course of remineralization and/or deep fluoridation.
- Maintain proper oral hygiene - cariogenic microflora in the cavity, feeding on food debris, produces acids that wash calcium from the enamel and lead to the appearance of both hypersensitivity and dental caries. Check out the link above for comprehensive hygiene tips, as well as videos on proper brushing and flossing techniques.
Sources:
1. Higher professional education of the author in dentistry, 2. Personal experience as a dental therapist, 3. National Library of Medicine (USA), 4. The European Academy of Paediatric Dentistry (USA), 5. “Therapeutic dentistry. Textbook" (Borovsky E.).
Drugs used in the treatment of hyperesthesia
All drugs for the treatment of dental hypersensitivity can be divided into 2 groups:
- Drugs that seal the dentinal canals reduce the flow rate of the cerebrospinal fluid. This group is represented by varnishes, oxalates, desensitizers, remineralizing liquids and gels. The drugs are used to carry out remineralizing therapy and fluoride teeth.
- Drugs that block nerve fiber signals that stop the transmission of pain impulses. The group is represented by local products based on potassium nitrate. They are applied in the form of gels and applications.
The named drugs (according to individual indications) are also used immediately after brushing and whitening teeth. A long-acting desensitizing gel is applied to the tooth surface. If severe pain develops, the specialist prescribes universal mouth guards with gel. The condition improves significantly after the 1st procedure.
- 1. Fluoride therapy.
The action of these drugs is determined by the reaction of fluoride ions and calcium ions. When they combine, they form calcium fluoride, an insoluble salt that clogs the dentinal canal. Different brands of fluorides work differently. To obtain a lasting, pronounced effect, the doctor must use a modern, effective drug.
- 2. Therapy with fluoridated varnishes.
Fluorinated varnishes reduce hypersensitivity for a short time. After a few hours or days, the varnish will be erased from the surface of the tooth. To make the effect of the varnish more pronounced and lasting, the varnish is applied in multi-layers. The advantage of this technique is the blockage of micropores and instant relief of the condition.
- 3. Therapy with remineralizing pastes.
Remineralizing pastes help restore the mineral balance of hard dental tissues. There are several varieties of these drugs - for use in the dentist's office and at home. Which of them and for how long to use is determined by the doctor.
- 4. Desensitizer therapy.
The name of the group of drugs comes from the English word desensitizer, which means “reducing sensitivity.” Desensitizers contain substances whose task is to seal dentinal canals by coagulating proteins. The preparations are used to restore the surface of teeth, for restoration or universally.
- 5. Oxalate therapy.
Oxalate preparations, like fluorides, are used to form insoluble salts in dentin. When using oxalates, there is no need to etch the enamel or use a photopolymerization lamp; oxalates do not irritate the gums. As a result of oxalate therapy, salt crystals tightly clog the dentinal canals, which effectively reduces hypersensitivity.