Treatment of cysts with calcium preparations in dentistry
Given the constant and continuous development, modern dentistry successfully combats most diseases of the teeth, gums and the oral cavity itself. One of these problems is a dental cyst.
Tooth cyst
is a disease expressed in the formation of an inflammatory capsule with dense walls, inside of which there is often a mass consisting of bacteria and dead cells. This neoplasm appears in the gums around the root of the tooth, and in the absence of timely and targeted treatment, it can cause undesirable consequences. Over time, the size of the cyst increases, gradually destroying the surrounding bone tissue.
The occurrence of a dental cyst is usually associated with an infection; less often, the cause of the disease can be an injury that can be obtained in a completely trivial way - for example, cracking nuts with your teeth.
To determine the presence of a dental cyst, an X-ray examination of the affected area of the jaw is performed. Most often, the patient does not even suspect the presence and development of a cyst, since it passes painlessly
without causing any discomfort. Only during exacerbation does profuse tissue inflammation occur, accompanied by purulent formations and “flux.”
For successful treatment of the disease, its timely diagnosis is very important. Modern dentistry uses two methods to treat inflammation: surgical and therapeutic.
For therapeutic treatment of cysts, the inflamed tooth is drilled and the root canal is disinfected using a special solution. However, the result of these manipulations is not always successful, therefore, six months after the treatment, a re-examination with X-rays will be required to exclude re-inflammation.
Treatment of cysts with a more modern therapeutic method used in dentistry is the use of depophoresis
.
During the treatment, calcium is used, or rather copper-calcium hydroxide, which is injected into the canal of the diseased tooth. At the same time, the tooth is exposed to a weak electric current - for better penetration of the suspension into the cyst and its removal. After three sessions of depophoresis, the tooth is filled. Also, in the treatment of dental cysts, preparations based on calcium and iodine are used ( Metapex
,
Calasept,
etc.).
When using the surgical method in dentistry, the cyst is removed along with the damaged part of the tooth root (cystectomy), or the entire root and part of the tooth above it are removed (hemisection), subsequently placing a crown on it. The site of the resulting defect in the bone tissue is filled with bone material.
Along with other sciences, dentistry does not stand still. Over the past 20 years, dental treatment methods have changed dramatically, starting from dental units that ensure the patient’s comfort while visiting a doctor, and high-tech devices that allow painless treatment, to modern instruments and effective medications.
Previously, such a form of the disease as “Granulating periodontitis of the tooth” or “granulomatous cyst” meant that the tooth had to be removed, as the council says. cartoon: “Execute, you cannot pardon,” then today it is possible to “pardon” and the treatment is significantly successful! Of course, these manipulations are not one-time; several visits will be required, because... The process of osteogenesis (bone formation) is long. But the results are positive and are observed after just half a year. Treatment of tooth canals is carried out using the drug “Kalasept”, which contains calcium hydroxide. How does calcium help?
He:
- Participates in the formation of bone tissue;
- increases the resistance of dental tissues to pathogenic influences;
- reduces tissue permeability and has anti-edema, anti-inflammatory, anti-allergic, hemostatic effects;
The mechanism of action of calcium hydroxide includes:
- High antimicrobial activity; Upon direct contact with calcium hydroxide, 99.9% of bacteria present in the root canal are killed within 1-6 minutes; Root canals and periapical tissues become sterile 1-4 weeks after filling the canal with calcium hydroxide;
- Ability to dissolve necrotic tissue;
- Regenerating effect;
- Inducing the formation of an osteocement apical barrier; Restoration of bone tissue occurs over a long period of time - from 2 to 18 months, which is X-ray confirmed by a decrease in the focus of rarefaction in the apex area.
Where is Calasept used? During treatment:
- caries and non-carious lesions;
- pulpitis;
- destructive forms of periodontitis;
- perforations of the bottom of the tooth cavity, canal;
- horizontal fracture of the tooth root;
- periodontal pocket;
- reimplantitis.
- Patient A., 52 years old Diagnosis: chronic granulating periodontitis of the 41st tooth
Destruction of bone tissue in the area of the root apex is 4-5 mm. After a year we see positive results.
- Patient E., 46 years old Diagnosis: chronic granulating periodontitis of the 36th tooth in the acute stage.
Destruction of bone tissue in the area of the medial and distal roots is 2-3 mm. A year later, the bone pattern was completely restored.
- Patient M., 28 years old Diagnosis: chronic granulating periodontitis of 34 teeth.
Destruction of bone tissue in the area of the root apex is 4-6 mm. After 9 months, the bone pattern was completely restored.
- Patient A., 36 years old, diagnosed with chronic granulating periodontitis of the 36th tooth (perforation in the distal canal from the pin). The pin was removed, and a calcium preparation was left at the perforation site for a month. A glass fiber pin is installed in the medial buccal canal (it is not contrasted on the radiograph). The tooth is covered with a crown.
Destruction of bone tissue in the area of ½ of the distal root at the level of perforation. Six months later, the bone pattern was restored.
- Patient M., 22 years old. Diagnosis: Chronic granulating periodontitis of the 12th tooth.
Destruction of bone tissue in the area of the root apex is 1-2 mm, after six months the bone pattern is restored
Dentist therapist Kolomeets A. A.
Dentists' prejudices
Despite the fact that calcium hydroxide has been used in dental medicine for more than half a century, dentists still do not have a consensus on the specifics of its use.
The official instructions for any drug warn that all materials with hydroxide should remain in the dental canals for no longer than one month, however, some experts practice installing hydrocalcium fillings for six months or more. This practice is not widely used, therefore, in dental practice, doctors prefer to adhere to the rules of the official instructions.
Studying statistics regarding the consequences of using Ca (OH)2 powder, dentists raised the question of the substance’s effect on a number of microorganisms that are not susceptible to the antibacterial capabilities of the substance and subsequently cause exacerbations and relapses.
In this regard, some specialists prefer to replace the installation of temporary linings in the form of a layer of calcium hydroxide with complete cleaning of the tooth cavity with sodium hypochlorite and the installation of temporary fillings made from modern preparations that provide complete sealing.
However, despite the development of dental medicine, calcium hydroxide continues to be widely used in dentistry, and specialists are opening up more and more areas for its use.
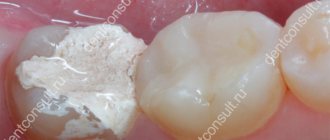
Procedure for filling teeth with calcium
A filling filled with calcium is temporary and, after a period determined by the doctor, changes to a permanent
one. Installation of a calcium filling involves several stages:
- The doctor mixes calcium powder with distilled water and glycerin to obtain a homogeneous paste.
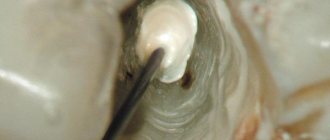
- Before filling, the doctor cleans the root canal and treats it with special preparations.
- Using a channel filler, the resulting paste is introduced into the recess
- To ensure that the substance adheres tightly to the walls of the canal, it is compacted with a pin, and then the hole is hermetically sealed.
As mentioned above, a calcium filling is temporary. How long it will stay in the tooth is decided by the doctor, based on the specific clinical case. After the prescribed period has expired, the dentist removes the temporary filling and places a permanent one in its place.
Popular calcium hydroxide materials
In dentistry, in addition to pure calcium hydroxide powder, materials based on it are used. Their difference lies in the complex composition, lower dosage of the main component, as well as in the release form.
The most popular and in demand include:
- Calcicur (aqueous suspension);
- Calradent (powder for suspension);
- Contrasil (varnish);
- Calcimol (calcium salicylate cement);
- Ultra-Blend (polymer material).
Each drug has its own characteristics, therefore, depending on the indications and purposes of use, a specialist can carry out procedures using one or another means.
Dental preparations with calcium hydroxide have a stimulating effect on the formation of dental replacement substances, prevent the penetration of pathological microorganisms into the pulp and have an anti-inflammatory effect.
Features of materials and their applications:
- Calcicur and Calradent are aqueous suspensions based on calcium powder. The chemical substance makes up about 40% of the total composition, the remaining 60% is water or saline solution. The paste does not harden. A disinfectant is used to disinfect the cavity being treated.
- Contrasil is a quick-drying varnish that contains 40% hydroxide and 60% impurities in the form of zinc oxide, solvent (highly volatile), resin and chloroform. The drug treats the area of dental tissue that is susceptible to caries. Varnish is used to temporarily protect tissues from an acidic environment when using dental cements.
- Calcimol is a substance of the calcium-salicylate group that hardens under chemical influence. The drug is used as a spacer before installing a permanent filling. The composition includes 50% hydroxide, 40% salicylic ether and 20% impurities (dyes and plasticizers). A gasket made of Calcimol does not have high strength, but does not affect the polymerization and color of the installed permanent filling.
- Ultra-Blend belongs to a group of polymeric materials that cure under the influence of light. The Ultra-Blend composition includes 40% calcium hydroxyl powder, 30% X-ray contrast filler and 30% polymer resin (hardener). The substance has high mechanical strength, but is used only for installing a gasket in case of shallow damage. In addition, the material has a weak therapeutic effect.
In modern dentistry, aqueous suspensions with calcium hydroxide are increasingly used, since it is believed that such a material has a better complex effect than other forms.
Characteristics of the substance
Calcium hydroxide is an inorganic type compound that is produced in powder form.
The pharmaceutical industry produces dental materials based on calcium hydroxide of various types. Their main difference is in the amount of chemical compound contained in the composition. Pure calcium powder is considered one of the most effective. Among the many different chemicals that are used in dental medicine, hydroxide-based materials
Formula and structure of the calcium hydroxide molecule
calcium is the most commonly used. This is due to the unique properties of the substance.
Calcium hydroxide has an alkaline reaction on tissue, as a result of which pathogens that cause destruction of dental canal tissue are destroyed.
In most cases, such materials are used for temporary filling of canals, with the aim of destroying organic tissue under the influence of an alkaline environment.
The result is observed 10-14 days after the temporary filling is installed. During this time, the reaction between the inorganic powder diluted in saline solution and the root tissue allows not only to destroy pathogenic bacteria, but also to disinfect all areas that are inaccessible to mechanical cleaning.
Pharmacological properties of the substance important for endodontics
The main pharmacological properties of calcium hydroxide are its antibacterial effects. Dental diseases associated with damage to the intracanal area of the tooth often develop as a result of bacterial growth.
Most microorganisms of this type cannot exist in an alkaline environment. Under the influence of the alkaline reaction of a calcium solution, some types of bacteria die immediately, while others take longer to destroy.
Calcium hydroxide reacts with saline solution, thanks to this reaction the antiseptic effect of the powder appears. After diluting the substance in an aqueous liquid, a reaction occurs to release hydroxyl ions, which have an antibacterial effect due to the destruction of the membrane and DNA bonds of microorganisms.
How does calcium work?
Staying in the canal for a certain time, calcium completely kills bacteria living in the tooth
After entering the root canal, the calcium mixture begins to interact with the tissues and microflora of the tooth. The oxide penetrates into the dentin and pulp. When the substance remains inside the canal for a long time, it completely kills the bacteria living in it. After such exposure, the doctor can safely carry out further treatment or fill the canal.