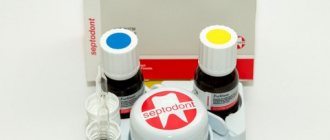
ARSENIC
is a chemical element of group V of the periodic table, belongs to the nitrogen family. Relative atomic mass 74.9216. In nature, arsenic is represented by only one stable nuclide 75As. More than ten of its radioactive isotopes with half-lives from several minutes to several months have also been artificially obtained. Typical oxidation states in compounds are –3, +3, +5. The name of arsenic in Russian is associated with the use of its compounds to exterminate mice and rats; The Latin name Arsenicum comes from the Greek “arsen” - strong, powerful.
What is arsenic - composition and what it looks like
Arsenic (arsenicum) is a chemical element that has necrotizing properties. That is, it and its salts literally poison living tissues, which leads to their death. This substance has long been used as a poison to combat insects and small rodents. But in dentistry it began to be used from the beginning of the 19th century. Here it is used in combination with hydrogen - this component used to be part of most devitalizing pastes.
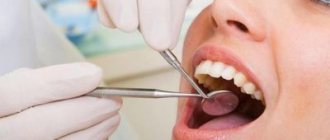
The mixture is used to carry out the devitalization procedure in case of damage to the pulp, that is, the neurovascular bundle. If there is no longer any chance of saving the nerve, it is removed, but not before it is completely killed. What arsenic looks like in a tooth is shown in the photo below.
The photo shows arsenic in a tooth.
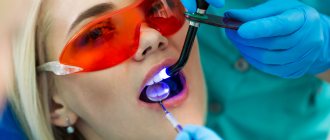
Chemically neutral dyes are added to the composition to create a contrast with the color of the enamel. Therefore, after application, the product looks like a homogeneous mass of dark blue color. But under the light of a dental lamp, hard tissues and the applied substance contrast sharply, which facilitates the process of cleaning dentin from deposits.
As for whether this substance is now used in dentistry, it should be noted that specialists usually resort to the help of more modern and effective devitalizing compounds, which are much less toxic and dangerous to the body. However, in some clinics, especially in public ones, this practice is still relevant, so it is too early to leave this technique out of the picture.
Examples of problem solving
| Exercise | Arsenic forms two oxides. The mass fraction of arsenic in them is 65.2% and 75.7%. Determine the equivalent masses of arsenic in both oxides. |
| Solution | Let us take the mass of each arsenic oxide as 100 g. Since the arsenic content is indicated in mass percent, the first oxide contains 65.2 g of arsenic and 34.8 g of oxygen (100 – 65.2 = 34.8); in 100 g of the second oxide, arsenic accounts for 75.7 g, and oxygen - 24.3 g (100 - 75.7 = 24.3). |
The equivalent mass of oxygen is 8. Let us apply the law of equivalents for the first oxide:
Meq (As) = 65.2 / 34.8 × 8 = 15 g/mol.
The calculation for the second oxide is carried out similarly:
Meq (As) = 75.7 / 24.3 × 8 = 25 g/mol.
Why is arsenic placed in a tooth - indications for installation
As mentioned above, the paste is usually used to treat pulpitis. Sometimes it is permissible to use the remedy for periodontitis, but this practice is quite rare. So, what does this substance do in the tooth and why is it put there in the first place? The main purpose of such drugs is to “kill” the pulp at the root before removing the nerve. Thus, the paste is placed inside the diseased tooth for a limited time, during which the drug gradually destroys the neurovascular bundle. At the end of the time specified by the doctor, the patient comes for a second appointment for final removal of the pulp and prosthetics.
The drug can be used in the treatment of pulpitis
Due to its cytotoxic effect on cells, arsenic paste blocks the functioning of nerve endings, which stop sending signals to the brain and are gradually destroyed. The blood supply to the pulp is also stopped and the cavity is disinfected. In some situations, this remedy is used as an emergency pain reliever, when the tooth hurts badly, and there is simply no other way to relieve the pain.
On a note! Many people are interested in the question: how much does it cost to install a filling with arsenic? So, if the cost of installing a temporary filling starts from about 350-400 rubles, which largely depends on the material used, then the price of fixing a filling with medicinal paste starts from 500 rubles
Thus, among the main indications for the application of a devitalizing agent, experts in the field of dentistry identify the following pathological conditions:
- all types of inflammation of the pulp with fully formed roots - pulpitis, including those complicated by periodontitis,
- lack of opportunity to perform vital pulpectomy, that is, the use of a faster and safer method of nerve removal. This procedure is usually refused if there is a high risk of an allergic reaction to the anesthetic,
- emergency cases when there are no other options to relieve the patient from acute pain due to pulpitis.
The toxic substance is not used if there are contraindications, for example, allergies, pregnancy and lactation, or increased intraocular pressure. In the latter case, the patient risks subsequently encountering glaucoma. Such preparations are also not used if the roots are not fully formed or if there is perforation of the root canal. But how much arsenic is assigned directly depends on the patient’s age and the individual characteristics of his clinical picture.
How long can a substance stay in a tooth?
We should dwell on the question of how long people usually wear a temporary filling; let’s look at it in more detail. The doctor determines the duration based on the composition of the product used, the age of the patient and the complexity of each individual case.
How long to keep a child, teenager and adult - how long does it take for the drug to kill the nerve?
The substance is usually used on adult patients, and is left on for just a couple of days. However, the exact duration of this process depends on the location of the tooth, the number of canals in it, and the complexity of the clinical picture. It is worth noting that there are long-acting devitalizing pastes, and such compositions can be left for a period of no more than 2 weeks. Today, children are no longer given dangerous poison. But before, he was left for no longer than one day. If we are talking about baby teeth, the permissible period was reduced to 16 hours.
Children are no longer given dangerous poison today.
What determines the period for which the devitalizing paste is left in place?
As mentioned above, the period depends on many different factors, including the age of the patient, his state of health and the clinical picture as a whole. The duration of action of the paste depends on what kind of drug the specialist used. Safer compositions, which often do not contain toxic components at all, last longer, which is why you have to wear a temporary filling for a week or even two.
How soon can you start eating?
The devitalizing substance is covered with a regular temporary filling. After its installation, you can eat and drink within 1-2 hours. However, experts recommend avoiding too intense touching of the diseased element, so it is better to give up solid foods for a while. You will also have to give up alcohol, since it enhances or, conversely, neutralizes the effect of a toxic substance, which can cause serious complications.
The photo shows a treatment regimen using arsenic
Notes[ | ]
- ↑ 1234
Sabina C. Grund, Kunibert Hanusch, Hans Uwe Wolf “Arsenic and Arsenic Compounds” in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, VCH-Wiley, 2008, Weinheim. (English) - Giant Mine - Northwest Territories Region - Indian and Northern Affairs Canada (unspecified)
(inaccessible link). Access date: August 28, 2007. Archived April 2, 2012. (English) - Holleman, A.F.; Wiberg, E. "Inorganic Chemistry" Academic Press: San Diego, 2001. ISBN 0-12-352651-5.
- Marcel Gielen, Edward RT Tiekink.
Metallotherapeutic Drugs and Metal-Based Diagnostic Agents. - Wiley, 2005. - P. 298. - Steven L. Soignet et al.
United States Multicenter Study of Arsenic Trioxide in Relapsed Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia (English) // Journal of Clinical Oncology (English) (Russian: journal. - 2001. - Vol. 19, no. 18. - P. 3852-3860 . - Antman, KH
Introduction: The history of arsenic trioxide in cancer therapy (English) // Oncologist: journal. - 2001. - Vol. 6(Suppl. 2), no. 1-2. - P. 2006. - Jun Zhu, Zhu Chen, Valérie Lallemand-Breitenbach, Hugues de Thé “How Acute Promyelocytic Leukaemia Revived Arsenic,” Nature Reviews Cancer 2002, volume 2, 1-9.
- Bobé Pierre, Bonardelle Danielle, Benihoud Karim, Opolon Paule, Chelbi-Alix Mounira.
Arsenic trioxide: A promising novel therapeutic agent for lymphoproliferative and autoimmune syndromes in MRL/lpr mice (English) // Blood (English) (Russian: journal. - American Society of Hematology (English) (Russian, 2006. - Vol. 108, no. 13. - P. 3967-3975.. - Lu J., Chew EH, Holmgren A.
Targeting thioredoxin reductase is a basis for cancer therapy by arsenic trioxide (English) // Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America: journal. - 2007. - Vol. 104, no. 30. - P. 12288—12293. - doi:10.1073/pnas.0701549104. - PMID 17640917. - Stanton v Benzler 9716830 (unspecified)
. US 9th Circuit Court of Appeals (June 17, 1998). — “(...) sad by a jury of first degree murder for poisoning her ex-husband. Her ex-husband's body was found with traces of arsenic trioxide in it." Access date: June 9, 2008. Archived April 2, 2012. - ↑ 1 2 Emsley, John.
Arsenic // The Elements of Murder: A History of Poison (English). - Oxford University Press, 2006. - P. 93-197. — ISBN 9780192806000. - Madame Bovary by Flaubert
- Arsenic Eaters - New York Times July 26, 1885
- Richard M. Allesch. Arsenik. Seine Geschichte in Österreich. 54.Band. Klagenfurt: Kleinmayr 1959.
- G. Przygoda, J. Feldmann, W. R. Cullen.
The arsenic eaters of Styria: a different picture of people who were chronically exposed to arsenic (English) // Applied Organometallic Chemistry (English) (Russian: journal. - 2001. - Vol. 15, no. 6. - P 457-462 - doi:10.1002/aoc.126.
How arsenic is used - description of the depulpation process
To kill a nerve, you will have to visit the dentist several times. If the case is standard, two visits to the doctor will be enough - to place the substance and remove it, followed by removal of the pulp. This process is discussed in more detail below.
How does the installation work?
The process of applying paste to the causative tooth is as follows:
- first, the pulp is released, carious lesions are removed,
- the doctor places a small ball of paste on the exposed tissue,
- a temporary filling is placed on top, usually based on artificial dentin,
- tooth treatment after arsenic involves removing the filling after the prescribed period, removing the remaining paste and cleaning the canals,
- At the final stage, a permanent filling is fixed.
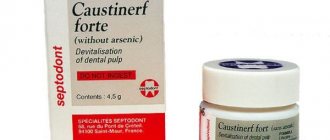
The photo shows arsenic paste
. Important! Do not overexpose the medicinal mixture. Most pastes can be worn for no more than 2 days. Then it will begin to act on the periodontal tissues, destroying them. Usually the doctor himself sets the date for the return visit. The absence of pain does not mean that the problem has passed - this is only the result of the use of painkillers.
How to get the drug
The dentist himself determines the time during which the product should remain in the tooth. The patient is strictly forbidden to remove the paste prematurely on his own or, as mentioned above, to walk with it longer than expected. How many hours or days the composition will have to be kept in the mouth is calculated taking into account the condition of the diseased tooth, the number of roots, the age of the patient and, accordingly, the purpose of using the paste.
In order to destroy one canal, on average it takes about 24 hours - this applies to adult patients. In the same case, if the doctor is dealing with several canals at once, it will take more time to kill them. However, walking with arsenic paste for longer than 48 hours is highly not recommended. The dentist must carefully calculate the effect of the product and schedule the exact time of the next visit to remove the drug.
Important! If we are talking about treating a child, then the permissible time for the presence of arsenic in the tooth is significantly reduced. In pediatric dentistry, such a medicine is usually not used for longer than 12-18 hours; in complex cases, an extension of up to 24 hours is allowed, but this is the maximum limit1.
The photo shows the process of removing a temporary filling.
Is it possible to extract it yourself?
If, after installing a temporary filling, the pain intensifies and persists for a long time, this may indicate further spread of the toxic effect of the drug. In this case, healthy tissues are at risk. This is an emergency situation, in which it is possible to independently remove a temporary filling with a bookmark. Of course, if there is no way to urgently get an appointment with a specialist.
This should be done as carefully as possible, after which it is recommended to rinse your mouth with a solution of soda, iodine or hydrogen peroxide. You can also rinse your mouth with milk - it effectively neutralizes the toxic effects of the poison. It is better, of course, to contact a specialist by phone to receive detailed instructions. You should visit your dentist as soon as possible to avoid complications.
How harmful is it and what will happen if the substance has been in the tooth for a long time
In everyday practice, dentists try to eliminate products containing arsenic from their work. Despite the fact that most examples of the use of such pastes are positive, their effect on the human body has not been fully studied. Most of the negative consequences known in dental practice are caused by the negligence of patients who ignore the doctor’s recommendations and wear the medicine for more than 3 days.
“As for me, arsenic is generally an outdated method! Is it really still used in dentistry?! I remember back in Soviet times, a friend of mine was given this paste, but he didn’t make it in time for the visit and arrived the next day. So some necrotic processes had already begun there, his gums began to darken, he barely had time! I wouldn’t risk it; I’m sure that today there are safer medications with a similar effect.”
Tin_78, Saratov, from correspondence on a thematic forum
The most common complications are the following processes and phenomena: swelling of the pulp, blackening of surrounding tissues, inflammatory processes in adjacent tissues - drug-induced periodontitis, necrotic processes in the tissues of the periosteum, toxic poisoning of the body and disruption of the natural metabolism of microelements.
PROPERTIES
The color on a fresh fracture is zinc-white, tin-white to light gray, quickly fades due to the formation of dark gray tarnish; black on a weathered surface. Hardness on the Mohs scale 3 – 3.5. Density 5.63 – 5.8 g/cm3. Fragile. Diagnosed by the characteristic smell of garlic when struck. Cleavage is perfect along {0001} and less perfect along {0112}. The fracture is grainy. Ud. weight 5.63-5.78. The line is gray, pewter-white. The luster is metallic, strong (when freshly fractured), quickly fades and becomes dull on an oxidized surface that has become blackened over time. Is diamagnetic.
Why does pain occur?
Painful sensations may persist if the patient has increased tooth sensitivity. In such a situation, he can feel the entire process of tissue necrosis. It is important to monitor the intensity of this symptom. In the normal course of events, the pain gradually subsides and eventually disappears, as does the process of death of the neurovascular bundle itself.
You may feel sore for a couple of days
Moreover, the duration of necrotization largely depends on the individual characteristics of each individual organism. It happens that the pulp dies literally within a day, and in other situations the process of killing it takes as long as 2 days. In order not to worry unnecessarily, you should listen to your feelings and monitor your body’s reaction. So, if swelling and obvious redness of the gums appear, as well as if the enamel darkens and a headache occurs, you should immediately consult a specialist - there is a possibility of complications developing.
Impact on the body
So, it is impossible to be poisoned by this semi-metal during dental treatment. However, if the poison enters the body in other ways and in large quantities, serious harm is caused to health.
A lethal dose of arsenic for an adult can be 0.1 - 0.2 g of poison. Sometimes a negligible dose of 0.05 g is enough for a child.
Under the influence of arsenic (after its rapid absorption into the blood), all organs and their systems are affected. The liver, heart, lungs and kidneys are especially affected, and this happens in just a day. After 2 weeks, the substance is found in bones, nails, hair and skin. Wherein:
- biochemical processes are disrupted,
- the nervous system is affected,
- oxygen exchange in cells is disrupted,
- the substance quickly binds to hemoglobin, etc.
Removal of poison from the body during arsenic poisoning occurs with feces and urine, and with urine much faster. The remnants of the received dose are stored in tissues and organs, continuing to have a detrimental effect.
Why might your temperature rise?
If arsenic is left in a tooth, the patient may develop a fever. There is no need to worry about this ahead of time, since during the period of root death this is a fairly common occurrence. After the procedure, the specialist usually recommends certain painkillers and antipyretics.
As for whether it is possible to get poisoned, here it is necessary to note the risk of drug-induced inflammation. This situation risks happening if the doctor places the filling too tightly. Poisoning in this case leads to the following symptoms: swelling, high temperature, severe piercing pain. The pathological process can also provoke the development of an abscess, so if you experience such symptoms, you should see a doctor as soon as possible.
After the procedure, there may be an increase in temperature
STRUCTURE
The crystal structure of arsenic is ditrigonal-scalenohedral symmetry. Trigonal syngony, c. With. L633L23PC. The crystals are extremely rare and have a rhombohedral or pseudocubic habit.
Several allotropic modifications of arsenic have been identified. Under normal conditions, metallic or gray arsenic (alpha arsenic) is stable. The crystal lattice of gray arsenic is rhombohedral, layered, with a period a = 4.123 A, angle a = 54° 10′. Density (at a temperature of 20° C) 5.72 g/cm3; temperature coefficient linear expansion 3.36 • 10 degrees; specific electrical resistance (temperature 0° C) 35 • 10-6 ohm • cm; NV = f 147; coefficient compressibility (at a temperature of 30° C) 4.5 x 10-6cm2/kg. The melting point of alpha-arsenic is 816 ° C at a pressure of 36 atmospheres.
Under atm. Arsenic sublimes under pressure at a temperature of 615° C without melting. Heat of sublimation 102 cal/g. Arsenic vapors are colorless, up to a temperature of 800°C they consist of As4 molecules, from 800 to 1700°C - from a mixture of As4 and As2, above a temperature of 1700°C - only from As2. With the rapid condensation of arsenic vapor on a surface cooled by liquid air, yellow arsenic is formed - transparent soft crystals of a cubic system with a density of 1.97 g/cm3. Other metastable modifications of arsenic are also known: beta-arsenic - amorphous glassy, gamma-arsenic - yellow-brown and delta-arsenic - brown amorphous with densities of 4.73, respectively; 4.97 and 5.10 g/cm3. Above a temperature of 270° C, these modifications turn into gray arsenic.
Possible problems and complications
Now let’s take a closer look at the question of why arsenic in a tooth is dangerous and what will happen if you walk with it for too long. If you overexpose a caustic substance, complications may arise. But we must admit that today such situations are very rare. Inflammation and necrosis of healthy tissues are usually the result of inept actions of the doctor. The reason may be an incorrect placement of the substance or an insufficiently tight seal. If the canals have been poorly treated, there is a risk of re-inflammation.
After installing a temporary filling, some discomfort is possible, but if the pain intensifies, becomes acute and swelling increases, such symptoms indicate further development of the pathological process. Perhaps the doctor performed the procedure incorrectly, and the active substance does not come into contact with the nerve endings. You should contact a specialist as soon as possible.
Leaving a toxic substance for too long can also lead to dentin darkening and gum necrosis. Hard tissues will begin to gradually deteriorate, and there will be a risk that the pathological process will spread to neighboring elements. But if you swallow arsenic, nothing bad will happen. Such precedents happened quite often. The dose in which the substance is placed in the pulp chamber is safe for the body. Therefore, if you happen to eat such a small amount, there is no need to panic ahead of time. However, in cases of larger overdose, serious disturbances in the functioning of the liver and gastrointestinal tract are possible.
Leaving the substance in the tooth for a long time can cause darkening of the tooth.
Receipt
The discovery of a method for producing metallic arsenic (gray arsenic) is attributed to the medieval alchemist Albertus Magnus, who lived in the 13th century. However, much earlier, Greek and Arab alchemists were able to obtain arsenic in free form by heating “white arsenic” (arsenic trioxide) with various organic substances.
There are many ways to obtain arsenic: by sublimation of natural arsenic, by thermal decomposition of arsenic pyrite, by reduction of arsenic anhydride, etc.
Currently, to obtain arsenic metal, arsenopyrite is most often heated in muffle furnaces without access to air. At the same time, arsenic is released, the vapors of which condense and turn into solid arsenic in iron tubes coming from the furnaces and in special ceramic receivers. The residue in the furnaces is then heated with access to air, and then the arsenic is oxidized into As2O3. Metallic arsenic is obtained in rather small quantities, and the main part of arsenic-containing ores is processed into white arsenic, that is, into arsenic trioxide - arsenous anhydride As2O3.
The main method of production is roasting sulfide ores followed by reduction of the oxide with coal (carbon):
2As2S3 + 9O2 →toC 6SO2↑ + 2As2O3 As2O3 + 3C →toC 2As + 3CO↑
Acceptability of use during pregnancy, breastfeeding and children
The use of toxic drugs during pregnancy or breastfeeding is strictly prohibited, and here are several reasons for this restriction:
- the toxic effect of such drugs on the fetus and child has not yet been fully studied, so the consequences for the baby can be the most unpredictable,
- there is a high probability of poison penetration into the gastrointestinal tract and severe poisoning of the entire body,
- a detrimental effect on the condition of dentin and its gradual destruction if the drug is not removed in time.
Before starting treatment, a woman is obliged to warn a specialist about her condition so that he can offer safer therapy. If we are talking about the treatment of primary incisors and molars, then the specialist adjusts the duration of the paste, taking into account the age of the small patient. Previously, in such cases, a toxic substance was placed for about a day. However, in the absence of serious problems, it could be removed after 16 hours. Today, this substance is not used in pediatric dentistry, and it has been replaced by modern and safer drugs.
Today, when possible, specialists try to avoid the use of such toxic substances in dental practice. However, if you have to use the paste, then the patient must follow all the dentist’s instructions as strictly as possible in order to minimize any risks of harm to the body.
1Borovsky Ya.V. Treatment of complications of dental caries: problems and their solutions, 1999.
Structure[ | ]
In liquid and gaseous (up to 800 °C) states it has the formula As4O6 (in the form of a dimer) and is isostructural with P4O6). When heated above 800 °C, As4O6 decomposes into As2O3 molecules, similar in structure to N2O3. In the solid state, three polymorphic forms coexist: cubic molecular As4O6 and two polymeric forms. Polymers that form single crystals upon cooling resemble the pyramidal structure of AsO3 with shared oxygen atoms.[3]
| arsenolite (cubic) | claudetite I (monoclinic) | claudetite II (monoclinic) |