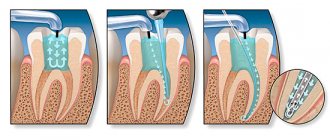
Orthodontics is a branch of dentistry aimed at correcting defects in the development of teeth and the maxillofacial skeleton. The result of orthodontic treatment largely depends on the correct diagnosis. Modern diagnostics in orthodontics
performed using special devices and equipment.
In this article we will consider popular methods of orthodontic diagnostics and answer frequently asked questions about orthodontics
.
Diagnostic methods in orthodontics
The treatment of defects of the masticatory-speech apparatus is carried out by a specialized orthodontist. After a visual examination of the patient’s oral cavity, the specialist decides on the need to conduct additional research procedures using modern diagnostic methods. Based on the analysis obtained, it is possible to establish an accurate diagnosis and select the correct treatment to achieve a successful result.
Diagnostic methods in orthodontics:
1. Radiography.
2. Tomography of the temporomandibular joint.
3. Orthopantomography.
4. Examination using diagnostic models (taking impressions of the patient’s jaw with subsequent production of working models).
5. Electromyography.
6. Mask model (determining facial asymmetry taking into account three planes).
7. Simon's photostat.
8. Teleradiography.
The most popular diagnostic methods in orthodontics are dental radiography and orthopantogram, which allow identifying various deviations of the dentofacial apparatus. In difficult cases, additional research methods are used to clarify the identified pathologies.
Diagnostics is carried out in several stages:
- Taking impressions of teeth
. For this, alginate or silicone material is used. Based on the casts, plaster jaw models are made. - Orthopantomogram
. For this, a special X-ray machine is used to take a picture of the jaws. Thus, the doctor determines the condition and location of the tooth roots and tissues around them. Achieving success in orthopedics directly depends on the general condition of the periodontium - teeth and tissues must be healthy. - Teleradiogram
. A lateral x-ray of the skull is taken. Using this image, the doctor determines the angle of inclination of the front teeth on both jaws and the direction of growth of the jaw structures. A teleradiogram helps the doctor conduct an orthodontic analysis, study the bone tissue in detail, and identify the level of location of the soft tissues of the oral cavity. - Computer tomogram.
- Photo protocol (diagnostic photographs).
- Facial aesthetics
is part of orthodontic treatment. When drawing up a treatment plan, the doctor takes into account the shape of the patient’s lips, chin, nose, facial contours and features of the patient’s smile.
An orthopantomogram provides the doctor with a high-quality image in which he sees bone tissue, main sinuses, roots and pathologies with visible boundaries.
The listed diagnostic methods enable the orthodontist to carry out detailed calculations for medical procedures and prepare a competent treatment plan.
Orthodontic treatment may be necessary and desirable. In case of violations at the aesthetic level with the absence of pathology of the dental system, the doctor prescribes the desired treatment. In this case, the patient can resort to treatment, refuse it, or postpone it for a while. Indications for the necessary treatment are obvious deviations leading to disruptions in the proper functioning of the dental system.
It is a mistake to think that only children and adolescents need such treatment. Every year, more and more age-related changes occur in the oral cavity of adults. Some of them can be observed by a person himself (for example, abrasion, yellowing of teeth, cracks), some can only be diagnosed by an orthodontist (deepening of the bite, crowding, lengthening of teeth, and so on).
A thorough diagnosis is necessary when a doctor decides whether to remove teeth during treatment. By removing some teeth, the doctor can solve the problem of lack of space and easily align the teeth along the arch. However, this is only an extreme case when treatment without removal is inappropriate. An experienced master does not resort to such methods and does everything possible to save all the patient’s healthy teeth.
Questions about orthodontics
Many patients have different questions about orthodontics. Let's look at the most popular ones.
Is it possible to correct dental defects without braces?
The vestibular brace system is by far the most effective way to correct bite defects. But as an alternative, the patient may be offered aligners. A set of mouth guards is made from impressions taken from the patient’s jaw. While wearing them, you must maintain careful oral hygiene. The orthodontic structure is changed once a month. The patient needs to regularly visit an orthodontist to monitor the treatment process.
Cons of aligners:
- Not suitable for everyone;
- not used in complex cases;
- are more expensive than braces.
How quickly do teeth straighten with braces?
On average, teeth move into an even arch after 3-4 months. These periods can be shortened or increased, depending on the type of braces chosen and the complexity of the particular case.
What is the function of orthodontic screws?
Screws in orthodontics
are used to stabilize the brace system in the absence of some teeth in a row, as well as in case of bone tissue atrophy. They eliminate the movement of supporting teeth and speed up the process of dental correction.
How do teeth move?
In some cases, it becomes necessary to move one or more teeth. For this purpose, orthodontists use removable or non-removable structures. Fixed bracket systems include bracket systems that ensure the movement of teeth in the desired direction, under the supervision of a specialist.
Types of tooth movement in orthodontics
:
1. Corpus technique, which involves moving the tooth crown and root in one direction.
2. Oblique-rotational – involves moving the crown and tooth root to different distances.
In orthodontic treatment, it is possible to move not only one tooth, but also a whole series. This technique is successfully used in the treatment of occlusion with a distal position of the lower jaw.
When are orthodontic implants installed?
When treating complex defects of the dental system, there is often a need to install orthodontic implants aimed at providing the necessary support for fixed structures that correct bite defects.
Indications for installation of orthodontic implants:
- crowded dentition;
- strong protrusion of molars or front incisors;
- distal bite;
- severe curvature of teeth;
- if it is necessary to change the size or position of the jaw;
- to ensure the required degree of impact on the dentition (if braces do not cope with this task);
- lack of positive results after wearing braces for a long time.
Implants in orthodontics
differ from standard designs used to restore lost teeth. They are smaller in size and thickness, are installed temporarily, and the implantation method itself is minimally invasive and does not require cutting the gums or suturing.
How will be correct?
Now we will tell you what steps our diagnostic presentation consists of.
Analysis of diagnostic models.
An electronic caliper is used to calculate the space deficit for each tooth on a plaster model of the jaws. The data is transferred to the presentation.
Analysis of X-ray images.
The data is calculated in special computer programs. Based on them, the main conclusions are drawn.
Assessment of periodontal status (level of gums and frenulum).
Assessment of facial parameters.
The main questions at this stage are: is it possible to delete? Won't this spoil the profile? Even if removal is required due to the bite, the face is always a priority.
Assessment of smile and incisor visibility at rest.
It is important to understand which teeth are more visible when speaking - the upper or lower ones. It has been proven that greater visibility of the upper teeth significantly makes the face look younger and more attractive. It works better than any anti-aging cream One of the basic goals of any treatment.
It has been proven that greater visibility of the upper teeth significantly makes the face look younger and more attractive. It works better than any anti-aging cream One of the basic goals of any treatment.
Width of a smile.
The more teeth you see in a smile, the wider and more open it appears.
Expressiveness of the smile line.
The most charming smile is considered to be the one that closely follows the contour of the lower lip. Also the basic goal of any treatment. More details about the canons of the beauty of a smile are written in our article - What is a beautiful smile.
Planning the positioning of braces on the teeth according to the findings of the smile analysis.
As you can see, half an hour spent in the chair by the patient results in a lot of “behind the scenes” work for the thoughtful orthodontist.
Treatment planning is creative, painstaking work. Unfortunately, not all orthodontists these days fully understand this process. They are not ready to lay this foundation, without which it is impossible to build good and stable treatment in the long term.
Orthodontics is not about fixing braces. Teeth can be as straight as desired, but the smile, nevertheless, remains very mediocre, the profile of the face - spoiled by removal “in the name of teeth.”
Our treatment directly affects the appearance, because the result remains with the patients forever! Therefore, the fundamental point in treatment is only the right choice of doctor!
The main thing is to get into reliable, experienced hands. And if you are reading this, then you are already on the right track!
Orthodontic treatment of bite defects in
Experienced orthodontists who see patients at the specialized dental clinic “Aesthetics” are ready to answer all your questions about orthodontics. The center is equipped with modern diagnostic equipment that gives highly accurate results, which guarantees a quick correct diagnosis and the correct choice of treatment protocol.
Orthodontic treatment uses high-quality lingual braces, mouth guards, plates and other structures that can effectively eliminate various malocclusion defects, even in the most difficult cases. You can make an appointment with an orthodontist by phone. The first consultation appointment is free.
All patients who leave reviews on our website are guaranteed to receive an additional 3% discount on everything dental (the discount is added to the client’s main discount). Share your opinion and experience of orthodontic treatment in our clinic, do not miss the opportunity to save your own money on the services of an experienced orthodontist!
What is diagnostics through the eyes of the doctors at our clinic?
More than one (!) hour of work in the clinic to create a presentation after the diagnosis, which will contain conclusions on a large number of evaluation criteria. Why is this happening?
You need to understand that all doctors have completely different approaches to analyzing diagnostic data.
Some people don’t do it at all and are ready to lay out a treatment plan immediately during the consultation without the slightest doubt. And this, in general, does not indicate high qualifications, rather the opposite.
For some doctors, one panoramic (overview) image and casts are enough. Which is also unacceptable for a modern orthodontist.
What does functional orthodontics include?
- joint treatment by an osteopath and a dentist;
- equalizing the pressure between the muscles of the tongue and the muscles of the cheeks and lips through special exercises - uneven muscle tension during the period of jaw growth can cause significant deformations of the jaws;
- wearing jaw growth activators;
- installation of removable pads;
- installation of non-removable expansion pads;
- jaw expansion using the Planas apparatus;
- expansion with ALF and Crozat devices;
- finishing linings to stabilize the bite and occlusal planes in the presence of tooth wear.
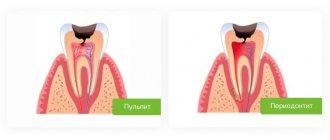
Pathological mobility of teeth, caused by inflammatory-destructive changes in periodontal tissues, is one of the leading symptoms of periodontitis. Many authors believe that splinting is indicated at the very first signs of pathological tooth mobility [1, 2, 6]. However, clinically it can be difficult to detect incipient tooth mobility, so splinting is often used at later stages of the disease [6]. At the same time, increasing tooth mobility can contribute to the progression of the disease. Previous studies have shown that without stabilizing mobile teeth with splinting structures, it is impossible to achieve positive results and prevent relapse of the disease [1, 3, 7]. Therefore, splinting teeth is an important stage in the treatment of periodontitis, especially moderate and severe cases [4, 7].
Assessing the condition of the periodontium today is possible using periotestometry, implemented by the electronic-mechanical device “Periotest S” (Siemens, Germany). The microcomputer of the “Periotest S” device registers the response to a push applied to the tooth crown, calculates the characteristics of the damping properties of periodontal tissue for 16 blows, and monitors the accuracy of the results. The “Periotest S” values are shown on the display and at the same time accompanied by audio information. The question of assessing the effectiveness of various types of splinting for periodontitis using periotestometry remains open, since the available studies are still few [1, 5].
The purpose of the study was to evaluate, using periotestometry, the effectiveness of splinting the anterior group of teeth in a patient with severe periodontitis.
Material and methods
Complex periodontal treatment was performed for patient Shch.A. A 60-year-old man who complained of tooth mobility, especially 4.2 (Fig. 1-A). According to the patient, while fishing in the winter, he began to tighten the knot of the fishing line with his teeth, as a result of which the tooth “jumped out of the gums.” He put it back in.
A comprehensive periodontal examination was carried out, supplemented by intraoral and panoramic radiography, as well as periotestometry of the teeth (three times for each tooth). Measurements were made according to the standard method specified by the manufacturer: the patient sits upright, the teeth of the upper and lower jaws do not contact, the tongue does not touch the teeth. The position of the tip is perpendicular to the tooth axis (± 200), the percussion point is in the center of the vestibular surface of the anatomical crown. During the measurement, the tip sleeve did not touch the tooth, but was located at a distance of 0.7–2.0 mm from its surface. Periotestometry was carried out before and after splinting teeth. Based on the results of the examination, a diagnosis was made, treatment was planned and implemented.
Results and discussion
Examination of the patient showed the following. Objectively: the mucous membrane is pale pink. Green-Vermillion hygienic index – 3.0, Muhlemann bleeding index – 2.5 points.
Teeth mobility according to Miller as modified by Flesar: 4.2-II, 4.1-I, 3.1-I, 3.2-II. On a panoramic radiograph: resorption of bone tissue of the alveolar processes of the jaws by 2/3 of the length of the root. On the intraoral radiograph: a horizontal fracture of root 4.2 in the middle third, its root canal is sclerotic, the lumen of the canal can be traced only in the lower third of the root (Fig. 2-A).
Diagnosis: chronic generalized severe periodontitis, horizontal fracture 4.2 in the middle third of the root, chronic apical periodontitis 3.3.
Treatment: 4.2 is temporarily splinted with 4.1 and 4.3 using Filtek Flow (3M ESPE) flowable composite in the area of the contact surfaces. Root canal 4.2 is passed to the fracture line. Next, using a Piezon Master 400 (EMS) ultrasonic device, the composite was removed from contact surfaces 4.1, 4.2, 4.3. Comparison of fragments, passage of the apical part of the root canal, expansion. The entire length of the canal is prepared for a titanium pin; after fitting, the pin is removed from the root canal, and the canal is temporarily sealed with Metapex (Biomed).
At the next visit, an “AH+” sealer (Dentsply) was inserted into the fracture line, the root canal was sealed with “AH+” at the apex, a titanium pin and a “Valux” filling (3M ESPE) were fixed in it (Fig. 2-A).
In parallel with treatment 4.2, local anti-inflammatory therapy was carried out: applications with a mixture of metronidazole with a 0.2% chlorhexidine solution, hard dental plaque was removed using an ultrasonic scaler "Piezon Master 400" and soft plaque using an "Air Flow" (EMS) device.
When choosing a splinting technique, we were guided by the clinical degree of tooth mobility. With degrees I–II of mobility, one could expect good long-term results using a conventional set of adhesive technologies. But in this situation, when mobility 3.2 was defined as II according to Miller, and based on periotestometry indicators (48 c.u.) it turned out that it was much more pronounced and corresponded to grade III, it was decided that it was necessary to create additional conditions for fixing the structure on the teeth. For this purpose, groove creation technology was used. According to the literature, no fundamental differences in the therapeutic effectiveness of fiberglass and polyethylene adhesive splints have been identified [1, 2]. When choosing a specific fiber system, with all other relatively similar parameters and capabilities, the determining criteria for a doctor are most often ease of use and price.
Using GlassSpan fiberglass tape, 4.3, 4.2, 4.1, 3.1, 3.2, 3.3 were splinted using an invasive technique: a cut was made along the lingual surface of 4.3, 4.2, 4.1, 3.1, 3.2, shaped like a reverse cone, to the thickness of the GlasSpan tape. , with a distance from the cutting edge of 2 mm. Chemical adhesion of the composite to tooth tissue is achieved through the “Single bond” bonding system; and a 38% etching gel was used to remove the dentin smear layer, increase surface area and micromechanical retention.
Since 3.3 was located under the crown as part of the bridge, it was decided to splint the tooth through the hole in the crown. Glass fiber tape "GlasSpan" was laid in the cut, covered with a fluid composite "Filtek Flow" + "Valux", the tire was ground and polished (Fig. 2-B).
A.N. Ryakhovsky et al. (2007) indicate that the “Periotest S” readings are representative for a splinting structure weight of no more than 12.71 ± 0.81 g. The results of periotestometry before and after teeth splinting are presented in the table.
When comparing the reference values and those we obtained before splinting, it turned out that they were greater than the normal values. After splinting the teeth, periotestometry indicators 4.3 and 4.2 were within the normal range, and 4.1, 3.1, 3.2 were less than normal.
After splinting the teeth, functional selective grinding according to Jenkelson was performed. A month after splinting, periotestometry indicators for this group of teeth decreased: for 4.1 – by 2.0. e.; for 4.2 and 3.1 – by 1; for 4.3 the indicators remained at the same level; and for 3.2 they increased by 1.00. e. We believe that the change in periotestometry indicators one month after splinting is associated with the adaptation of periodontal tissues to the redistribution of the load associated both directly with the combination of teeth into a splint and with the elimination of supracontacts during selective grinding. Before splinting, periodontium 3.1, 4.1, and 4.2 (due to fracture) had a deficiency of chewing load, and after splinting, the ligamentous apparatus of the teeth was not ready for the load applied to it, demonstrating its rigidity.
The direction of pathological mobility of teeth depends on their location in the dental arch, the state of occlusion, and it is always natural. From our point of view, the best result when splinting is achieved by combining teeth whose mobility vectors lie in intersecting planes. For incisors and canines, the mobility vectors lie in planes located at an angle to each other. To immobilize the frontal group of teeth, we used a structure that combines incisors and canines (anterior immobilization).
The glass fiber tape “GlasSpan” filled with filling material, used in this clinical situation for splinting teeth, becomes rigid after polymerization and does not have elastic properties. Therefore, the fixed attachment of the teeth to each other and, as a result, the absence of a minimal, but physiologically necessary excursion of the teeth in relation to each other, to the dentition and the alveolar process are a significant drawback of this method of splinting (Fig. 1-B)
The main negative result when using this method of splinting is the rapid destruction of the periodontal supporting structures, due to which the teeth are stabilized as part of the structure.
As a result, traumatic tangential stresses arise on the supporting teeth of the splinting structure, similar to those for cantilever dentures [7].
conclusions
- Periotestometry is a fairly informative modern method for assessing the condition of the periodontium, allowing one to assess the degree of elasticity of the ligamentous apparatus of the teeth. An increase in periotestometry values relative to reference values is an early sign of a violation of the elastic properties of the periodontium, which requires temporary splinting of teeth (for the period of active treatment of periodontitis or longer).
- The presented clinical case clearly shows that teeth whose mobility vectors lie in intersecting planes must be combined into a splint.
- Negative periotestometry indicators after applying a splint made of glass fiber tape "GlasSpan" indicate that this method of dental immobilization is unphysiological.