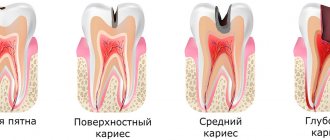
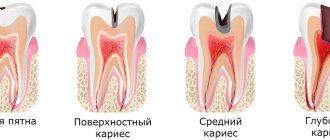
Anesthesia without adrenaline has been used in dentistry for quite a long time; it allows painless treatment even for those patients who have contraindications to common means of local anesthesia. Typically, drugs that do not contain adrenaline are used in cases where it is necessary to treat teeth in patients with high blood pressure, heart disease, and pregnant or breastfeeding women.
What is Articaine and what is its composition?
Articaine is an amide anesthetic intended for local, infiltrative or conductive anesthesia for both simple and complex dental procedures. A local anesthetic blocks the generation and conduction of nerve impulses, presumably by increasing the threshold of electrical excitation in the nerve, slowing the propagation of the nerve impulse, and decreasing the rate of rise of the action potential.
The uniqueness of Articaine as a member of the amide family is that it contains an ester group and a thiophene instead of a benzene ring. The thiophene ring increases the lipid solubility of articaine, facilitating more efficient diffusion of the anesthetic across the lipid membrane of nerve cells into surrounding tissues. Articaine is widely used in dentistry due to its safety during short procedures that require rapid onset of anesthesia.
The onset of action of the drug Articaine is:
- from 1.5 to 1.8 min. with infiltration of the upper jaw;
- from 1.5 to 3.6 min. with block anesthesia of the lower jaw.
Articaine pulp anesthesia lasts from 30 to 120 minutes. Anesthesia of soft tissues with the drug lasts ~ 2.25 hours for infiltration of the upper jaw, 4 hours for blockade of the lower jaw.
The drug is produced in the form of an injection solution - a transparent, colorless or yellowish liquid. For retail sale to pharmacy chains, Articaine is supplied in ampoules made of colorless chemically pure glass, enclosed in blister packs and/or cardboard packs.
Composition of articaine in dentistry:
- active agent - articaine hydrochloride;
- Excipients: sodium chloride (to make the solution isotonic) and distilled water.
1 ml of solution contains 40 mg of active agent.
In odonto-dental anesthesia, articaine is used alone or in combination with epinephrine (adrenaline). Epinephrine, diluted to 1:100,000 or 1:200,000 and added to the solution, slows down the passage of articaine into the general bloodstream and thus ensures long-term maintenance of the concentration of the active substance in the tissues, allowing a small hemorrhagic surgical field to be obtained.
It is possible to replace Articaine with synonyms with the same active substance, such as:
- Artikain-Binergy;
- Ultracaine;
- Artikain-DF;
- Articaine with Epinephrine.
The decision to use analogues is made by the attending physician, taking into account the individual characteristics of the patient.
Local anesthetics in dentistry –
At the moment, the most modern anesthetics in dentistry are drugs based on articaine hydrochloride. We have already said above that this group also includes Ultracain, Ubistezin, Septanest and others. Anesthetics of the articaine series are more effective than lidocaine - 1.5-2 times, and Novocaine - 5-6 times. As for the duration of anesthesia with drugs based on articaine, it will depend, among other things, on the concentration of vasoconstrictors in the anesthetic composition.
Vasoconstrictors, due to the narrowing of blood vessels at the injection site, can reduce the leaching of the anesthetic, and this leads to an increase in the depth and duration of anesthesia. Manufacturers always produce the same anesthetic with different concentrations of vasoconstrictors. The following concentrations of the vasoconstrictor epinephrine are usually used - 1:100000, 1:200000 + option and without a vasoconstrictor at all. This allows for optimal use of the drug in patients of different risk groups. The most commonly used anesthetics are:
1) Anesthetic “Ultracaine” –
The anesthetic Ultracaine is produced in France in 3 possible versions, which will differ in the presence/absence of epinephrine in the composition, as well as its concentration. A separate article is devoted to this most popular and safe anesthetic (link above). Forms of release of ultracaine:
- “ultracaine DS forte” (with epinephrine concentration 1:100,000),
- “ultracaine DS” (with an epinephrine concentration of 1:200,000),
- "ultracaine D" (without epinephrine, without preservatives).
2) Ubistezin - instructions for use
Good anesthetic, produced (Germany). The composition of Ubistezin is absolutely no different from similar forms of Ultracain, and there are only different release forms. The first option is “Ubistezin” (with an epinephrine concentration of 1:200,000), and the second is “Ubistezin forte” (with an epinephrine concentration of 1:100,000).
Read a detailed description of the anesthetic and its indications for use here: → Ubistezin forte - instructions for use (PDF)
3) Septanest: instructions for use
Septanest has been used in dentistry for a very long time. This anesthetic has 2 release forms with adrenaline concentrations of 1:100,000 and 1:200,000. But compared to ultracaine and ubistezin, this anesthetic contains a slightly larger amount of preservatives (sodium metabisulfite and EDTA), which is undesirable in a number of patients, for example, with frequent allergic reactions, bronchial asthma, etc.
Read a detailed description of the anesthetic and its indications for use here: → Septanest 1:100,000 – instructions for use (PDF)
4) Scandonest: instructions for use
Anesthetic from Septodont (France) based on 3% Mepivacaine.
Does not contain vasoconstrictor components or preservatives. Scandonest in dentistry is used mainly only in patients at risk who cannot take anesthetics with adrenaline and epinephrine, as well as in patients with bronchial asthma. A complete analogue of Scandonest is the anesthetic Mepivastezin, produced (Germany). Read a detailed description of the anesthetic and indications for use here: → Scandonest - instructions for use (PDF)
Manufacturers Articaine
On the Russian pharmaceutical market, the anesthetic Articaine and its analogues are represented by domestic and foreign manufacturers. You can buy articaine in St. Petersburg and Moscow using the link.
The products of the following enterprises are most in demand:
- JSC "Biokhimik" (Russia);
- CJSC "Binergy" (Russia);
- LABORATORY INIBSA, SA (Spain);
- Welfarm LLC (Russia);
- Armavir biofactory FKP (Russia);
- Borisov Medical Preparations Plant (Republic of Belarus);
- Sanofi-Aventis Deutschland GmbH (Germany).
Preparations based on articaine, created at different enterprises, may have certain differences due to production technology, quantitative and qualitative composition of excipients, but at the same time retain the main direction of action of the active substance.
How to improve the quality of pain relief?
A patient who is indicated for anesthesia without adrenaline in dentistry can make sure that the effect of the painkiller lasts longer and is of better quality. To do this, he only needs to follow a few general recommendations:
- Before visiting a doctor, if there is strong anxiety and fear of treatment, it is better to take a sedative, preferably based on herbs (for example, about 30 drops of valerian root tincture).
- The day before visiting the dentist, you should not drink alcohol, since alcohol in the blood weakens the effect of the anesthetic.
- If you are taking any medications or have any allergic reactions, you should inform your dentist at the treatment planning stage.
- It is better not to visit a doctor if you feel unwell or during menstruation.
Articaine: side effects
Such qualities of Artican as low fat solubility, high% binding to blood proteins, low half-life ensure low toxicity of the drug. However, depending on the general condition, age, individual reactions of the patient and his existing systemic diseases, side effects may be observed during anesthesia with the drug, such as:
- disturbance or confusion;
- vertigo;
- headache;
- nausea;
- dyspnea;
- decreased blood pressure;
- diplopia;
- muscle tremors;
- allergic and local reactions, manifested in symptoms of urticaria, conjunctivitis, rhinitis, skin hyperemia, swelling and inflammation at the injection site.
Articaine should be used with caution during dental procedures in patients with impaired cardiovascular function, vascular diseases, liver and kidney failure.
Articaine during pregnancy in dentistry
Articaine is usually well tolerated at all stages of pregnancy. There is no data on the long-term effects of the drug on the neurophysiology of the newborn. Also, no teratogenic damage was observed after use of the drug in the first trimester.
There are no data from clinical studies of the penetration of Articaine into breast milk. To minimize possible risk to the baby, breastfeeding mothers may choose to express milk for approximately 4 hours after the injection. After which breastfeeding can be resumed.
Instructions for use
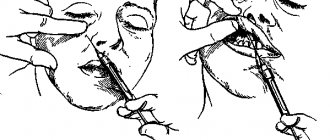
To exclude or minimize intravascular administration of Articaine, an aspiration test is required before using the drug. An accurate and slow technique for injecting the drug is required with control of the pressure on the syringe plunger depending on the sensitization of the tissue.
The instructions for use in dentistry recommend using Articaine in a dosage corresponding to the nature of the manipulation:
- 1.7 ml of solution per tooth for uncomplicated extraction of the upper jaw tooth;
- 0.1 ml for anesthetizing incisions when creating a palatal depot and suturing;
- 0.5-1.7 ml per tooth for grinding teeth for crowns and in case of cavity preparation.
After each injection of Articaine, careful and constant monitoring of vital signs of the cardiovascular and respiratory systems (adequacy of ventilation) and the patient’s state of consciousness should be carried out.
using Articaine in dentistry for infiltration anesthesia during extirpation of mandibular premolars.
No pain – anesthesia in modern dentistry
General dentist Lelekov Alexander Mikhailovich tells.
Dentists don't like to hurt. Civilized dentistry strives for complete painlessness at all stages of treatment.
The most unpleasant procedures, such as treatment of deep caries and pulpitis, tooth extraction, are unthinkable without effective anesthesia.
There are many everyday myths and outdated ideas associated with anesthesia. I’ll tell you more about this useful tool, which makes treatment comfortable, without suffering, pain and tears.
Why is it painful to be treated in some clinics, but not in others?
The patient’s sensations depend on many factors, but the most important is the anesthetic drug itself. At the beginning of the twentieth century, dentists began to use novocaine, and from the middle of the century - the more powerful lidocaine. At one time, this was a real breakthrough in medicine. The treatment became tolerable, but the pain could not be completely eliminated.
Modern clinics use anesthetics based on articaine.
Before treatment, be sure to ask what drug is used to relieve pain:
- Based on articaine, it shouldn’t hurt.
- Lidocaine, novocaine - most likely get ready for a test of patience.
For comfortable and safe treatment of my patients, I use:
- Articaine Inibsa (Spain),
- Ultracaine Sanofi (France),
- Scandonest Septodont (France).
I use Articaine in most situations. Ultracaine D, Scandonest, which do not contain adrenaline - if the patient has health problems. They can be used in elderly people, patients with diabetes mellitus, hypertension, cardiovascular diseases, and bronchial asthma. The listed anesthetics do not penetrate the placental barrier and are approved for pregnant women.
Do anesthetics contain adrenaline?
Many patients are afraid that they will be injected with adrenaline along with the anesthetic. Adrenaline (epinephrine), indeed, is contained in anesthetics; dentists value it for its vasoconstrictor effect:
- The removal of anesthetic from tissues is slowed down, so the anesthesia lasts longer.
- Bleeding is reduced, which is important when removing a tooth, treating gums or caries in the gingival area of the tooth.
But there are also undesirable effects: adrenaline can increase your heart rate and increase your blood pressure. A healthy person, as a rule, does not even notice this. But for children and patients with cardiovascular diseases, drugs with adrenaline are contraindicated.
They are given an anesthetic with reduced or no adrenaline. Earlier I mentioned the drugs Scandonest and Ultracain D - they do not contain adrenaline at all.
A mosquito is about to bite
Whether the injection will be unpleasant depends on several factors:
- Which tooth are we treating: anesthesia can be very sensitive when placed in the area of the upper and lower incisors. Mandibular anesthesia is unpleasant: an injection into the area of the mandibular nerve.
- Doctor's manual skills. If the doctor has “trained his hand” properly, is not in a hurry and has set himself the goal of making the treatment as pleasant as possible for the patient, then the injection may not be felt at all.
- The equipment of the clinic: for the patient’s comfort, thin needles and special carpule syringes were invented. For children, topical anesthesia is used - the gel is applied to the gum and “freezes” it before the injection.
Carpule syringe
You may have noticed the unusual but recognizable shape of an anesthesia syringe. It has rings on the sides to make it fit more comfortably in the doctor's hand.
But the main thing about it is a mechanism that allows you to carry out anesthesia quickly, effectively and safely in absolutely sterile conditions. The capsule with the drug is opened by this mechanism right inside the syringe. Fewer hands means fewer germs.
The needles for the carpule syringe are thin and flexible, they are easy to bend at the desired angle. With them you can get close to awkwardly located teeth and provide pain relief in the best possible way.
If anesthesia is contraindicated
In most cases, anesthesia is not completely contraindicated, but only requires a more careful, balanced approach. The doctor takes into account the patient’s age, health characteristics and selects the optimal drug and dosage.
Be sure to tell your doctor if you have the following diseases:
- Heart diseases: arrhythmia and tachycardia, previous heart attacks and heart surgery.
- High blood pressure.
- Problems with the endocrine system: diabetes and thyroid lesions.
- Glaucoma.
- Liver failure.
- Psychoneurological diseases, including epilepsy.
- Individual intolerance to the components of the drug.
Allergy to local anesthetics deserves special attention. If you have ever had an allergic reaction to an anesthetic, be sure to remember its name.
In diagnostic laboratories you can order an allergy panel - an analysis of the body's reactions to various drugs. This way you will find the anesthetic approved for you. There is no need to buy it or bring it to your appointment! When making an appointment with a dentist or for a consultation, check whether the clinic can purchase the required anesthetic for you.
General anesthesia
If it is impossible to use any local anesthetic, we will not torment the patient with pain anyway. In such cases, anesthesia is used - dental treatment during sleep.
The procedure is carried out under the supervision of an anesthesiologist-resuscitator, who monitors the patient’s condition using special equipment.
To make the anesthesia work better
A few tips for maximum pain relief:
- Don’t be nervous before your appointment; you can take a mild sedative;
- Do not drink alcohol or liters of coffee, they can reduce the effectiveness of anesthesia;
- Don't delay treatment. If pus forms near the tooth, it will prevent the anesthetic from working.
High-quality anesthesia is not only about the comfort and peace of mind of the doctor and the patient.
Most patients who are afraid of dental treatment are actually afraid of the pain, not the treatment itself. And the fear goes away when they come to the clinic, where reliable pain relief is used.
Having got used to good anesthesia, the patient does not delay treatment and keeps his teeth healthy!
Articaine in pediatric dentistry
The pharmacodynamics of local anesthetics in children is comparable to that in adults. In pediatric dental practice, extreme caution must be exercised when using amide local anesthetics as lower intrinsic clearance or decreased serum protein binding may easily lead to an increased risk of toxic reactions. The route of administration is one of the main safety factors when using local anesthetics in neonates and children.
Anesthesia in dentistry with the drug Articaine , carried out using intraosseous injection, is effective in achieving deep anesthesia of teeth affected by MIG with hypersensitivity associated with chronic inflammation of the pulp in children.
In pediatric dentistry, it is recommended to use Articaine 2% due to the lower Cmax and shorter half-life of the drug.
Why is adrenaline needed in anesthesia?
Adrenaline is a vasoconstrictor - a substance that narrows blood vessels. Therefore, on the one hand, its presence in the drug provides a longer-lasting analgesic effect, and on the other hand, it reduces the risk of bleeding during dental procedures (for example, during tooth extraction).
Given this, dentists always warn patients that anesthesia without epinephrine in dentistry has a shorter lasting effect and is not suitable for long procedures. In cases where the patient is indicated for pain relief using non-adrenaline anesthetics, treatment must be carried out very quickly or divided into stages so that the doctor has the opportunity to provide anesthesia before each subsequent stage of manipulation.
If you have a problem similar to that described in this article, be sure to contact our specialists. Don't diagnose yourself!
Why you should call us now:
- We will answer all your questions in 3 minutes
- Free consultation
- The average work experience of doctors is 12 years
- Convenient location of clinics
Single contact phone number: +7
Make an appointment
Reviews from dentists about the drug Articaine
Most practicing dentists consider Articaine to be the best representative of local anesthetics due to its high effectiveness. At the same time, when using the medication, there is a low incidence of allergic reactions, the possibility of safe use in pregnant women, and the absence of addiction. The only small drawback of Articaine, according to experts, is the inability to prescribe it to children under 4 years of age. In all other cases, Articaine is rightly called one of the drugs of choice.
This information is intended for medical professionals and specialists.