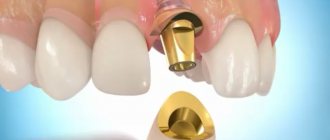
Modern dental prosthetics in Minsk is one of the most popular dental procedures. Loss of teeth and, as a result, malocclusion, the development of serious diseases of the oral cavity and the whole body are quite common. But if a couple of centuries ago there was no fight against this, today doctors are already offering a number of technologies for restoring the dentition.
Metal-ceramic dental are durable, easy to use and reliable, and they also look like real teeth. That is why many patients prefer to restore their teeth using metal-ceramic prosthetics. But in order to maintain the natural appearance of the crowns, it is necessary to properly care for them. The Family Dentistry Medical Center offers you to familiarize yourself with the list of basic recommendations for caring for metal-ceramic teeth.
Content
- What are the dangers of improper crown care?
- What to do after installing crowns
- When to see a doctor
Crowns are the most popular method of restoring damaged and lost teeth. Following the rules of care will help keep your teeth beautiful and healthy after dentures. Despite the fact that the tooth is artificial, plaque continues to accumulate on it. Also, do not forget that there are neighboring living teeth and soft tissues that may be damaged due to careless handling.
PROMOTION
Installation of crowns, dental bridge
RUB 3,450
Getting used to it after six months
When the healing process has come to an end and the patient has had the adaptive prosthesis replaced with a permanent one, care after dental prosthetics can be divided into two parts:
- Daily brushing as if you were your own teeth
- Professional cleaning by a doctor
In both the first and second cases, everything should be clear, especially for those patients who have been looking after their teeth all their lives, but the stars aligned so that now the teeth have become artificial. For those who have not done this, you will have to develop a new habit, since artificial teeth are no different from real teeth (except that they do not hurt and are not susceptible to caries).
What are the dangers of improper care after prosthetics?
Bad breath and visible plaque are only superficial manifestations of poor hygiene. In fact, the consequences are much more serious:
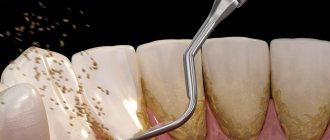
- Plaque, accumulating near the surface of the gums, contributes to the formation of tartar.
- Tartar, in turn, is a breeding ground for bacteria.
- The waste products of harmful microorganisms have a destructive effect on the natural tissues of teeth and soft tissues, and provoke inflammation of the gums.
- When the gum becomes inflamed, its structure becomes loose. Such gums are not able to protect the cervical area of the teeth.
- If left untreated, seemingly harmless inflammation of the gums leads to much more serious consequences - periodontitis, the formation of gum pockets.
Simply put, dental hygiene and oral health are inextricably linked.
Dry mouth or increased salivation
A feeling of dryness or, on the contrary, increased salivation occurs due to the adaptation of the mucous membranes to a foreign body. If the design is made correctly, the discomfort quickly passes. If your mouth is dry, you should drink water more often and rinse, but do not use alcohol solutions. It is worth limiting the consumption of tea, coffee, and at least temporarily giving up smoking. You need to get rid of dryness quickly, otherwise your gums will be injured.
Excessive salivation is a reaction to a foreign body in the mouth, to constant contact with the mucous membrane. It goes away on its own in a few days. You can simplify the adaptation process for the mucous membrane by rinsing with decoctions of chamomile, oak bark or sage, or solutions recommended by your doctor.
Rules of conduct after installing crowns
There are several rules that you can follow to keep your mouth healthy:
- Brush your teeth twice a day – immediately after waking up and before going to bed.
- Rinse your mouth if possible after every meal. This will get rid of food debris and slow down plaque formation.
- Thoroughly clean areas where plaque and food may accumulate. We are talking about the space under the hinged crown of the bridge. To do this, you can use an irrigator, brushes and other devices.
- You should avoid eating too hard foods and chewing on non-food items. Nail chewing, nuts, candy chewing – all of these should be avoided to maximize the life of your crowns.
- You should reduce your consumption of coffee, black tea, red wine, and other coloring foods.
- Gum care is also a very important attribute of healthy teeth. Rinsing and careful attention to the condition of soft tissues are required.
- Cleaning your tongue is a very useful activity. Plaque also accumulates here and must be removed.
Careful care will help maintain health and maximize the service life of any restorations.
Adaptation to new crowns and dentures.
What do you need to know?
Modern dentistry has made great strides, with its help you can make your smile truly radiant.
However, many types of treatment require patience and endurance from the patient. Adaptation to a denture takes a lot of time. Therefore, it is necessary to listen to specialists who give valuable recommendations on how to get used to dentures in a short period of time. When the prosthetics are completed, we recommend not to eat hard food for a couple of days - it’s not quite familiar yet and you can accidentally bite your lip, cheek or tongue. While eating, chew slowly, control the movement of food in different directions, as well as the position of the lips and tongue while eating (to avoid injury to the mucous membrane). Eliminate hard and viscous foods (nuts, crackers, crackers, hard sausages, persimmons, chewing gum, etc.). Remember, the facial and chewing muscles are not yet ready to function in a new position after prosthetics. Xerostomia (dry mouth) or increased salivation may occur.
There is a feeling of limited space for the tongue.
After restoration of the height (increase) of the bite, a restructuring of muscle reflexes occurs.
Irritability, sleep disturbance, and minor discomfort in the muscles and temporomandibular joints are also possible. The first few days the diction may even be changed. This happens when prosthetics involve several front teeth. Which decisively influence, and indeed create, diction and phonetics. To speed up adaptation, more training is recommended: talking more, chatting on the phone, perhaps using myogymnastics, i.e. talk in front of the mirror. The more training, the faster pronunciation is restored.
Often these phenomena disappear after 2 months of using orthopedic structures.
We must also remember that there are teeth under the crowns, and while crowns can withstand barbaric treatment of them, teeth cannot always. Therefore: do not limit food intake and treat the crowns as if they were your own teeth. Eat as usual, do not conduct experiments (open bottles, chew bones, metal or wires), brush as you would your teeth.
Clean and care for crowns in the same way as other teeth. No additional care required. After eating, you can rinse your mouth with plain water to wash away all the remaining food from under the artificial teeth. If it gets stuck between the crown and an adjacent tooth, then clean it with floss (dental floss), a brush or an irrigator.
Food should not get under the crowns themselves. But for artificial teeth - maybe. Let me explain.
Artificial teeth can be made very tightly to the gum. Modern impression materials and technologies make it possible to do this easily. But in this case, food will certainly get between the artificial tooth and the gum. The gums are very pliable. While chewing food, small pieces can move it away and squeeze between it and the artificial tooth. There is no way to get them out of there. This will cause gum inflammation over time. Everyone knows that any inflammation is accompanied by edema, that is, an increase in volume. The gums will “hug” the remaining food. It will be impossible to get to him at all. Inflammation will increase, and the gums will swell even more. It's a vicious circle. This can only be stopped by removing the remaining food. But it’s unlikely to be possible to do this on your own.
To prevent this, a distance is created between the artificial tooth and the gum. Officially, this gap is called the flushing space. This was not invented by us - this is done all over the world. That is, when making crowns with artificial teeth, rinsing spaces are required. They make it possible to wash away all food residues by simply rinsing with water.
It is important to know that... a) Brush your teeth and dentures regularly, at least twice a day. Brush the contact and side surfaces of the bridge with a toothbrush in the same way as natural teeth. b) To clean the spaces between teeth, dental floss (floss), toothpicks, special interdental brushes, brushes and an irrigator can be used. Clean the inner surface of the denture, as well as the interdental spaces of the bridge, especially carefully. c) The surface of the dental crown and adjacent gums is best cleaned with a brush, using regular toothpaste (but not abrasive, which can damage the surface of the denture). At the same time, try to actively carry out sweeping movements at an angle of 45°, directed from the gums to the cutting edge or chewing surface of the prosthesis. d) After cleaning the denture, it is recommended to rinse the oral cavity thoroughly with water or mouthwash.
We wish you patience and health!
Do not forget that the success of treatment now largely depends on you.
Performed by orthopedic dentist S.V. Mogilnikov.
A crown was installed. What happens to the tooth?
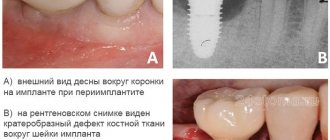
A protective covering is placed on a tooth to preserve it and restore its shape, appearance and functionality. However, there is a myth that teeth under crowns deteriorate faster. What happens after the structure is installed? Depending on the load, care, hygiene, and general health, changes in the condition of the oral cavity and bone tissue occur. The gum margin may gradually recede and expose the edges of the crown . In this case, the connection loses its tightness, saliva gets under the crown and gradually washes out the cement connecting it to the tooth.
Microbial flora has a destructive effect on dental tissue, and the fixation of the structure is disrupted. Wearing such a crown for a long time can actually lead to an unfavorable development of the situation and tooth loss. At the same time, the doctor, discovering the failure of the orthopedic structure, will offer an adequate replacement. If the problem is detected in a timely manner, only the crown is replaced, and the supporting teeth are preserved and serve for many more years. How can you tell when it's time to change your crowns? Here are the main signs that you should see a doctor when they appear:
- The edge of the crown is exposed . The gingival margin can rise on the upper jaw or fall on the lower jaw and expose the roots of the teeth. In this case, the development of root caries and damage to dental tissues under the crown is possible.
- The gums around the crown are inflamed . Changes in gum color, redness, swelling, and bleeding during brushing indicate that the marginal fit of the crown to the tooth is broken.
- The structure has become movable . Unstable fixation, loosening of the crown or bridge indicates decementing and loss of fastening strength. Improper load distribution can also lead to loosening of supporting teeth, so it is important to promptly reline bridge structures.
- The integrity of the coating has been compromised . Even minor chips can lead to negative consequences. Sharp edges injure the mucous membrane, the height of the bite changes, and antagonist teeth begin to experience excessive stress. A crack or chip allows salivary fluid access to the cement and then to the tooth tissue, which can cause caries under the crown.
- An unpleasant smell or taste appeared , pieces of food began to get stuck between the crowns or crowns and teeth. Such phenomena indicate a violation of fixation and the onset of a pathological process under the influence of bacteria.
Fillings are now strong and better than crowns
Yes, the filling material of excellent quality is now used. Durable and stable. But installing a filling will save the tooth if the destruction is no more than 30-40%
. In other cases, the filling will not be able to provide stability to the walls of the unit. Severely crumbled teeth are often depulped, there is no tissue nutrition, and some become fragile. Therefore, under constant load, the crown of the tooth will break off at the root along with the filling. We try to preserve every unit, so we recommend installing dentures in a timely manner.
The crown cannot be replaced; the entire tooth may fall off
The tooth root is firmly fixed in the bone tissue; a profile tool is used to remove the worn-out prosthesis. Therefore there is no danger. In our clinics, such manipulation is performed quickly and painlessly. You can easily remove a used denture and put a new crown on a tooth (the price depends on the type chosen).
It is wiser to find out how much it costs to put a crown on a tooth in your particular case during a visit to the dentist, when you undergo an examination and choose the material for the prosthesis. Contact the doctor on time, without waiting for fatal consequences, and he will help you save your own unit.
How long does it take to get used to dentures?
Dentists distinguish 3 phases of adaptation:
- The first phase is irritation
. And although doctors mean irritation of nerve receptors, the name of the phase perfectly conveys the patient’s condition. Irritation and the desire to pull out a foreign object are the 2 main feelings of the first day. A psychological attitude and any, preferably enjoyable, activity helps to overcome them. - The second phase is partial braking
.
Then comes the reward for patience and perseverance. Restoration still interferes, but not as much. Salivation decreases, nausea goes away. Cheeks and lips are less tense. Chewing function is restored. This phase takes about 5 days
. - The third phase is complete braking
. Diction is normalized, chewing no longer causes discomfort, and there is no sensation of a foreign body. The patient experiences discomfort when the jaw is not in place. Adaptation is complete.
On average, getting used to dentures takes 10-30 days.
.
What you will have to face at the beginning
Of course, dentures help solve many problems, but at the same time, they give rise to many new problems. And no wonder, because a foreign object in the oral cavity, which, in fact, is a denture, causes a normal defensive reaction of the body - irritation, rejection, etc.
One of these problems is the difficulty of getting used to dentures.
- Gagging . The gag reflex is a normal reaction of the body to the penetration of an object that is not food into the oral cavity.
- Profuse salivation . If the body “perceives” an object in the mouth as food, the brain gives a signal to turn on the corresponding functions - saliva begins to be released, which is necessary to facilitate the penetration of food into the throat, and gastric juice is secreted.
- Speech and diction disorders . “New teeth” are not always a complete copy of the original ones; it takes time to “reconfigure” articulation when speaking. In addition, dentures often “interfere” with the tongue, which constantly “clings” to them, which also does not contribute to intelligible speech.
- Discomfort when chewing . It occurs especially often when using removable dentures, including clasp dentures. This is due to the fact that the distribution of loads when chewing with removable dentures may differ from natural.
- Partial loss of taste . The fact is that not only the tongue takes part in the formation of the sensation of taste. The sensation of taste is indirectly affected by the mucous membranes of the oral cavity, some of which may be hidden under the prosthesis.
Operational period of popular types
Depending on objective and subjective factors, the service life of artificial structures ranges from 3 to 15 years.
Objective factors include the type of material from which the structure is made, the service life of the cement or glue, the condition of the supporting tooth, and the general health of the patient. Subjective ones include the quality of manufacturing and installation of the microprosthesis, the conditions of its operation.
Material is the main factor that determines the service life of a crown. Depending on it, the patient can count on the following service periods:
- Plastic (provisional) - up to 3 years.
- Metal-plastic – up to 5 years.
- Metal from base metals - up to 10 years, from gold alloys - up to 15 years.
- All-ceramic – 7-10 years.
- Metal-ceramic - up to 10 years.
- Zirconium dioxide – 10-15 years.
Their service life is also greatly influenced by their operating conditions. The quality of oral care, food preferences, the presence or absence of bad habits, following or ignoring doctor’s recommendations can significantly increase or decrease the average service life of a microprosthesis.
How to make addiction easier
But it is entirely within your power to make it easier to get used to dentures. This will require you to do a few simple steps that don't require much effort.
- When experiencing attacks of nausea and vomiting, take a deep breath several times, try to turn your thoughts to some neutral topics, distract yourself - turn on the TV or read a book.
- Sucking on lollipops will also help with nausea.
- But if there is excessive salivation, lollipops are contraindicated. It is better to rinse your mouth with a weak salt solution.
- Reading aloud will help you cope with diction problems. You can start with quiet reading, gradually moving to loud recitation with expression.
- Tongue twisters with a large number of “dental” letters (z, zh, sh, sch, h, s) will also help speed up the restoration of diction. For example, “Sasha walked along the highway and sucked on a dryer.”
- During the adaptation period, refrain from eating hard foods that require effort when biting and chewing. Also exclude from your diet those foods whose particles can get under the prosthesis and cause additional discomfort - crackers, nuts, croutons.
And, above all, be patient, remember that most difficulties are temporary and will soon disappear on their own. Therefore, it is necessary to overcome the first desire to immediately pull the interfering prosthesis out of your mouth (when using removable structures) - the more time the prosthesis spends in the mouth, the less time it will take to get used to it.