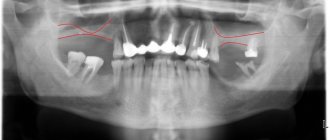
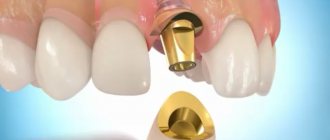
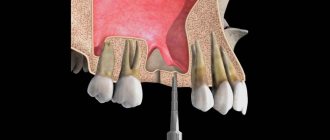
A sinus lift is a procedure aimed at restoring lost bone tissue. Where there is insufficient volume, this procedure allows the installation of implants.
Sinus lift is a popular procedure. The term is clear to specialists working in the field of implantology, but means little to ordinary people. This also applies to potential patients who are planning to use the services of orthopedic surgery.
Complications after sinus lift
deserve separate consideration. This is not a new procedure; it has been used in implantology for the past 30 years. The first experiments were not the most successful. This is why specialists have an incentive to develop improved materials and tools.
When is a sinus lift indicated?
The structure of the bones of the upper and lower jaws has a significant difference. Both of them form the basis of the facial skeleton. Chewing, swallowing, speaking and breathing are just a few of the functions they perform. Sinus lifting is aimed at restoring bone tissue by creating optimal bone volume. This is achieved by introducing bone growth material into certain areas. Such zones are located under the maxillary sinus. There is no trauma during the procedure. Over time, the stimulator turns into ordinary bone tissue and grows with blood vessels. This is an excellent basis for placing a dental implant.
Perforation of the maxillary sinus
The most common and specific possible complication of sinus lifting is perforation of the protective membrane of the maxillary sinus with infection or penetration of osteoplastic material. Perforation does not always lead to any adverse consequences, since much depends on its size.
The dentist’s actions depending on the degree of perforation:
- Perforation up to 2 mm does not require any intervention from a doctor and heals on its own. A fixed membrane will provide additional protection against progression of rupture and movement of osteoplastic material.
- Perforation of the membrane up to 4 mm in size can lead to various adverse consequences, and therefore requires prompt surgical intervention. The rupture is not severe enough to interrupt the sinus lift, but sutures are still required. Thus, the doctor prevents further enlargement of the hole and prevents infection.
- Perforations greater than 4 mm are a serious complication that requires refusal from further sinus lifting. The doctor focuses entirely on eliminating the perforation and preventing foreign elements from entering the sinus. After a while, it is possible to perform a sinus lift again.
Perforation of the maxillary sinus is a fairly common complication of this type of bone grafting. In such a situation, the main task of the surgeon is to detect the problem in a timely manner and minimize the adverse consequences of the error.
What dangers do you have to deal with?
Many patients are afraid of surgery because they believe that the maxillary sinus may be damaged. If you end up in the hands of a good doctor, there is no need to be afraid of this. This should not be an ordinary implantologist, but an oral and maxillofacial surgeon. Modern sinus lifting has nothing in common with the outdated techniques previously practiced in surgery. The risk of complications is minimized here. Modern operation:
- Painless;
- Carried out using ultrasound;
- Requires only local anesthesia;
- Does not require general anesthesia.
- Sometimes the procedure takes no more than 15 minutes.
Complications after sinus lift: can they be avoided?
A lot depends on the patient. He must strictly follow the dentist's advice. Complications can be dangerous, so you should not treat them irresponsibly. If all instructions are followed, adverse effects are also possible. This indicates a lack of detailed examination before surgery. That is why it is wrong to say that sinus lifting is necessarily associated with complications. They are possible in two cases:
- When a patient is negligent about his health;
- When a doctor approaches a procedure irresponsibly.
Various complications are possible after sinus lift
. Symptoms that should alert you:
- heat;
- bleeding;
- difficulty in nasal breathing.
The dentist monitors each patient for several days after the intervention. The first visit is after 3 days. The doctor only needs to look at the operated area once to draw conclusions about the patient’s compliance with all the recommendations prescribed to him. If there are problems, the doctor immediately eliminates them. In the worst case, when the patient gets to an amateur, no attention is paid to his well-being. Then the person can only independently determine whether there are deviations from the norm and contact another dentist.
Pain and other similar complications after sinus lift
do not occur normally! Even if you just feel unwell without any external signs, go to the doctor!
Bleeding
This nonspecific and rare complication for sinus lifting occurs immediately after the end of the operation. The bleeding should stop within a few minutes after the stitches are placed. Some scanty discharge may continue for several days, but a full outpouring of blood should not occur.
Profuse bleeding from a wound can be caused by blood clotting pathologies and, less pronounced, by taking blood thinning drugs. If such a problem does arise, then we can immediately talk about a poor examination of the patient at the preparatory stage. The patient’s condition should be treated as soon as possible, since in a short time he can lose a critical amount of blood.
Treatment for this complication depends on the cause of its occurrence. Typically, the wound is pressed with a finger or a cotton swab to reduce blood loss. A person is given special, and sometimes disease-specific, remedies. For example, in hemophilia, the patient must receive the missing clotting factor in order for the blood clot to form.
Sinusitis
Speaking about complications after sinus lift
, the symptoms of sinusitis are considered leading. The doctor may damage the Schneiderian membrane. It is located in the area of the maxillary sinuses. This is possible if the dentist uses hand instruments instead of an ultrasonic device. An infection gets into the upper jaw, causing sinusitis or sinusitis. Exacerbation of sinusitis is a contraindication to sinus lift. The disease must first be cured. Usually the doctor prescribes a 2-week course of antibiotic therapy.
Contraindications
Intervention on the maxillary sinus is not performed in the following cases:
- reduced immunity;
- blood clotting disorders;
- fragility and low level of bone tissue regeneration;
- diseases of the cardiovascular system;
- rhinitis, sinusitis;
- exacerbation of chronic diseases;
- malignant tumors of any location;
- abnormal location of the maxillary sinuses (proximity to each other);
- aggravated medical history of the patient.
What should you not do to prevent complications after a sinus lift?
Adviсe
Physical activity
- Physical activity should be minimal on the day of surgery. Otherwise, complications such as tachycardia and bleeding are possible.
- Avoid lifting heavy objects after a recent sinus lift.
- For about 2 weeks after surgery, avoid intense sports or other strenuous physical activities.
Diet
- You should not eat food immediately after a sinus lift. You can eat after the anesthesia wears off. But it is recommended to chew on the opposite side for at least the next 24-48 hours.
- For the next few days, eat pureed food and avoid solid foods. Hot food, herbs and spices that can cause irritation at the surgical site are prohibited. Avoid carbonated drinks for the next 3-4 days.
- Drink plenty of fluids between meals.
- Be patient and you will gradually return to your normal eating routine.
- It is not advisable to touch the place where the procedure was performed with sharp objects (cutlery, toothpicks, fingers or other objects).
Oral hygiene
Good oral hygiene is important. The dentist will recommend a special solution for you to rinse your mouth with every day. Rinsing is usually done after breakfast and before bed for 30 seconds. But in the first 24 hours after surgery, it is not recommended to rinse your mouth. It is desirable to have minimal impact on the operated area to prevent bleeding. After a day, take warm water and use it to rinse. It will remove food debris and ensure quick healing.
You are allowed to brush your teeth, but it is better not to touch the operated area. Use a soft-bristled toothbrush in close proximity to it. Keeping the area clean is important to prevent infection. Hygiene promotes tissue healing.
How to deal with pain?
- Minor pain or discomfort is normal. This is not considered a complication after a sinus lift
. You can take painkillers prescribed by your dentist: Ketanov, Nurofen and others. - Your doctor may prescribe you antibiotics. Strictly follow the instructions for taking the drug!
- If you suddenly catch a cold and have a runny nose, contact your doctor. He will prescribe you vasoconstrictor drops or other medications as needed. He will also warn you that in any case you should not blow your nose.
General Tips
Do you want to avoid complications after sinus lift?
? Follow these tips:
- Don't blow your nose for 1-2 weeks.
- Don't pinch your nose before sneezing. Sneeze with your mouth open to avoid sinus pressure.
- Don't drink through a straw!
- While sleeping, do not lie down on the area that was operated on.
- Diving and flying create pressure in the sinuses. Eliminate them for a while.
- Avoid bending forward too much, lifting heavy objects, or playing musical instruments that require blowing.
- Do not smoke for the next 10-14 days. Nicotine interferes with tissue healing and can cause bleeding.
- Do not touch the operated area to avoid causing bleeding or infection.
Any activity that increases pressure in the oral cavity and sinuses is contraindicated! Even walking on stairs can be dangerous!
Allergy to anesthetics
A serious complication during a sinus lift may occur due to intolerance to anesthetics for local anesthesia. An allergic reaction to lidocaine-type drugs is a dangerous condition called anaphylaxis and requires immediate resuscitation measures.
Clinical picture of anaphylaxis:
- the problem occurs a few minutes after administration of the medicine;
- shortness of breath (shallow rapid breathing);
- severe swelling;
- severe tachycardia;
- loss of consciousness due to a drop in blood pressure;
- severe pallor;
- patient's panic.
The doctor’s task is to immediately increase blood pressure readings. This is achieved by administering adrenaline. Then the allergic reaction itself is stopped by using hormonal drugs (prednisolone, hydrocortisone). The patient’s life depends on the speed and correctness of the doctor’s actions, but survival rate during anaphylactic shock remains low.
It is easy to avoid such a complication - a provocative test is performed before administering the anesthetic. To do this, small and diluted concentrations of the drug are administered intradermally and the reaction is observed. In addition, modern anesthesia involves the risk of anaphylaxis, and therefore anesthesia drugs contain small amounts of adrenaline.