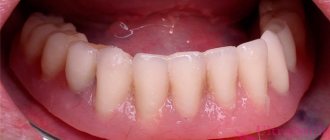
Main or preparation room.
This room is designed to perform the basic processes for the manufacture of dentures (modeling, setting teeth, finishing dentures, etc.). The height of the working room must be at least 3 meters. Each worker must have at least 13 m3 of production space and at least 4 m2 of area.
The walls of the main laboratory room should be painted with light-colored oil paint to facilitate their maintenance. The floors should be covered with linoleum. Windows must meet a number of sanitary and hygienic requirements: 1) the light coefficient (the ratio of the glazed surface of the window to the floor area) is provided for at least 1/5; 2) windows should be located at an equal distance from each other and from the corners of the building; 3) the upper edge of the window should be as close as possible to the ceiling (20-30 cm); 4) window sashes should be narrow and sparse, it is better if they are solid glass; 5) the permissible angle of incidence of light rays formed by a beam of light and a horizontal plane, i.e. its inclination to the horizon, at the workplace is at least 25-27 degrees; 6) workplaces should be positioned so that the light falls directly or on the left side of the worker; 7) the distance of the work place from windows in rooms illuminated by natural side light should not exceed three times the distance from the floor of the room to the upper border of the window opening; the maximum width illuminated by windows on both sides of the room should be practically 15-18 meters.
Fulfilling all these requirements is of great importance for the health of dental technicians, since they perform delicate jewelry work with constant eye strain. When equipping laboratory premises, it is necessary to provide special ventilation units (supply and exhaust), hot and cold water supply with mixer taps. Concealed electrical wiring of the lighting and technical network must also be provided for each workplace.
What is a dental laboratory
A dental laboratory is an entire dental department where dental prosthetics of any complexity are manufactured, and orthopedic structures can subsequently be fixed both on natural teeth and on implants, as well as on completely toothless jaws. Why do you need a dental laboratory? Here it should be understood that dental prosthetics in modern conditions is a rather expensive process that requires qualified personnel (dental technicians), high-precision equipment, which also costs a lot of money. Therefore, the manufacture of prostheses must take place under certain conditions, in compliance with all technological and hygienic requirements.
It is worth adding that dental technicians (sometimes they are also called laboratory assistants, although we would better call them jewelers!) are engaged not only in the manufacture of dental prostheses. Such an important field as orthodontics also cannot do without these specialists. Orthodontic leveling and tooth-replacing plates, therapeutic, preventive and sports mouthguards, and a number of other devices are also manufactured by dental technicians.
DENTAL PROSTHESIS ON 4 IMPLANTS - from RUR 170,000.
The price includes all procedures for installing Osstem implants (South Korea), including anesthesia and diagnostics.
Hurry up to sign up for a free consultation and fix your prices.
Call now or request a call
Opening hours: 24 hours a day - seven days a week
Workplace of a dental technician.
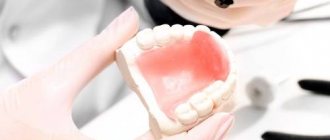
For the convenient, fast and most efficient implementation of all processes associated with the manufacture of dentures, each dental technician must have an individual workplace, which consists of a laboratory table, the surface of which should be marble or, at a distance of 20 - 25 cm from the edge of the table, covered with sheet brass or stainless steel. The surface of the table has a semi-lunar cut-out, in the center of which there is a special cut-out for trimming models - a finagel. Directly below the cutout there are one or two drawers for storing tools and collecting waste of plaster, plastic, metal scraps, etc.
On the right side of the laboratory table there are bedside tables for storing models, materials, prostheses at different stages of manufacturing, etc.
On the surface of the table there is a lighting device on the left or directly above the table, a cable motor or a specially built-in drill, a gas burner, an electric spatula for heating wax and other operations related to wax.
Each workplace must have ventilation (exhaust).
A chair for a dental technician should have a swivel backrest.
Great importance should be attached to the design of the dental technician’s workplace, since this is where he spends most of his working time, and it must meet all the requirements of ergonomics and occupational safety and health. Along with technical requirements, elements of aesthetics and modern design must also be taken into account.
Where analogues of living teeth are made - design and equipment of a modern dental laboratory
Article navigation
- What is a dental laboratory
- What are laboratories?
- License
- Requirements
- Pros and cons of the laboratory
- What types of prostheses can be made?
- How is the laboratory organized?
- Set of necessary equipment
- Main or blank cabinet
- Workplaces for specialists
- Special rooms
- Manufacturing methods
- Manufacturing of prosthetic structures
- How long does it take to make in the laboratory?
- Is a dental workshop really necessary?
Question for a specialist
A dental laboratory is the most important place in a dental clinic where dental prosthetics are performed. But when a person goes to the dentist to install a prosthesis - crown, bridge, clasp, etc., he hardly thinks about the nuances of its manufacture. To have an idea of where and how dental prostheses are made, we suggest getting acquainted with a modern dental laboratory - its structure and equipment, requirements for equipment and personnel.
Plaster room.
In the plaster room, all casting of models, plastering into the occluder, plaster of prostheses into cuvettes before polymerization, release of prostheses from the plaster mold, etc. are carried out. The room contains a large table, the surface of which is made of metal. Hot and cold water is supplied to the table. A hopper for storing gypsum, a press for squeezing gypsum out of ditches, and a regular press are installed on the table. Cuvettes, an occluder, articulators and other equipment and instruments are stored in table drawers or on shelves.
What manufacturing methods are popular today
Over the past decades, scientific and technological progress has led to automation and computerization of many areas of life and industry. If previously dental technicians made products manually using plaster casts - and this is a long and multi-stage process (and the finished products very often have errors), now CAD/CAM systems are gradually coming to the forefront. Yes, the equipment for them is expensive, but it pays for itself in the accurate and fast production of orthopedic structures, and modern materials for artificial teeth last 3-5 times longer. However, the vast majority of dental organizations in our country still work “the old fashioned way” - with plaster models, because cannot allocate funds for the latest equipment and retraining of specialists.
Molding and polymerization room.
In this room, plastic is prepared, molded and polymerized.
In the room there is a table designed for preparing dough from various plastics and molding it into cuvettes. The table should have a smooth surface that is easy to clean. One or two dental presses are placed on the table to press plastic dough into cuvettes before tightening them into clasps. There should also be a hermetically sealed vessel on the table to collect plastic residues after molding into cuvettes in order to reduce the evaporation of methyl methacrylate.
At least two open-type sterilizers or similar devices are installed on a gas stove. One of them is used for melting wax from cuvettes, the other for polymerizing plastic. An exhaust probe (hood) of the ventilation unit must be installed above the table and gas stove.
What are modern laboratories like?
There are 2 main types, which can be either independent or located directly in the clinic:
- independent laboratories: these organizations are independent of any clinic and collaborate with orthopedists, orthodontists and implantologists from different dental medical centers, or doctors working individually in small offices. Independent organizations are quite large, have a large staff of personnel who produce any dental structures for thousands of patients a year. The largest organizations take orders not only from their city, but also from the region, from other cities of the country - depending on the popularity of the company, equipment and the number of orders,
- dental laboratory at a large private dentistry or public clinic: in this case, dental technicians are mainly aimed at producing individual structures for patients of a particular clinic or dental network. Naturally, if the department is not fully loaded with “their” orders, technicians can also be hired by third parties (from other medical centers) to increase their salary and the overall profit of the company.
In any case, all preparatory work - grinding, taking impressions and their direction for the manufacture of a dental structure of the chosen type is carried out exclusively by the attending physician (orthopedist, orthodontist).
Polishing room.
This room houses tables with several cable motors for polishing prostheses made of metals and alloys. A dust collector for polishing dentures made of precious metals (gold, silver-palladium alloys) is installed separately, since all dust, polishing paste, sandpaper and other materials used for finishing, grinding, polishing precious metals are collected and delivered to a metal recycling plant for extraction from of them metals in their pure form. All loop motors are supplied with a powerful dust collection system and good lighting.
The soldering room is equipped with one or more fume hoods, where soldering apparatuses are installed, equipped with compressors for automatic gasoline supply. Fume hoods also usually house a muffle furnace for melting wax from flasks when casting parts from precious metals. In the cabinets, individual parts of test runs are soldered, and they are bleached after soldering. The soldering room is also provided with powerful exhaust ventilation.
Should a laboratory have a license?
There are certain nuances to this issue. For example, if a dental laboratory is a department of dentistry where patients are treated, then such an institution should begin work only after obtaining a license to conduct medical activities. If the laboratory (regardless of its affiliation) performs orthodontic and orthopedic structures from precious or semi-precious materials, then a license is required to carry out jewelry work.
South Korean implant Osstem - from 35,000 rubles.
Hurry up to sign up for a free consultation and lock in promotional prices.
Call now or request a call
Opening hours: 24 hours a day - seven days a week
And if dental technicians work only for themselves (that is, they register an individual entrepreneur or LLC and are not legally affiliated with a medical center), and also do not perform designs made of gold and other jewelry materials, then they do not need a license - since they do not directly treat are engaged. However, in any case, work must be carried out in accordance with the following requirements:
- production and sale of products in accordance with existing legislation,
- compliance with the Order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of September 8, 2011 1027n: regulating the procedure, features and timing of inspection of organizations producing medical devices,
- compliance with Federal Law No. 99-FZ of May 4, 2011, Article 22: indicating that medical equipment does not require licensing from the moment of its full installation and commissioning after maintenance,
- compliance with Federal Law No. 184-FZ of December 27, 2002, Article 46, Part 1: regulating relations arising during the development and production of structures,
- compliance with the All-Russian Classification of Products (OK 005-93 and OKPD-2): products for internal prosthetics are designated by codes 93 000, 96 9600 0, 32.50.22.190.
Foundry room.
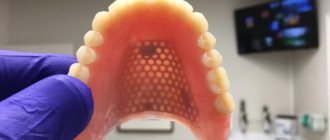
For high-quality production of modern prosthetic designs, such as bridges, metal-ceramic, clasp, etc., individual casting is required, where the components of such prostheses are cast in lost wax molds individually for each patient.
Wide possibilities for the manufacture of such prostheses have opened up thanks to the creation of an original installation, where high-frequency induction melting of metal alloys is combined with centrifugal casting and new technology for preparing casting molds. Using induction currents, you can melt any metal used for the manufacture of crowns, bridges and clasp dentures, removable denture bases, implants, splints in the treatment of periodontal diseases.
How are prosthetic structures made?
The production of a prosthetic structure begins after the dentist receives an impression of the patient’s jaws and data on the assessment of central occlusion (a facebow is used for this) or the results of a digital scan. In the second case, the modeling and manufacturing process takes place with the help of high-precision programs and machines - and here the specialist is more of an observer than a performer (after all, almost all the work is done by machines, and a person only coordinates their actions). Therefore, we will consider the “manual” or classical method of making complete dentures, which is carried out in several stages:
- a working model is created: a plastic impression template (or matrix) is covered with wax and acrylic, a plastic bite block and artificial teeth are installed on this matrix,
- fitting the temporary model to the patient and checking the occlusion data: takes place in the orthopedist’s office. If there is discomfort, the doctor can independently remove excess plastic from the temporary model or send it to a technician for revision. If the model meets all the parameters after the first fitting, then it is sent to the next stage of production,
- production of a permanent structure: a temporary model is placed in a mold, filled with plaster or plastic (to create a permanent base or an analogue of gums), hardened and boiled in boiling water. After this, the wax is removed, and the artificial teeth remain in their places in the model (as they will be located in the finished prosthetic structure). The model is filled with pink-painted acrylic “dough”, pressed and then beaten so that the blank can be removed from the plaster,
- finishing: the sharp edges of artificial gums are ground with a special wheel, after which the entire structure is treated with sand and wet pumice, and then polished until a natural shine appears. After this, the prosthesis is disinfected and sent to the orthopedist for transfer to the patient.
How long does it take to manufacture in our own or in a third-party laboratory?
Production always depends on the workload of the dental organization. And patients of clinics with a dental department have their own advantages, because... they are considered “first priority”, i.e. You will have to wait a maximum of 3-4 days for the production of a new or repair of an old prosthesis, and in some cases a temporary orthopedic structure can be made even in a few hours.
Patients who are treated in another clinic (without a dental department) wait at least 2 weeks for “new teeth” to be made or repaired. And the lion’s share of the time here is taken not by the production itself, but by transportation to fitting and back. If several corrections to the temporary model are required, production may take a month or more.
“I suffered for a long time without teeth, because the old dentures, made a year ago by one prosthetist “through an acquaintance,” cracked with alarming regularity. It was impossible to eat in them. I thought for a long time about what to do until the children found me a good clinic. She gave me to glue my “jaw”. The guys did everything very quickly and did it very well, I must say, because there were no more such frequent breakdowns. They also treated me very cordially, gave me a pension discount, told me “what, how and why” was wrong with my old “teeth”, that they were constantly breaking - there were some violations in the technology, hence the fragility. I will only order new jaws here, because they even have a guarantee.”
Taisiya Andreevna, quote from the dentistry.rf forum