Why do my legs and arms go numb? What diseases can lead to these symptoms? Which doctor should I contact? How to diagnose the cause?
Numbness in the arms and legs is a neurological symptom that most often indicates damage, inflammation, or compression of sensory nerves. Often, numbness is accompanied by pain and unpleasant sensations such as tingling and “crawling goosebumps.” Many nerves are mixed, that is, they contain both sensory and motor fibers. In such cases, numbness is combined with a decrease in muscle tone and impaired movement.
There are many reasons for numbness in the limbs. Most often they are associated with pathological processes in peripheral nerves. The larger the nerve, the larger part of the limb loses sensation. In rare cases, the symptom is caused by disorders of the brain and spinal cord.
Numbness from compression of nerves and nerve roots
One of the most common conditions that leads to compression of the nerve roots is intervertebral hernia. Most often it forms in the lumbar spine, as it experiences the heaviest loads. Fortunately, in most cases, if you consult a doctor in a timely manner, intervertebral hernias can be treated without surgery.
Carpal tunnel syndrome leads to numbness, tingling in the hand and other symptoms. In the wrist area there is a tunnel formed by bones and ligaments. It contains a nerve that, under certain conditions, can be compressed.
In the area of the shoulder girdle and collarbone is the brachial nerve plexus - all the main nerves innervating the arm depart from it. During injuries (most often road accidents), these nerves are stretched and compressed, resulting in numbness and, in severe cases, paralysis of the arm.
With spondylolisthesis, the upper vertebra “slips” a little from the lower one, this leads to compression of the spinal cord and nerve roots, and sensitivity disorders.
Physiological causes of numbness
Numbness occurs with prolonged immobility. Whatever position we are in, some vessels become pinched, and we risk that the nerve endings, which do not receive proper nutrition, will lose sensitivity. Our body must move, changing the areas that have been subjected to compression, and then we will not be in danger of numbness. This usually happens during the day. But during deep sleep, we can lie in the same position for quite a long time without changing posture. And then, when we wake up, we notice that we have rested some part of our body, for example, a hand placed under our head.
Numbness is caused by exposure to cold. When in contact with cold air, the skin loses sensitivity. Local blood circulation is disrupted, and we cease to feel the nerve endings. If this situation lasts longer, frostbite is possible, but in most cases it is enough to rub the area of skin that has lost sensitivity or return to warmth, blood circulation will be restored and the numbness will go away.
If numbness occurs without an obvious connection with a specific situation, then it probably has a pathological cause.
Vascular disorders
One of the complications of diabetes is diabetic neuropathy, damage to sensory, motor and autonomic nerves as a result of impaired blood flow in small vessels. One possible symptom is numbness in the limbs.
There is a large group of diseases - vasculitis. Autoimmune inflammation develops in the vessel wall, it thickens, becomes weakened, and scarring occurs. In the lumen of the vessel, areas of narrowing appear in which blood flow is disrupted. Various organs, including nerves, can suffer from this.
With one of the systemic connective tissue diseases - Raynaud's disease - a spasm of the small vessels that supply blood to the fingers and toes occurs. In response to cooling or stress, a feeling of coldness and numbness occurs in the fingers.
Numb hands keep you from sleeping
Even healthy people can get numb hands during sleep: by placing their left or right hand under their head and deeply immersed in the world of dreams, a young body can sleep through the night without ever turning over to the other side. Moving the limb and lightly rubbing it quickly returns it to normal and the unpleasant sensations are forgotten. It’s another matter when your hands systematically go numb at night, when a tingling feeling appears in the daytime, when others are added to this symptom: pain, weakness, cramps. There are different options for numbness of the upper extremities, each of which may indicate a specific pathology:
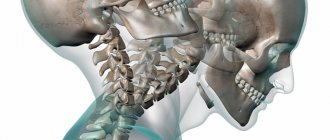
diagram of the nerves of the hand, compression of which is possible due to osteochondrosis and other reasons
- Your hands go numb at night, and during the day you suffer from pain in the head, neck, back (and periodic numbness if you stay in one position for a long time) with osteochondrosis of the cervical spine
and herniated intervertebral discs
; - The cause of numbness in the thumb may be a
hemangioma or
neurofibroma
, which compresses the nerve endings, as well as a compressive effect on the median nerve passing through the carpal tunnel (
carpal tunnel syndrome
).
Meanwhile, if the thumb “does not come to its senses” for half an hour or more, you should not postpone a visit to the doctor, otherwise its muscles may even atrophy
; - ulnar nerve neuropathy
occurs . Some patients may not even know that they have this pathology. The disease develops imperceptibly in those people who are forced to rest their elbow on a hard surface for a long time and thus compress the ulnar nerve (a computer desk, for example), moreover, right-handed people often put stress on their right hand, and in left-handed people their left hand goes numb;
Hands go numb at night, there is pain in the hand, fingers become “wooden” (one or 4, because the little finger is not involved here) in case of median nerve neuropathy or carpal tunnel syndrome
. The most likely cause of pathological changes may be old bruises and fractures, as well as inflammatory processes localized in this area (arthritis and arthrosis). Often a similar picture is caused by edema caused by pregnancy or decreased thyroid function (hypothyroidism);- The symmetry observed in numbness of the fingers and hands is characteristic of polyneuropathy
(
a complication of diabetes mellitus
). By the way, with polyneuropathy, not only the fingers of the upper extremities suffer; the toes often go numb, and, in addition, the surface of the foot can be affected anywhere with the development of the corresponding syndrome. vascular causes of numbness - spasm or damage to arterioles
They lose their natural color (turn white or blue), become cold to the touch, and the fingers hurt and go numb when blood circulation in the microvasculature is impaired, caused by a sharp spasm of blood vessels. This most often occurs in Raynaud's disease and scleroderma
;
- It should be noted that chronic alcoholism and
severe poisoning also contribute to the appearance of signs of polyneuropathy, namely, numbness of the fingers and toes during sleep and in reality; - Of particular concern are cases when only the left hand
and, especially, its thumb are numb, which is most often associated with the development of atherosclerosis, cardiac pathology, osteochondrosis of the cervical and/or thoracic spine. But if the loss of sensation in the thumb of the left hand mainly suggests diseases of the cardiovascular system, then numbness and other symptoms regarding the right hand are perceived as a suspicion of cervical spondylosis, which, however, does not affect young people; - Heart problems
by numbness in the little finger of the left hand, and if it stops showing “signs of life” together with the ring finger, then it is time for the patient to think about a visit to a cardiologist.
If both arms go numb at the same time or an unpleasant tingling sensation is localized in a specific area of the left or right arm, or affects the hands or fingers, and the clinical picture is diluted by additional symptoms (weakness, pain, numbness of other parts of the body), the thought of development of the above-mentioned serious diseases (multiple sclerosis, neoplastic process). If this happens suddenly, then a TIA or stroke can be suspected.
Looking for a reason
Each person has pain and numbness in his own way and, probably, not all options for numbness in the fingers have been considered, however, if stiff limbs are increasingly waking you up at night, and a person cannot find an explanation for this, then perhaps a short list of reasons will help him that cause these unpleasant sensations:
- Professional activity;
- Osteochondrosis of the cervical and thoracic spine;
- Intervertebral hernia;
- Iron deficiency in the body;
- Endocrine diseases;
- Inflammation of the pancreas;
- Pathological changes in joints;
- Venous stagnation;
- Arterial hypertension;
- Sharp spasm of microcirculatory vessels;
- Polyneuropathy.
In addition, to determine the true cause of hand numbness, you should pay attention to other symptoms that accompany these unpleasant, and sometimes painful, episodes:
- Weakness of the hand;
- Low contractility of the muscular system;
- Possible pain in the shoulder and forearm;
- Fatigue, malaise, bad mood;
- Dizziness;
- Heaviness in the head, noise in the ears;
- Inconsistency of movements;
- Unstable blood pressure (jumps and falls);
- Impaired functioning of the vestibular apparatus;
- Flashing "flies" before the eyes.
Some of the listed diseases and their symptoms can cause your toes to go numb, so it’s time to talk about this too.
Video: hand numbness
Video: 3 reasons for hand numbness in the “Live Healthy!” program
Diseases of the brain and spinal cord
One of the most common causes of numbness in different parts of the body associated with brain damage is a stroke, as well as a transient ischemic attack, which is popularly called a “mini-stroke”. Severe injuries to the brain and spinal cord can lead to sensory impairment.
Less common are such lesions of the central nervous system as an aneurysm (a pathologically enlarged, weakened area) of a cerebral vessel, arteriovenous malformation (incorrect communication between an artery and a vein, when blood is discharged directly, bypassing the network of capillaries), tumors of the brain and spinal cord, paraneoplastic syndrome ( damage to the nervous system caused by a tumor that is located outside the brain).
The article lists only the main common causes of numbness in the arms and legs. There are others. In order to get an accurate diagnosis and begin proper effective treatment, you need to visit a doctor.
Numbness of the head, face, lips, tongue
Part of the head may become “foreign” as a result of suffering from the nerves and blood vessels passing there.
Numbness is often accompanied by pain and cramps in individual muscle fibers. Unpleasant sensations can be limited to a specific place on the face, localized in some part of the head (left or right half) or cover the entire head, spreading to the back of the head. Other patients complain only of problems affecting the oral cavity (numbness of the tongue), but do not notice them in other parts of the head. Thus, numb areas can find a place in various parts of the facial skull, oral cavity, move to the back of the head or move to the neck and shoulder girdle:
- Severe headache, convulsive twitching, numbness of the face - symptoms characteristic of trigeminal neuralgia
; - As a cause of pain, numbness of the tip of the tongue, dryness of the oral mucosa without changing its color, glossalgia
, which is often present in people with a main diagnosis of
vegetative-vascular dystonia (
NCD, autonomic dysfunction, etc.); - Autonomic dysfunction
can cause pain and numbness in other parts of the head (face, temporal region, back of the head), as well as numbness of the fingers, trembling, increased body temperature, the appearance of panic attacks and other autonomic disorders; - A sudden numb spot on the face, an aura that followed the numbness with nausea and multi-colored circles, zigzags, flashes, glare in front of the eyes and the addition of a severe headache a little later - a picture that most likely represents a combination of symptoms of migraine
; - Along with dizziness, tinnitus, heaviness in the head and other symptoms, the feeling that the back of the head has become “wooden” is often present in people with osteochondrosis of the cervical spine
and impaired blood flow in the vertebral arteries (vertebrobasilar insufficiency). - Problems in the oral cavity (smooth “varnished” tongue, numbness) can be caused by B12 deficiency anemia
. It should be noted that the triad characteristic of this disease (damage to the blood, gastrointestinal tract and nervous system) entails the appearance of many other symptoms, including sensitivity disorders in different parts of the patient’s body; - A rash, redness of a “dead” area on the face, periodically occurring “lumbago” in a problem area may be signs of herpes zoster
.
Localization of a herpetic infection
in the mouth can be manifested by suffering in the upper or lower lip, tip of the tongue, mucous membrane of the cheeks, and palate. In addition to the fact that with herpes the tongue or an area of facial skin goes numb, this infection, even affecting relatively small areas, can result in a violation of the general condition of the body (high temperature, malaise, fatigue, decreased performance); - The color of the oral mucosa changes, painful ulcers form, the tongue hurts and goes numb when a fungal infection
(candidiasis, thrush) spreads in a given place and stomatitis develops; - Injuries
to the facial and masticatory muscles, previous dental and plastic
surgeries
,
fractures
and
dislocations
can have consequences such as numbness of the head, face, tip of the tongue and other areas located near the affected cranial nerve;
If, with the feeling that your tongue is going numb, you begin to feel dizzy, weakness appears, and numbness in your arms, legs, or other parts of the body is added, there is a danger that this is associated with the development of a serious pathology: transient ischemic attack, pre-stroke, multiple sclerosis, brain tumor, or malignant anemia (megaloblastic anemia).
Video: cervical osteochondrosis as a cause of facial numbness
"Impatient" language
{banner_banstat9}
For no apparent reason, this muscular organ is somehow not subject to numbness. It’s another matter if he turns out to be too “curious” or other (not very terrible) reasons make him numb.
- More often, the tongue of children who are learning about the world around them becomes numb,
although they may not say so.
They taste life in the literal and figurative sense: they can’t wait for the tea or soup to cool down, or out of curiosity they try with the tip of their tongue a metal surface sparkling in the winter sun - such numbness goes away in a couple of days, when the mucous membrane is completely restored. Adults
sometimes behave like children when the tip of the tongue becomes a kind of analyzer; - The tongue goes numb due to the improper use of certain medications
(why it is recommended to swallow chlorpromazine and libexin whole and not chew it) or prolonged and also improper use of medications containing hormones and intended to relieve attacks of bronchial asthma (various types of inhalers); - The tongue goes numb, the sense of smell and taste of smokers changes for the worse,
so the profession of a taster is clearly not in danger for them, but they only have themselves to blame. - Not only the tip of the tongue, but the entire organ becomes numb and refuses to fulfill its functional purpose in the dental chair after the introduction of an anesthetic (Novocaine, Ultracaine) for the purpose of tooth extraction or other operations;
Numbness that has one of the above reasons and disappears when it is eliminated is not a pathological condition and does not require the help of a doctor. Here a person helps himself and draws conclusions about what is possible and what is not: damage to the tip of the tongue in the cold, as a rule, happens only once in a lifetime, but sooner or later everyone goes through this.
In conclusion, I would like to remind the reader that many episodes of numbness are a signal for action. Often, a transient ischemic attack is manifested by a short-term decrease in sensitivity and may soon be forgotten, however, today is a TIA, and tomorrow is a stroke, so if there are concerns that the numbness is associated with problems in the head, you should immediately call an ambulance, because acute cerebrovascular accident (stroke) ) can also happen on the way to the clinic.
Who should I contact?
A neurologist is involved in the diagnosis and treatment of neurological disorders, such as sensory loss and numbness in the extremities. In order to correctly assume what was the possible cause and choose the right direction of the diagnostic search, the neurologist must examine the patient, find out in which parts of the body numbness occurs (only in the fingers, in the hands or feet, in the entire arm or leg, in one limb , or right and left symmetrically), are there any other neurological symptoms or concomitant diseases.
Depending on the results of the examination, the neurologist may refer you to other specialists:
- For vasculitis, Raynaud's disease - see a rheumatologist.
- For cardiovascular pathologies, see a cardiologist.
- For diabetes mellitus, see an endocrinologist.
- In case of tumors or injuries, see a neurosurgeon.
- For infectious diseases - see an infectious disease specialist.
- In case of poisoning with harmful substances at work, contact an occupational pathologist.
Provoking factors
A completely healthy person rarely experiences numbness; they may indicate a hidden pathology in the form of:
- consequences of injuries;
- various diseases of the spinal column;
- joint inflammation;
- degenerative or destructive diseases of the cartilage and ligaments of the hand;
- nervous and mental disorders;
- persistent decrease in blood pressure;
- diseases of the endocrine glands.
There are currently no clear scales that determine the severity of hand numbness. If the unpleasant sensations bother you from time to time and go away after simple movements or rubbing, then you hardly need to worry. However, in case of frequent repetition of numbness, when it happens several times a week or the discomfort increases, you should consult a doctor as soon as possible, as this may be the beginning of the disease.
Examination for numbness of extremities
- Depending on the suspected cause of numbness in the limbs, the doctor may prescribe different types of diagnostics. X-rays help diagnose diseases associated with disorders of the skull and spine, such as intervertebral hernia. If there is a suspicion of vascular pathology, angiography is performed - an X-ray examination with the introduction of a contrast solution into the vessels.
- If necessary, you may be prescribed other imaging methods: ultrasound, CT, MRI.
- In order to check in which nerves the conduction of impulses is impaired, electroneuromyography is used - a study using special electrodes.
- Sometimes they resort to the method of evoked potentials. Special sensors are placed on the patient's head to record brain activity. The affected nerve is stimulated through the skin using electrical impulses and the brain is observed to respond to the stimulation.
Since dozens of different reasons can lead to numbness in the arms and legs, the diagnostic program must be individual for each patient. In some pathologies, if left untreated for a long time, even more serious, irreversible neurological disorders may occur. Visit a neurologist, make an appointment by phone: +7 (495) 120-08-07
Why do limbs become numb normally?
The reasons for tingling and the feeling that some area has become “foreign” in healthy people arise primarily from their behavior and the situations in which they, of their own free will or at the whim of others, found themselves:
- When standing for a long time
on a crowded bus, even people who know nothing about varicose veins and venous congestion can feel their toes going numb. Something similar happens if you hold onto handrails for a long time, which are located at a sufficient distance (you have to reach), hold the telephone receiver for hours without changing your ear and hand, or try to hang curtains from the ceiling (hands linger for a long time above the level of the heart), however, in such cases, problems arise in the upper extremities - the fingers go numb; - A gaze fixed on the monitor, tense muscles of the face and neck,
rapid hits on the keyboard, an inability to react to others are signs that a person is immersed in a computer game or carried away by an interesting job. When he descends “to the sinful earth,” he will discover numbness in the tips of his fingers, or even the entire hand, suffering in the gluteal muscles and tingling in the legs. Occupation is perhaps one of the most common causes of hand numbness. Performing monotonous movements day after day with hands raised above the heart, a person dooms his limbs to a constant lack of the required amount of blood, which will certainly sooner or later result in their numbness. After some time, the work associated with carrying heavy loads becomes noticeable, as well as work involving mental tension, anxiety, and stress; - Numbness of the toes and hands in frosty weather
indicates that the limbs are asking for warmth, where they will quickly warm up and come to life. An area of the face that has turned white and numb in the cold can become frostbitten if measures are not taken in time. - Sound, healthy sleep often involves lying in one position,
which does not fully ensure the movement of blood in compressed areas. Numbness of the hands, the back of the head, or some area of the face during sleep is not such a rare phenomenon, which requires taking a break from pleasant dreams and massaging the numb surface.
Healthy people's hands go numb at night because the weight of the body or uncomfortable tight clothing compresses the blood vessels, and the hand comes away after the person releases it and thus restores blood flow.
A person cannot always prevent unpleasant tingling and numbness, but he must strive for this. After all, it’s not difficult to worry in advance about comfort during sleep, choose comfortable bedding (preferably orthopedic), put on soft, luxurious pajamas, and take a comfortable position.
You should treat a walk in sub-zero weather in the same way: if you expect to stay in the cold for a long time, you need to choose the right clothes and shoes.
It is somewhat more difficult for people performing work that constitutes their functional responsibilities, however, here too you should try to alternate static loads with exercises that restore blood flow.
Symptoms
A person in a state of alcoholic intoxication does not pay attention to the first alarming symptoms: pain in the legs, muscle weakness, mild numbness. Moreover, they begin to appear from the very beginning of alcohol dependence. Gradually the symptoms become extensive:
- • convulsions appear;
- • fingers and hands become numb;
- • the sensitivity of the legs is impaired - the symptom is described as “woolly” or “soft” legs that do not support their owner;
- • tendon reflexes decrease;
- • incomplete and complete paralysis of the legs is diagnosed (in the severe stage);
- • shins and feet become bluish and cold;
- • pigmentation and trophic ulcers are formed;
- • muscle atrophy occurs.
At first, symptoms affect only the legs, but gradually spread to the whole body. In the later stages, mental disorders begin: memory loss, impaired speech function, sudden mood swings, manic states, disorientation.
The greater the damage, the more pronounced atoxic lesions appear, which, together with impaired tendon reflexes, resemble late neurosyphilis.
Hyperhidrosis, edema, disruption of the nerves of the skull - all these are consequences of the disease.
Causes of alcoholic polyneuropathy
The disease is provoked by alcohol intoxication and the associated toxic effect on peripheral nerves, their damage, and metabolic disorders. There are several additional factors that cause alcoholic polyneuropathy:
- "dietary". Unbalanced, poor nutrition often accompanies alcohol addiction. The diet contains an excess of carbohydrates and a lack of vitamins. Deficiency of folic acid, thiamine, and other B vitamins slows down the utilization of ethyl alcohol and its breakdown products, which increases the toxic effect of alcohol;
- oxidative stress. With constant consumption of alcohol, excessive formation of free oxygen radicals occurs, and the activity of antioxidants decreases. The balance of pro-oxidant and antioxidant systems shifts, which causes disturbances in the activity of cellular structures, and, in particular, in the work of endothelial cells (“responsible” for the metabolic support of the brain, regeneration, tissue growth, and perform barrier functions). A decrease in endothelial activity provokes endoneurial hypoxia, against which neuropathy appears;
- direct damage to the peripheral nervous system. Occurs under the influence of alcohol and ethyl alcohol metabolites. Acetaldehyde destroys the barrier protection of the nervous system and damages the nerve fiber.
Treatment with folk remedies
The following recipes help with numb hands:
- as a compress or therapeutic bath, use a mixture of 2 liters of milk, 600 g of salt and 50 g of honey, heated to 60? C;
- apply an infusion of wild rosemary with apple cider vinegar (1:3) 3 times a day;
- infusion of garlic (several cloves) in vodka (400 ml) taken orally, 3-5 drops dissolved in water;
- for 1 liter of vegetable oil - 100 g of ground black pepper, cook for 30–40 minutes, rub the cooled product into the skin of the affected limb.
How to determine the true cause?
Initially, a patient with numbness of the finger is examined by a neurologist and, based on the clinical picture, determines the necessary list of examinations.
“
The Clinic of Professor Kinzersky has an extensive diagnostic base in all possible areas to quickly and accurately determine a patient’s diagnosis.
“
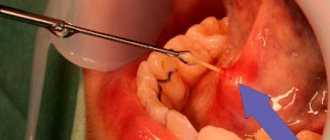
The gold standard for most carpal tunnel syndromes is electromyography (EMG). Based on the results of the study, the doctor determines how much the function of a particular nerve is reduced.
Ultrasound of peripheral nerves is used to assess structural changes in nerves .
elastometry technology on the AIXPLORER V6 ultrasound device made it possible to measure the pressure in the tunnel area (it is significantly increased compared to the norm) and control it during treatment.
Diagnosis and treatment
Based on the medical history, study of symptoms and physical examination, the doctor prescribes an examination plan, which includes both instrumental and laboratory examination methods.
To treat numbness, first of all, it is necessary to find out the cause of this symptom. If numbness is associated with circulatory disorders, diabetes or multiple sclerosis, the underlying disease is treated, both with the help of conservative treatment methods and surgical methods (for example, for vascular diseases). For orthopedic problems, such as disc herniation, osteochondrosis, treatment can also be either conservative or surgical (for example, when it is necessary to decompress the nerve root).
Numbness of the left hand
If your left hand is numb, you should always think about whether a person has heart disease, from mild forms of pathology to very complex and even deadly variants. What heart diseases can numbness in the left arm indicate? Pathological conditions that are accompanied by deterioration of sensitivity in the upper limb on the right include:
- high blood pressure of various origins;
- angina pectoris;
- myocardial infarction.
All these heart diseases require attention from a cardiologist, as they are fraught with consequences and can cause death in the patient.
If numbness of the left arm does not go away after changing body position, lasts more than one hour and is accompanied by pain in the area behind the sternum, then the patient should immediately seek qualified help.