Studies using a magnetic resonance imaging scanner are informative. A distinctive feature of MRI is a targeted examination of a selected area and the ability to detect pathology at the very beginning of development. But patients are prevented from undergoing this procedure by the presence of contraindications. Many people are particularly interested in whether it is possible to do MRI of the pituitary gland or other parts of the body with dental implants and metal crowns. More details later in the article.
When you can and cannot do an MRI of the brain with dental implants and metal crowns
Article navigation
- How does MRI work?
- When and who should not undergo the study
- MRI in the presence of an implant
- Do metal dental implants move?
- MRI of the head, brain and neck with implants
- Risks of MRI diagnostics with titanium dentures
- Should I tell my doctor about implants?
- Admission to tomography in the presence of crowns
- MRI of the brain in the presence of braces
- Myths for patients with implants
question to a specialist
In the age of modern technology, only the lazy have not heard of such a wonderful diagnostic device called a tomograph. There are several types, but the most accurate is the magnetic resonance machine. Doctors of various specialties refer for MRI. But a number of patients have a question: is it possible to do an MRI with implants and metal crowns on teeth? The answer to this question will surprise many - read further in our article about diagnostic methods for people with metal dentures and contraindications.
How does MRI work?
Let's figure out what a magnetic resonance imaging scanner is and how it works. This device is designed for targeted examination of tissues and blood vessels of the body. Modern devices with a power of 1.5-3 Tesla are capable of identifying problem areas smaller than 0.2 mm. The principle of operation is based on radio waves and the magnetization properties of the nuclei of hydrogen atoms, which are located everywhere in the body (and we remember that a person is 70% water).
The nuclei of hydrogen atoms “respond” to a powerful magnet (enter into resonance), and a special program records a picture and displays it on a computer. The diagnostic result consists of many virtual sections or sections of the desired organ - the brain or spinal cord, liver, vascular system, etc. And the radiologist makes a written report on the data obtained.
%akc54%
In general, there are two types of tomographs that are installed in specialized institutions - a cone-beam tomograph (CT) and an MRI machine itself. The first, even with implants, does not distort the image, but is also not suitable for studying small areas (for example, brain tumors). During an MRI, a magnet may cause some image distortion in the area of metal products in the body - but whether implants are included in this list will be discussed later.
On a note! Tomographs are also available in dentistry - they are less powerful and give a much worse picture (however, for the needs of the clinic this is enough). Neither the presence of implants nor the presence of metal crowns is a contraindication to this study. However, such devices are cone-beam and do not contain magnets.
When and who should not undergo the study
In response to the question: “Is it possible to perform MRI with dental implants?”, doctors answer in the affirmative. But a number of conditions must be observed - they do not relate to the implants themselves, but are of a general nature. First, let's systematize the contraindications to this study. They are divided into 2 groups – relative and absolute. The following are considered absolute contraindications:
- any large ferromagnets in the human body: large metal implants on bones, middle ear prostheses, metal fragments in soft tissues. But dental implants are not included here,
- electronic stimulators: on the heart, middle ear prosthesis.
Ferromagnets are substances and alloys containing nickel, chromium, steel, cobalt, and any compounds with a large percentage of iron. Highly susceptible to magnetism. In a powerful magnetic field, ferromagnets can move if they are located in soft tissues. The consequences of such a movement are almost always unpredictable and can cause harm.
Relative contraindications - this term hides restrictions on MRI that can be circumvented. For example, undergo diagnostics later or on a different device. Let's consider the relative contraindications to MRI:
- inability to lie still during the examination: this may include small children and patients with nervous disorders. They are put into a short medicated sleep,
- early pregnancy: due to the lack of confirmed data on the harmful effects of the magnetic field on the fetus,
- hemostatic clamps in blood vessels,
- tattoos: if metal is present among the components of the pigment, then it will heat up in the device, even causing burns,
- braces, crowns or other prosthetic devices that contain ferromagnetic metals - primarily steel. But there are some peculiarities - if the prosthesis is in the mouth, and you do an MRI of the leg, then there are no risks.
Contraindications mainly relate specifically to MRI, and the closed type - when the patient is completely placed in the machine. There are also open-type tomographs - they have fewer restrictions for diagnosis, but their accuracy is lower.
Contraindications for MRI
When prostheses with plates are securely attached to the bones and do not move, then implants of a different location can easily move under the influence of a magnetic field. Therefore, under such circumstances, MRI is not performed - it is strictly prohibited. The main constructions for which screening cannot be done are:
- artificial heart valves;
- clips on vessels of different locations;
- ear implants;
- electronic pacemakers;
- artificial eye lens;
- Ilizarov device;
- insulin pump;
- impressive sized metal structures.
For consultation and clarification of all questions regarding diagnostics, call the hotline. A representative of the support center will help you choose a clinic for tomography, tell you about the restrictions, and will be able to book a place for an appointment with a doctor with a bonus of up to 1,000 rubles.
Magnetic resonance imaging in the presence of a dental implant
So why wouldn't a dental implant be an absolute limitation to MRI? Here you need to understand that implants are made from metals endowed with diamagnetic and paramagnetic properties. What it is? The operation of an MRI scanner is based on the magnetizing properties of certain substances. So, para- and diamagnets react weakly to powerful magnets, such as those installed in the tomograph.
Paramagnetic materials are almost not subject to the action of a magnetic field and do not shift in it. These are the following materials:
- titanium: the main metal from which modern implants are made,
- aluminum: medical gurneys made of this metal can be brought into the room where MRI is performed,
- platinum: softer and more expensive than titanium.
Diamagnets - magnetization is not significant, it occurs in the direction of the applied field:
- hydrogen: it was the presence of this element in the human body that made magnetic resonance imaging possible,
- copper: oxidizes quickly, not suitable for implantation into the body,
- gold and silver: very soft metals.
Magnetic resonance imaging can be performed on any part of the body. If the organ being studied is located in the lower half of the body, then the implant will not affect the result in any way. And if the upper part is examined, then there may be some distortions - however, the implant itself will not move, that is, it will not be magnetized and will not break out of the body.
How are crowns removed from teeth, indications?
In cases where the crown or bridge has moved during the MRI, they are removed and installed again or replaced with new prostheses. They do this in the following ways:
- sawing - the prosthesis is drilled out using drills with a cooling system; after removal, the structure is unsuitable for further use;
- ultrasound – ultrasonic waves destroy the cement, and the crown is easily removed from the stump;
- Koch apparatus - a special drill breaks the bond with gentle pushes, then the structure is lifted and removed;
- Coronaflex apparatus - compressed air is supplied under the edge of the prosthesis, this is the only method that eliminates damage to the structure and supporting teeth;
- special tools or sliding crown removers - used after destruction of the adhesive base using one of the above methods.
Orthopedic structures are also removed in case of resorption of cement, chips of ceramic lining, damage to the frame, inflammatory processes in the root canals, or the patient’s desire to replace the prosthesis with a better one.
It doesn't hurt to remove crowns
Is it possible to shoot on your own?
Sometimes the bridge or crown is so loose that the patient can tear it off himself. However, this should not be done, because... possible:
- damage to the prosthesis;
- fracture of the stump or root system of the tooth;
- traumatization of the mucous membrane or adjacent units.
If the denture becomes loose, the only correct option is to contact a dental clinic.
Does it hurt?
Removing dentures does not hurt at all, unless, of course, the patient rips them off himself. Because crowns and bridges are placed on already decayed teeth; in most units the pulp has been removed. Therefore, unpleasant sensations are excluded. There may only be a feeling of pressure on the jaw.
If the tooth under the crown is not pulpless or its roots are inflamed, dentures are not removed. The doctor administers anesthesia to eliminate pain.
How long does the procedure take?
The duration of prosthesis removal depends on the method. So, using a cut, the structure is removed in 10-15 minutes. But preliminary decementing of crowns using ultrasound, a Koch or Coronaflex apparatus can take several visits.
Artificial teeth are not an obstacle to magnetic resonance imaging. Modern designs are made from bioinert materials that do not harm the patient and do not affect the examination. If there is one of the items prohibited for examination in the mouth, it is removed and then fixed again or replaced with a new one.
Do metal dental implants move during examination?
To understand whether an implant can move under the influence of a magnet, you need to know what it consists of. Dental implants are a modern replacement for your own lost teeth. It consists of a metal implant (reliably fixed in the jaw bone and replaces the tooth root), an abutment (connecting part) and a crown - an analogue of the upper part of the tooth. If the prosthesis is installed efficiently, then it is not at all perceived as a foreign body. It looks like it's your own tooth. These sensations are achieved thanks to the special structure of the implant - it contains micropores, and bone grows into them over time. Thus, it fully replaces the tooth root and does not wobble.
Why the implant does not move during MRI:
- rigid fixation in the jaw: the bone securely holds the tooth root prosthesis in place,
- consists of titanium: i.e. does not magnetize and does not heat up.
MRI of the head, brain and neck for patients with dental implants – can it be done or not?
The brain is the control center for all organs of the body, and its proper functioning is vital. And nature could not leave such a necessary organ without protection, i.e. skulls But it is precisely this that creates a serious obstacle in the study of diseases of the brain and its blood vessels. X-rays and ultrasound cannot “enlighten” the skull, and computed tomography is low-power and will not be able to show pathological areas smaller than 1 mm in size. For this reason, MRI is prescribed to study the soft tissues of the head - the brain and blood vessels - as the most informative method.
MRI of the head with titanium dental implants has no contraindications and can be done. Just first you need to check with your dentist what material the implant is made of (although you should also have this information on hand), but the prosthesis. If you have metal-ceramic crowns installed, they may contain steel impurities - then it is better to refuse magnetic resonance imaging and undergo PET (positron emission tomography) or CT (computed tomography).
On a note! If one center refuses to give you an MRI, go to another - modern devices can muffle the “noise” from metal implants. But, naturally, these are the latest generation devices and you need to look for them.
Before undergoing an MRI, you must indicate in the questionnaire that you have a dental implant. Tell the specialist about this immediately before diagnosis.
Risks of MRI diagnostics with titanium dentures
Due to the fact that prostheses implanted into the jaw bone are mostly made of paramagnetic titanium, magnetic resonance imaging with dental implants is a completely feasible and completely safe procedure. Titanium is a biologically inert material, i.e. it is not able to oxidize and release harmful substances during contact with bones, muscles and blood vessels of the human body. Of course, in medicine it is not pure titanium that is used, but its alloys with a small amount of other elements. This is done to make the material durable and light. But they also do not have any negative impact when undergoing an MRI.
By the way, titanium is comparable in strength to steel, and in lightness - to aluminum. Therefore, this metal has received recognition not only from dentists, but also from traumatologists and orthopedic surgeons.
Titanium is also used to produce abutments, gum formers, and metal arches (bases) for dentures.
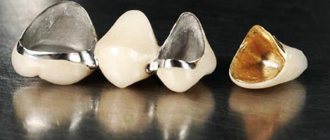
What are endoprostheses made of in the 21st century?
All plates with pins used in traumatology and orthopedic departments consist of various alloys. Different implants contain different amounts of paramagnetic and ferromagnetic materials. Its properties depend on the composition of the product. Not all prosthetics are created only from metal. Most are made of ceramic or polyethylene. The latter does not interact in any way with magnetic vibrations, which means it is 100% safe for MRI. However, there is one point. Ceramics usually contain aluminum oxide, but it does have some magnetic susceptibility. Therefore, it is necessary to notify the doctor about the presence of any prostheses in the body.
There are several possible combinations of materials in built-in structures:
- ceramics;
- metal;
- ceramics with polyethylene;
- metal together with polyethylene;
- ceramics with metal alloy.
Artificial compositions of joint additions include:
- titanium;
- zirconium;
- cobalt;
- chromium;
- tantalum.
Having studied the component parts of the implant, it will become clear exactly how it will respond to electromagnetic resonance.
The magnetic abilities of endoprostheses are determined not only by the material used to make the product, but also by its shape and dimensions. Pins and steels, the length of which reaches more than 20 cm, can heat up above the permissible values.
Should you tell your doctor that you have dental implants?
A patient with installed dental implants must notify the doctor about this. Then the specialist makes the necessary adjustments, taking into account the location and composition of the prostheses. These settings eliminate the appearance of blurred distortions (also called field artifacts). And then the results of the examination will be clear and precise.
But if a person decides to keep silent about “non-native” teeth, then the picture will turn out blurry, because implants, although slightly, do affect the quality of the pictures. And such a careless patient will have to pay for the procedure and undergo diagnostics again. Why does the blame in this case fall on the patient? Because before the MRI, he will definitely be asked about the presence of implants and what kind of metal they are made of.
“Mom 2 years ago had an MRI of the head and blood vessels, using a high-field tomograph. And she’s had implants installed in her upper jaw for about 5 years now. And nothing, everything went fine. There are no special sensations during the procedure. Just be sure to tell the girls at the reception that there are implants before starting the procedure. They warn the doctor themselves, and then the device is reconfigured.”
Vitalina, from correspondence on the woman.ru forum.
Myths about MRI
Our team has collected for you the top 3 common false theories about magnetic resonance scanning:
- During an MRI, the implants heat up and move. The specific gravity of the metal fastening elements of the structures is minimal, which means there are no defects in the examination results and no discomfort for the patient. But it is imperative to notify doctors about the material from which the product is made. Safe prostheses are considered to be those made of zirconium dioxide, ceramics or other expensive alloys. If you have a metal-ceramic structure, you need to clarify which metals and impurities were used in the creation.
- MRI cannot be performed during pregnancy. This is only half a lie. Due to the fact that in the first trimester the formation of tissues and organs in the unborn child begins, any effect on the fetus (chemical, physical or biological) must be excluded. In late pregnancy, tomography allows you to determine the position of the baby and determine the size of the mother’s pelvis. The results of the examination allow the obstetrician to prepare for childbirth without consequences for the child and the pregnant woman.
- MRI with prostheses is painful. Complete lie. Tomographic examination is one of the most painless and safe diagnostic techniques. MRI is allowed even with titanium inserts. Scanning can only be denied if the structure is implanted with steel, since it can heat up and move under the influence of magnetic vibrations. Only such a process can lead to injury to the subject.
If you have implants or not, but want to undergo an MRI, use. Our platform is designed to quickly search and select a clinic for diagnostics. The service presents dozens of medical centers, collects current prices for tomography and real reviews from visitors. To make an appointment, just call the hotline. When you reserve a place with a doctor using our resource, you will receive up to 1,000 rubles as a gift!
Is it possible to have access to tomography if I have crowns?
Are there any special features in MRI diagnostics for patients with dental crowns? This question also worries many. Some people worry that under the influence of magnets, metal, metal-ceramic crowns and pins can fly out of their places and damage something in the mouth. Experts note that metal crowns and pins have absolutely no effect on MRI results, but only if they are made of pure ceramics, zirconium dioxide or high-quality alloys. If the crown is made of metal-ceramics, then it is worth clarifying the metal content in the base - it is likely that you will not be allowed to conduct research.
Other problems with crowns
In addition to affecting MRI results, metal crowns cause other problems: they break, chip, and the root canals and gums underneath may become inflamed, or the tooth stump may collapse. But most often, fixed dentures become loose or fly off.
What to do if the crown of a tooth is loose or has fallen off?
Crowns or bridges made of diamagnetic or ferromagnetic metals may begin to wobble after MRI. This is due to the displacement of the prostheses during the examination and subsequent decementation. In the future, the structures will fall out.
The presence of metal structures does not affect the results of a CT examination
However, the causes of poor fixation are not always related to magnetic resonance imaging. Sometimes dentures become loose and fly off due to:
- washing out the cement from under the crown - if its edge does not fit tightly to the neck of the tooth, the bond (adhesive composition) is gradually destroyed under the influence of saliva and drinks;
- poorly made design - it will not fit tightly if it does not follow the shape of the tooth in the smallest detail;
- small volume of the stump or its destruction - the remains do not hold the prosthesis, and it flies off.
Regardless of the reason, contact an orthopedic dentist. He will correct a loose or fallen crown and re-fix it. If the prosthesis cannot be repaired, a new one will be made and installed.
Swallowed a crown...
When a crown falls out, it is often swallowed along with saliva, food or drinks. There is no reason to worry - it will come out on its own along with the feces in a few hours or 1-2 days.
The only dangerous situation is when the prosthesis splits. In this case, an x-ray is taken, the location of the bridge or crown is determined, and then the stomach is washed out or an enema is given.
If you swallow a crown, it will be passed out in your stool within a maximum of 2 days.
But, in any case, the swallowed crown is reported to a gastroenterologist, surgeon or traumatologist. Magnetic resonance imaging is postponed until the structure is removed from the body.
MRI of the brain in the presence of braces
At the beginning of the article, we talked about relative contraindications to undergoing magnetic resonance imaging. These include various bracket systems. Such structures rarely contain titanium (the structure is still bulky, and titanium is not a cheap metal), so they are made from inexpensive ferromagnetic materials (mostly medical steel). These materials, in turn, are magnetized in an MRI scanner. Therefore, braces, retainers and clasp dentures are prohibited from MRI scanning of the head and neck.
But you can undergo diagnostics of the lower part of the body or in an open-type apparatus.
But if the clasp prosthesis is easy to remove and undergo diagnostics without problems, then difficulties may arise with braces. There are 3 ways here:
- Braces and retainers can be removed: if urgent examination is required,
- undergo PET or computed tomography: there are no contraindications for them,
- undergo an examination after the end of the period of wearing braces or retainers: if the diagnosis is not urgent.
DENTAL PROSTHESIS WITH 4 OSSTEM IMPLANTS - RUB 170,000!
Implantation even with bone tissue atrophy. Work guarantee! Save RUR 20,000.
on promotion >> Free consultation with an implantologist +7 (495) 215-52-31 or write to us
Computed tomography of teeth
Why is CT scan needed in dentistry?
This research method allows you to see various pathologies and diseases of the jaw and bone tissue of the patient’s face in a three-dimensional image, in other words, thanks to a 3D image. Such diagnostics helps to identify abnormalities in the early stages, and as a result allows for their timely treatment. Also, a dental CT scan, which shows in detail the structure of the jaw, is of great importance when installing dental implants for a patient. This diagnosis plays a decisive role if surgery on the maxillofacial region is required. The dentist gives the patient a referral for a computed tomography scan of the teeth to avoid surgical errors, to identify anatomical features and determine the exact location of the incision. The indications for performing a dental CT scan include the following:
- patient's malocclusion;
- various injuries of the maxillofacial apparatus (these include dislocations, bone fractures);
- presence or suspicion of unerupted teeth;
- presence or suspicion of tumors, cysts;
- oral cavity subjected to carious destruction;
- anatomical abnormalities in the development of the patient's jaw;
- postoperative period (to control the recovery and healing process).
Myths for patients with implants
The most common myth about magnetic resonance imaging scares most patients. An incompetent interlocutor - a work colleague or a neighbor next door - may say in horror: “What, you can’t do a tomography with implants - the prosthesis will be pulled out of the jaw by a magnet and it will stick somewhere, or the device will be damaged.” And the person will believe and refuse MRI in favor of a less informative, but more harmful examination (for example, computed tomography).
Every patient referred for magnetic resonance imaging should remember that dental implants are not a contraindication. And if you are denied such an examination, then you need to look for a clinic with modern equipment and a qualified radiologist.
Author: Vasiliev A. A. (Thank you for your help in writing the article and the information provided)