With age, people's dentition becomes incomplete; various reasons are to blame: dental diseases, injuries, heredity. Over time, everyone faces the problem of choosing technology and ways to restore it so as not to suffer from imperfections in the functions of chewing, speaking and smiling. Patients often contact Amazing Price Dentistry asking for advice on the specifics of materials for modern prosthetics and choosing the best option for specific clinical conditions. Let's consider the question of which dentures are better to install - plastic or ceramic.
What are dental crowns
This is an artificial denture that is installed on a pre-treated natural crown. The purpose of prosthetics is to restore the anatomical shape, aesthetic appearance, and chewing function. Crowns can also be part of some other orthopedic structure: support for a partial removable or fixed denture, splinting for loosening of the dentition, etc.
Crowns on teeth
The design must meet certain requirements:
- restore the anatomical shape of the tooth, its aesthetics and color;
- support chewing and speech function;
- fit well to the neck of the destroyed tooth, make correct contact with neighboring units, as well as with teeth on the opposite side, without creating an obstacle to the closure of the dentition;
- do not interfere with the motor activity of the lower jaw;
- do not cause allergic reactions or tissue irritation.
All designs of this type have their pros and cons.
pros
Of all types of dentures, this one has a number of positive qualities, in some cases giving advantages over other types of prosthetics:
- rapid restoration of appearance and chewing function;
- large selection of materials for prosthetics;
- correct distribution of the load, eliminating the risks of abrasion of adjacent teeth and malocclusion;
- prevention of destruction of periodontal tissues and atrophy of jaw bone tissue;
- the ability to install several prostheses at once;
- if the root is partially destroyed, it is possible to install the prosthesis on a pin; if there is a complete absence of a root, it can be installed on an implant (titanium root).
Minuses
Negative qualities:
- the need to grind a tooth, sometimes a healthy one, if it performs a supporting function;
- a short period of discomfort after installation of the prosthesis; with the correct selection of material and compliance with installation technologies - very short;
- allergic reactions to certain dental materials;
- possible complications are reduced to a minimum with proper prosthetics;
- high cost of high-quality materials and insufficiently good appearance of cheap ones.
Preparation for prosthetics and its stages
Whether it is metal-ceramics or metal-plastic, the general technology of prosthetics with these materials is practically the same.
Preparatory activities include
professional visual examination and control x-ray to ensure there are no foci of inflammation. If there are any, they must be eliminated therapeutically;- if there are previously sealed canals, monitor their condition; if necessary, damaged seals are removed and new ones are installed;
- tooth depulpation procedure - nerves are removed followed by canal filling. When installing a prosthesis on a front tooth, this is mandatory; in the case of a multi-rooted tooth, the decision is made by the dentist based on the individual characteristics of the patient and the condition of the tooth. This need is caused by the high probability of pulp destruction with accompanying unpleasant symptoms, which will entail removal of the prosthesis and additional treatment. Therefore, this moment is extremely important;
- in case of carious tooth damage, therapeutic treatment is carried out until the process is completely eliminated;
- if the tooth is destroyed by less than 50%, then a pin is installed in the root canal. Next, the tooth crown is restored using filling materials;
- complete or critical destruction of the coronal part of the tooth requires the installation of a stump inlay.
Stages of prosthetics
- circular grinding of the tooth to the thickness of the walls of the crown, thus forming a stump;
- the color of the future prosthesis is selected using a special scale;
- a measuring impression is taken, on the basis of which the dental technician creates a metal-ceramic or metal-plastic prosthesis;
- the patient is temporarily (7-10 days) fitted with a special plastic crown. This is done to protect the ground tooth and eliminate the patient’s psychological discomfort, because a ground tooth looks unaesthetic;
- direct installation of the finished prosthesis, including fitting and, if necessary, adjustment.
Indications for installation of dental crowns
Dental crowns are installed for the following diseases and conditions:
- injuries and pathological processes of hard dental tissues, accompanied by the destruction of crowns by more than half and the impossibility of restoration with fillings - deep caries, increased abrasion, fractures and dislocations, wedge-shaped defects;
- congenital and acquired defects in the shape, height and position of teeth; congenital underdevelopment of crowns (hypoplasia);
- changes in tooth color - fluorosis, darkening after treatment;
- for support with partially removable and fixed dentures;
- as part of another orthopedic design, for example, splinting loose teeth due to periodontal diseases (periodontitis or periodontal disease).
Contraindications for installation
To place a crown on a tooth, you need to take into account not only the indications, but also the contraindications. Absolute contraindications include:
- healthy (intact) teeth; the exception is the situation when they are used as a support for other orthopedic prostheses;
- high pathological tooth mobility;
- chronic foci of infection of dental tissues that cannot be treated.
Relative:
- insufficient oral hygiene, caries - prosthetics are carried out after complete sanitation of the oral cavity;
- destruction of the crown by more than half - if the root is preserved, prosthetics are carried out after the pin is installed;
- destruction of the tooth root with its subsequent removal - prosthetics after implantation of a titanium root;
- chronic periodontitis (inflammation of the ligament that holds the tooth in the cell) - prosthetics after complete elimination of the causes of the disease - cysts, fistulas, etc.;
- not fully formed dental roots;
- severe general diseases - high blood pressure, stroke, myocardial infarction - prosthetics are possible after stabilization of the patient’s general condition.
Let's compare the disadvantages
The materials discussed in the article have not only advantages, but also disadvantages.
Disadvantages of metal-ceramic crowns
- It is necessary to grind down more of your own tooth tissue due to the large thickness of the walls of the prosthesis.
- Almost always, tooth depulpation is required.
- An allergy to metal (except precious metals) may develop.
- If manufacturing technology is violated, artificial teeth may have a darker color.
Disadvantages of metal-free crowns
- High price.
- Complex manufacturing process.
- Slightly inferior in strength to metal.
Based on the totality of these characteristics, it can be noted that zirconium or metal-free crowns are better than metal-ceramics and can be recommended to those patients who want to get the most beautiful smile.
Types of crowns for teeth
Since dental crowns are designed for different purposes, they can be made from different materials. The orthopedist decides which crowns are best to put on the teeth in a particular case. Based on the material of manufacture, the following types of dental crowns are distinguished: metal, plastic, ceramic, metal-ceramics, glass-ceramics, zirconium dioxide, metal-plastic.
Plastic crowns for teeth
Temporary plastic crowns
Plastic (mostly acrylic) is a short-lived material, so currently a plastic crown on a tooth is mainly a temporary structure. These types of dental crowns have the following advantages:
- temporarily restore appearance, support chewing and speech functions;
- protect prepared (processed for prosthesis) teeth from pain when exposed to mechanical, chemical and temperature stimuli;
- prevent displacement and loosening of prepared teeth in the absence of their support by neighboring units;
- prevent the development of pulpitis and periodontitis with preserved dental pulp.
Minuses:
- possible burn of the pulp during installation, as well as allergic reactions to acrylic and inflammatory processes of periodontal tissues;
- fragility and breakage (but repair is possible using special glue);
- color change due to food coloring;
- limited validity period (2 years) - this is enough for temporary dentures, but not for permanent ones.
Metal crowns for teeth
Metal alloy crowns
These are the very first materials used to make dentures. Metal crowns on teeth are still in demand today, provided they are used correctly. They are made from alloys of precious and base metals with the addition of nickel, chromium, cobalt and other metals. Models made of gold are also alloys, since gold is a very soft and short-lived material, and the alloy will last for decades, having a beneficial effect on all tissues of the oral cavity. Models made of steel with gold plating are no different in appearance and wearability from gold ones, but do not have a positive effect on the periodontal tissues. If the question arises, which crown is better for a chewing tooth, dentists often recommend metal. Pros of a metal dental crown:
- validity period of at least 10 years; with proper care – decades; rarely break;
- biocompatibility with tissues;
- absence of corrosion in the alloys used;
- tolerate chewing load well;
- reasonable prices.
Minuses:
- not very attractive in appearance, since they differ as much as possible from natural units; therefore, they try to place a crown on a metal tooth on the lateral (chewing) units;
- sometimes they cause allergies and galvanic (electrochemical) reactions (if there is already a tooth made of another alloy in the mouth).
Ceramic crowns for teeth
Ceramic crowns
Ceramic tooth crowns are made from the most fragile material – pressed porcelain without any additions. They have their pros and cons. Pros of a ceramic dental crown:
- very beautiful – the appearance completely corresponds to natural teeth;
- strength;
- validity period - with proper care 10 years or more;
- completely biocompatible with tissues, do not cause allergies or gum irritation;
- do not change color when using food dyes;
- require minor grinding of hard dental tissues.
Minuses:
- fragile, breakages in the form of chips are more common than other materials;
- cannot withstand high chewing loads, so these crowns are placed on the front teeth;
- high price.
Zirconium dioxide dental crowns
Zirconium crowns
Zirconium crowns are made from the mineral zircon (silicon acid) through special processing using additives. The result is a very hard, durable material that also has the necessary plastic properties so that it can be used to make a denture. Zirconium crowns are made either from zirconium alone or by covering it with ceramics. The latter look more beautiful, so they cost more. Pros of a zirconium dental crown:
- the most durable material, service life - 15 years or more;
- zirconium crowns are beautiful - metal-free ceramics based on zirconium dioxide give a good aesthetic effect, but pure zirconium prostheses also look good;
- the possibility of manufacturing a structure for both anterior and lateral (chewing) units;
- completely biocompatible with human tissues, do not cause allergies or irritation.
Minuses:
- increased wear of teeth on the opposite side is possible;
- the top layer of ceramics may chip;
- high price.
Metal-ceramic crowns on teeth
Metal-ceramic tooth crowns have a metal alloy frame, which ensures the strength of the prosthesis, and a ceramic coating, which creates an aesthetic appearance. Advantages of a metal-ceramic dental crown:
- quite durable - service life is about 8 - 10 years;
- aesthetic appearance;
- cheaper than metal-free ceramics;
- if the frame is made of gold or platinum, then the prosthesis does not cause tissue irritation or allergies.
Minuses:
- metal-ceramic tooth crowns are not as beautiful as those made from porcelain or zirconium;
- chips of ceramics may appear;
- sometimes they darken, acquiring a grayish tint;
- frames made of base metals sometimes cause tissue irritation and allergies.
Glass-ceramic dental crowns
Glass-ceramic crowns
One of the most modern dental materials, combining high aesthetic qualities and sufficient strength. This type of dental crown is made on the basis of glass and ceramics using lithium disilicate (Empress Esthetic), lithium disilicate (E-max), zirconium silicate (Ceramage), etc. Advantages of a glass-ceramic dental crown:
- thin, therefore allowing for minimal tooth treatment;
- smooth surface and good adhesion to natural hard dental tissues - reduces the risk of developing caries;
- transparency and aesthetics - outwardly no different from the enamel of natural teeth;
- Lightweight design increases wearing comfort;
- do not change their color throughout use;
- validity period – more than 10 years;
- biocompatibility due to the absence of metal in the frame - does not cause gum irritation or allergic reactions.
Minuses:
- high price;
- hardness – can cause increased wear of teeth located opposite;
- fragility - can crack, repairing it is problematic.
Metal-plastic dental crowns
Metal-plastic crowns
A metal-plastic dental crown has a metal (usually base metal alloy) frame and a plastic covering. Temporary structures are most often made from this dental material, as it is not durable. A metal-plastic dental crown has the following advantages:
- ease of installation and repair of the structure;
- low cost.
Minuses:
- short validity period - about 2 - 3 years;
- allergies and tissue irritation may occur;
- loose fit to natural hard tissues – risk of caries and inflammatory diseases;
- color change due to the use of food coloring.
From the table you can find out which dental crowns are best suited for you:
| View | Aesthetic indicators | Period operation | Compatibility with the body | Allergy |
| Plastic | low | 2 years | not always | often |
| Metal | low | 10 or more years | not always | often |
| Ceramics | high | 10 years | high | No |
| Zirconium dioxide | high when combined with ceramics | 15 or more years | high | No |
| Metal ceramics | average | 10 years | not always | It happens |
| Glass ceramics | high | 10 or more years | high | No |
| Metal-plastic | average | 2 – 3 years | not always | It happens |
Dental prosthetic options
The main factors that determine the choice of dental prosthetics (if we do not take into account the financial factor for now) are the purpose of the procedure (esthetics or chewing function), as well as the number and location of teeth to be restored. To improve the appearance of healthy (usually front) teeth that have external defects (darkening, chips, cracks, misalignment or size), veneers (special ceramic onlays) or crowns are used.
Crowns are also used to preserve weakened or noticeably damaged (for example, broken or worn down) teeth. They are a kind of caps that are put on a ground tooth. They are made of metal (this outdated technology is still used in some clinics) or modern materials: plastic (temporary crowns), metal-ceramics and ceramics (porcelain, zirconium dioxide, etc.). Both veneers and crowns are non-removable prostheses.
In the absence of 1-2 teeth, either a bridge prosthesis is used - a metal structure (bridge) is attached to the adjacent teeth, used as a support, onto which crowns are fixed, completely reproducing the appearance and function of the lost teeth. Or it will be a prosthesis (crown or bridge) supported by implants.
The advantages of prosthetics on implants are the absence of the need to grind down adjacent teeth, the absence of additional load on them, and the transfer of chewing load to the jawbone (through the metal root), which prevents its atrophy.
The disadvantage is the rather high cost and the need to undergo surgery (implantation of an artificial metal root). If several teeth are missing in a row and it is impossible (or unwilling) to perform implantation, a removable denture is made. For example, clasp (design on a durable metal plate).
In case of complete absence of teeth (edentia), a prosthesis made of acrylic plastic is made. A distinctive feature of removable dentures (both clasp and acrylic) is the ability for the patient to remove and install them independently. The structure is fixed in the oral cavity with special clasps or micro-locks (for clasp ones), or by suction to the gum (for acrylic ones).
Fixed bridge
Restoring teeth with the installation of dentures that the patient cannot remove on their own is called permanent dental prosthetics. These include veneers, crowns (metal-ceramic or ceramic), dental inlays and bridges. Prosthetics on implants is also classified as a non-removable type.
But in some cases, prostheses are placed on implants, which are called conditionally removable. This is due to the fact that you cannot remove them yourself, but a dentist can easily dismantle them by unscrewing the fastening screws - for example, for professional cleaning, repair or replacement. The implants themselves will remain in place.
Crowns
Long gone are the days when crowns were made only of steel and gold. Today, many modern materials are used for dental prosthetics, which are not inferior in strength or aesthetics to natural teeth. The choice of a specific crown material is dictated by both the method of procedure and the financial capabilities of the patient.
Let's look at the advantages and disadvantages of the main types of dental crowns for prosthetics:
- metal ceramics – lining a metal frame with a ceramic composition,
- ceramics – made from porcelain, zirconium dioxide or glass ceramics.
Metal crowns can (and are sometimes) used today. They have undoubted advantages: high strength, teeth need to be ground less for them. But it is necessary to choose solid crowns made of high-quality metal and use them only for the farthest chewing teeth, where they will not be visible.
Ceramic crowns made from porcelain are cheaper, but are the least durable; glass ceramics are the most durable and beautiful, but the most expensive. Zirconium dioxide is the golden mean. Ceramic crowns are not used for prosthetics of chewing teeth due to their insufficient strength for this function. Their area of application is the front teeth, where aesthetics are very important and the chewing function is secondary.
Metal ceramics
Metal-ceramic crowns are excellent for restoring chewing teeth. They can also be used for prosthetics of front teeth, but in this case it is necessary to check their compatibility with existing natural teeth.
Metal-ceramic crowns are opaque (otherwise the metal base will show through the coating), so if your front teeth have a high coefficient of transparency, then teeth with crowns will differ from natural ones. If, nevertheless, a decision is made to prosthetize the front teeth with metal-ceramics, then it is better to choose crowns with shoulder mass, since they do not cause cyanosis of the gums, unlike conventional ones.
Complete dental prosthetics
In case of complete absence of teeth, it is necessary to make a removable or fixed denture. The removable option involves making an artificial jaw from polymer materials (acrylic, nylon, etc.). The structure is fixed in the oral cavity by suction to the gums, just like a suction cup is attached to glass.
The production of such a prosthesis is quite fast, their prices are moderate, and installation does not involve any serious interventions. However, they also have serious disadvantages. The prosthesis must fit perfectly. If it does not fit perfectly, or if during use the shape of the soft tissues has changed slightly (and it will change, because the design does not transfer the chewing load to the jaw bone, which is why bone atrophy will continue), then the prosthesis will not hold well and keep falling out.
The removable version is very massive, extends far beyond the dentition, rests on soft tissue and in some patients causes a gag reflex. Getting used to such a design is a very slow matter (up to 1 month), and some people do not manage to get used to it at all. Hard dentures often rub the gums during chewing, while soft dentures distribute the load unevenly, causing discomfort. The service life of removable polymer dentures is 5-7 years in the most favorable case.
An alternative is complete dental prosthetics using fixed (or conditionally removable) structures supported by implants. The most commonly used are 3 methods: basal implantation, prosthetics on 4 implants (All-on-4) or prosthetics on 6 implants (All-on-6). Basal implantation means the placement of 8-12 elongated implants into the dense layers of the jaw bone.
The advantage of this method is the absence of the need to do bone augmentation, the ability to do without cutting the gums and drilling the bone, the initial strong fastening of the implants, which allows you to immediately install a prosthesis on them. On the other hand, placing a large number of implants makes the procedure more complex, and the lack of large-scale studies of the behavior of implants over many years does not allow for firm guarantees, unlike other implantation methods, which provide a lifetime guarantee on the implants.
Prosthetics on 4 implants
More predictable and well-researched is the method of dental prosthetics on 4 implants. It also allows you to receive a ready-made fixed prosthesis within 3 days after surgery. But the peculiarity of this type is that this design will be temporary and will have to be replaced with a permanent one in a few months (from 5 to 24 months, depending on individual characteristics).
The main difference between the different types of temporary structures is the presence of a metal frame. A temporary prosthesis with a frame is optimal - it is strong enough to last 2-3 years before being replaced with a permanent one. But embedding a metal frame with a screw connection with implants into an acrylic base is a very labor-intensive procedure, due to which the cost will be noticeably more expensive.
An acrylic temporary denture without a metal frame will be cheaper, but it has noticeably less strength, which is why its service life does not exceed 5 months, and even during this time, structural failures are common, especially in men with large and well-developed jaws. A temporary (adaptation) prosthesis must be properly maintained - once every six months (and sometimes more often) it requires professional cleaning by a dentist, and once a year - replacement of the fixing screws.
There are many types of permanent structures for all-on-four prosthetics, so the desired option is selected individually in each clinic, according not only to the specific clinical situation (for example, the amount of space for dentures, determined by the degree of atrophy of the jaw bone), but also to the capabilities of the clinic and the patient.
The highest quality are titanium-polymer prostheses from Nobel Biocare, however, they are characterized by high cost and require a large amount of space for prosthetics, i.e. Patients with a slight degree of bone atrophy will not be able to install them.
Another option is bridge-like structures made of zirconium dioxide or metal ceramics. Their frame can be made of titanium or zirconium dioxide, and in some cases of nickel-chromium alloy, but the beam must be milled. The use of cast structures reduces the strength and accuracy of fit, which can lead to problems in the future.
Prosthetics on 6 implants
The previous method is not suitable for all patients. In large men, young men (under 55 years of age), those who prefer solid foods (meat, fresh vegetables), and those with very soft bones, implants located on the side will experience increased stress, which will inevitably lead to their loosening, resorption of bone tissue around the implants and breakage (or loss) of the prosthesis after a few years.
For such patients, dentures with 6 implants are always recommended as a more reliable and suitable option to avoid overloading the lateral implants. The operation can also be performed using surgical guides or the traditional method with incisions. Loading of installed implants with a prosthesis can be performed within 2-3 days after surgery.
To install a prosthesis, it is better to use branded Multi-unit abutments, since to remove the prosthesis in the future (if it is necessary to clean or replace a temporary one with a permanent one), Multi-unit abutments, unlike standard ones, allow you to remove only the prosthesis, and other abutments will have to be removed along with it , injuring the gums, which creates a risk of infection and the development of inflammation of the tissue around the implants, and this, in turn, can lead to rejection.
A temporary (adaptive) prosthesis is usually included in the cost of prosthetics using the “all on 6” system, just like the “all on 4” system. And the permanent one will have to pay extra. Temporary, as already discussed above, it is better to choose one with a metal frame, especially for men, even though it will be more expensive. It is better to choose a permanent one based on milled titanium or zirconium beams, or, in extreme cases, cobalt-chrome beams. Cast beams are significantly less strong and their fit is less precise.
It should be noted that prosthetics using the “all on 4” and “all on 6” systems always imply implantation with immediate loading, i.e. the prosthesis (temporary) is placed immediately - within 3 days after the operation. Some clinics offer installation using a delayed loading protocol - i.e. after 4-6 months, during which you will have to use a conventional removable acrylic denture. But this is not an “all on 6” (or “all on 4”) technique, but a conventional two-stage implantation.
Partial prosthetics
In the absence of part of the dentition, partial dental prosthetics is performed using a bridge or clasp prosthesis. Those. In this case, structures can be removable or non-removable. To install a fixed bridge, healthy abutment teeth must be preserved at the edges of the edentulous area. The bridge is a metal arch on which crowns are located, simulating missing teeth.
Along the edges there is a system of attachment to the supporting teeth. They are ground down and crowns are also put on them. In the absence of supporting ones, it is possible to install a bridge prosthesis on implants. A removable bridge with partial absence of teeth also implies that the structure will be attached to the supporting teeth. These can be dentures made of acrylic or nylon, or clasp ones.
Partial plastic dentures have clasps with which they are attached to the supporting teeth. Because of this, this type of denture is not used in cases where the supporting ones are located in the smile area, because the clasps will be visible. In addition, such dentures can cause discomfort and pain when chewing. It will be more convenient to install clasp frames.
Clasp prosthetics
A characteristic design feature of clasp dentures is a special metal arch (clasp). In the upper jaw structure it passes through the palate, and in the lower jaw it passes behind the front teeth, adjacent to the alveolar ridge of the jaw bone. The metal base is made of titanium, cobalt-chrome alloy, or precious metals.
Its strength makes it possible to reduce the total weight of the structure and the thickness of the plastic base, which has a positive effect on the ease of use of the prosthesis. For clasp dentures, the supporting teeth located on both sides of the jaw must be preserved.
This is one of the most optimal options for a removable bridge, because:
- clasp dentures effectively restore chewing function,
- firmly fixed on the jaw,
- do not impair diction,
- have a long service life.
To fix the clasp structure, various mechanisms are used - clasps (wire loops), micro-locks and telescopic crowns. The best, most reliable and aesthetically impeccable are clasp dentures with micro-locks and especially telescopic crowns.
They have one drawback - they are very difficult to manufacture and require highly qualified orthopedists and dental technicians, and therefore have a higher cost. But they better transfer the chewing load to the supporting teeth and practically do not cause their destruction, which, for example, occurs with the clasp system on clasps.
Prosthetics of lower teeth
The procedure has a number of features. First of all, aesthetic requirements for the lower teeth are less stringent, since the lower teeth are not as visible as the upper teeth. Also, the lower teeth are subject to a much greater chewing load, which places greater demands on the strength of the prosthesis and the reliability of its fixation.
And in addition, the anatomical features of the lower jaw (absence of a hard palate, frenulum of the tongue, etc.) make dentures difficult, making the task of achieving a strong fixation of the prosthesis much more difficult. As a result, prosthetics for the lower teeth turns out to be somewhat more complex, and the dentures may have a slightly different design. However, the same technologies apply to the lower teeth.
To restore healthy teeth with partial external damage, veneers and crowns are used here, and if 1-4 teeth are completely lost, a permanent bridge can be installed, supported by ground adjacent teeth. Or a removable plate made of acrylic or nylon, with clasps made of metal wire or polymer material.
If there are supporting teeth on both sides of the jaw, it is possible to install a clasp prosthesis, the design of which will differ from that used for prosthetics of the upper teeth in the shape and location of the arch. In case of complete edentia (absence of teeth) in the lower jaw, the dentition is restored using a removable full plate bridge, or a conditionally removable one on implants.
The latter option has a secure fit and impeccable functionality. In the lower jaw, implantation is easier, and the higher bone density often makes it possible to avoid lengthy and expensive bone augmentation surgery. Implants completely imitate natural teeth, including transferring the chewing load to the jawbone, which slows down its atrophy and allows you to use the prosthesis without correction or replacement for a longer time.
Prosthetics of anterior teeth
Front teeth always play an important role in a person’s appearance, so their restoration is almost always an urgent and pressing task that is important to solve as quickly as possible. As a result, prosthetics of the front teeth is associated not only with recreating the shape and appearance of the tooth itself, but also with the aesthetics of a smooth and beautiful gingival margin.
You can correct aesthetics (darkening, abrasion and small chips, gaps between teeth) with the help of veneers or lumineers, and you can restore severely damaged teeth by installing crowns on them. When one or more front teeth are lost, the problem of prosthetics is best and most effectively solved by installing implants.
The chewing load on them in this area is minimal, and quick prosthetics after tooth loss eliminates bone resorption and makes bone grafting unnecessary. When implanting with immediate loading, the patient receives a fully functional structure immediately (however, several months later, after the implant has completely engrafted, the prosthesis will have to be replaced with a permanent one).
In the case of a two-stage implantation protocol, while the implant is healing, the hole is closed with a temporary butterfly prosthesis, fixed with polymer clasps to the adjacent teeth. And after a few months, a gum former is placed, and after another 3-4 weeks - a permanent option. If implantation is not possible, one of the best options would be to install a clasp prosthesis.
Urgent prosthetics
If it is necessary to restore the integrity of the dentition as soon as possible, the patient is offered emergency dental prosthetics, which usually involves installation within one day. These can be temporary removable structures made of acrylic or nylon, other types of plastic, or non-removable ones - for example, temporary crowns. This type of dental prosthetics is used during tooth extraction and during the restoration process.
Another option is express implantation. Installation of a special implant with a bioactive surface can be non-surgical, or rather performed without an incision in the gum. A temporary crown or prosthesis can be immediately installed on such implants.
A characteristic feature of urgent prosthetics is that it is always a temporary structure that must be replaced with a permanent one after some time. Such prostheses are not very durable and have a limited service life.
Turnkey prosthetics
When calculating the cost of dental prosthetics, it is important to take into account all the nuances and costs at all stages. Clinics often try to show a lower cost of the procedure, without including in the price list the cost of some materials or procedures, which the patient will nevertheless have to pay.
That is why such an item as turnkey prosthetics arose. This means that by paying the specified amount, the patient will receive a fully functional prosthesis and will not have to pay anything else for this. However, it is necessary to take into account that in some cases the turnkey cost includes only the cost of manufacturing and installing a temporary prosthesis, which will later have to be replaced with a permanent one.
The cost of a permanent structure and its installation is not included in the price of the turnkey procedure, primarily because the permanent structure is installed several months (6 or more), or even 2-3 years after temporary dental prosthetics. And it is simply impossible to calculate in advance the cost of permanent dentures for months and years in advance, without knowing what type of prosthesis will be installed and how prices will change.
Which crowns are best for teeth?
All types of dental crowns have their own indications and contraindications. Certain types are used on different teeth. Recommendations about which crown is better for the chewing tooth and which for the front tooth are given to the patient by the orthopedist. But, for example, a metal-ceramic crown can be installed on any tooth.
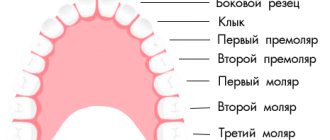
Crowns for front teeth
Incisors and canines are always visible when talking and smiling. In total, each jaw has 4 incisors (2 central and 2 lateral) and 2 canines. Their main function is to bite food, create an aesthetic appearance and maintain correct diction. What crowns are best for such teeth? Most often, ceramics and glass-ceramics are used for crowns on the front teeth. These dental materials allow you to create the maximum aesthetic effect, as well as maintain chewing and speech function.
Crowns for lateral (chewing) teeth
These types include premolars and molars. When smiling, they are not always visible (sometimes 1 premolar is visible) and perform a chewing function. Crowns on chewing teeth are most often installed metal or zirconium. At the patient's request, glass ceramics can also be used. If the first premolars are visible when smiling, ceramics, glass ceramics or zirconium crowns are installed on them.
The final decision on which crown is best suited for a chewing tooth is made by the doctor together with the patient. Plastic or metal-plastic is most often used as a temporary structure.
Patient reviews
Dental problems started during pregnancy. Then there was a period of lactation, at the end of which I was left without two front teeth. At the clinic, an orthopedic dentist recommended making a metal-ceramic prosthesis. It didn’t suit me at all, they adjusted it four times, but to no avail. Then they replaced it with zirconium crowns. I've been using them successfully for three years now. I am no longer ashamed of my smile, but, on the contrary, proud of it.
Natalya, 34 years old
After caries treatment, I was left without one front tooth. The situation for a person who works with people is not the most pleasant. In my case, there was no doubt; I immediately chose prosthetics with zirconium crowns. In my opinion, this prosthesis is the most successful, although not cheap. Adaptation went quickly, no discomfort arose, and the smile remained the same; outwardly, the artificial incisor cannot be distinguished from the real one. I believe that only zirconium is suitable for restoring front teeth.
Alexander Sergeevich, 42 years old
Several years ago I had metal-ceramic crowns installed.
I was very pleased with the prosthesis, nothing interferes, my teeth are still in excellent condition. Many people were afraid that my gums would turn blue, but nothing like that happened in my case. I eat whatever I want, even hard apples, but no chips have arisen during this time. So I recommend this option to everyone I know. Angelina
Installing a crown on a tooth
The process of installing a crown on a tooth is strictly regulated. It is carried out in stages. The appearance, functionality and lifespan of the prosthesis depend on how the crown is placed on the tooth and how carefully the work is done.
Inspection
Installing a crown on a tooth begins with an examination by an orthopedic dentist. He examines the oral cavity and, if necessary, prescribes x-rays. Based on the results of the inspection and examination, preparatory measures are carried out.
Treatment
A complete sanitation of the oral cavity is carried out. Treatment includes caries, gum and oral cavity diseases. In severely damaged units, the pulp is removed and the root canals are cleaned (depulpization). Professional dental cleaning is required. Only after the doctor is convinced of the complete absence of foci of infection can prosthetics be performed.
Turning
It is not easy to crown a tooth. To install a crown on a tooth, it needs to be ground - remove the surface layer of hard tissue with a thickness equal to the thickness of the future prosthesis. Structures can be made of different materials and have different thicknesses, so turning will also be carried out to different depths.
Grinding a pulpless tooth before installing a crown is painless. It is recommended to grind a living, non-pulpless tooth under local anesthesia.
Taking an impression and making a model
An impression or impression is taken from a unit that is fully prepared for prosthetics, reflecting the condition of the prosthetic part of the dentition. For this purpose, an elastic dental material is used that retains its shape for a long time (silicone mass, dental wax, plaster).
The oral cavity is dried, the material selected for making an impression is placed in a special mold (spoon), and it is applied to the place of prosthetics in the dentition. The patient can only clench his jaws and keep them clenched for several minutes until the impression hardens. The resulting impression is washed under running water, placed in a special solution and sent to a dental laboratory. Using the cast, a plaster model is first made, it is tried on, and then a prosthesis is made from the selected material.
Fixation of crowns
The installation of the crown ends with its strengthening - fixation. First, the crown is strengthened with a temporary compound. The patient wears the prosthesis, assessing the degree of comfort, for 2 to 4 weeks. If everything is normal, the temporary fixation is replaced with a permanent one, strengthening the prosthesis with cement. If the prosthetic unit has enough natural tissue, then the prosthesis is placed directly on the treated and filled tooth. If there is not enough tissue, the prosthesis can be fixed on an inlay, a pin or an implant (titanium root).
On the tab
Fixation of the crown on the core tab
This is the best option for prosthetics. The inlay is made in the laboratory from an impression and reliably covers the damaged tooth. Even if the crown is destroyed for some reason, the inlay will not be damaged and re-prosthetics can be carried out easily. A prosthesis on an inlay can last a very long time, from 7 to 10 years or more, depending on the material of manufacture.
On the pin
Crown on pin
The orthopedist decides which crown is best to install on the chewing tooth and how to strengthen it, but most experts believe that a supporting structure in the form of a pin is most suitable. The pin is inserted into the preserved tooth root when there is significant destruction (at least half) of the crown. Before this, treatment and removal of pulp from the root canals is carried out. Contraindications for the installation of a pin are any inflammatory processes, including pulpitis and periodontitis, split roots, narrow curved root canals.
Pins are placed mainly on the lateral (chewing) teeth, but sometimes on the front teeth. The price depends on the material of manufacture. Cheaper metal ones with threads (anchors) are placed mainly on chewing teeth. More modern fiberglass ones are transparent, without threads, installed on cement.
On an implant
Crown on an implant
An implant is a titanium root that is implanted into the jawbone. Installed when the root is destroyed, on which it is impossible to install a pin. Dental implantation can take place immediately after removal of the natural root (single-stage technology) or after some time (delayed).
An adapter (abutment) is installed on top of the titanium root, onto which the prosthesis is attached. The abutment can be metal and then it will be visible through transparent metal-free crowns. Zirconium abutments can be placed on any teeth, metal ones - mainly on the lateral ones. Usually, a temporary structure is first installed, and after the implant has healed, it is changed to a permanent one.
Main features of metal-ceramic prostheses
This type of prosthesis is a type of solid cast structure; it consists of a metal base (frame) with ceramic lining. It is created from special alloys (zirconium dioxide, cobalt/chrome or nickel/chrome) designed specifically for dental needs. Sometimes alloys containing precious metals (gold, silver, palladium) are used to make the base. Depending on what metals the metal ceramics contain, the price of prostheses may vary.
Possible complications
Depends on how the crown is placed on the tooth. If all indications and contraindications for prosthetics are observed, the correct choice of dental material, prosthetic technique, and high-quality performance of all work, complications, as a rule, do not occur or are reduced to a minimum. Sometimes the cause of complications is the individual characteristics of the patient’s body.
Pain under the crown
After treatment and prosthetics, moderate pain may persist for some time (1–5 days), decreasing in intensity. But if the tooth under the crown hurts, and the pain does not decrease, but increases, tissue swelling appears, pus is released from the gums or the temperature rises, you should immediately consult a doctor - this is a sign of an inflammatory process. The cause of inflammation may be incompletely cured caries or incompletely removed pulp from the root canals. Another reason is violations during the installation of the prosthesis, its loose fit to the remains of the natural crown and infection getting under it.
Pain under the prosthesis with irradiation into the jaw also occurs when the root canal is perforated with a pin or when a small part of the instrument used to clean the root canal is broken off. What to do: you should not try to treat a bad tooth on your own; this requires urgent help from a dentist. Usually the crown is removed, the pathological process is treated, and then the crown is reinstalled (new or old, if it is not destroyed). Sometimes pathology can be eliminated without removing the crown, simply by drilling a hole in it. The hole is then repaired using photo-curing filling materials.
If the toothache under the crown is very severe, before seeking medical help, you can take a painkiller: Paracetamol 500 mg tablet, Ketorol 10 mg or Naise 100 mg.
Unpleasant smell
Indicates the presence of an infection in the mouth. This may be a slow inflammatory process, or it may be an acute one, in which case the tooth also hurts. The cause of an unpleasant odor from a tooth under a crown can also be insufficient oral hygiene, smoking and eating a lot of sweets. What to do: consult a doctor; this symptom can only be eliminated in the dentist’s office.
Allergy
Allergic reactions are most often associated with the installation of crowns made of non-precious alloys of metal and plastic (acrylic). Redness and swelling of the gums and pain appear. The allergic process is dangerous because it can quickly spread to surrounding tissues. At the same time, the tissues of the larynx swell, breathing is impaired (Quincke's edema). What to do: contact your dentist immediately. Help consists of replacing the prosthesis that has caused an allergy to a structure made of a different material. At home, the patient can take a tablet of any antihistamine: Zodak, Claritin, Tavegil, etc.
Caries
The cause of the development of dental caries under the crown is most often incompletely cured primary caries. But sometimes, even after careful treatment, caries develops again (secondary caries). This happens especially often when the crown does not fit tightly (an infection gets under it), poor oral hygiene, or consumption of large amounts of easily digestible carbohydrates. What to do: Contact your dentist as soon as possible. The product is removed, caries is treated, and then the structure is reinstalled. If it is worn out, install a new one.
Prosthetic stomatitis
The appearance of painful ulcers on the gums in the area of prosthetics and their spread to the oral mucosa largely depends on how the crown is placed on the tooth. Prosthetic stomatitis is a consequence of improper design or installation of a crown, squeezing small blood vessels of the gums, leading to malnutrition and destruction of the mucous membrane. Sometimes the cause of stomatitis is the toxic effect of dental material (acrylic) on oral tissue. If an infection is added to the inflammation, stomatitis can be purulent. What to do: consult a dentist, find out and eliminate the cause of the complication.
How is a crown installed?
When the choice of prosthesis is made, all that remains is to install it. Many people worry and reluctantly go to the dentist, not knowing what awaits them. To have at least some idea about a visit to the dentist, you should understand how he will install the crown.
- The installation procedure is not as fast as we would like, and definitely takes more than one day.
- First of all, you need to visit a dentist so that he can determine the extent of damage to the tooth, and whether you need a crown or not.
- After the examination, you will be sent for an X-ray to identify any defects.
- Next comes the preparatory stage for installation. If necessary, the doctor treats caries and other dental diseases. If the tooth has been completely destroyed, a permanent pin is installed in the root.
- As we already know, the crown is delivered on the filed edges of the tooth, so the next step will be grinding. This is necessary to ensure that the crown sits firmly and does not create backlash.
- After grinding, the process of making a cast of the future prosthesis begins.
- Melting the crown itself includes choosing the shade of the future “replacement” tooth.
- As soon as the crown is ready, you need to try it on to make sure that it fits you exactly and will not interfere, press or cut your gums. The denture is installed for a certain period of time.
- If temporary wear does not cause any discomfort, then the dentist fixes the prosthesis permanently using medical cement.
Caring for dental crowns after prosthetics
How long the installed structure will last depends not only on the quality of dental services, but also on proper care. After installing a crown, it is important to follow these recommendations:
- You will be able to eat 2 hours after installation of the prosthesis, and drink immediately;
- For the first few days, it is better to chew solid food on the opposite side; over time, the load can be increased, but you should no longer chew nuts at all;
- after installing prostheses made of plastic or metal-ceramics, it is better to avoid taking coloring foods: coffee, beets, red wine, etc.;
- after each meal you need to rinse your mouth, using an irrigator to rinse the interdental spaces; It is better not to use dental floss, as they can damage the denture;
- brush your teeth twice a day with a soft toothbrush and toothpaste without abrasive particles; President pastes with an RDA abrasiveness rating of less than 50 units are suitable. (Preggy for pregnant and nursing mothers and Junior).
Crown care products
Main types of metal-free structures
Metal-free crowns do not have a metal frame and can be made from the following materials:
- Porcelain. Porcelain crowns are made by firing and subsequent glazing. This method allows you to obtain a fairly durable and at the same time aesthetic denture.
- Zirconium dioxide. The most popular material today. Like cermets, zirconia serves as a framework onto which the ceramics are applied. Only the latter material has a natural white color and does not change the shade of the artificial tooth, unlike dark metal.
It is worth noting that metal-free prostheses are manufactured using modern CAM/CAD technology. This technique is considered the most advanced today and allows you to achieve outstanding accuracy of the finished crown. After the doctor takes impressions of the jaws, they are transferred to a computer, which cuts out the frame from a zirconium dioxide blank with maximum precision. A crown made in this way does not require further adjustment and grinding after installation.
In general, metal-free crowns can be considered the most modern, aesthetic and expensive.
How much does a tooth crown cost?
To find out how much it will cost you to install a crown on a tooth, you will need to make an appointment with a prosthodontist. During your consultation, a specialist from the St. Petersburg clinic “Yulistom” will recommend the type of crown that is most suitable for you and will evaluate the amount of work involved in preparing and carrying out prosthetics. All this will add up to the total cost of installing the prosthesis. The cost also depends on the location of the clinic, its accreditation category and the qualifications of the specialist performing the work. Only a dentist can decide which crown is suitable for the chewing tooth and which for the front one so as to have a sufficiently high quality prosthesis at minimal cost.
The price range (cost of product + cost of work) can be significant:
- metal made of base alloys - from 3,000 to 16,000 rubles;
- metal ceramics - from 7,000 to 40,000 rubles;
- ceramic – from 20,000 rub. and more.
Pros and cons of metal ceramics
Advantages:
- They are visually pleasing, can be matched to the color of your teeth, and have the same visual properties as natural teeth.
- Durability. They are extremely durable dental materials that easily withstand the stress of chewing and years of wear and tear. Thus, they can last for several years.
- Minimal grinding.
Flaws:
- Some patients have individual intolerance to metals.
- The ceramic part sometimes peels off from the metal structure.
Are you interested in a metal-ceramic crown? The price is clarified in the corresponding section of our website, by phone or directly at the dentist’s appointment.