A lump in the throat during neurosis is the first signal that malfunctions are occurring in the functioning of the nervous system. Patients who have problems with swallowing and sore throat seek help from many specialists, but few of them associate these symptoms with psychosomatics. “Pharynx neurosis” refers to a pathology that affects the funnel-shaped canal - the link between the mouth and the esophagus.
1.General information
Laryngospasm (spasm of the larynx) is an involuntary and uncontrolled contraction of the muscles of the larynx, during which the glottis closes, the flow of air into the airways is blocked and a state of inspiratory asphyxia occurs (inability to inhale).
Prolonged asphyxia can lead to general oxygen starvation of tissues and death.
Due to the age-related characteristics of the structure and functioning of the ENT organs, laryngospasm is most often observed in children in the first months and years of life, but it also occurs in adults.
A must read! Help with treatment and hospitalization!
Diagnostic measures
If there are frequent manifestations of spasms that are not related to the effects of chemical and mechanical irritants, or the emotional background of the patient, then a specialist will prescribe a comprehensive examination. Thanks to diagnostics, it will be possible to identify the causes of the patient’s pathological condition and prescribe appropriate treatment.
The main methods for diagnosing diseases that are accompanied by the formation of a spasm in the throat include several studies.
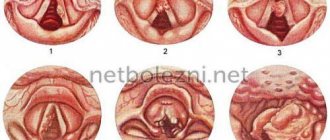
Pharyngoscopy - the study involves a visual examination of the throat using a spatula. The doctor takes a swab from the throat and prescribes biochemical and general blood tests, which will show possible inflammatory processes affecting the pharynx. If a tumor formation is suspected, a tumor marker test is prescribed.
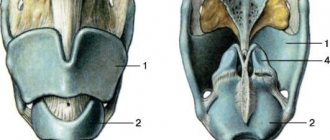
Laryngoscopy is a diagnostic method that makes it possible to assess the condition of the pharyngeal mucosa and vocal passage.
Fibroesophagogastroduodenoscopy - with this method you can find the cause of the disease along the digestive tube.
The doctor may also prescribe an ultrasound examination for spasms, which is used to rule out thyroid disease.
The choice of one or another diagnostic method for spasms depends on the pathology progressing in the body, which led to the occurrence of a spasmodic condition in the throat.
2. Reasons
Laryngospasm is a neuromuscular reflex that can be caused by many factors.
The main groups of such reasons include:
- inflammation in the respiratory system (pneumonia, bronchitis, tracheitis, laryngitis, etc.);
- neurodegenerative diseases (especially those affecting the spinal cord);
- infections and tumors of the central nervous system;
- severe generalized infections (eg, tetanus);
- irritation of the larynx with chemicals, allergens, medications, very cold or hot air;
- deficiency of vitamins and/or microelements;
- vascular pathology (severe hypertension, aortic aneurysm, etc.);
- neuropsychic factors (psychotrauma, hysterical attack, nervous overstrain, severe crying in children, fear or laughter);
- foreign bodies or tumors in the upper respiratory tract.
Visit our Otolaryngology (ENT) page
Cramps due to eating
Eating certain foods causes a sharp contraction of the muscles of the pharynx and esophagus. The cause of spasms in the throat can be a large lump of hard, dry food.
Accidental ingestion of sharp bones also leads to esophageal obstruction.
Errors in nutrition play an indirect role in reflux disease: eating spicy, fatty foods is a factor in increasing the acidity of gastric juice.
In a patient suffering from this disease, hydrochloric acid is partially released into the esophagus. The contents of the stomach irritate the walls of the organ and cause them to contract sharply, which feels similar to the feeling of a lump when swallowing.
A gastroenterologist decides how to relieve unpleasant spasms in the throat with reflux esophagitis.
3. Symptoms and diagnosis
Against the background of the above conditions, diseases and influences, laryngospasm often develops suddenly. However, in some cases it is preceded by such warning signs as shortness of breath, hoarseness or decreased voice volume (up to complete aphonia), and a “barking” cough with laryngitis. The classic clinical picture of laryngospasm includes changes in complexion, noisy shallow breathing, and panic (which in this condition can rapidly develop not only in a child, but also in an adult). The head is usually thrown back, and with severe hypoxia, cyanosis is observed. Choking, the patient may lose consciousness; in severe cases, cardiac arrest occurs. Sometimes laryngospasm is accompanied by an epileptiform seizure, including involuntary relaxation of the sphincters.
The duration of laryngospasm ranges from a few seconds to several tens of seconds. With hysteria, the attack passes spontaneously and does not require outside help (most often it is enough to eliminate the psychogenic situation or simply deprive the patient of the audience, i.e. leave the room).
If there is a predisposition to laryngospasms, they may occur repeatedly during the day. There is a tendency towards seasonality: laryngeal spasms are more often observed in the cold season.
The diagnosis is established clinically and anamnestiically. During laryngoscopy, a tight closure of the vocal cords and arytenoid cartilages is observed.
About our clinic Chistye Prudy metro station Medintercom page!
Laryngospasm. Spasm of the larynx. Help with laryngospasm.
Laryngospasm is a sudden involuntary contraction of the muscles of the larynx. Causes partial or complete closure of the glottis and occurs with inspiratory dyspnea (difficulty breathing).
Sometimes it is combined with tracheospasm, when the smooth muscles of the posterior membranous part of the trachea simultaneously contract.
This condition can occur in adults, but most often it affects children aged 3 months to 2 years, especially if there are risk factors. This is due to the fact that precisely at the age of up to 2 years, the physiological lumen of the glottis is very small, and the nervous system is too labile and unstable, which can easily provoke a sudden attack of laryngospasm. Attacks of laryngospasm can last from a few seconds to 1-2 minutes, and occur several times a day.
Etiology of laryngospasm
The reason for this pathological condition is the increased reflex excitability of the neuromuscular apparatus of the larynx. During an attack, the aryepiglottic ligaments (two sheets of mucous membrane, separated by connective tissue, are located at the entrance to the larynx) are brought to the midline, the vocal cords are tightly closed, the arytenoid cartilages (paired cartilages to which the vocal cords are attached) are brought together and everted. Therefore, after a noisy inhalation, breathing first becomes shallow, and then may stop altogether, since air cannot pass through. The mucous membrane of the larynx does not change in any way.
Causes of laryngospasm in children:
• lack of calcium in the body;
• deterioration of the body's reactivity;
• birth injury;
• metabolic disorders;
• presence of diseases: chorea, spasmophilia, bronchopneumonia, rickets, etc.;
• pathological changes in the organs of the respiratory system – trachea, lungs, pharynx;
• instillation of various active substances (for example, adrenaline) into the nasal passages.
Laryngospasm in children occurs during:
• severe cough;
• hysterical crying;
• laughter;
• fright.
Etiology of laryngospasm in adults:
• the effect of various medications used to treat the laryngeal mucosa;
• infringement of a benign tumor;
• inhalation of air that contains a certain amount of allergens (dust, pollen, various aromatic substances, etc.);
• swelling of the surface of the larynx;
• inflammation of the surface of the larynx;
• irritation of the recurrent laryngeal and vagus nerves (for example, due to an aneurysm, stressful situations that are accompanied by severe anxiety).
!!! A characteristic feature of laryngospasm is its unexpected appearance.
Symptoms of laryngospasm:
• noisy, whistling and difficult breathing develops;
• unable to clear throat;
• the skin turns pale, a bluish tint appears, and the nasolabial triangle is clearly visible;
• the muscles of the face, neck, and abdomen are tense, the mouth is open, the head is thrown back;
• profuse sweat appears;
• the pulse is hard to palpate, and the breathing process may temporarily stop;
• the reaction of the pupils to light is absent or weakened.
Symptoms of severe laryngospasm:
• loss of consciousness;
• depression of cardiac activity;
• limb spasms;
• foam at the mouth;
• involuntary urination, defecation.
!!! In case of a prolonged attack, if help is not provided immediately, death from asphyxia will occur.
In adults, hysterical laryngospasm is combined with convulsions of the pharynx, esophagus and limbs. As a rule, the attack quickly stops on its own. This attack resembles an epileptic seizure. In mild cases, there is a short-term narrowing of the glottis, a prolonged wheezing breath, pale or blue discoloration of the face, short shortness of breath, and sobbing.
Diagnosis of laryngospasm
The diagnosis of laryngospasm is made based on the clinical picture of the attack and the patient’s complaints.
First aid for laryngospasm
With laryngospasm, it is not the attack itself that needs to be treated, but the cause of its occurrence. To avoid complications, you should call a doctor or an ambulance at the first sign of laryngospasm. Until the doctor arrives, adults should do the following:
1. During an attack, the patient should be reassured, a calm environment should be created, and fresh air should be provided (unbutton the collar, bring it to the window).
2. Reflex methods for relieving spasms: splash cold water on the face and body, or irritate the nasal mucosa with a cotton swab, or blow into the nose, apply ammonia or press on the root of the tongue with a spatula.
3. In the event of a severe attack, the child should be laid on a flat, hard surface, since cardiac arrest is possible, requiring resuscitation measures.
4. It is imperative to administer calcium gluconate intravenously at a dosage of 1 ml per year of life, since the cause of spasmophilia is hypocalcemia. In especially severe cases, the world's only depolarizing muscle relaxant, succinylcholine, is used.
5. If there is no effect, perform intubation or tracheotomy to ensure airway patency.
6. In case of cardiac arrest, resuscitation measures are carried out: indirect cardiac massage.
7. Considering that hypoxia develops as a result of laryngospasm, oxygen therapy must be administered after breathing is restored.
Prevention of laryngospasm
Hardening procedures and restorative treatment are prescribed. Often prescribed are vitamin D, medications containing calcium, ultraviolet irradiation, consumption of dairy and plant foods, long walks in different places (forest, park, embankment).
Relaxation activities for children are recommended. This could be some special games, massage, drawing. The main rule: the child cannot be forced to do this, as this will no longer be relaxing. When choosing a distraction activity, it is very important to observe what the child likes and what calms him down. A balanced diet and vitamin intake can also contribute to a speedy recovery.
Only by following simple recommendations and regularly being examined by an ENT doctor can you get rid of laryngeal muscle spasms forever.
Prognosis for laryngospasm
With timely and adequate treatment, the prognosis is favorable. It is also worth noting the fact that often, as the child grows up, laryngospasm completely disappears and treatment is no longer required.
So, as you understand, laryngospasm is a life-threatening condition, therefore it is very important to recognize it as early as possible and also quickly provide first aid and call a doctor.
4.Treatment
First aid includes providing a supply of fresh, preferably moist, air. It is extremely important to calm the patient and stop panic, but if laryngospasm occurs in a child, this is extremely difficult to do in practice. In some cases, locally distracting pinching, patting, artificially inducing vomiting, or sprinkling the face with drops of water help. It should be remembered that prolonged asphyxia can be fatal; Thus, laryngospasm is an emergency condition and requires an immediate call to the ambulance. In the most severe cases, the patient is intubated or an emergency tracheostomy is performed, but it is obvious that these operations can only be performed by a doctor.
Treatment strategy and tactics are determined by the results of a mandatory diagnostic examination. In particular, the primary measure may be to eliminate hypovitaminosis and micronutrient deficiency. In other cases, neurological or psychotherapeutic treatment is necessary. Physiotherapeutic procedures, restorative measures, and sanatorium-resort treatment play an important role.
It is noted that the tendency to laryngospasm in children usually decreases spontaneously during puberty and adulthood.
Prevention
It is completely impossible to insure yourself against the manifestation of throat spasms, however, by following some rules, you can reduce possible risks to a minimum.
Recommendations to help avoid throat spasms, pain, and choking:
- Observe the work and rest schedule. Eat properly.
- Avoid stress.
- Treat associated ailments in a timely manner.
Throat spasms are an unpleasant and dangerous painful condition that can lead to the death of the patient. Therefore, when you notice the first signs of throat spasms, you should seek help from a doctor, which will make it possible to prevent the occurrence of serious complications.
Endocrine pathologies
The feeling of squeezing of the throat and lack of air is sometimes caused by pathology of the thyroid gland. This is due to the pathological growth of organ tissue - goiter. The throat is subject to compression in moderate to severe cases of the disease. Then the pain may join.
Severe muscle spasms in the throat are also caused by damage to the parathyroid gland. A decrease in the level of parathyroid hormone leads to a pronounced lack of calcium and an excess of phosphates in the blood. Such an imbalance in the body is the cause of painful cramps.
The pain affects almost all muscle groups, including the esophagus.