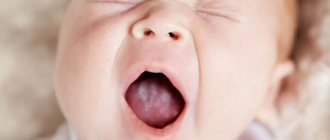
What does thrush look like in a child?
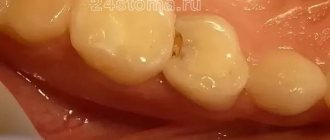
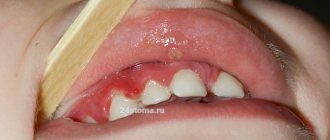
Any part of the oropharynx can be affected: tongue, lips, corners of the mouth, gums, mucous membranes of the cheeks, palate, pharynx, tonsils. White grains (spot coating) appear, reminiscent of curdled milk, or a film (solid coating) of a cheesy appearance. These elements are easily removed by scraping with a spatula, revealing a bright red base, sometimes with a bleeding surface. As a rule, the course of the infection is painless and has only local manifestations. General health is not affected.
Prevention of thrush in newborns
To prevent thrush from returning, as well as for preventive purposes, you should follow simple rules:
- boil bottles, nipples and pacifiers if the child eats formula after each feeding;
- cleanse your baby’s skin daily using hygiene procedures;
- wash your hands before playing or interacting with the child, before feeding;
- pay enough attention to mother’s breast hygiene if the newborn receives mother’s milk as food;
- after feeding, clean the mouth with water or special products sold in pharmacies or children's stores (foam, solutions, etc.);
- strengthen the child’s immunity (long-term breastfeeding, hardening procedures, daily walks, massage, etc.);
- Toys should be washed at least once a week;
- monitor the condition of the baby’s intestines.
Thrush is an unpleasant phenomenon, but it is quite treatable, provided that therapy is started on time and carried out after consulting a doctor. Complications after suffering from candidiasis almost never occur, so preventive measures and close attention to the hygiene and well-being of the baby are quite enough to avoid relapses and re-infection.
To learn how thrush manifests itself in infants and how to get rid of it, watch the video:
This article has been verified by a current qualified physician, Victoria Druzhikina, and can be considered a reliable source of information for site users.
Bibliography
1. https://www.antibiotic.ru/cmac/pdf/6_2_168.pdf
Rate how useful this article was
4.4 7 people voted, average rating 4.4
Did you like the article? Save it to your wall so you don’t lose it!
How to treat thrush in a child?
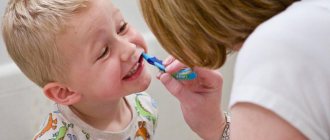
The disease is treated at home. Local medications are used and only as prescribed by a doctor: pediatrician or dentist! Special antifungal agents are used in the form of solutions, sprays, gels, and drops. For maximum effectiveness of therapy, the drug must remain in the oral cavity (on the mucous membrane) for as long as possible. Therefore, the main way to use them is by rinsing or lubricating.
Treatment is long, up to 2-3 weeks.
It is important!
Often thrush in the mouth of infants is associated with candidiasis of the skin of the nipples and areola in the mother. In this case, the woman experiences redness, irritation, and a burning sensation on her chest. In this case, treatment should be comprehensive, for mother and baby.
How to distinguish thrush from the consequences of regurgitation
Some parents (especially if the child is the first-born) mistakenly mistake the plaque for the remains of curdled milk after the baby has burped. Indeed, it can be very difficult to visually determine the nature of the contents of the oral cavity.
To understand what exactly caused the symptom, you can do a small test. You need to moisten a piece of clean cloth with boiled water or chamomile decoction and try to remove the plaque.
If this is the remains of milk after regurgitation, then the baby’s mouth will be easily cleaned, and all the contents will end up on the tissue. If you have thrush, it is not so easy to remove plaque (after the procedure, irritated areas will remain at the site of inflammation).
Child nutrition
Simple carbohydrates are the main nutrient medium for fungal growth. Therefore, sweets, sugar, cookies, etc. must be excluded from the patient’s diet. Breastfeeding certainly continues.
If the child is bottle-fed or mixed-fed, then preference should be given to formulas containing probiotic microorganisms, which have the largest evidence base for their effectiveness. These are LGG and BB-12 from Chr. Hansen. It has been proven that LGG and BB-12 inhibit the growth of opportunistic microorganisms and fungi, protect against the development of caries and infections, and effectively prevent atopic eczema. Nutrilak Premium Comfort is enriched with LGG probiotic.
The mechanism of development and features of candidiasis in infants
Candidiasis manifests itself as a white coating
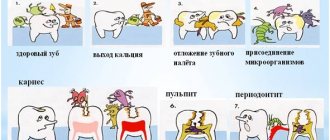
As noted earlier, no one is immune from thrush or, scientifically, candidiasis. This state of affairs is not difficult to explain, because the provocateurs of this pathology can exist quite peacefully in the body of any person.
Why? All because of their conditional pathogenicity. If the human body is in good shape and is able to organize its high-quality defense, then the activation of Candida fungi will not occur. But as soon as it gives the slightest glitch, the unfavorable microflora is activated, begins to actively multiply and literally “eat” healthy tissue.
Fungal microorganisms can and often do live in all parts of the human body. The largest accumulation of candida microflora can be found in:
- oral cavity;
- intestines;
- genital area.
As a rule, the activation of fungi in one area entails the unfavorable activity of their “brothers” in another part of the body. In infants, candidiasis is an inflammatory disease that develops either in the mouth, or in the groin area, or both.
Many parents are interested in “Where could their child, seemingly born quite recently, pick up fungal microflora?” In fact, anywhere. Often, Candida fungi are transmitted to children at birth and live in their bodies for the rest of their lives.
Naturally, only with the activation of unfavorable microflora does the development of pathology and its accompanying manifestations take place.
Possible deviations
All infectious diseases in children tend to quickly spread to other organs and systems. Girls, even in infancy, can develop vaginal candidiasis. Vulvovaginitis is dangerous because in girls, who at this age have extremely delicate mucous membranes, there may be fusion of the vagina or labia. This problem can only be solved surgically. That is why the mother should regularly check the condition of the child’s genitals: for redness and discharge. In addition, against the background of thrush, other, much more serious and dangerous conditions can often develop - generalization of the process and the development of sepsis (an infectious disease caused by the spread of bacterial or fungal flora from the source of infection into the blood, lymphatic tract, and from them into all tissues and organs). Therefore, a serious approach to prevention, early detection, effectiveness and timely treatment of thrush is necessary. The process may be complicated by the addition of a bacterial infection, spreading to the gastrointestinal tract.
With insufficient treatment, oral candidiasis can take a chronic, relapsing course. The child may begin to refuse to eat, sleep is disturbed, and the baby becomes irritable. Changes occur in the protective function of the child’s body, allergic reactions develop, and a predisposition to the development of various diseases, such as bronchial asthma, is formed.
Diagnosis of candidiasis
A pediatrician usually has no problems diagnosing thrush on the oral mucosa.
This is a common disease with characteristic symptoms, so an experienced specialist can easily identify it. In particularly difficult cases, when diagnosing a sore throat, sputum analysis may be required to identify the pathogen. The situation is more complicated with the diagnosis of candidiasis on the genital mucosa. In this case, you will have to take a smear for microflora, which will show the presence of inflammation and help identify the causative pathogen.
Thrush on internal organs is even more difficult to detect: external symptoms may be absent. Blood, urine, and stool tests may be required to detect mycosis.
Treatment
Fungal diseases in children can be treated by a pediatrician, an infectious disease specialist or a dermatologist. If we are talking about the treatment of oral thrush, then therapy can also be carried out by a dentist.
The diagnosis of candidiasis is determined in most cases based on an examination of the oral cavity performed by a specialist. If there is any doubt, the doctor refers the patient for additional examinations. More often, to confirm the disease, a laboratory test is used to test a smear taken from the mouth for the presence of fungus.
Treatment of thrush in children requires an integrated approach. If the disease is not advanced, then local therapy is carried out in combination with measures to strengthen the immune system. In severe cases, oral candidiasis in children is treated with systemic drugs, local agents and compliance with preventive recommendations.
Disease prevention
To get rid of candidiasis completely, you need to adhere to a number of simple preventive measures. Among them:
- compliance with basic hygiene rules: wash your hands thoroughly, care for the skin and mucous membranes of the child;
- maintaining an optimal microclimate in the apartment;
- strengthening the child's immunity.
Thrush in a baby is a serious disease, the recurrence of which can only be avoided by timely consultation with a doctor. It is prohibited to independently treat childhood candidiasis, without undergoing the necessary examinations, based on knowledge obtained from newspaper (magazine) articles.
Symptoms of pathology
Candidiasis in infants
The development of thrush in newborns and very young children is more than pronounced. In general, the pathology occurs in three stages, at each of which specific symptoms are observed.
If we consider each stage of candidiasis in more detail, we should highlight:
- Absence of discomfort in a sick child at the first stage of the disease. It is indirectly indicated only by redness in the mouth, a slight cheesy coating on the tongue and the appearance of a sour odor from the baby’s mouth.
- A more pronounced manifestation of the noted symptoms in the second stage of the disease, also supplemented by the formation of small erosions in the oral cavity and pain in the child. The latter, by the way, are expressed in the constant crying of the baby, which cannot be calmed down.
- The most severe manifestation of pathology is at the last – third stage. Symptoms at this stage of thrush are the most pronounced and severe. It often manifests itself in damage to the entire oral cavity, which results in the appearance of large areas covered with a cheesy coating. Often additional signs of the disease are fever, abnormal bowel movements and insomnia in infants.
Perhaps the most obvious signs of candidiasis in a small child are:
- strong sour odor from the mouth;
- the appearance of a cheesy coating in the oral cavity;
- temperature rise to 38 degrees Celsius.
Having discovered at least one of the noted manifestations in their child, parents must show it to the pediatrician.
At a minimum, before starting treatment, it is important to confirm with a specialist the fact of thrush and receive basic recommendations for combating the pathology. It is better not to self-medicate candidiasis in infants, for example, due to its considerable danger.
Causes of thrush
The cause of the development of thrush is the proliferation of a fungus of the genus Candida. The key condition for the activation of this microorganism remains a decrease in the body’s immune defense. The weakening of protective mechanisms, in addition to the immaturity of the immune system, can be provoked by the following factors:
- Inadequate child care. If basic hygiene rules are ignored, the amount of fungus that gets on the baby’s mucous membranes increases. This creates an additional burden on the immune system of the infant or newborn.
- Abuse of sweets. Candida is a fungus that successfully uses glucose to reproduce. Against the background of impaired immune system function, frequent eating of sweets increases the chance of getting sick.
- Congenital or acquired immunodeficiency. Seasonal viral infections and exacerbations of chronic somatic diseases increase the risk of thrush.
- Decreased protective function of saliva. With dental diseases, there may be a decrease in the performance of the salivary glands, which also contributes to changes in the microflora of the oral cavity.
Infection with fungi can occur from the mother during pregnancy, when using contaminated dishes or personal hygiene items. Therefore, it is extremely important in early childhood to boil pacifiers, jars, and wash hands before contact with the child.
General information
Candidiasis in children is a common disease among children. Normally, small amounts of fungi are part of the opportunistic microflora and are constantly present in the body. If the child’s immunity is strong, microorganisms are safe for health. In weakened children, the fungus begins to multiply uncontrollably, affecting the mucous membranes, skin, and genitals. If candidiasis is left untreated, serious health problems can follow. The main task of parents in the fight against the disease is to establish good nutrition and strengthen the child’s immunity.
About the disease
Thrush is one of the most common diseases that occurs against the background of increased activity of fungi of the genus Candida.
The disease got its name because of the characteristic white (“milky”) coating that forms on the affected mucous membranes. The pathogen is normally present in small quantities on the surface of the oral cavity, skin, and objects of daily use. However, this concentration of fungi, provided the immune system is functioning normally, is not enough to cause any clinical manifestations of pathology.
Newborns and infants are automatically at risk of developing the disease. This is due to the immaturity of the immune system and the minimum number of natural barriers to the penetration of fungi into the baby’s body. Therefore, thrush is a relatively common problem that many parents may encounter. In 90% of cases there is no need to be afraid of the disease, but you also cannot ignore the symptoms due to the risk of developing complications.
Causes of candidiasis
The main cause of candidiasis in children is a yeast fungus of the genus Candida, present in the human microflora. But to activate it and increase the number of microorganisms, a number of factors are required:
- weakened immune system;
- frequent viral and colds;
- thyroid diseases;
- diabetes;
- hypovitaminosis;
- taking hormonal drugs or antibiotics for a long time;
- chronic diseases;
- HIV infection;
- intestinal dysbiosis.
The disease often occurs in premature infants and weakened children. If the mother's birth canal has been affected by candida, the baby, passing through it, becomes infected. The risk of developing candidiasis in such a newborn is much higher.
Treatment of candidiasis
The goal of treatment for candidiasis in children is to eliminate symptoms and prevent further proliferation of fungi in order to reduce their number. General recommendations for strengthening the baby’s body are as follows:
- reduce the consumption of sweet, salty and flour foods, which create a favorable environment for the growth of candida;
- take vitamin complexes, including folic and ascorbic acids, probiotics to normalize microflora;
- give the child drugs to strengthen the immune system;
- For newborns on artificial nutrition, switch to medicinal mixtures containing probiotics and vitamins.
If candidiasis has affected the oral cavity, treatment of the mucous membrane with antifungal agents is prescribed:
- a solution of baking soda, fucorcin or brilliant green;
- Miramistin (antiseptic);
- Clotrimazole (antifungal ointment);
- Nizoral, Pimafucin (antimycotic medications);
- spray for sore throat, stomatitis.
It is recommended to lubricate nails infected with fungus with iodine, antifungal ointments Clotrimazole, Decamine, Mikoseptin and varnishes. If the vagina is affected in girls, antifungal suppositories are recommended. You should not select medications yourself. It is better to consult a doctor and get examined. Self-medication can only worsen the baby’s condition. If thrush, despite the measures taken, does not go away, you may need to consult an immunologist, because This condition is usually associated with weak immunity.
Diagnosis of thrush
Oral candidiasis is diagnosed based on clinical findings, and additional mycological testing usually does not need to be performed. The positive effect of local specific therapy confirms the correctness of the diagnosis.
A complete diagnosis of candidal lesions is based on data from the clinical picture, microscopic and cultural studies, and serological reactions.
During a microscopic examination, scrapings are made from the mucous membranes and the material is examined under a microscope. This method allows you to identify yeast-like cells and filaments of mycelium of Candida fungi.
During a bacteriological examination, a culture is performed to determine the number of colonies of Candida fungi, the type of Candida fungus and its susceptibility to antifungal drugs. To do this, fungal colonies grown on a nutrient medium are treated with various antifungal drugs and see which drug is more effective.
Sometimes the reason for ineffective treatment of candidiasis may be the insensitivity of the fungal species to treatment with certain drugs. In this case, such a study must be carried out.
In a serological test (a test in which antibodies are tested in human serum), the most reliable test is the complement fixation reaction (CFR) with yeast antigens. The study detects antibodies to Candida fungi. In most patients, RSC is positive even with a small amount of antibodies.
Advertising