Unfortunately, some patients do not want to have their teeth treated, which often leads to serious complications, including gumboil or periostitis. The person experiences severe pain, cannot eat, drink, or sleep, the cheek swells, and the temperature rises. In this case, you will need prompt assistance from a professional from the Center for Modern Dentistry, who will provide treatment without pain and stress using modern techniques and anesthetics. In our article we will talk in detail about the causes of tooth flux, why it is dangerous to health, as well as methods of treatment and prevention of caries and periodontitis.
What is tooth flux
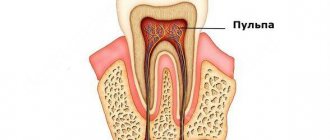
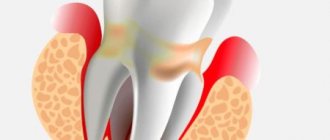
Tooth gumboil is usually an exacerbation of diseases such as periodontitis or periodontitis. An acute inflammatory process begins in the area of the tooth root, when the nerve has already died and an infection develops in the root canal.
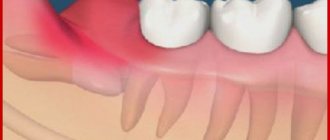
Periostitis is a common disease among children and adults. The inflammatory process manifests itself as follows: a cavity filled with pus appears on the mucous membrane of the jaw - a purulent bubble. As a rule, flux is accompanied by severe swelling of the cheek, pain and increased body temperature.
In the absence of professional dental care, the inflammatory process will develop further. Tooth flux can cause serious complications: phlegmon and sepsis. The patient will need a lot of time to recover.
Let's talk in more detail about the main types of fluxes.
Acute serous periostitis. As we wrote above, the inflammatory process occurs quickly and passes within a few days. It is characterized by severe swelling of the soft tissues. It is localized directly on the area with the diseased tooth, which is the main reason for the development of gumboil. The degree of inflammation depends on the structure of the vessels in the periosteum. The cause of the development of an acute form of serous flux can also be bruises and fractures. In this case, periostitis is called traumatic or post-traumatic. Most often it goes away on its own, but in some cases it can cause severe inflammation and the development of another type of flux - ossifying (fibrous growth).
Acute purulent periostitis. This type of gumboil is characterized by severe pain, which is often pulsating and spreads to the organs of vision and hearing, causing migraines. Pain is managed with medications and cold compresses. You should not heat the swelling site - this can lead to increased pain.
Purulent flux occurs with an increase in temperature to 37.5-38 degrees, the patient develops weakness and general malaise. It should be noted that the course of the disease depends on the location of the inflammation: in the lower jaw the process is more complicated.
The localization of inflammation depends on the location of the lesion:
- 1
Maxillary incisors - an inflammatory process on the upper lip and can spread to the nose. - 2
Maxillary canines and premolars - an inflammatory process in the periosteum.
- 3
Molars - an inflammatory process in the upper part of the cheeks.
- 4
Premolars - inflammation is localized in the lower part of the cheeks.
Chronic periostitis. The rarest form, which is usually localized in the periosteum of the lower jaw. In the chronic course of the disease, local inflammation is present, which does not change facial features. Characteristic symptoms are swelling in the mouth, enlargement of the periosteum, and lymph nodes. The development of this type of periostitis is a long process that takes from 4 to 8 months.
Symptoms of tooth flux
Among the first signs of periostitis are the formation of a painful infiltrate on the alveolar process, fluctuation, and swelling. The tooth itself usually doesn’t hurt anymore
If you discover symptoms of periostitis, we strongly recommend that you consult a doctor who will stop the spread of infection and remove inflammation. But if you haven’t decided or haven’t found the time to make an appointment with a dentist, then let’s figure out how the situation will develop further.
If the spread of infection is not stopped, then at the next stage the flux will manifest itself visually, as we wrote about earlier - a bubble appears on the gum, the cheek swells. In this case, urgently go to the Center for Modern Dentistry, otherwise you risk ending up in the hospital in a couple of days. Surgery will be complex and may last for a week or more.
FAQ:
How to remove a tooth abscess?
Obviously, it is worth contacting a qualified doctor who will help correct the situation. Usually, people turn to him when it already becomes a problem and in most cases, treating flux at this stage already requires surgical intervention - opening the abscess and draining the pus. Dentists at Dudko and Sons in Minsk perform this operation effectively and without pain. Treatment of gums is carried out with the help of antibiotics and antibacterial drugs prescribed by a doctor after examination and consultation.
How to rinse gumboil on a tooth to make it break out?
If your gums are swollen and your tooth hurts, we recommend that you rinse your mouth with various antiseptic and antimicrobial agents (for example, chlorhexidine). In addition to all this, you can rinse with sodium saline solution, sage infusions, and calendula tincture. The main thing to remember is that breaking through the gumboil does not mean curing it. Treatment of the causative tooth is necessary, otherwise after a while the cheek will swell again.
Diagnosis of tooth flux
At the dentist's appointment, a thorough examination of the oral cavity and an X-ray examination - a targeted or panoramic image - is carried out. In some cases, two studies will be required to make an objective diagnosis.
As soon as the diagnosis is made - exacerbation of chronic periodontitis and the diseased tooth is identified, the doctor begins treatment.
Types of periostitis
Due to the occurrence:
- odontogenic (most common cause): due to dental diseases;
- traumatic;
- hematogenous: infection spreads through the blood;
- lymphogenous: the infection penetrates through the lymphatic vessels.
By localization:
- diffuse: affects many teeth;
- limited: within 1-2 teeth.
According to the type of disease:
- acute periostitis: pronounced symptoms, rapid course. It is divided into two forms: serous (the presence of transparent exudate in the tissues) and purulent - purulent exudate that can form an abscess. Sometimes purulent discharge enters the oral cavity through a fistula on the gum.
- chronic: quite rare, formed due to an untreated acute form.
How is tooth flux treated?
If the cause of the inflammatory process is a diseased tooth, then at the first stage the question of the possibility of preserving it is resolved. Our experienced specialists will do everything to avoid removal.
Treatment usually involves five stages:
- first: the doctor, under local anesthesia, removes all tissues affected by caries, old fillings and creates direct access to the tooth canals
- second – removal of the nerve and determination of the length of the root canal
- third - expansion of the root canal of the tooth to gain access to its deeper areas
- fourth - installation of a paste containing calcium into the canal to stop acute inflammatory processes.
- fifth – temporary filling of the root canal
If necessary, an incision is made in the gum, the pus is removed and drainage is installed. For tooth flux in an adult, the doctor may also prescribe antibiotics or other drug therapy. In three to seven days you will need to come back for a follow-up appointment. If the doctor sees that there is no pus, the abscess is completely stopped, and the swelling of the cheek has subsided, he will seal the dental canal. The final stage of treatment will be the restoration of the crown of the tooth.
Causes of periostitis (flux)
- complication of caries;
- consequences of illiterate root canal treatment;
- as a complication after periodontitis;
- injuries of the maxillofacial area;
- hypothermia;
- inflammation of the gum pocket;
- complications after tooth extraction.
If you do not seek medical help in time, the infection from the subperiosteal region will spread to the bone and soft tissues, and serious surgical intervention will be required in a maxillofacial hospital. In addition, in advanced stages of periostitis, doctors resort to tooth extraction.
Tooth gumboil: what medications to take?
This is the most common question in Internet search engines when people try to deal with the problem on their own. Our answer: “Do not take anything before consulting a doctor!” Only the attending physician, taking into account the stage of the disease and your individual characteristics, can prescribe an antibiotic for tooth flux, which stops the inflammation process. The dentist will also advise which drug is best to use as an anesthetic.
How can a dentist help if a patient has developed gumboil?
As a rule, advanced flux requires surgical dental intervention - that is, a dental surgeon opens the periosteum and gums and inserts a rubber tube there to remove the purulent contents. In this case, the tooth most often cannot be preserved for further restoration and is completely removed. To combat inflammation, the patient is prescribed antibiotics and antihistamines.
If the flux has just begun to develop, then perhaps there will be no need to cut the tissue - the doctor will simply open the tooth canals, treat them with an antiseptic and antibiotic, and the pus will come out on its own - in the few days that must pass before the next visit to VivaDent and filling the canals .
In any case, the decision about what treatment should be in a particular case - conservative or surgical - will be made by the dentist only after receiving x-rays of the tooth and the tissues around it.
Prevention of flux in adults and children
Since the main cause of gumboil in both adults and children is complications of caries, careful oral care and timely dental treatment at the Center for Modern Dentistry are necessary. We recommend brushing your teeth morning and evening, rinsing your mouth after meals, and using dental floss and irrigator.
In addition, once every six months you need to come for a preventive examination at the dentist, where the doctor will identify caries and immediately begin treatment. An effective method for preventing diseases of the teeth and gums is a professional hygiene procedure in the dentist’s office, during which a specialist will remove hard dental plaque from the teeth, which is simply impossible to get rid of at home.
The Center for Modern Dentistry employs experienced specialists who use progressive techniques to treat tooth flux, as well as modern anesthetics that will relieve you of the pain of stress. Therefore, if you feel pain, do not delay your visit to the doctor, put off work and any other activities. Your health is much more important.
Diagnostic methods and treatment methods
An accurate diagnosis is a guarantee of successful treatment. To do this, the doctor conducts the necessary examination. It includes a diagnostic examination and fluoroscopy. To assess the degree of the inflammatory process, laboratory blood tests are performed.
There are two methods of flux treatment used in dentistry:
- Making an incision on the gum to open the purulent sac. After removing the pus, drainage is installed, which prevents premature healing.
- Cleaning an abscess through a root canal. This procedure is carried out when the cause of the flux is caries or the infection has penetrated through an existing crack in the tooth.
Special rinses are effective in treating flux. Solutions have regenerating and anti-inflammatory properties, therefore they can speed up healing. The simplest composition that can be used for rinsing with flux is a soda solution. If you carry out the procedure every couple of hours, you can quickly reduce pain and inflammation. To prepare the composition, dissolve a couple of teaspoons of soda in a glass of warm water. This amount of solution is enough for a day.
You can reduce swelling with a weak solution of manganese. This composition has strong disinfectant properties, which makes it possible to fight pathogenic microorganisms. For a similar effect, you can use the antiseptic agents Chlorhexedine or Miramistin. These drugs need to be used to irrigate the oral cavity.
An effective medicinal preparation for rinsing is Rotokan. It has a natural composition and contains extracts of chamomile, yarrow and calendula. For the solution, one spoon of the product is dissolved in a glass of warm water. Rinsing is carried out 4-5 times a day.
Is it necessary to remove a tooth during periostitis?
Previously, with an advanced form of the disease, a unit whose roots were damaged was torn out. Today doctors prefer conservative technologies. Removal is carried out only when the crown is completely destroyed and the quality of the roots is unsatisfactory.
If the image confirms that the root canals are not inflamed, prosthetics are performed. A tab is installed inside the root. It is held securely in place by dental cement. A crown made of metal, metal-ceramics, zirconium oxide or other material is fixed on top.
What happens if periostitis is not treated?
It's simple. An increasing amount of pus will cause further development of swelling and puffiness of the face. Further, the lymph nodes located in the neck may become larger. Inflammation will also cause fever and pain.
A very dangerous complication of flux is phlegmon. This is a breakthrough of the “bag” in which the pus is located, and the free spreading of the contents over the muscles and tissues of the cheek, neck, etc.
Jaw osteomyelitis is another possible complication of untreated gumboil: it is an inflammation of the jaw bones (usually this occurs in the lower jaw).
In other words, it is better not to allow serious consequences, but to seek qualified medical help as soon as possible.
What causes flux?
Flux on the gums is formed, as a rule, for three reasons:
- advanced caries or pulpitis;
- poorly treated periodontitis or pulpitis;
- inflammation of the gums, which can complement the above factors.
It is worth dwelling in more detail on each of the possible causes of purulent inflammation.
Untreated caries or pulpitis
If the treatment of carious formation is delayed, then the infection that gets into the pulp leads to the onset of the inflammatory process.
Pulpitis occurs quite often. Its distinctive feature is a spontaneously occurring aching or sharp pain, which you should contact your dentist if you feel it. If you again ignore the signals sent by the body, the inflammatory process will continue to develop rapidly, and the infection, going beyond the boundaries of the pulp, will affect nearby tissues. The result is purulent inflammation near the upper parts of the root, called periodontitis.
An abscess appears near the top of the root, often referred to by non-medical people as a pus-filled sac. The inflammatory process begins to be accompanied by the release of pus that gets under the gum mucosa. When pus penetrates the tissue, gumboil develops and the gums become swollen. In most cases, with flux, the facial tissues also swell, which becomes asymmetrical.
Having taken an x-ray, you can easily notice that the abscess looks like a dark area in the area of the upper part of the root.
Poor quality canal filling
An abscess near the upper root zone can form due to ignoring caries and poor canal filling, which is not the patient’s fault. The need to fill root canals arises in the treatment of periodontitis, pulpitis, as well as during preparatory procedures before prosthetics.
The dentist’s task is to fill the canal completely, but often it is not filled to the very top of the root due to the carelessness or inexperience of the doctor. In the unsealed part of the canal, excellent conditions are created for the rapid proliferation of pathogenic bacteria. As a result, the microflora, consisting of pathogenic microorganisms, will sooner or later extend beyond the boundaries of the tooth, and then purulent inflammation will occur near the tips of the roots with poorly sealed canals.
Exacerbation of periodontitis
There is an attachment between the gum and the edge of the tooth, which is destroyed during periodontitis, resulting in pockets. There is always hard deposits on the root, which is filled with pus. If the pocket is deep, then due to poor drainage of pus, a fistula may appear on the gum.
Antibiotics
To eliminate the infection, doctors must prescribe antimicrobial therapy, without which the treatment of purulent processes would not be effective.
Standard antibiotic regimens are a combination of Metronidazole with Lincomycin or Clindamycin - drugs that kill gram-positive and anaerobic bacteria and protozoan microorganisms. The course is designed for ten days - 1500 mg of Metronidazole and 900 mg of Clindamycin (or 1500 mg of Lincomycin) per day. The daily dose is divided into 3 doses.
Modern dentistry abandons Lincomycin in favor of Clindamycin, since the first drug often causes allergic reactions, manifested in the form of intestinal disorders and rashes on the body. If Lincomycin cannot be replaced, it is better to take it not orally, but intramuscularly in the form of a 30% solution - 2 ml twice a day. Clindamycin can also be injected.
General spectrum antibiotics are effective in combating purulent inflammation:
- Amoxiclav;
- Flemoxin Solutab;
- Sumamed;
- Unidox Solutab;
- Tsifran St et al.
How to treat gumboil gums at home
It is impossible to cure odontogenic periostitis on your own. At home, you can only relieve pain and speed up the rehabilitation period after dental treatment.
For severe toothaches, the following will help:
What to rinse with?
Most often, hypertonic (soda-salt) baths and antiseptic rinses are prescribed. The former facilitate the release of pus and ichor from the wound, the latter disinfect the oral cavity and prevent the infection from spreading to neighboring tissues.
Rinsing does not have to be intense - just put the solution in your mouth and hold it on the “sick” side for 30 seconds. 4-5 mouth baths and rinses are enough per day.
Flux ointments
To completely eliminate the effects of flux after a gum incision, healing ointments and gels are used:
- Levomikol;
- Metrogil Denta;
- Holisal;
- Asepta (balm for gums);
- Stomatophyte;
- a mixture of streptocidal and ichthyol ointments.
Apply the medicine using a cotton swab.