From this article you will learn:
- treatment of gums for inflammation - drugs, regimens,
- means for strengthening gums,
- best ointment for teething gums.
The article was written by a dentist with more than 19 years of experience.
In this article, we will conduct a detailed analysis of which gel for gum disease will be most effective, and which of them can also be used to relieve teething symptoms. It should be noted that it is advisable to treat gums only with drugs in the form of gels, because they have the property of being well fixed to the moist mucous membrane of the oral cavity.
But fat-based products, for example, ointment for gums against inflammation, are pointless to use for two reasons. Firstly, the active components from such a fatty base practically do not penetrate the mucous membranes. And secondly, fatty substances adhere very poorly to moist mucous membranes, and therefore, immediately after application, the ointment is quickly swallowed with saliva.
Gel for gums for inflammation -
Preparations for the treatment of gum inflammation in the form of gels are best combined with antiseptic rinses. Then you will be able to carry out an almost complete professional course of anti-inflammatory therapy, which a dentist would prescribe for you. In this article we will tell you in detail how you should use dental gel for gums (including in combination with rinsing your mouth with antiseptics). But you must understand that without removing tartar from a dentist, the effect of such therapy will not be very long-lasting.
Content:
- Types and purpose
- Anti-inflammatory
- Painkillers
- Wound healing
- Comprehensive periodontal treatment
- Rules of application
The products of the pharmaceutical industry are extremely diverse, including those for dental clinics. Without outside help, it can be difficult to figure out when gum ointment is needed and how an anesthetic dental gel differs from it. The review article will help classify the products prescribed by dentists according to their effects and composition, but this is in no way a guide to their independent use.
Types and purpose
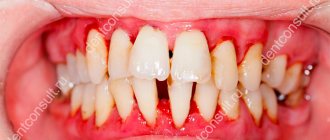
Gum inflammation is a widespread problem. There are many reasons for it, but the results are always the same: they turn red and bleed, and there is an unpleasant odor from the mouth. Periodontists practice complex treatment: antibacterial medications for oral administration, physical therapy and local therapy.
For local therapeutic effects, antiseptics and analgesics are used in powders and rinsing solutions, but ointments and gels that act in a targeted, effective and long-lasting manner are more convenient. They are quickly absorbed, therefore they actively influence the affected tissues, shorten the healing time and alleviate the patient’s condition. Their peculiarity is the almost complete absence of contraindications, except for individual intolerance and a minimum of adverse reactions compared to other dosage forms.
All such preparations, spread and rubbed into the oral cavity, are usually classified into groups that differ in the basis that binds the active components:
- gels are water-soluble, they are light and have good absorption, so the active components immediately reach the diseased organ in full, in addition, the film formed on the surface acts as an additional protection for the mucous membrane:
- ointments are oily, have a dense and heavy consistency, which is poorly absorbed and washed off with saliva.
Only a doctor will be able to select the right type of medicine, based on the clinical picture of the disease and taking into account the individual characteristics of the patient.
Signs of teething
Most often, the first teeth appear at the sixth to eighth month, but in some babies the incisor may emerge as early as four months or, conversely, teething will be delayed for six months. All this is quite normal for a healthy little organism.
Since the tooth literally needs to cut through soft tissue to appear, the first symptoms will be redness and slight swelling of the gums in this place. In addition, the following symptoms may indicate the rapid eruption of the first teeth:
- Increased amount of saliva.
Over the course of a few weeks, you may notice that drool is dripping and even leaking from your mouth - this is normal during the teething period. - Itchy gums.
The tooth that is preparing to appear irritates the gums, causing itching and unpleasant pain. The child, trying to reduce discomfort, more often puts toys and pacifiers, various other objects and his hands into his mouth. - Appetite and sleep disturbances.
Unrelenting itching prevents the child from falling asleep and prevents him from eating properly. - Heat.
Some children experience an increase in temperature during this period; be careful; if the fever does not subside for more than two days, consult a doctor. - Stool disorder.
Diarrhea often accompanies the appearance of the first teeth, but you should also be very careful with it. If it intensifies, is too intense, or lasts more than two days, or is accompanied by a change in the color and smell of the stool, be sure to tell your doctor. - Symptoms of ARVI.
Since a cutting tooth causes inflammation in the oral cavity, it is quite logical for a runny nose and cough to appear. The main thing is not to confuse these symptoms with a real disease.
Anti-inflammatory
They help relieve pain, relieve swelling and itching, and reduce bleeding. They are prescribed after dental operations on the gums, after tooth extraction, implantation and other complex manipulations. This is a large group for the complex treatment of diseases with inflammatory and infectious processes:
- Gingivitis. Infection of the oral cavity occurs due to insufficient hygiene due to the accumulation of microorganisms. Bleeding of the affected areas and the development of severe complications are possible.
- Stomatitis is painful inflammation localized on the tongue, cheeks, and gums.
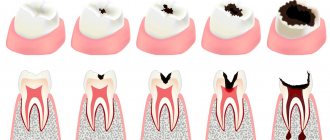
- Periodontitis is a disease that threatens the loss of a fragment of the jaw, with the formation of plaque, stones, and suppuration. It is painful.
- Periodontal disease is the gradual destruction of tissues surrounding and holding the elements of the jaw in their sockets, as well as mucous membranes and bone, causing atrophy, a decrease in bone volume with exposure of tooth roots.
Very popular in this line:
- Metrogyl Denta is a combined antibacterial gel for the treatment of infections of various etiologies.
- Dental, in addition to anti-inflammatory properties, has analgesic and wound healing properties.
- Solcoseryl is most in demand in dental practice. Unlike many others with similar effects, it is a medicine, not a balm, therefore it is often used for candidiasis, viral, traumatic and ulcerative necrotic stomatitis. Accelerates tissue regeneration.
- Cholisal - antimicrobial and analgesic effects. Inhibits the inflammatory process, reduces heat at the site of application.
Injections of antibiotics into the gums –
I would like to say a few words about such a treatment method as injections of antibiotics into the gums. This method of treatment has never been used abroad due to the enormous harm that such injections cause to the gums. In Russia, this method of treatment was previously very common due to its low cost and low qualifications of dentists (in conditions where the treatment of periodontal diseases is not carried out by periodontologists specially trained for this, but by any ordinary dentist).
Below we will explain why, if a clinic offers you a course of antibiotic injections into your gums, you should immediately run away from this clinic and look for another clinic/another doctor. The visible part of the treatment is basically that injections into the gums can actually lead to a decrease in the intensity of inflammation (bleeding, pain, swelling and redness of the gums are reduced). Although some patients may already experience gum abscessation at this stage, this is especially common in the presence of deep periodontal pockets.
How are antibiotic injections given in the gums?
Injecting an antibiotic directly into the gum results in the creation of a terrifyingly high concentration of antibiotic in the gum and bone tissue around the tooth. The antibiotic lincomycin is usually prescribed. In low concentrations it is bacteriostatic, but in high concentrations it begins to have a bactericidal effect, which leads to the immediate destruction of a very large number of pathogenic microorganisms (and not gradually, as it should be). The death of pathogenic bacteria is always accompanied by the release of a large number of toxins, various pathogens, as well as so-called “cytokines” (inflammatory mediators).
When too many of them are thrown out at the same time, this leads to the appearance of multiple foci of necrosis in the periodontium (the periodontium is the ligamentous apparatus of the tooth, with the help of the fibers of which the tooth is connected to the bone tissue). Such areas of necrosis heal with the formation of scar tissue, the formation of which initially gives the appearance of strengthening the tooth, but, unfortunately, the joy does not last long. Normal periodontium of teeth is adapted to bear a large mechanical (chewing) load, which cannot be said about scar tissue. And as soon as the area of attachment of the tooth to the bone decreases due to the normal periodontium, a mechanical overload of the ligamentous apparatus of the tooth occurs.
As a result, the bone tissue around the tooth begins to dissolve, which leads to an even greater increase in its mobility. Moreover, in this case, mobility will no longer be associated with inflammation, but with a decrease in bone level, as well as a decrease in the area of periodontal attachment of the tooth root to the bone. And this is irreversible mobility, which cannot be corrected by any treatment.
Painkillers
Indicated for severe pain, rubbed into the location of the pain symptom, after surgical manipulations to alleviate the condition during the recovery period. Anesthetic gel for teeth is often used during teething in babies.
All medicines are different in composition, so they are divided into categories:
- Anesthetic. It contains lidocaine, which can cause allergies, so it should only be prescribed by a doctor. They are used for severe pain and are characterized by a rapid effect. A prominent representative is the pain-relieving gel for gums Kamistad; Kalgel and Dentinox are popular and effective.
- Antiseptics. Lidocaine and other analgesics are not included; the anesthetic effect is imparted by an anti-inflammatory effect that reduces swelling. A typical representative is Cholisal, indispensable for teething, as it does not cause side symptoms and rarely gives allergic reactions.
- Homeopathic - created on the basis of plant extracts, therefore they are often used in pediatric dentistry. They can relieve pain for a short time, but do not cope with severe pain. The most popular children's dental ointment is Baby Doctor or Pansoral.
Diarrhea after taking antibiotics –
Taking antibiotics can often lead to the development of diarrhea, and there is even such a term as antibiotic-associated diarrhea. Most often, diarrhea is caused by penicillin derivatives and cephalosporins (β-lactam antibiotics) - especially their tablet forms, although the development of diarrhea is possible after their intramuscular or intravenous administration. The main pathogen that leads to the development of diarrhea is Clostridium perfrogens. The rapid growth of this pathogen occurs due to the fact that antibiotics suppress not only pathogenic flora, but also bifidobacteria, lactobacilli, enterococci and Escherichia coli, which under normal conditions inhibit the growth of Clostridium perfrigens.
But the mechanism of development of diarrhea can be complex, i.e. may take into account not only the suppression of beneficial microflora. For example, clavulanic acid as part of a number of antibiotics can increase intestinal motility, thereby causing hyperkinetic diarrhea. Antibiotics of the cephalosporin group (especially cefixime or cefoperazone) are poorly absorbed from the intestinal lumen, which can lead to so-called hyperosmolar diarrhea.
Diarrhea most often occurs –
- in 10-25% of cases – when prescribing drugs “amoxicillin + clavulanic acid”,
- 15-20% – when prescribing cefixime (this is a cephalosporin),
- 5-10% – when prescribing ampicillin or clindamycin,
- 2-5% – when prescribing other cephalosporins (except cefixime), as well as macrolides (erythromycin, clarithromycin),
- and only 1-2% when prescribing fluoroquinolones.
Conclusions: i.e. If you have already had cases of diarrhea after taking Amoxiclav or Augmentin (containing amoxicillin and clavulanic acid), then it is better to opt for other groups of antibiotics. First of all, these are modern fluoroquinolones, and it is especially worth paying attention to those fluoroquinolone preparations that are combined with tinidazole (for example, Tsiprolet-A or Tsifran-ST).
Another type of severe antibiotic-associated diarrhea is called “pseudomembranous colitis”. Its development is already associated with another microorganism - Clostridium difficile. The development of pseudomembranous colitis is primarily associated with the use of clindamycin, ampicillin and cephalosporins. Moreover, unfortunately, experience shows that the risk of its development when taking Russian antibiotics is much higher.
How to reduce the risk of diarrhea after taking antibiotics -
Firstly, taking probiotics in parallel can help you with this. These are drugs that contain bacteria that are beneficial to our intestines. There are a large number of probiotics, for example, some of the best are the drug Linex, as well as Bifiform. Keep in mind that it is better to choose multicomponent preparations that contain several types of beneficial bacteria.
Probiotic Bifiform (30 capsules) –
Another option to reduce the risk of diarrhea is to choose an antibiotic combined with tinidazole or metronidazole (if the risk of diarrhea is high, and if indicated). We hope that our article: Antibiotics for toothache and gum disease was useful to you!
Sources:
1. Dental education of the author of the article, 2. Based on personal experience as an oral and maxillofacial surgeon, dental surgeon, 3. National Library of Medicine (USA), 4. “Systemic antibacterial drugs in periodontology” (Mazur I.P.), 5. “Sensitivity of microbial associations of periodontal pocket exudate and odontogenic focus to antibacterial drugs” (Makeeva I.M.).
Wound healing
Their main purpose is to accelerate natural regeneration and stop the inflammatory process. Used in dentistry for the treatment of injuries in the following cases:
- surgical intervention, for example, when removing a chewing element or surgery on bone tissue;
- in the presence of ulcers, fistulas, ulcers and necrosis;
- mechanical injury;
- for burns of the mucous membrane (for example, hot food or drinks).
Also indicated for a complex of therapeutic procedures. For example, in case of periodontal damage, pain-relieving ointment for gums Levomikol or Parodontocyte is often used for restoration and accelerated regeneration.
Attention! Almost all of the above medications are over-the-counter, but the choice of a specific drug should only be made by a doctor. Particular care must be taken when using anesthetic dental gel for infants.
Where can I buy
Traditional herbal medicine puts forward high quality medicinal raw materials as the main requirement for independent production of medicines. High-quality folk remedies in finished form, as well as ingredients for their preparation, are offered by the Russian Roots online store. Delivery of ordered goods in Moscow and the Moscow region is carried out by couriers, and in other regions by mail. You can also purchase the required product in our herbal pharmacies in Moscow.
Attention! All materials published on our website are protected by copyright. When re-publishing, attribution and a link to the original source are required.
Comprehensive periodontal treatment
Therapy for periodontal diseases is long and complex. The process of destruction of the tissues surrounding the tooth has already begun, and ointment for strengthening the gums or preparations with a gel structure are effective to strengthen them. Depending on the condition of the oral cavity, ointments are prescribed:
- Heparin. Slows down blood clotting, normalizing microcirculation. The benzocaine it contains provides pain relief. Apply by appliqué.
- Levomekol. Heals wounds, relieves inflammation. It is also applied as applications, as it is poorly absorbed by the mucous membrane.
- Troxevasin/Troxerutin. A gel-based anti-inflammatory medication with venotonic, angioprotective (improves blood flow and metabolism) and anti-edema effects. Strengthens the walls of capillaries and increases their elasticity.
- Asepta. Antiseptic ointment with propolis containing chlorhexidine and metronidazole to fight infections. Contains coenzyme Q10, so it adheres well to the gums without being washed off by saliva. Antimicrobial, antipruritic, analgesic agent accelerates epithelial regeneration and improves metabolic processes.
- Cryogel. Also, for strengthening, with an antimicrobial and drainage effect, it is placed in the periodontal pocket.
Most of them are dispensed from pharmacies without a prescription and have no special contraindications or adverse reactions. But they must be prescribed by a dentist, in accordance with the clinical picture.
You may also be interested in
CHILDHOOD
Finger wipes from 0 to 3 years ASEPTA BABY
For gentle oral hygiene of babies and massage of gums during the eruption of the first teeth
More about the product
CHILDHOOD
Children's gel toothpaste from 0 to 3 years ASEPTA BABY
Designed for gentle care of baby's gums and baby teeth
More about the product
Rules of application
In order for medications to have the necessary effect, before using them you need to brush your teeth, rinse and dry your mouth thoroughly, and wash your hands with soap. Apply gels and ointments with your finger, rubbing them into the mucous membrane with a light massaging movement. After this, you should not drink or eat for half an hour. The duration of the therapeutic course is determined by the attending dentist, but usually until the inflammatory and other symptoms disappear.
For preventive purposes, you can use herbal preparations and rinsing solutions. Toothpastes that have proven their effectiveness and are recommended by professionals are useful: Lakalut, Paradontax, President. They should be used for prevention for a month, and then take a break.
Expert opinion . Even the best toothpastes are only preventive measures; they can promote healing, but are not a cure, so if any dental ailments appear, you should consult a doctor, and not try to eliminate them with home recipes: they still won’t help, and any disease will is much more treatable in the initial stages.
Gum inflammation: patient mistakes
Working as a periodontist, I observed thousands of patients with gum inflammation, and in most cases, patients came with severe forms of the disease and complications that could have been avoided (if treated in a timely manner). Mostly patients make the following mistakes:
1) When periodontitis or gingivitis develops, only antiseptic rinses and applications of gels to the gums are used, but they ignore the need to remove dental plaque using ultrasound at a dentist’s appointment. This situation leads to chronic inflammation, and if the patient only had gingivitis, then thanks to self-medication it will turn into periodontitis. If the patient already has periodontitis, this only threatens to worsen its shape, cause tooth mobility and pose a threat of the need to remove them.
2) Patients often think that antiseptics and antibiotics are enough to control gum inflammation, and therefore use them in regular courses (ignoring the need to remove the cause of inflammation). Remember that even long-term use of antiseptics and antibiotics does not allow complete “disinfection” of dental plaque, periodontal pockets or root canals in the tooth. All this acts only superficially and has a temporary effect.
3) With slight inflammation of the gums in the area of 1-2 teeth, patients often do not go to the dentist at all, but constantly rinse their mouths with antiseptics and smear various gels on the gums. Please note that if inflammation of the gum is caused by the presence of “supercontacts” or injury to it by the overhanging edges of fillings/crowns (we are talking about a localized form of periodontitis), then anti-inflammatory therapy will not stop the process of bone destruction around the tooth at all - until the factor traumatic to the gums is eliminated. Those. You still have to go to the dentist.
4) If you experience periodic swelling of the gums in the area of 1-2 teeth due to periodontitis, then anti-inflammatory drug therapy (including antibiotic therapy) is completely useless. In this case, inflammation is caused by an infection in the root canals, and until the root canals of this tooth are properly filled, the inflammation will not go away.
Important: therefore, it is very important to understand that treatment at home can be effective - only in terms of conducting a course of anti-inflammatory therapy for gingivitis and periodontitis (after removing plaque from the dentist). Home treatment can also be used to strengthen the gums - during periods between the main courses of anti-inflammatory therapy, but in this case, products that do not contain antiseptics and antibiotics should be used.