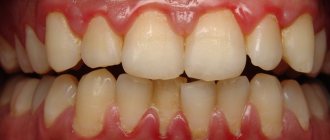
If your gums bleed when brushing your teeth, you don’t need to put up with this problem. This is a fairly common phenomenon that occurs in children and adults. There can be several reasons for the pathology: from improper brushing of teeth to serious diseases that occur hidden in the body.
Healthy gums should not bleed. If you see blood in your saliva while brushing your teeth, it means that not everything is in order, something has gone wrong in the body. Do not aggravate the problem, contact your dentist if you notice that your gums are bleeding. The doctor will prescribe the correct treatment.
Bleeding gums and other symptoms
Bleeding should already be considered the main symptom of gum disease, but this phenomenon is also often accompanied by such manifestations as:
- bright red gums and swelling
- pain when eating and when touched
- specific smell and altered taste
- plaque at the edge of the gums
- high concentration of saliva
Any of these symptoms are a good reason to visit your doctor's office. You should also remember: bleeding gums often develop against the background of poor oral hygiene and reduced immunity. Read more about this in a separate article.
How to quickly stop bleeding
If you suddenly suddenly start bleeding from your gums, you can stop it in the following ways:
- slight bleeding of the gums can be stopped with plain cold water or a special mint mouth rinse (if you don’t have it, you can use chamomile or calendula tincture diluted in warm water);
- buy homeopathic protective strips for the gums at the pharmacy and stick them on the affected area;
- You can stop bleeding from the gums using a cotton swab soaked in chlorhexidine (apply tightly to the sore spot and wait until the bleeding goes away).
Why do my gums bleed when brushing my teeth?
Hormonal background
Hormonal changes (mostly affecting pregnant women and teenagers) are one of the many causes of bleeding gums. Dentists note: hormonal changes in the body are accompanied by changes in the chemical composition of saliva, which leads to rapid mineralization of plaque on the teeth.
Lack of vitamins
A deficiency of vitamins C or K also causes blood to appear on the gums. An insufficient amount of vitamin C (especially during seasonal vitamin deficiency, a decrease in general immunity) leads to rapid wear of blood vessels and bleeding gums, and the lack of vitamin K, responsible for blood clotting, depletes the gums and makes them extremely sensitive and loose.
Microflora
Bacteria inhabiting the oral cavity are responsible for the accumulation of dental plaque, which can, over time, with poor hygiene, become tartar, causing inflammation and bleeding.
Changes in the composition of saliva in the body against the background of periodontitis and gingivitis directly affect both the respiratory tract and the normal functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
Why you need to treat gum disease
Some expectant mothers put off treatment for bleeding gums. They think that this problem can be dealt with after childbirth. This attitude towards the disease is incorrect. Only with good immunity can the body independently cope with inflammation and prevent its rapid progression. In all other cases, competent dental therapy should be carried out.
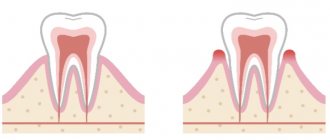
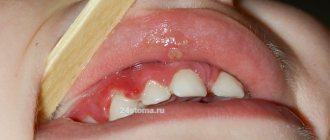
Under the influence of pathogenic microflora, which actively spreads when gingival tissue is damaged, the epithelium begins to collapse. If at the very beginning this process is reversible, then it will be quite difficult to correct the situation.
At some point, the pathogenic flora that has spread spreads to the periodontium. It gets damaged. This is manifested by tooth mobility. If you do not start treatment even with such symptoms, you can lose some units at a young age.
Doctors know of cases where the infection has affected the jaw bones. Then an irreversible change in the facial skeleton occurs, and fistula tracts are formed.
Don't start gingivitis. After undergoing professional hygiene and simple drug treatment, you will recover very quickly.
Causes of gum bleeding when brushing teeth
Why do my gums bleed when brushing my teeth? The causes of bleeding gums can be different, and one of them is mechanical damage. The simplest thing is inept or hasty handling of a toothbrush. The situation can be the most everyday: you are late for work, you decide to reduce the usual time for brushing your teeth, you start aggressively pressing the brush on your teeth - and here is the result: the gum tissue is damaged and bleeding. It's unpleasant, but not fatal. Another reason from the same series is an incorrectly chosen toothbrush: your teeth and gums are sensitive, periodically react sharply to hot or cold, and instead of a brush with soft or medium bristles, you chose one with hard ones. The result: severe bleeding, pain, inflammation and even slight detachment of the gum from the tooth. Therefore, it is important to choose the right brush.
Why you shouldn’t ignore bleeding gums
If you notice that your gums are bleeding and there is pain when brushing your teeth, you should visit the dentist without delaying it. The fact is that gum disease can have disastrous consequences - tooth loss. Gingivitis and periodontal disease develop over a long period of time and do not have an acute phase, but in an advanced state it is completely impossible to cure periodontal disease. According to statistics, in Russia 60% of the population suffers from this disease. It is better to treat gums in the initial stages.
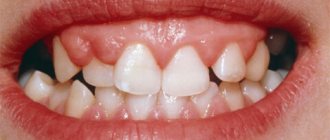
The first symptoms that you should immediately pay attention to are bleeding, swelling and changes in the shade of the gums. Periodontal disease is also accompanied by bad breath. When periodontal disease affects the teeth, teeth may lengthen, roots become visible, teeth become loose and their position changes.
The trigger for contacting a specialist should be the presence of dental plaque, stone and other deposits. By brushing your teeth on time, you can avoid serious damage to your gums. Another obvious symptom of periodontal disease or gingivitis is pain when chewing solid food.
What to do if your gums constantly bleed?
The chronic nature of bleeding gums is an alarm bell for any person. How to treat and what to do in such a situation? Some important tips for preventing and treating bleeding gums.
- Choose the right toothbrush, floss and toothpaste. The toothbrush and floss should not be hard, and the toothpaste should not contain abrasive particles.
- Switch to balanced foods. Lack of vitamins (for example, group B, as well as C, K, B, A and E) and minerals (for example, zinc, calcium) destroys teeth and depletes gums. Eat more solid vegetables, meat, dairy products, citrus fruits and nuts.
- Visit your dentist. Timely professional teeth cleaning by a specialist will help prevent the development of gum diseases such as gingivitis and periodontitis.
- Avoid mouthwashes that contain alcohol. Although alcohol-containing rinses kill most bacteria, they dry out the gums excessively, which only aggravates the course of oral diseases due to bleeding gums.
- Give up bad habits. Smoking and alcohol irritate the mucous membrane in the mouth and worsen gum disease.
What can a dentist do?
The more serious the cause of bleeding, the more important it is to start treatment in a timely manner. The best person to distinguish inflammation from injury or infection is a doctor. The dentist can help:
- Make the correct diagnosis and prescribe treatment. If there is an infection, the doctor will prescribe an antibiotic and determine what further procedures need to be performed. Anti-inflammatory drugs and antiseptics in the form of rinses can also be used as medications. Treatment cannot be interrupted, otherwise the problem may return. After completing the course, as a rule, a second examination is carried out, where the dentist evaluates the condition of the gums.
- Clean your teeth. Various deposits on the enamel often cause inflammation and bleeding. It is recommended to carry out such a procedure regularly, without waiting until the gums begin to bleed.
- Rinse the periodontal canals. It is one of the stages of treatment, carried out by a doctor. Allows you to remove particles of pathological tissue and bacteria.
- Choose the right toothpaste. Many manufacturers produce special products for people with bleeding problems.
How to prevent bleeding gums
Attention! Anti-bleeding toothpastes are mainly an emergency measure. They can quickly eliminate the symptom, but should not be used for more than three weeks.
Bleeding when brushing teeth in pregnant women
Reduced immunity
Bleeding gums in expectant mothers often occur when hormonal levels change. This leads to an inevitable decline in immunity (both general and local - in the oral cavity) and an imbalance in the acid-base balance, which provokes the growth of bacteria and accelerates the accumulation of plaque. All together causes inflammation, pain when brushing teeth and bleeding.
Poor hygiene
During pregnancy, gums bleed when brushing your teeth, also due to poor oral hygiene, or even lack thereof, as a result of which harmful bacteria multiply on the gums, contributing to the formation of plaque on the teeth. Hence inflammation, redness, pain - and, as a result, gingivitis, which over time can develop into a much more serious form - periodontitis.
Lack of calcium
Pregnancy is a huge burden on the female body. Calcium deficiency in an organism experiencing severe stress leads to the development of gingivitis, therefore, in the treatment of bleeding gums during pregnancy, an integrated approach is important: proper nutrition, vitamins and healthy sleep.
Important!
Choose the right brush and don’t forget that you need to change it every 3 months. Remember: a toothbrush is a purely individual thing, no one but you should use it. Also rinse the brush thoroughly after each use.
Signs of violation
If your gums bleed during pregnancy, you can assume the presence of gingivitis. During different periods of pregnancy, this disease manifests itself in different ways. Typically a woman complains about:
- inflammation and swelling of soft tissues;
- bleeding even with minor mechanical stress;
- feeling of constant itching;
- transformation of the gingival papillae - they cease to be pointed and become dome-shaped;
- pain when chewing solid foods;
- elevated body temperature.
There are three forms of gingivitis:
- Light. Only the gingival papillae are damaged.
- Average. The inflammatory process has spread to the gums.
- Heavy. The entire gum is inflamed.
The disease can affect one or more teeth, or affect the entire dentition. In any case, treatment must be carried out as soon as possible.
Treatment of gingivitis in children in the dental clinic
If your child exhibits characteristic signs of gingivitis, make an appointment for your child at the specialized dental clinic “Aesthetics”. High-level children's specialists with extensive professional experience work here.
The center is equipped with modern equipment that allows high-precision diagnostics and painless treatment of any diseases of the teeth and gums. When treating gingivitis in children and adults, qualified dentists use only high-quality medications from reliable global suppliers.
The center has a flexible pricing policy. All patients who leave their reviews on the Aesthetics website are guaranteed a 3% discount on all dental services.
Herbal medicine will help with gum inflammation during pregnancy
In addition to sanitation of the oral cavity, you will need a course of treatment using various herbs. For these purposes, oak bark, calamus root, string, yarrow, calendula, sage, chamomile and St. John's wort are used. They are absolutely harmless during pregnancy, but at the same time they have a very strong anti-inflammatory effect. To prepare the decoction, pour boiling water over 2 tablespoons of the herb and cook for 5-7 minutes. Then the broth is cooled, filtered and used for rinsing after each meal during the day, but not less than 5 times.
What measures are prohibited during pregnancy?
- Use arsenic.
- Carry out dental prosthetics and teeth whitening procedures.
- Use anesthesia (for pain relief, gentle agents are used that do not contain adrenaline).
Situations where doctors may forget about a patient’s pregnancy due to inattention are quite possible. Therefore, it is very important for the woman herself to monitor the actions of the dentist and specify each drug that is supposed to be introduced into her body. If the sensations are too painful, you can resort to anesthesia. The stress of a pregnant woman can cause more harm to the unborn child than the use of an anesthetic drug.
Diagnosis and treatment of gingivitis in young children
Gingivitis in children is diagnosed during a standard dental examination. If a visual examination is not enough to make a diagnosis, the doctor may order an x-ray.
Treatment of gingivitis in children under one year of age
and older requires an integrated approach. The course of prescriptions is selected individually, taking into account the form of the disease and the age of the small patient.
Complex treatment of gingivitis in children under 2
years and older:
1. Removing soft microbial plaque and hard dental deposits from the surface of teeth.
2. Polishing tooth enamel with special brushes.
3. Antiseptic mouth rinses.
4. The use of anti-inflammatory gels and ointments to treat inflamed gums.
5. Sanitation of the oral cavity. When gingivitis is diagnosed,
treatment in children 3 years of age
and younger is based on gentle techniques. For example, to remove carious formations, teeth are silvered without drilling.
In severe forms of gingivitis with a high risk of complications, antibacterial agents are included in drug therapy. The drug and dosage are selected by the attending dentist.
When diagnosed with gingivitis, treatment in children (4 years
and younger) with the use of antiseptic solutions for rinsing the oral cavity is successfully replaced by applications using cotton swabs soaked in a medicinal composition. This recommendation is relevant if the baby refuses or cannot independently perform the mouth rinsing procedure.