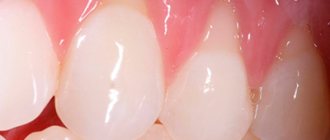
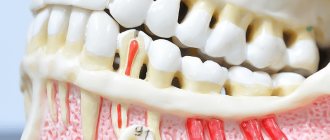
Healthy gums are the key to strong teeth and a beautiful smile. Normally, they are pink, cover the alveolar processes and necks of dental units, and are not damaged. Based on their condition, the dentist can judge the health of the oral cavity.
Soft tissues are the first to react to negative changes occurring in the body. Redness of the gums is one of the main signs of inflammation. It can be associated with various factors - from drinking too hot drinks to the development of periodontitis. Find out if it is dangerous and in what cases you need medical help.
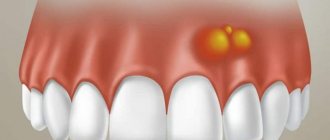
Why do ulcers appear on the gums, and is it always dangerous?
There are many possible reasons. To understand how dangerous the appearance of certain lesions on the gums is, you need to look at additional accompanying symptoms:
- in case it is trivial mechanical damage. The gums can be damaged by hard food, a toothbrush, or a foreign object. These lesions may resolve in 3-5 days. If a person does not brush his teeth, then infection is added to these damages, and healing may take several weeks.
- Sometimes ulcers can appear as a result of wearing orthodontic structures, braces or removable dentures.
Principles of treating gum disease
The treatment regimen is developed by the doctor depending on the type of pathology that is accompanied by redness of the gums. Each dental disease requires an individual approach.
Gingivitis
The problem is characterized by inflammation of the periodontal papillae and the appearance of small pimples in this area. Treatment of the problem begins with the removal of hard and soft deposits from the surface of the enamel. After this, local anti-inflammatory and decongestant drugs are prescribed. The prognosis for recovery from gingivitis is usually favorable.
Periodontitis
The disease is considered a more serious form of gum tissue damage. If left untreated, the periodontal papillae atrophy, and balls filled with pus form in the periodontal pockets. Treatment of the disease is carried out in stages: taking or injecting antibiotics into the gums; splinting of moving elements of a row; surgical formation of atrophied areas of the gums.
Inflammation of the gums requires immediate treatment, since if the pathological process is complicated, periodontal disease or complete loss of the dentition may develop. There are many ways to combat the problem at home. Therapy includes the use of pharmacological drugs and traditional medicine. Mild forms of inflammation can easily be eliminated in a few weeks if all the rules outlined by the dentist are followed.
The most common diseases of the oral cavity in which ulcers appear
- ulcerative necrotizing gingivitis. The cause of this disease is bacteria that multiply when immunity decreases. Extensive ulcers appear on the gums, regional lymph nodes become enlarged, and the temperature may rise
- chronic recurrent aphthous stomatitis. Up to 4-5 white spots first appear in the mouth, which later turn into ulcers. There is no temperature or other problems related to well-being. If such symptoms appear 1-2 times a year in small quantities, then there should be no cause for concern. Frequent occurrence is associated with weakened immunity and possible intestinal diseases, as well as allergies.
- acute herpetic stomatitis. Herpetic stomatitis occurs in a child when he first encounters the herpes virus. Many bubbles appear on the gums, which, after bursting, turn into ulcers that merge with each other. The gums are always bright red, and the ulcers themselves are very painful, the temperature may rise
Symptoms of the problem
You should consider the main diseases that cause redness of the gums and their distinctive signs:
Causes of gum inflammation
- Gingivitis. The disease is associated with damage to the tissue near the tooth by harmful agents. The main cause of the problem is improper oral care. Untreated gingivitis is complicated by periodontitis or periodontal disease, and tooth loss. The main signs are pain when eating and brushing teeth, bad breath, and fever.
- Periodontitis. In pathology, the soft tissues around the tooth are affected. The disease is acute with pronounced symptoms, as well as changes in pain intensity. The pathological process develops within 7-14 days. If not treated in a timely manner, periodontitis can lead to heart attack, stroke, loss of dentition, and intoxication of the body.
- Periodontal disease. During the disease, the tissues surrounding the teeth also become inflamed. A distinctive feature of the pathology is sluggish development. The problem occurs with hidden symptoms for several years, but ultimately leads to the loss of units. The main signs of periodontal disease: unsteadiness of elements, red growths on the gums, divergence of teeth in different directions. Untimely treatment of periodontal disease can lead to diseases of the gastrointestinal tract due to inadequate chewing of food.
First aid
If the temperature rises, you can take an antipyretic drug. In the future, before visiting a doctor, nothing should be done. Do not take antibiotics yourself or try to get into the ulcer with any object.
How to relieve symptoms of ulcers
- do not eat sour and salty foods
- food should be warm, no hot dishes or drinks
- Care should be taken to ensure that the child does not put dirty hands in his mouth
- teeth should be brushed, but make sure that the bristles do not touch the gums with ulcers
- It is recommended to rinse your mouth with herbal solutions (oak bark, chamomile) 3-4 times a day
You should be careful when using antibacterial solutions. They must be prescribed by a doctor. If such solutions are used incorrectly, they can provoke the development of thrush. The antibacterial agent will “kill” the beneficial microflora, which can result in a fungal infection.
Prevention of ulcers
- professional oral hygiene at least 2 times a year
- Regularly replacing your toothbrush
- Proper brushing of teeth at least 2 times a day
- using additional hygiene techniques such as irrigators, dental floss, and tongue scrapers
- Children should be monitored for bad habits such as putting dirty fingers and other objects into their mouths
- It is important to treat your teeth in a timely manner. Microbes that are found in carious teeth and rotten roots can serve as a source of infection for ulcers
If you have problems in the oral cavity, contact the specialists of the Center for Family Dentistry!
Removal of epulis on the gum
The need to remove the supragingival tissue occurs when the tumor is large, is growing rapidly, or is at risk of cancer. The procedure is complex and can only be performed by an experienced oral or maxillofacial surgeon.
Removal of epulis on the gum takes place under local anesthesia or sedation. The essence of the operation is to remove the lump and excise the affected tissue. Excision of the epulis itself can be done with a scalpel or laser. Dentists prefer a laser that can instantly stop bleeding and make precise “cuts.”
If the pathological process has penetrated deeply, it is possible to remove a section of bone using a cutter or bur. If teeth are damaged in the area where the tumor is located (loose teeth, exposed roots, etc.), the surgeon removes these teeth as well.
After the operation, the patient is covered with iodomorphic gauze. If there is a large area of dissection, the surgeon will apply sutures. A sterile bandage is applied over it.
In case of angiomatous and fibromatous appearance, removal of epulis on the gum can also be carried out if conservative therapy has not yielded results or the patient seeks help in the presence of complications.
Dentists' recommendations
Epulis is a gum tumor that poses a great danger to the health of teeth and the entire body. Treatment of the pathology is complex and lengthy, but even with high-quality treatment, the risk of relapse cannot be ruled out.
It is not always possible to prevent the occurrence of epulis on the gums of a child or an adult, but with timely consultation with a specialist, complications, complex treatment, long recovery and aesthetic defects that remain after surgery can be avoided.
The best prevention is to visit the dentist every 6 months. If you are concerned about discomfort and a feeling of rubbing of the mucous membranes or gums, you should immediately consult a dentist, without waiting for a tumor or other pathologies to occur.
Causes of gum swelling
Physiological
Normal gums are pink, painless and of normal size. But sometimes they swell for natural reasons:
- during teething - in children and adults (wisdom teeth);
- after tooth extraction—slight swelling and redness of the gums is observed for up to 3 days;
- after injury - damage to the soft tissues of the gums leads to their swelling for some time while integrity is restored;
- during pregnancy - under the influence of hormones and due to the redistribution of blood in the body, gums may swell in women carrying a child;
- injury from dental structures - veneers, braces and fillings, if installed incorrectly, come into contact with gum tissue, causing damage to them.
There is no need to panic if the gums of a child aged 1 to 7 years are swollen. At this time, baby or permanent teeth erupt, which may cause swelling and redness in this area. Sometimes small balls appear - cysts. They are safe and in most cases go away on their own over time. If the cyst interferes with tooth eruption, it is surgically removed in dentistry in 1 session. The procedure is performed under anesthesia and does not cause any discomfort.
Pathological
In most cases, gum swelling occurs due to inflammation. Pathological reasons:
- periodontitis - local inflammation above or below the tooth;
- periodontitis - inflammation of periodontal tissues;
- gingivitis - inflammation of the gums;
- periodontal abscess - suppuration localized at the edge of the tooth;
- stomatitis - ulcers that appear on the soft tissues of the oral cavity;
- secondary infection against the background of immunodeficiency - with HIV or hepatitis, even opportunistic microorganisms can cause oral diseases;
- atypical sore throat - spreads to the gums, the main symptom is that it is painful for a person to swallow;
- Vitamin deficiency C - a lack of vitamin affects the gum tissues, causing them to swell.
Swelling of the gums due to an allergic reaction is also considered pathological. It can develop from an injection of an analgesic during dental treatment or from any irritant to which a person is sensitive.
If your gums bleed due to inflammation
Bleeding gums, associated with their swelling, is characteristic of periodontitis and gingivitis. In this case, the tooth does not hurt and does not cause discomfort. The difference between these diseases is that gingivitis occurs primarily. And if this condition is repeated more than once, it is already periodontitis - a pathology with a chronic course. Other symptoms of the disease include:
- bright red gum color with a bluish tint;
- pain at the site of swelling or throughout the jaw;
- swelling of the gums partially covers the tooth.
But the main distinguishing feature of periodontitis is bleeding gums. There are several reasons for this condition:
- diabetes mellitus in the stage of decompensation;
- the presence of systemic inflammatory pathologies;
- ARVI and acute respiratory infections;
- Tartar deposits;
- injuries of soft tissues of the oral cavity, occurring with complications;
- long-term treatment with glucocorticoids;
An x-ray is taken to confirm the diagnosis. It shows a noticeable reduction in the interdental septa, and less often, exposure of the tooth root.
When gums are inflamed and even your cheeks hurt
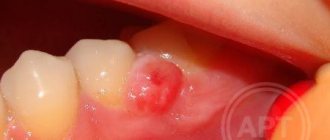
Sometimes the gums not only swell, but a new growth becomes noticeable on it. It is often pale in color due to the presence of pus inside. This is what a periodontal abscess looks like:
- the surface of the neoplasm is elastic and tense;
- swollen tissue around the abscess;
- the palate and cheek swell;
- sometimes the general body temperature rises, more often local;
- swollen tissues of bright red color;
- fluid movement is felt inside the abscess.
This disease is often called "flux". It has a rather characteristic picture. An abscess develops due to lack of treatment for periodontitis: suppuration appears that cannot come out. “Flux” is accompanied by very severe pain and swelling.
Treatment of an abscess is carried out only surgically and in a hospital setting. Attempts to cure flux at home with lotions or self-opening can result in phlegmon, sepsis and, in rare cases, even death. In the best case scenario, the patient will receive major surgery with pus removed through large incisions in the face instead of a small hole in the gum. Therefore, you should not delay visiting the dentist.