Tonsillitis is an infectious disease in which inflammation of the tonsils (glands) occurs. This disease affects both adults and children aged 2 years and older. Tonsillitis in a child most often occurs between the ages of five and ten years, and inflammation can recur several times a year.
The acute form of the disease is nothing more than the well-known sore throat. A person who has suffered from a sore throat at least once, during which he experienced severe pain in the throat, will not confuse it with any other diagnosis. Sore throat is an insidious disease that can cause serious complications in related organs and even lead to disability. What effective measures should be taken in the treatment of inflammation of the tonsils to avoid complications? We will talk about this in detail in our article.
Tonsils on guard
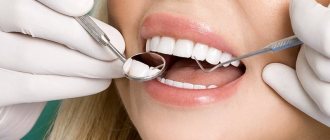
The tonsils (or tonsils) are located on both sides of the throat. All bacteria and viruses that enter the body through the mouth are encountered first. Externally, the tonsils have a porous structure; this structure helps them “examine” all the substances that enter the body and decide what to do with them. In the thickness of the palatine tonsils there are special depressions - lacunae, and the convoluted channels in the thickness of the tonsils are called crypts; they are difficult to see in a photo or with the naked eye. There are also target cells that act as “traps” for microorganisms. When it comes into contact with them, the tonsil decides whether to fight them or not, whether they will cause harm to a person or whether they will be harmless.
When a person is healthy and his tonsils are strong, when any infection enters the body, they begin to actively produce white blood cells to fight the infectious pathogen. But when inflammation affects the tonsils themselves, they lose their protective function and themselves become a source of infection. Pathogenic viruses and bacteria settle firmly in the gaps. What function can inflamed tonsils perform? None! As a result, the tonsils fall out of the body's general defense system and there is a high chance of developing chronic tonsillitis in children.
Causes of tonsil hyperplasia
For the occurrence of the disease, a damaging factor, for example, a burn, is important. In such situations, not only the tonsils are affected, but also the tissues adjacent to them. Not only too hot water, but also alkaline and acidic substances can damage the tonsils. For treatment of such patients, hospitalization is mandatory.
Among the reasons are the impact of a third-party object. Most likely these are small fish bones that violate the integrity of the lymphatic tissue. When swallowing, a person in such cases feels as if something is stabbing in his throat. The next reason is tumors and abnormal development of the tonsils. An organ can also be damaged if:
- contact with infected mucus (adenoiditis)
- mouth breathing, resulting in prolonged inhalation of cold air
- diseases to which the child was exposed at a young age
- relapses and frequent diseases of the ears, throat and/or nose.
The following children are at risk for tonsil hyperplasia:
- malnourished
- with poor living conditions, without proper care from parents or guardians
- imbalance of hormones in the body
- lymphatic-hypoplastic constitutional anomaly plays a role
- exposure to radiation for a long time
- lack of vitamins
Activation of the production of lymphoid cells plays a role in pathogenesis.
Causes of tonsillitis
As a rule, the cause of the disease is bacteria and viruses (usually streptococcus). Typically, infection occurs through airborne droplets, especially when children are in large groups (kindergarten, school, various clubs and sports sections). If the causative agent of the disease is bacteria, you can become infected through dishes, a handshake, or through the patient’s personal items (towel, spoon). A child only needs to play with the toys of another sick child to become infected. Alas, acute tonsillitis is a highly contagious disease; and it is very easy to become infected with it.
Another cause of the disease is microorganisms that constantly live on the mucous membranes. This is the norm. A healthy body controls their amount and does not allow them to be exceeded. But as soon as the immune system weakens, the number of pathogenic microorganisms begins to increase: and in essence it turns out that the body infects itself. That is, the development of inflammation can occur with prolonged exposure to unfavorable factors on the child’s body that cause a decrease in immunity: dry indoor air, cigarette smoke, polluted air in big cities, etc.
Surgery to remove tonsils
The importance of the tonsils cannot be underestimated. We found this out at the very beginning of the article. The main goal of any therapy is to try to reduce the tonsils without surgery and preserve them as an organ of the immune system. Many adult patients mistakenly believe that they will have less pain after surgery. It is a myth! Yes, the tonsils will stop bothering you. But now the infection from the outside will enter the pharynx and further into the respiratory tract without encountering any obstacle, which will not have the best effect on the incidence of respiratory tract diseases.
The operation to remove the tonsils is called tonsillectomy.
Certain indications are required for the operation. The patient's fatigue due to frequent exacerbations and unpleasant symptoms is not such an indication.
Surgical intervention is prescribed in the following cases:
- recurrence of sore throats more than four times throughout the year;
- a peritonsillar abscess that has occurred;
- poor performance of rheumatic tests;
- complications on other organs and systems of the patient.
Before deciding to undergo surgery, it is necessary to try to treat a child or adult patient conservatively, that is, to reduce the tonsils without surgery.
Symptoms of the disease in children
The first symptoms in children suffering from acute tonsillitis appear already on the first to third days after infection, among them:
- high body temperature (with fever, the temperature may rise to 40°C);
- severe pain in the throat, it is very difficult and painful for the child to swallow;
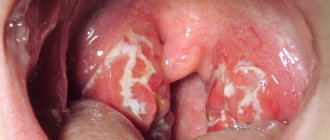
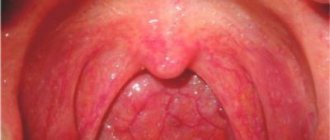
- the tonsils increase in size and turn red; pustules may be noticeable on them;
- headache;
- sick children lose their appetite;
- weakness, lethargy;
- enlarged lymph nodes;
- gastrointestinal tract disorders are possible;
- bad breath.
In children with chronic tonsillitis, the symptoms are not as pronounced. The body temperature remains at the subfebrile level for a long time (37-37.5°C). The tonsils become loose - a sign that they have lost their protective function.
Literature
- T.I. Garashchenko. Sore throats in children and their systemic antibacterial therapy. Consilium Medicum. Pediatrics. (Add.) 2008; 02: 14-20.
- E. I. Krasnova, N. I. Khokhlova. Differential diagnosis and treatment tactics for acute tonsillitis (angina) at the present stage. Attending physician No. 11/2018; Page numbers in the issue: 58-63.
- Clinical recommendations (treatment protocol) for providing medical care to children with tonsillitis (acute streptococcal tonsillitis), FSBI NIIDI FMBA of Russia, 2015.
- Tatochenko V.K.. Once again about antipyretics. Issues of modern pediatrics. Volume 6 No. 2 2007, p. 128-130.
- Instructions for the drug HEXORAL® SOLUTION.
- Instructions for the drug HEXORAL® in AEROSOL form.
- Instructions for the drug HEXORAL® TABS.
- Instructions for the drug HEXORAL® TABS CLASSIC.
- Instructions for the drug HEXORAL® TABS EXTRA.
Up to contents
Complications
It may seem that acute tonsillitis is a completely harmless disease. “Sore throat, fever - what’s wrong with that? A common manifestation of infection,” you say. But let us remember the nature of the disease. Its causative agent, streptococcus, can cause serious consequences.
Complications after tonsillitis can be divided into local (they are localized and noticeable in a certain area) and general (when changes affect the whole body).
Local ones include:
- paratonsillar and parapharyngeal abscess;
- mediastinitis (when a purulent infection descends into the heart sac);
- bleeding from the tonsils, provided that there were ulcers on their surface;
- otitis and eustacheitis (ENT organs are directly connected to each other, so an infection from the throat can easily migrate to the middle ear cavity, the auditory tube and cause an inflammatory process there);
- swelling of the larynx (with this condition, asphyxia develops. This condition is very dangerous, even fatal. A characteristic sign is a bluish tint of the skin against the background of severe suffocation);
- phlegmon and abscesses (purulent inflammation).
Common complications include diseases of the heart, kidneys, joints (rheumatism), tonsil intoxication and sepsis. In order to avoid dangerous consequences for the child’s body, it is very important to promptly begin the fight against tonsillitis under the supervision of a qualified otolaryngologist.
Friends! Timely and correct treatment will ensure you a speedy recovery!
Make an appointment right now!
Call us by phone or use the feedback form
Sign up
How to cure tonsillitis in a child
Treatment methods for sore throat depend on the nature of the pathogen: for bacterial sore throat, the doctor will prescribe effective antibiotics (the drugs Augmentin, Amoxiclav, Erythromycin are more often prescribed), for sore throats of a viral and fungal nature - anti-inflammatory and antifungal drugs, respectively. The name of the drug, its dosage and the duration of its use can only be determined by an ENT doctor. Excessive parental independence can interfere with the effective treatment of acute or chronic tonsillitis.
If a child's temperature rises above 38°C, an antipyretic based on ibuprofen or paracetamol should be given. Due to blood thinning and the risk of bleeding, aspirin is strictly contraindicated in children.
It is necessary to adhere to strict bed rest and a gentle diet. Eating and drinking should not cause additional strain on the throat. It’s better to make do with warm soups, broths and purees for the first time. Oral antiseptic sprays, special lozenges and tablets (for example, Faringosept) are perfect for relieving a sore throat.
Chronic tonsillitis in a child: treatment methods
This disease is diagnosed in children if inflammation of the tonsils occurs more than twice a year. In case of chronic disease, the tonsils themselves become a source of infection. The immune system weakens, and the child is often exposed to illness.
Chronic tonsillitis should be treated by an experienced otolaryngologist. Some ENT doctors recommend removing the tonsils immediately. But you need to remember, by removing the tonsils, you lose the body’s natural defenses against bacteria and viruses forever!
At the ENT Clinic of Doctor Zaitsev, we treat chronic tonsillitis, and we resort to removal of the tonsils only in the most extreme cases, when conservative treatment methods have been completely exhausted.
The procedures for ultrasonic medicinal irrigation of the tonsils using the “Tonsillor” apparatus (it can be seen in the photo) have a good therapeutic effect. Our clinic also has a unique vacuum attachment for this device, which has no analogues in other medical institutions. This attachment is painless, safe and can be used to treat children starting from school age.
Diagnostics
An experienced doctor pays attention to the facial expression of a small patient. It is important to interview parents, and, if possible, the child himself, to identify the main complaints. The history may indicate such points as low immune defense of the body, respiratory diseases (several per year), and a stuffy nose for a long time. Laboratory tests are important to determine the diagnosis. It is necessary to identify the pathogen and check its response to commonly used medications. The patient is prescribed bacterial culture from the throat.
The patient's blood must be taken for analysis, including acid-base balance, and urine must be taken for analysis to detect inflammation. Instrumental diagnostic methods are also relevant when diagnosing tonsil hyperplasia. Ultrasound diagnostics of the pharynx, pharyngoscopy, fibroendoscopy and rigid endoscopy are performed.
Tonsil hyperplasia can be caused (must be taken into account when diagnosing):
- cancer in the tonsils
- tuberculosis
- granulomas of the pharynx of an infectious nature
- leukemia
- lymphogranulomatosis
Prevention of tonsillitis
To reduce the risk of developing the disease, you need to devote time to preventing this disease and strengthening the immune system. It is necessary to accustom children to hardening procedures. Hardening will bring positive results if you do it gradually, and at the same time consistently and regularly.
It is important to eat healthy and varied, eat foods rich in vitamins and avoid seasonings that irritate the throat. You also need to remember the relationship between the ENT organs and the surrounding tissue. Therefore, it is extremely necessary to promptly treat dental diseases and any inflammatory processes in the nasopharynx and larynx.
From an early age, children should be taught sanitary standards: washing hands, washing fruits, covering their mouths when coughing with a handkerchief or napkin. During periods of epidemics, it is advisable to avoid places with large crowds of people.
Following these simple measures will help avoid inflammation and the unpleasant consequences of this disease.
Causes of chronic inflammation of the tonsils
Inflammation in the tonsils in an adult or child is caused by streptococcus and staphylococcus bacteria, which begin to actively multiply and take root in the lacunae of the tonsils, poisoning the body with the products of their vital activity.
The causes of infection entering the tonsils may be:
- past infectious diseases;
- chronic diseases of the nose and paranasal sinuses (rhinitis, sinusitis);
- pharyngitis;
- dental diseases (caries);
- deviated nasal septum;
- nasal polyps;
- overgrown adenoid vegetations in a child;
- stress;
- allergic reactions;
- reduced immunity.
One of the most common causes of chronic inflammation is improperly treated or undertreated acute tonsillitis - a sore throat we all know.
Therefore, it is extremely important to begin treating the disease in the early stages, and treatment of tonsils in adults and children should initially be carried out by a competent otolaryngologist.
"ENT Clinic of Doctor Zaitsev"
Treatment of tonsillitis in children in Moscow is offered by many medical institutions: from district clinics and multidisciplinary centers to private clinics. The main thing is to make the right choice!
Our clinic accepts patients from the age of three. The ENT clinic has everything necessary for the successful treatment of sore throat and chronic tonsillitis: the most modern equipment and instruments, its own treatment methods, and most importantly, highly qualified ENT specialists with extensive practical experience. A visit to a doctor for a small patient is always stressful, and our task is to make the appointment as calm and easy as possible for the child. The examination takes place in a playful way: the baby no longer perceives the treatment as something scary and unpleasant, and the mother’s saved nerves are worth a lot. Our clinic is equipped with a children's corner where a child can play, read, or just drink tea and cookies while the mother and the doctor discuss the treatment regimen. Prices for our services have not changed for more than three years and remain one of the best in Moscow.
If you have discovered the first signs of a sore throat in your child, or he has been suffering from relapses of chronic tonsillitis for several years, please do not delay and make an appointment. We will help you cope with this illness.
Treatment
Treatment requires a comprehensive approach, including the use of medications, physical therapy and, if necessary, surgery. In grade I (classification described above), special medications and rinses are prescribed. For the latter procedure, cauterizing and astringent agents are suitable, including a tannin solution; Antiseptics are also prescribed.
Hypertrophied areas are lubricated with a 2.5% solution of silver nitrate. The following medications are suitable for treatment:
- tonsilgon
- tonsilotren
- umkalor
- lymphomyosot
Topical physiotherapy techniques include:
- ultrasound
- ozone
- Microwave
- UHF
In some cases, endopharyngeal therapy with laser is needed. Mud ultraphonophoresis, electrophoresis, inhalation with decoctions of medicinal herbs, and vacuum hydrotherapy are often prescribed. In cases of II and III degrees of hyperplasia, surgical operations are resorted to. Most often, part of the overgrown tonsil is removed. This method is relevant for patients under seven years of age, if there is no polio, diphtheria, infectious diseases, or blood diseases.
Cryosurgery is a method of treating tonsil hyperplasia, in which the organ is affected by low temperatures, which allows you to get rid of pathological growths. In this case, the patient does not feel pain, and there is no blood either. This operation is indicated for patients with heart failure, atherosclerosis and heart defects.
The next method of treating the pathology in question is diathermocoagulation, in other words, cauterization. When agreeing to treatment with this method, consult your doctor about the high likelihood of various complications.