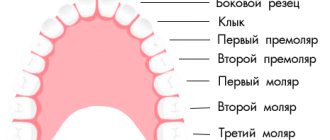
Enamel is the hardest tissue in the human body and a natural protective barrier for teeth. However, some people are diagnosed with its deficiency. Hypoplasia of dental enamel - as this condition is professionally called - can have different causes, but appropriate treatment methods must be used each time.
The main function of enamel in the oral cavity is to protect teeth from harmful factors: the action of bacteria, thermal and chemical irritants, as well as abrasion during chewing. Although there are proven ways to strengthen enamel, its gradual erosion is associated with various reasons. Some patients, even children, are also diagnosed with underdevelopment of this tissue. Dental hypoplasia can have many causes and each time requires appropriate treatment.
Ideal teeth size
In dentistry, teeth of a certain size and anatomical shape are considered normal, depending on the size of the jaw and their location in it. They must be smooth, fit tightly to each other and have a thickness within certain limits: for example, the height of the lateral incisors in an adult is normally 7 - 11 millimeters. Of course, this does not mean that they need to be measured with a ruler - overall aesthetics and proportionality are much more important (for example, for people of short stature and fragile build, a small teeth size is appropriate). Many parents are interested in why their child has small teeth, but usually there is no reason to worry: normally, the baby incisors are small and located at a distance from each other.
However, if the patient really has very small teeth, you should definitely consult a dentist to confirm or exclude the diagnosis of microdentia.
Anomalies in tooth shape
In orthodontics, the most common concept is considered to be “malocclusion”, that is, the closing of the jaws and the position of the teeth at the same time. However, the beauty of our smile is also affected by the irregular shape of the teeth - for example, when they are of different sizes, rotated around their axis, or shifted to one point.
Changes in the shape of teeth, violation of their position are also anomalies of the dental system, but, like malocclusion, they are treatable.
EXPERT OPINION
Correction of bite with internal braces Win - 180,000 rubles.
All inclusive! Preparation and treatment of the oral cavity, consultation with an orthodontic specialist, installation and adjustment of orthodontic structures. The price is for one jaw.
Free consultation with an orthodontist +7 (495) 789-39-31 or write to us
Diagnosis of microdentia
According to statistics, about 5% of people face the problem of microdentia – abnormally small teeth in an adult. There are several signs that allow you to distinguish microdentia from other dental pathologies.
Symptoms of microdentia
- teeth of regular shape, but with a significantly reduced crown;
- distances between teeth visible to the naked eye;
- damage mainly to the front teeth;
- wavy or jagged shape of the cutting part of the affected tooth.
In most cases, the presence of microdentia can be determined by visual examination of the patient, but for a more accurate diagnosis, hardware diagnostics are performed. For example, the doctor can measure the overall width of the incisors of both jaws using a special instrument, as well as resort to x-rays. A deviation is considered to be a reduction of teeth by 1.5 mm or more relative to the norm. Based on the results of the examination, one of three types of microdentia is determined.
Isolated
If the patient has one or two small teeth, then we are talking about isolated microdentia. Most often, the front incisors (mainly the lateral incisors) are underdeveloped.
Relative
Relative microdentia is said to occur when the patient has an abnormally enlarged jaw. On such a jaw, even normal-sized crowns can look disproportionately small. Thus, relative microdentia is an overly large gum and small teeth on it.
Generalized
In the most severe cases, when small teeth are located throughout the jaw, the patient is diagnosed with “generalized microdentia.”
What types of teeth are there: irregular shape
- oversized teeth: these are overly large teeth that can interfere with the eruption of neighboring ones, distort the dentition and cause crowding of teeth. Most often, the problem concerns the front teeth (the so-called “bunny smile” occurs), the size of which can be increased up to 6 mm in length relative to the rest in the row. One of the most serious disadvantages of giant teeth is their abnormal appearance, which attracts unnecessary attention and does not meet generally accepted standards of beauty.
- Too small teeth: This is a problem in which the jaw contains teeth with small crowns. The problem often spreads to all the teeth in the mouth. The teeth may be regularly shaped but often grow at large intervals. In addition, due to the too small size, the teeth of the upper and lower jaws do not meet tightly, as a result of which the patient has problems chewing solid food, since the chewing surfaces of the opposite teeth do not connect,
- teeth in the form of spikes: that is, wide at the base (at the gums) and very narrow in width at the tips, in the form of a spike or cone,
- teeth of any abnormal shape: they have a wide variety of irregular shapes that cannot be structured or described,
- Hutchinson's teeth: teeth that are wider at the base and narrower in thickness at the cutting edge. The problem usually affects the front teeth of the upper or lower jaw. The lower cutting edge also has a small semicircular notch (it is this feature that the scientist characterized as one of the main ones for determining congenital syphilis). On the lower cutting side there is often no enamel and the inner dentin of the tooth is exposed,
- Fournier teeth: similar to Hutchinson teeth, that is, they are shaped like a flat-head screwdriver. But Fournier proved that in the presence of congenital syphilis, there may not be a semicircular notch on the cutting surface of the front teeth,
- Pflueger teeth: the problem affects only the first chewing molars. Outwardly, they resemble an unopened bud - that is, they are greatly underdeveloped in size.
Reasons why teeth become small
As a rule, most of the reasons leading to the appearance of small front teeth in adults come from childhood, when pathological processes interfere with the formation of body systems. Microdentia can be a consequence of:
- severe infections suffered before the age of 2 years;
- exposure to radiation;
- inflammatory diseases in the mother during pregnancy;
- early removal of baby teeth;
- underdevelopment of the alveolar ridge and, as a consequence, lack of sufficient support for “growing” teeth of normal size.
How does caries work in a child?
The most acute form of caries. Please note that there is no usual dark coloring. Fabrics simply fall apart faster than they can accumulate pigment.
The course of caries in children is radically different from that in adults. They have weakly mineralized enamel and very loose, permeable dentin. Bacteria that synthesize organic acids consume the tissue of baby teeth at an incredible speed, if only they have managed to gain a foothold. Classic chronic caries almost never occurs in children. Chronic caries is when it develops so slowly that it manages to be stained by tea, coffee, cigarettes and borscht. The result is the classic, familiar black dots on the teeth. If you probe them, they give in, but are still quite dense. But children have uncolored caries. Can not get in time. When probing, it resembles rotten wood, which crumbles into layers under the instrument. As a result, it can take a little more than a month from the beginning to the complete fracture of the crown.
Because of its tenderness, children's enamel is especially vulnerable to the malicious microflora of the oral cavity of adults. The worst scenario is when a grandmother or grandfather with a mouth full of carious teeth tries to see if the child’s food is hot with his own spoon. As if there is no other way to measure temperature. It would be better to even dip your finger. Therefore, make sure that the child has his own separate spoon, which no one but him uses.
Very often, when caries is identified, the question arises about the advisability of treatment. “Let’s get through it, it’s still milky! I had all my teeth pulled out when I was a child, there’s no point in treating it anyway.” You look at your mother, and there is an impressive malocclusion and defects in the development of the jaws. In fact, there is no point in removing a carious tooth without any additional action if it is about to change anyway. In other cases, there are two options: we either treat fully, or we remove a completely hopeless tooth, but come up with a temporary structure to close the defect. Baby teeth take longer to work than they think. The same fangs change at 12–14 years of age! And without them, the bite will simply move away and become asymmetrical. There will be inevitable deformities and joint problems.
It is also impossible not to treat. This is simply dangerous. The infection will go deeper and can destroy the germ of the permanent tooth under the diseased milk tooth. In a very severe case, the infection can result in phlegmon, mediastinitis and sepsis. There are very wide spaces for its distribution throughout the fatty tissue.
So, given the speed of spread, there cannot be any options of “let’s continue like this for a couple more months.” Moreover, there is already excellent anesthesia, and masks with nitrous oxide, and sevoflurane, if the case is advanced and more than 10 teeth have to be treated at a time. Fortunately, a well-working team can carry out such a large-scale treatment in just a couple of hours. If you are interested, you can look at one of the previous posts, a colleague there spoke in detail about nitrous oxide and anesthesia.
Dangerous consequences of microdentia
At first glance, it seems that small teeth in an adult cause only aesthetic inconvenience, but this is not so. Dentists identify several quite serious problems that microdentia can lead to.
- Distal displacement of teeth,
that is, their gradual shift back relative to the optimal position in the jaw. - The appearance of gaps between the teeth
(the so-called diastemas and threes), which lead to disruption of the contact of the lateral surfaces of the teeth. Without support, the ligaments in the dental bed stretch and the tooth becomes unstable. - Diction disorders,
excessive amplification of hissing and whistling sounds in speech. - Periodontal disease
is a disease of the soft tissues of the jaw, caused by accumulations of bacteria in the interdental spaces and an enlarged periodontal pocket due to the high mobility of the tooth.
Possible consequences if left untreated
The front incisors, which are slightly longer than the others, do not cause any problems to a person and are even an object of fashion. This is due to the fact that enlarged crowns give the face a more youthful appearance and are not always an aesthetic flaw. Pathological enlargement of dental elements leads to unpleasant consequences.
- Very wide teeth can push, twist, and protrude beyond the row because there is not enough room for them. An abnormal bite develops, affecting not only the beauty of the smile, but also the digestive processes.
- If a child has a very large molar, it can become an obstacle to the eruption of neighboring elements.
- If the incisors have become larger over time, and were not this way from birth, then this indicates problems with the gums. In such a situation, before fixing the teeth, it is necessary to treat the gum tissue.
- Speech is distorted under the influence of pathologically large dental elements.
- A person with such a defect experiences psychological discomfort. He avoids communication and does not smile or does it very stiffly, controlling the process.
How to fix small teeth?
Small tooth: what to do if it causes inconvenience, reduces self-esteem and worsens quality of life? Depending on the severity of the picture, the dentist may suggest the following correction methods:
- In case of isolated microdentia, small teeth can be corrected by installing veneers or lumineers - thin plates that are attached to the front surface of the tooth. This method is also suitable for eliminating threes and diastemas and increasing the width of the visible part of the crown. If your teeth grow unevenly, you will most likely need orthodontic correction using braces before placing veneers.
Celebrities with big teeth
Celebrities often have large front central incisors. They give the image something special and unusual. Such a smile makes a person stand out from the rest. The list of public figures with large incisors:
- Hilary Swank;
- Steve Tyler;
- Jon Heeder;
- Ann Hataway;
- Keira Knightley;
- Tom Cruise.
Large front dental crowns are not always a reason to improve your smile. They add a more youthful appearance and make your smile unique and unique from everyone else. Correction of the size of the front incisors is recommended if they are outside the normal range and create problems for their owner. There are several ways that help change the shape of large crowns, and only a specialist can choose the most suitable option in a particular case.
What helps you choose the color of veneers
- Illumination
. The room should be adequately lit. Bright light encourages you to choose lighter shades, dim light encourages you to choose darker shades. - Removing plaque
. Professional teeth cleaning lightens them slightly, which affects the choice of shade. - Lack of bright colors
in the area where the selection takes place. Bright lipstick, makeup, and clothing details can disrupt color perception. - Wet surface
of teeth. The shade of moistened teeth is the most accurate.
Large clinics, such as ROOTT MCDI, use digital smile technology - Digital Smile Design
. The patient can see the results of the treatment even before it begins. This makes choosing the color of the overlays much easier and reduces frustration. If there is no such technology in dentistry, then the sample is brought to the teeth and a photo is taken to evaluate the appearance.
Emax veneer color
Emax glass ceramics differ in their properties. Therefore, 3 parameters are used to designate its shades. Color scale, Vita 3D Master, includes:
- Brightness
_ Measured on a scale from 1 to 5 - Tone
. R – reddish, L – yellowish and M – intermediate - Saturation
. Use numbers from 1 to 3.
Thus, the color code consists of 3 symbols, 2 numbers and one letter.
Classic B1 for Emax is designated as 1M1.
The color palette in 3D Master is wider. It includes 26 natural shades and 3 ultra-white (Bleach).