December 7, 2010 - Tuesday
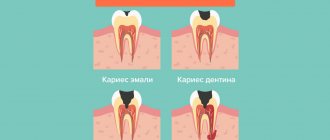
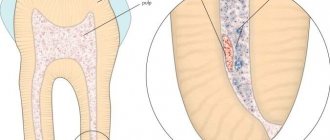
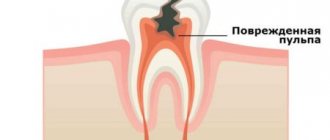
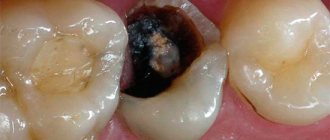
Pulpitis is an inflammation of the dental pulp , or, as it is often called, the dental nerve. Dental pulp is a soft tissue located in the internal cavity of the tooth. The dental pulp consists mainly of nerve fibers and blood vessels. In a healthy tooth, the pulp practically does not reveal its presence, but as soon as it becomes inflamed, a person is ready to “climb the wall” from unbearable toothache. It is for this reason that treatment of pulpitis is primarily aimed at eliminating pain symptoms.
Symptoms of pulpitis
The main symptom of acute pulpitis is the occurrence of spontaneous pain, especially at night. The pain can be paroxysmal, localized in one tooth. Hot, cold, sweet only increases the intensity of the pain. Pain from pulpitis can radiate to the ear, temple, and neck. There may be a sensation of pain even on the opposite jaw.
With chronic pulpitis, mild spontaneous pain and mild pain after eating, hot or cold are periodically bothered.
Treatment of pulpitis is aimed both at relieving pain and eliminating the cause of pain itself - namely, removing the inflamed pulp.
Complications of pulpitis
You can, of course, endure pulpal pain by using folk remedies and modern painkillers toothache But such self-medication usually leads to the development of serious complications. Treatment of pulpitis at home is possible only in emergency cases by calling a dentist at home, who will arrive with all the equipment necessary for treatment. In other cases, treatment of pulpitis with folk remedies will not lead to anything other than complications. One of the most common complications of pulpitis is periodontitis . The infection located in the inflamed pulp slowly but surely penetrates beyond the tooth and causes inflammation of the tissues surrounding the tooth root - periodontitis develops. Periodontitis is dangerous because with this disease there is a gradual destruction of bone tissue near the roots of the tooth. In chronic periodontitis, the formation of granulomas, cystogranulomas and perihilar cysts often occurs . Such chronic foci of inflammation respond very poorly to therapeutic treatment and often lead to the removal of the diseased tooth. In addition, these chronic inflammatory foci cause the spread of infection through the bloodstream throughout the body, which can provoke chronic diseases of the internal organs of a person.
What happens if pulpitis is not treated?
It can be difficult for a modern person to find time to visit a dentist in his busy schedule. The most common mistake is to try to ignore painful symptoms by “masking” them with a large number of painkillers. You should know that even if the pain was calmed, treatment of pulpitis still cannot be avoided - pathogenic organisms in the pulp chamber continue to multiply, destroying the tooth and surrounding tissues. Changes occur inside the tooth that lead to the death of the pulp, its decomposition with the formation of pus.
Subsequently, the pus extends beyond the root and a flux, known to many, occurs - inflammation of the periosteum. This is accompanied by severe symptoms - high body temperature, severe swelling and facial asymmetry, and also entails not only unpleasant, but also life-threatening consequences. In advanced cases, we are no longer talking about preserving the tooth, but about preserving health - there is a possibility of developing phlegmon, damage to the bone tissue of the jaw, and blood poisoning.
Chronic pulpitis can occur with the preservation of the tooth for up to several years, especially at a young age, but this does not mean that the symptoms can be ignored - it is better to visit a dentist in a timely manner in order to save the tooth and prevent serious complications.
Complications in the treatment of pulpitis
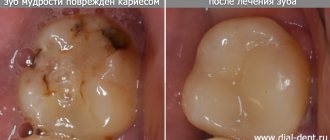
Although diagnosing pulpitis is not difficult and dentistry has everything necessary for the treatment of pulpitis complications still occur . For example, if a tooth hurts after treatment for pulpitis , this is often due to insufficient antiseptic treatment of the root canal before filling it. Inexperienced dentists may make mistakes when treating pulpitis, which cause pain after pulpitis treatment.
Complications in the treatment of pulpitis include incomplete filling of the root canal; removal of the filling material beyond the apex of the tooth root.
Less common complications of pulpitis treatment are:
- undetected and, accordingly, not sealed additional root canal;
- fracture of an endodontic instrument in the root canal;
- perforation of the root canal wall or tooth wall.
Pulp amputation in childhood
Childhood is a special case. Unfortunately, caries occurs even on baby teeth. With this factor, the pulp also becomes inflamed. The choice of pulp treatment for children depends on:
- From caries resistance.
- From the patient's condition.
- Depending on the patient's age.
- It depends on how serious the caries is.
Vital pulp amputation in children is not performed:
- If the tooth cannot be restored.
- If there is destruction of bone tissue.
- If root resorption is observed.
- If a permanent tooth comes out.
Devital amputation is not performed in children:
- If purulent pulpitis is observed.
- If there is gangrene of the pulp.
- If there are changes in bone tissue.
Children's temporary teeth are treated only with devitalizing agents that do not contain arsenic. In this composition, the active ingredient is paraformaldehyde. The product has the necessary antimicrobial and analgesic effect. Also, under its influence, the pulp is mummified and sterilized.
Based on reviews from some dentists, I would like to note the following. Pulp amputation in children is a common occurrence. Most often, the procedure is performed within the walls of government institutions. Of course, the choice of medications here is small, but it is there. In one hundred percent of cases, pulp treatment or removal is successful and without consequences.
Treatment of pulpitis in children
The peculiarity of the structure of milk teeth is such that the development of pulpitis occurs rapidly, bypassing the stage of deep caries. Treatment of pulpitis in children is based on the same principles as treatment of pulpitis in adults. However, it also has some peculiarities. It is important to prevent the spread of inflammation to the periodontal tissues, in which the rudiments of permanent teeth are present, and also to use materials that will not affect the resorption (resorption) of the roots of baby teeth. Therefore, to treat pulpitis of baby teeth, filling pastes are used, which dissolve simultaneously with the roots when baby teeth are replaced with permanent ones.
Treatment of pulpitis of baby teeth should be carried out under high-quality anesthesia, harmless to the child’s body. Treatment methods for pulpitis in children are aimed at preserving baby teeth from premature removal. Early removal of baby teeth can cause malocclusion.
Vital amputation
This method is used very often today. A tooth can be cured in one visit to the doctor. The essence of the method is the mechanical removal of pulp. To do this, they give an anesthetic injection, which acts locally.
To carry out vital removal, the viability of the root part of the pulp, the absence of symptoms of the disease and the inflammatory process must be determined.
This type of amputation is very often used for treatment in children. The roots of teeth that develop have many ribbon-like tubules. They simply need to be preserved. With baby teeth, the buds of permanent teeth cannot be damaged.
This type of amputation can be performed on the roots and crowns of the teeth.
Vital amputation is indicated in case of
- If the patient has teeth whose roots are not formed.
- If the biological method was unsuccessfully applied before.
- If the patient has chronic, concremental or acute serous-purulent pulpitis.
- If the patient has traumatic pulpitis, whose coronal part is damaged.
- If the roots of permanent teeth are not fully formed.
How is vital amputation performed?
- Determining the exact disease, making a final diagnosis, deciding on a treatment method.
- Cleansing the surface of teeth from deposits and plaque.
- Conducting anesthesia (pain-relieving injection). Anesthesia is given with modern drugs, so the entire procedure is almost painless. To carry out this stage, an anesthetic and a syringe are required.
- Isolation of teeth from saliva. This is done using a rubber dam. This is a special latex scarf with special holes made for teeth. As a result of such actions, microorganisms do not enter the root canals.
- Carrying out cavity treatment for caries. The inflamed tissue from the crown is removed and plaque is cleaned. This stage requires tips and burs.
- Opening the tooth and opening the cavity. Here, root treatment is carried out using dental instruments. Tips and burs are also needed for these purposes.
- Pulp amputation using a bur. Practice has shown the importance of this stage. Correctly done amputation is a practical success. The channels are treated with medications. At this stage, an excavator and several types of burs are needed: spherical, for deep amputation and endoburs, a probe and tips.
- Stop bleeding using a special tampon.
- Application of calcium preparations to the mouths of the canals.
- Applying an insulating pad.
- Installation of a permanent filling.
After treatment, you need to monitor the condition of the pulp every 3 months for a year.
Treatment methods for pulpitis
When treating pulpitis, dental procedures are aimed at eliminating inflammation in the pulp. In dentistry, there are two methods of treating pulpitis: biological (conservative) and surgical.
Conservative treatment of pulpitis involves preserving all or part of the viable pulp. But it is worth noting that the conservative method of treating pulpitis is advisable only in case of reversible inflammatory phenomena in the dental pulp.
Biological method of treating pulpitis . This treatment method is used for traumatic pulpitis, as well as for accidental opening of the pulp during the treatment of deep caries. In the biological treatment of pulpitis, antiseptic agents are used, which carefully treat the exposed pulp. Then a biological dressing (pad) based on calcium hydroxide or tricalcium phosphate is applied to the exposed area of the pulp. And after that, a filling is placed on the tooth. The biological method of treating pulpitis can eliminate inflammation of the pulp, but for control, control X-rays of the treated tooth should be taken once a year.
Reviews
Pulp amputation was performed on my son. The procedure was carried out in two days. She literally dragged her son to the hospital. He's a terrible coward. We thought we wouldn’t survive these two days. Somehow they pulled it through. On the first visit they put me on medication. My son cried and said that his whole mouth hurt. But I didn’t trust him much. She knew she was exaggerating. On the second, everything was cleaned and a seal was put in. The doctor explained something about the pulp. I didn’t listen much, I looked at my son’s roaring eyes. Now I understand. I didn’t think, didn’t know, didn’t imagine that the nerve could be removed from children’s baby teeth.
The tooth hurt, ached obsessively and gave no rest. I delayed with caries. Plus, some kind of inflammation also formed. Somehow I made it to the doctor. I thought that everything would be done in a day, but I was wrong. I had to go to the dentist 5 times. Every day I had something cleaned, washed, cut. The doctor said that the pulp was removed from the tooth. What it is, I understood after reading the information. It turns out now my tooth is half dead. It's a pity that this is so. It's my own fault.
Sources used:
Stages of pulpitis treatment
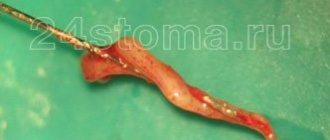
The surgical method of treating pulpitis is based on complete removal (extirpation) of the pulp followed by filling the root canals of the tooth.
The surgical method is most often used in clinical practice for the treatment of both acute and chronic pulpitis. This method consists of several stages.
The vital method of treating pulpitis is the treatment of pulpitis without the use of arsenic; the nerve is removed under anesthesia. Under local anesthesia, carious tissue is removed and the tooth cavity is opened. Then the inflamed, infected pulp is removed. The root canals of the tooth are carefully processed with special (endodontic) instruments in order to remove residual pulp and remove a layer of infected tissue from the inner surface of the root canals. During mechanical treatment, the crown canals of the tooth are repeatedly washed with antiseptic solutions (chlorhexidine, sodium hypochlorite, etc.). This is especially important in the treatment of gangrenous pulpitis, when pulp necrosis and infection of the tooth root occur.
Treatment of pulpitis is often carried out with preliminary temporary filling of the root canals with anti-inflammatory antiseptic pastes. And only then the roots of the tooth are finally filled.
The devitalizing method of treating pulpitis is based on the use of devitalizing agents. Simply put, the nerve is killed using arsenic or less toxic non-arsenic agents. The devitalizing agent is applied for several days, after which the insensate nerve is removed.
The final stage of pulpitis treatment is filling the root canals of the tooth. Modern methods of treating pulpitis provide both complete treatment of the root canals of the tooth and subsequent hermetic filling (obturation).
When filling root canals in the treatment of pulpitis, there are several main methods:
- method of lateral and vertical condensation of cold gutta-percha (filling tooth canals with gutta-percha);
- filling the root canals with softened (heated) gutta-percha;
- filling with heated gutta-percha on a carrier (filling root canals with Thermofil).
Along with the traditional method of root canal treatment and filling using the “lateral condensation of gutta-percha” method, our clinic can offer you innovative technologies in the treatment of pulpitis and periodontitis. In this case, nickel-titanium rotating instruments are used to treat the root canals of the tooth - the latest word in dentistry. When using such instruments, the quality of root canal treatment is significantly improved due to the increased taper of the instrument and its high cutting efficiency. Working with such instruments requires special skills from the doctor, and indicates his high qualifications.
After such treatment, as a rule, heated gutta-percha or “Thermafil” is used to fill the root canals. With these methods of canal filling, three-dimensional obturation occurs, including small branches in the canal, which, accordingly, increases the quality and reliability of treatment, and also allows us to hope for a very positive prognosis for the further functioning of the tooth.
Devital amputation
If vital removal cannot be performed, then devital amputation is resorted to. The main indications look like this:
- Stroke, heart attack and other severe pathologies.
- If you are allergic to anesthetics.
- If it is not possible to administer anesthesia.
- If before this a vital method was used, which ended unsuccessfully.
The removal method involves treating the coronal pulp with a special paste that deadens it. After this, the pulp acquires a fibrous appearance and is easy to remove from the hole. The other part of the pulp, the root, remains intact. In addition, mummification of the coronal part of the pulp occurs due to the impregnation of the soft tissue with drugs. The pulp becomes dry and takes on the appearance of a sterile cord.
It is believed that the devital method should be used extremely rarely. This kind of amputation leads to severe periodontal inflammation. It should only be used when roots are growing. When the roots finally grow, pulp excision (further cleansing of the canals) should be carried out.
Stages of devital amputation
Devital amputation is designed for 3 visits. On the first visit, the doctor conducts an examination. On the spot, he will clean the deposits on the teeth. The procedure, of course, is carried out using anesthesia. Appliqué is usually used. The next stage is preparation of the carious plane. Next, the affected dentin is removed and the entire cavity is treated with an antiseptic. By opening the pulp horns, paste is applied to the exposed nerve. As a result, she becomes irritated. At this time, the patient feels painful sensations. Therefore, the doctor often talks about the use of painkillers.
It happens that specialists use a paste with arsenic. Then the second stage should take place on the second day. If the doctor puts a paraformaldehyde composition on the tooth, then the second visit may be after 7 days. It is very important to adhere to scheduled visit times.
The second visit goes like this. The doctor removes the temporary filling and performs the preparation. Part of the pulp is promptly removed using a bur and an excavator. An obligatory stage of this visit is treating the cavity with an antiseptic. The cavity is dried and a medicinal composition is applied to the removal site. A temporary filling is again placed on the tooth.
The third appointment is scheduled after three or five days. The doctor replaces the temporary filling with a permanent one. Here he definitely carries out its restoration with a composite.
Emphasis should be placed on special pastes. In dentistry, there are a sufficient number of special pastes with antiseptic and anti-inflammatory effects. Their choice directly depends on what kind of inflammation is present in the tooth and to what extent it is complicated. For example, in order to preserve the root part of the pulp, pastes with antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory and desensitizing effects are used. In parallel, these agents should enhance the plastic ability of the pulp. To improve the effect, the doctor often prescribes antibiotics and sulfa drugs.
Let's summarize on devital removal. The stages of treatment are as follows:
- Carrying out actions to ensure accessibility to the dental cavity.
- Application of a special devitalizing composition. For the first two steps you will need artificial dentin, instruments, burs, and tips.
- Removing the filling using tools. In case of probing, bleeding and pain do not occur.
- Opening the dental cavity and amputating the pulp. Here the bur is moved in a special way: they start from the cavity of the tooth. Correct actions lead to the opening of expanded channels.
- Treatment with medications. This treatment helps to obtain a clean cavity.
- Carrying out channel processing. The stage is carried out using impregnation methods, depophoresis and electrophoresis. The result is disinfection of the canals and their inaccessibility to infections.
- Tooth restoration. A permanent filling is placed on the treated tooth.