Leukoplakia is an inflammatory process accompanied by keratinization of the mucous membranes of the oral cavity and a white coating.
In some cases, the disease is not dangerous and goes away without a trace over time. In others, it may develop into a precancerous condition and later into oral cancer. This is why prevention of leukoplakia of the oral mucosa is so important: it is easier to prevent complications than to deal with the consequences.
The risk of the disease in men is much higher than in women: 80% of patients versus 20%
“The influence of cryodestruction and antioxidants on the activity of hydrolases in blood leukocytes of patients with leukoplakia” Dr. med. Mashkilleyson A. L.
Hairy leukoplakia of the mouth or tongue - symptoms and treatment
Content:
What is oral leukoplakia
Causes of leukoplakia in the oral cavity
Symptoms of hairy leukoplakia
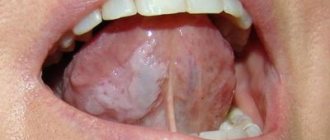
What does hairy leukoplakia look like?
What are the dangers of leukoplakia?
How to treat hairy leukoplakia
Various diseases occur on the oral mucosa, which are a manifestation of reduced immunity. A common condition is hairy leukoplakia of the tongue.
Treatment of leukoplakia
Treatment of leukoplakia largely depends on the patient’s age, stage of the disease, its location, medical history and concomitant disorders.
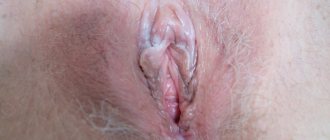
Leukoplakia of the external genitalia in women
To treat vulvar leukoplakia, it is necessary to follow a set of measures aimed at normalizing the functioning of the body as a whole:
- get enough sleep;
- maintain a daily routine;
- take regular walks in the fresh air;
- do gymnastic exercises;
- balance the diet (avoid spicy, salty and spicy foods, reduce carbohydrate content);
- do not wear tight underwear made of synthetic materials;
- maintain hygiene.
Leukoplakia of the vulva is often treated with conservative methods: physiotherapy in combination with general and local drugs. Additionally, washing with a decoction of chamomile or baking soda is recommended, which will help reduce tissue inflammation. Surgery can be used only if conservative treatment is ineffective to prevent the development of cancer.
Leukoplakia of the cervix
Treatment of cervical leukoplakia in the earliest stages can be limited to conservative methods, however, the asymptomatic nature of this disease in most cases causes it to be diagnosed too late. Most clinics use surgical methods using modern equipment to remove the keratinized area of the cervical mucosa: electrocoagulation, cryo- and laser therapy.
Leukoplakia of the bladder
To treat leukoplakia, both drug and surgical therapy are used. Conservative methods include taking antibacterial drugs to suppress the identified pathogen, additional irrigation of the bladder walls and physiotherapeutic procedures aimed at reducing inflammation and pain.
If drug treatment does not give the expected effect or the disease is too advanced, a surgical treatment method using cytoscopic transurethral cutting of the affected area of the bladder mucosa may be chosen. Most reviews after surgery to remove leukoplakia of the bladder confirm the high effectiveness of this treatment, which, if infections are treated in time, does not cause relapses.
Leukoplakia of the esophagus
The most effective treatment for this disease is surgery using liquid nitrogen, a laser or an electrocoagulator, and it is cryosurgery that gives the most lasting results with a minimum number of relapses of the disease.
When treating leukoplakia in the esophagus, it is important to follow an integrated approach: in addition to cauterizing the damaged areas, the patient will need to undergo a course of antibacterial therapy, as well as adhere to a fairly strict diet without alcohol, heavy, spicy and salty foods.
Oral leukoplakia
For the treatment of oral leukoplakia, doctors prefer conservative treatment methods based on saturating the body with fat-soluble vitamins, as well as general strengthening of the body. The course of the disease is unpredictable and individual for each patient - some live for decades with the initial form of leukoplakia, which does not cause discomfort, while others may develop squamous cell carcinoma after a few months. If conservative treatment is ineffective, the patient is indicated for surgical intervention with removal of the tumor and its careful histological examination.
What is oral leukoplakia
Leukoplakia is a lesion of the oral mucosa in which excessive keratinization is observed. Located on the cheeks, hard and soft palates, and tongue.
Types of leukoplakia:
- Flat is the most common form. Usually does not cause discomfort. Discovered by chance at a dental appointment.
- Verrucous - more pronounced keratinization than with the flat form. Patients note a feeling of roughness and tightness on the mucous membrane, a burning sensation.
- Erosive – is a complication of the previous two forms when exposed to a traumatic factor. Characterized by pain. which occurs when talking or eating.
- Hairy leukoplakia is a disease caused by the Epstein-Barr virus. Often observed in patients with HIV.
- Tappeiner's leukoplakia - it is found in long-term smokers. It is observed on the soft and hard palate.
Some forms of this disease are considered precancerous. If left untreated, they develop into malignant tumors. Therefore, it is important to contact a dental clinic in Moscow when you first detect pathological changes in the mucous membrane.
What are the symptoms of oral hairy leukoplakia?
First of all, it is worth noting that self-diagnosis of oral cavity disease by a patient is possible in the early stages, that is, during the period of the onset of tongue disease. However, due to the lack of pain in patients, infected people can inadvertently progress the infection to a precancerous state. About ten percent of diseases in patients with leukoplakia of the tongue end in malignancy of the oral cavity, that is, cell mutation and loss of the DNA repair (restoration, reconstruction) mechanism.
As a rule, at the initial stage of tongue disease, patients develop dull white folds along the edges of the tongue, which after some time merge with the healthy area and cease to clearly contrast both visually and tactilely.
Below are the main symptoms of this disease of the oral cavity and tongue:
- unexpectedly appearing whitish halos on the inner sides of the patient’s cheeks, at the root area of the tongue or its sides, throughout the entire oral cavity;
- foci of infection - flat in appearance, hard to the touch, rough, whitish or transparent in color, resembling papillomas, not exceeding 1 centimeter;
- patients have an uneven surface of infected halos, visualization of cracks and hairs;
- furrows, abscesses, processes of destruction of the epithelium in patients, the presence of infiltration in the affected areas;
- absence of discomfort or pain in the patient’s tongue upon tactile influence on its infected areas or, on the contrary, an acute reaction to cold or hot water;
- When testing a sample taken in a laboratory, patients are diagnosed with HIV or EBV diseases.
Causes of leukoplakia in the oral cavity
To date, scientists have not reached a consensus on why the disease occurs. There are factors that can lead to the development of excess keratinization:
- Constant exposure to irritating factors: smoking, regular burns from hot food, strong alcohol, etc.
- Work in industries where there are chemicals, alkalis, acids.
- Living in a hot, dry climate.
- Taking drugs that reduce immunity.
- Local traumatic factors: failed fillings, sharp edges of dentures and damaged teeth, poor-quality braces.
- Endocrine pathologies: diabetes mellitus, hyperthyroidism, hypothyroidism.
- Reduced immunity: HIV, AIDS, immunosuppressive state. Oral hairy leukoplakia is often observed in patients with HIV and AIDS.
Prevention of leukoplakia
The key measures for the prevention of leukoplakia are basic rules of personal hygiene and strengthening the immune system:
- regular hardening;
- sufficient physical activity;
- balanced diet;
- timely treatment of any disorders;
- regular preventive examinations;
- giving up bad habits, heavy and spicy foods that irritate the esophagus;
- careful intimate hygiene and visiting a gynecologist;
- compliance with all doctor’s recommendations during a preventive examination.
This article is posted for educational purposes only and does not constitute scientific material or professional medical advice.
How to treat hairy leukoplakia
Before starting treatment, you need to conduct a number of studies. The patient is referred to a therapist at the clinic. There, the doctor can prescribe laboratory tests: biochemical blood test, testing for sexually transmitted diseases, etc.
If a person is diagnosed with HIV infection, antiretroviral therapy is administered. With long-term use of drugs, the patient’s well-being improves, and the disease in the mouth goes away.
The dental clinic provides oral examinations, dental diagnostics, and professional hygiene. If sharp edges of fillings or failed prostheses are detected, they are replaced. Treatment of caries and its complications is carried out. Recommendations are given for home dental care: personal hygiene products (brushes, pastes, dental floss, rinses) are selected.
Keratolytic drugs are suitable for local treatment. In advanced cases, they resort to surgical manipulations: excision of the affected areas with a laser.
Causes
Different localizations of leukoplakia are caused by different reasons and require an individual approach in developing a treatment strategy.
Hairy leukoplakia develops against a background of reduced and weakened immunity, so most often this type of disease is diagnosed in patients with HIV, various immunodeficiencies and during rehabilitation after organ transplantation, when a course of immunosuppressants is prescribed.
- Leukoplakia of the external genitalia in women develops most often during menopause, when reverse development processes occur in tissues and cells. Mucous tissues and skin become drier, hair loss is observed, which is a normal physiological process.
- Leukoplakia of the esophagus develops after heartburn or burns of the mucous membrane of this organ; more than half of the cases of this disease cause the appearance of a cancerous tumor.
- Leukoplakia in the oral cavity is most often localized on the mucous membranes of the inner side of the cheek, the hard and soft palate, as well as in the angular folds of the mouth. Leukoplakia of the tongue is extremely rare in medicine.
To this day, official medicine does not know the exact reasons for the development of this disease in the mouth. However, a number of factors have been identified that increase the chances of developing leukoplakia:
- metabolic disorders;
- genetic predisposition;
- lack of vitamin A;
- smoking;
- chronic injuries to the mucous membranes (for example, due to improperly manufactured dentures);
- activities associated with direct contact with coal and coal tar, as well as their processing processes;
- HIV and AIDS;
- chronic inflammatory processes in the mouth associated with neurological disorders.
Leukoplakia of the bladder is a protracted chronic disease that is characterized by the degeneration of transitional epithelial cells into squamous epithelial cells. The keratinized epithelium is unstable to urine components, which causes inflammation in the bladder cavity. The main cause of the development of the disease is ascending infection with sexually transmitted pathogens. Therefore, leukoplakia in the bladder develops more often in women - their urinary canal is much shorter than the male one, so it is easier for infections to penetrate through it.
In some cases, the cause of leukoplakia can be a downward infection, when a pathogen penetrates through the bloodstream from nearby organs: staphylococci, Proteus, streptococci, E. coli and others. The development of the disease is favored by:
- chronic diseases of the abdominal organs located next to the bladder;
- all factors that reduce immunity: hypothermia, stress, bad habits, chaotic lifestyle;
- foci of chronic inflammation located at a distance from the bladder: tonsillitis, caries, sinusitis, etc.;
- disturbances in the functioning of the endocrine system;
- the IUD was not removed in time in the uterine cavity;
- promiscuous sex life without the use of barrier contraception.
Leukoplakia of the cervix is called whitish formations (spots or plaques) that appear on the mucous membrane. To diagnose the disease, a preventive examination using a gynecological speculum is sufficient.
Like dysplasia, cervical leukoplakia requires mandatory treatment, since it is a precancerous disease. There are many reasons for the appearance of such tissue changes:
- decreased immunity for various reasons;
- injuries due to careless examination, termination of pregnancy, childbirth;
- interruptions in the functioning of the endocrine system;
- ovarian dysfunction;
- current or previous infectious diseases of the genital organs.
Features of leukoplakia disease and its treatment
Go back Leukoplakia affects the oral cavity, nasal mucosa, gastrointestinal tract, genitourinary and respiratory systems. The main danger of leukoplakia is the risk of malignancy. In dentistry, the main symptom of the disease is thickening of the mucous membrane in the form of serous-white areas and their peeling. The pathology covers the red border of the lips, the inner surface of the cheeks, gums, tongue, and palate.
Causes
- Mechanical. Damage to the mucous membrane from low-quality dental implants, fillings, and teeth due to malocclusion.
- Chemical, thermal. Smoking, drinking alcohol and illegal drugs, temperature changes, eating spicy food, working with harmful substances (benzene, varnishes).
- Galvanism created by metal implants.
- Decreased immunity, vitamin deficiency, stress, infection, inflammation.
- Heredity.
Peculiarities
- Flat (simple) leukoplakia, the initial form, is accompanied by tightness and itching. Does not cause any significant inconvenience. The lesions are swollen, rough, dry up to 4 cm, white-grayish.
- The verrucous form occurs with an increase in the foci of pathology, their compaction, and pain. It is divided into plaque and warty in appearance.
- The erosive form causes pain, the lesions resemble ulcers.
- Tappeiner's leukoplakia is common in patients who smoke. The pathology affects the palate, causing blockage of the salivary ducts, transforming them into cystic red nodules.
- Soft – benign oncological growth.
- Hairy with papillary growths. Characteristic of persons infected with HIV.
If leukoplakia is suspected, a diagnosis is carried out, including visual examination, cytological analysis, histology, bacterial culture, blood tests, incl. to Wasserman's reaction. Differential diagnosis is important, because Leukoplakia has common characteristics with other diseases, for example, hyperplastic candidiasis, lichen planus, secondary syphilis, precancerous hyperkeratosis, Bowen's disease.
Treatment
- Urgent abolition of provocateurs - smoking, taking toxic substances. Replacement of implants.
- Psychotherapy for persons with neurological symptoms, for children.
- Sanitation of the oral cavity.
- Therapy with drugs containing vitamins C, B, A, their intake orally, in the form of injections, oily compresses.
- Restoration of the mucous membrane, its integrity, immunity.
- Cryodestruction.
- Electrocoagulation.
- Physiotherapy.
Additional support with folk remedies. Applications with Kalanchoe, rinsing with decoctions of herbs with a regenerating effect (chamomile, calendula), and green tea are shown.
The longer the symptoms are observed, the faster the spots grow, the higher the risk of the pathology turning into cancer. Bleeding and the bright red color of painful areas should also alert you.
Diagnosis for suspected HIV infection
For differentiated diagnosis of HIV infection from similar dental diseases, the following tests are used:
- Blood test for PCR reaction (aimed at detecting HIV).
- Immunoblotting technique.
- Linked immunosorbent assay.
- Checking immune status.
If the results are unclear, additional blood tests, as well as bacteriological studies, may be prescribed. Early diagnosis of the root cause of diseases can significantly alleviate the course of the disease.
What is HIV? What is HIV infection
The human immunodeficiency virus, or HIV, was identified and described relatively recently. Invading the human body, it primarily affects macrophage cells and T-lymphocytes, which are responsible for recognizing and destroying hostile bacteria. Thus, the body's immune barrier loses its ability to resist both external bacterial attacks and internal opportunistic flora.
The immunodeficiency virus is transmitted exclusively through sexual contact or through direct contact of a healthy body with infected blood. Transmission of the virus through household or food contact is impossible.
HIV infection is a slow-onset disease caused by a virus and occurs against a background of suppressed immunity. It can take years from the introduction of the virus to the clinical manifestations of the disease. During this entire period, the virus does not manifest itself in any way, and its presence can only be diagnosed using a laboratory method.
Bacterial infections
Ulcerative-necrotizing gingivitis develops in HIV-infected individuals both during various periods of clinical manifestations of AIDS, and without them in the presence of antibodies against the virus. Patients complain of pain and bleeding gums while brushing their teeth and eating; bad breath. Upon examination, a gray-yellow plaque (necrotic film) is found covering the gingival margin and interdental papillae. The mucous membrane in the gum area is hyperemic, swollen, and tense.
After treatment, the symptoms disappear, but there is a tendency to relapse. A prolonged course can lead to deep ulcers with damage to bone structures and necrotization of the interdental septum (Fig. 4).
Rice. 4. Herpes simplex on the lip.
The consequence of gingivitis is periodontitis (periodontitis) with irregular generalized destruction of bone tissue and the supporting-retaining apparatus of the tooth. Treatment of patients does not provide lasting results.
Symptoms of the disease
The main danger of hairy leukoplakia is that it may not manifest itself for a long time, and only a visit to the dentist can help identify this disease in time. The first and most typical symptom that should alert you is a strong white or gray coating covering the back and bottom of the tongue.
As a rule, those suffering from leukoplakia do not feel any particular discomfort - except in cases where the disease is accompanied by a fungus.
The following symptoms are characteristic of this disease:
- The appearance of folds and plaques formed from plaque;
- Cracks in the tongue;
- Erosion in the advanced stage of the disease;
- General signs of immunodeficiency: diarrhea, sudden weight loss, night sweats, fever that occurs for no apparent reason, general pain and weakness.
Treatment options
If during the examination the Epstein-Barr virus was detected in the patient’s blood, then he is indicated for antiviral treatment using the drugs Acyclovir, Ganciclovir, Zidovudine and others. However, such therapy only helps to weaken acute symptoms and put the body into a state of remission. Since when this virus enters the blood, it remains in the cells for life, relapses of the pathology may occur, especially with a significant decrease in immune forces.
Treatment of hairy leukoplakia depends on what factor caused the disease
If a problem is caused by wearing braces, improper installation of dentures or poor-quality filling, this factor is eliminated, after which the disease goes away on its own. If leukoplakia is caused by regular trauma to the mucous tissue or smoking, the patient must himself eliminate the problems that provoke an exacerbation - carefully care for the oral cavity and get rid of nicotine use.
In patients with manifestations of hairy leukoplakia who suffer from HIV infection, there is a high risk of degeneration of epithelial cells into malignant ones, so they are indicated for radiation therapy or chemotherapy. Such measures are necessary for the aggressive manifestation of Burkitt's lymphoma.
The main methods of treating hairy leukoplakia:
- Laser treatment. The therapy is carried out absolutely painlessly and bloodlessly, under local anesthesia or without any anesthesia at all. In this case, only the affected areas are treated, while healthy tissues are not damaged.
- Cryodestruction (cauterization with liquid nitrogen). The method is less effective than laser treatment, but just as bloodless and painless. The affected tissues are cauterized in isolation from the healthy ones, and the whitish plaque from the roughened areas is removed quickly and accurately.
- Surgical intervention. This method of treatment is indicated for patients in whom the manifestations of pathology have caused severe deformation of the mucous surface of the cheeks and tongue. During the operation, the surgeon cuts off the affected tissue using a scalpel. Before the intervention, the patient must undergo an examination with the collection of material for a biopsy, to exclude or confirm the cancer etiology of the disease.
After surgery, a patient with cancer cells in the tissues may be prescribed chemotherapy or radiation therapy; in order to avoid complications and relapses of the disease, the patient should be under the supervision of an oncologist.
Laser treatment of dental diseases is very effective and painless
Diagnosis of the disease
The diagnosis is made based on examination and questioning of the patient. Mandatory diagnostic studies confirming the diagnosis include:
- Cytology is the collection of epithelial cells to identify cancerous lesions.
- Histology is taken to perform a biopsy, which allows examination of the affected epithelial tissue to detect cancer cells.
- Blood from a vein.
Additional clarifying studies make it possible to distinguish leukoplakia from other pathologies.
Epidemiology
The only source of infection is a person infected with this virus. The most dangerous are those who do not have any clinical manifestations: virus carriers are the main source of the spread of HIV infection among the population.
During a dental appointment, infection can occur in the following cases:
- when using medical instruments contaminated with blood or other biological fluid that have not been disinfected (various devices, discs, burs, probes, needles, syringes, cutting and piercing instruments, etc.);
- in the presence of wound surfaces and ulcerations in the oral cavity;
- in case of extensive contamination of the skin of healthcare workers with blood, blood getting into the eyes;
There are known examples of infection during acupuncture treatment.
(There is no airborne transmission of infection.)
The immunodeficiency virus is found in the highest concentration in the blood. Next in descending gradation are sperm, vaginal and cervical secretions of the glands, breast milk, and saliva. Blood and other specified biological fluids are factors in the transmission of HIV from an infected person to other persons.
The virus is moderately resistant outside the human body. In the external environment (biosubstrates), its infectious effect lasts up to 2 weeks, in a dried state (discharge on linen, objects, etc.) - up to 1 week. Radiation exposure and ultraviolet rays do not affect it. When boiled, the virus dies within 5 minutes; when heated to 56°C, inactivation occurs after 30 minutes. Disinfectants used in the practice of medical institutions (chloramine, calcium hypochloride, hydrogen peroxide, alcohol, etc.) in concentrations provided for the disinfection of hepatitis viruses are guaranteed to destroy HIV upon direct contact of the disinfectant with contaminated blood or other human biological fluid on the surface of an object, including a hollow one ( internal surfaces of the syringe, needles, capillaries, probes, etc.).
Treatment
Treatment of oral leukoplakia should begin with identifying the possible causes of its occurrence. If viral DNA is detected in test results, the doctor will most likely prescribe the patient antiviral drugs such as acyclovir, zidovudine, ganciclovir. Taking antiviral drugs can lead to the disappearance of plaques and symptoms of leukoplakia of the tongue, however, there is always a risk of relapse of the disease with another sharp decline in immunity.
When leukoplakia of the oral mucosa occurs in people with AIDS, the risk of developing lymphoma increases, so treatment with radiation and chemotherapy is indicated. Otherwise, against the background of the underlying disease and the complete lack of body resistance to infections, leukoplakia in the mouth can develop into a malignant cancerous tumor.