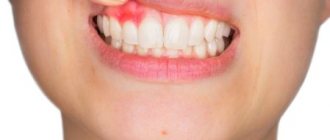
Why do ulcers appear on the gums, and is it always dangerous?
There are many possible reasons. To understand how dangerous the appearance of certain lesions on the gums is, you need to look at additional accompanying symptoms:
- in case it is trivial mechanical damage. The gums can be damaged by hard food, a toothbrush, or a foreign object. These lesions may resolve in 3-5 days. If a person does not brush his teeth, then infection is added to these damages, and healing may take several weeks.
- Sometimes ulcers can appear as a result of wearing orthodontic structures, braces or removable dentures.
White plaque on the gums (candidiasis) –
If your gums turn white, then you can suspect not only leukoplakia, but also oral candidiasis, in which a white coating may appear on the gums, tongue, mucous membranes of the cheeks and palate. Candidiasis is caused by fungi of the genus Candida. Most often it occurs against the background of reduced immunity, endocrine diseases, gastrointestinal diseases, anemia, hypovitaminosis, diabetes mellitus, HIV infection, chronic hepatitis, and smoking.
Long-term use of antibiotics and mouth rinses containing antibiotics and antiseptics can also lead to candidiasis. The presence of untreated carious teeth, inflammation of the gums, and poor oral hygiene also plays a big role in the occurrence of candidiasis.
White plaque on gums: photo
The most common diseases of the oral cavity in which ulcers appear
- ulcerative necrotizing gingivitis. The cause of this disease is bacteria that multiply when immunity decreases. Extensive ulcers appear on the gums, regional lymph nodes become enlarged, and the temperature may rise
- chronic recurrent aphthous stomatitis. Up to 4-5 white spots first appear in the mouth, which later turn into ulcers. There is no temperature or other problems related to well-being. If such symptoms appear 1-2 times a year in small quantities, then there should be no cause for concern. Frequent occurrence is associated with weakened immunity and possible intestinal diseases, as well as allergies.
- acute herpetic stomatitis. Herpetic stomatitis occurs in a child when he first encounters the herpes virus. Many bubbles appear on the gums, which, after bursting, turn into ulcers that merge with each other. The gums are always bright red, and the ulcers themselves are very painful, the temperature may rise
Diseases in which a lump on the gum does not hurt
There are diseases in which the resulting compaction does not bother the patient with pain. It is because of this that people are in no hurry to see a doctor, which can subsequently complicate treatment. In what diseases does a lump that appears on dental tissue not hurt?
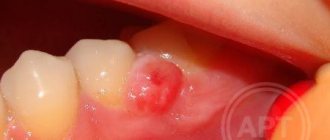
Fistula
If a lump with pus appears in the gum, for the flow of which there is a hole in the gum, we are talking about a fistula. The formation is a growth 3-5 mm in size with a white tip. When the outlet is not blocked by compacted exudate and pus flows freely, such compaction, as a rule, does not hurt. The reason for the formation of a fistula is a complication of periodontitis, in which the tissue grows and becomes infected by accumulated bacteria. Despite the fact that pus periodically flows out and does not accumulate in large quantities, if left untreated, an acute fistula becomes chronic. If the fistula is not treated, there is a risk of infection spreading through the periodontium and tooth loss.
Exostosis
Exostosis is a type of jaw abnormality when the bone protrudes slightly to the surface. Such a lump is hard and painless to the touch, since it is, in fact, a bone or osteocartilaginous growth of a benign nature. The causes of occurrence are hereditary predisposition, congenital pathology or consequences of injury. With such an anomaly, prosthetics are difficult or even impossible: the prosthesis will rub the skin on the bone growth, which can cause injury and infection.
Important! Exostosis is determined by x-rays. The decision to remove is made by the patient, but it is worth considering that such growths can become malignant over time.
Epulis
If a lump appears above the gum, shaped like a mushroom on a stalk, pale pink or red in color, we are talking about epulis - a pathological formation, common mainly in women, and also occurs in children when their first teeth erupt. The reasons for the appearance of epulis are often post-traumatic in nature (large filling, tartar, chips), however, a pathological growth can also appear due to malocclusion, hormonal disorders or wearing low-quality dentures. The symptoms of epulis are similar to those of gingivitis, so for an accurate diagnosis, the doctor uses radiography or a histological test.
Periodontitis
You should think about periodontitis if a lump has formed on the gum - hard to the touch, up to 10 mm in diameter. The causes of inflammation of the periodontal tissues are usually unsealed dental canals and their infection. An abscess forms at the root apex. A characteristic sign of the disease is that when you press vertically on a tooth, pain appears. If the pus has already drained, there may be no pain, but the disease cannot be ignored, as it can lead to tooth loss and further spread of infection.
Attention!
If a seal appears on the gum, under no circumstances should you apply a warm compress or hot rinses: this can aggravate the course of the disease!
Hematoma
A soft-to-touch swelling with watery contents – a hematoma – is formed as a result of tissue injury during tooth extraction. This bump, as a rule, does not require special treatment, dissolving a few days after its appearance.
Do not ignore preventive visits to the dentist.
It is enough to visit a specialist 1 – 2 times a year, which will allow you to promptly identify any dental problem at an early stage of development. This means that its elimination will be quick, easy and without complications.
By clicking the “request a call” button you agree to the personal data processing policy.
First aid
If the temperature rises, you can take an antipyretic drug. In the future, before visiting a doctor, nothing should be done. Do not take antibiotics yourself or try to get into the ulcer with any object.
How to relieve symptoms of ulcers
- do not eat sour and salty foods
- food should be warm, no hot dishes or drinks
- Care should be taken to ensure that the child does not put dirty hands in his mouth
- teeth should be brushed, but make sure that the bristles do not touch the gums with ulcers
- It is recommended to rinse your mouth with herbal solutions (oak bark, chamomile) 3-4 times a day
You should be careful when using antibacterial solutions. They must be prescribed by a doctor. If such solutions are used incorrectly, they can provoke the development of thrush. The antibacterial agent will “kill” the beneficial microflora, which can result in a fungal infection.
Prevention of ulcers
- professional oral hygiene at least 2 times a year
- Regularly replacing your toothbrush
- Proper brushing of teeth at least 2 times a day
- using additional hygiene techniques such as irrigators, dental floss, and tongue scrapers
- Children should be monitored for bad habits such as putting dirty fingers and other objects into their mouths
- It is important to treat your teeth in a timely manner. Microbes that are found in carious teeth and rotten roots can serve as a source of infection for ulcers
If you have problems in the oral cavity, contact the specialists of the Center for Family Dentistry!
Why does the gums around the crown become inflamed?
In addition to mechanical damage, the gums can react with swelling due to the irritating effect on it of chemicals contained in oral hygiene products - toothpaste, rinses.
However, swelling of the gums near the tooth under the crown can be caused by more serious reasons. For example, swelling may be a sign of:
- Gingivitis or periodontitis. It usually appears due to poor oral hygiene, the presence of dental plaque, malocclusion, poorly fitting crowns, as well as hypovitaminosis and endocrine disruptions. At first, the gums swell and bleed, darkening of the gums around the tooth at the crown may be observed, and later suppuration and tooth mobility occur.
- Flux, or periostitis. This disease affects the hard periodontal tissues and, in particular, the periosteum of the jaw. Very often, tooth flux under the crown is a consequence of asymptomatic pulpitis or periodontitis. If the flux is not treated, there are two possible options for the development of the disease - involution of the flux and its spontaneous opening. In the second case, a fistula forms on the gum (tooth under the crown), through which purulent contents flow. In this case, the pain subsides, but the inflammatory process itself continues and without appropriate treatment, osteomyelitis of the jaw can form.
- Alveolar process abscess is another complication of pulpitis, periodontitis or caries occurring in the tooth under the crown. With this disease, the patient will complain not only of swollen gums above the crown of the tooth, but also of severe pain in the jaw, aggravated by exposure to heat, facial asymmetry, and unilateral enlargement of the submandibular and cervical lymph nodes.
- Overloading a denture with irrational prosthetics can lead to the tooth crown moving away from the gum and food starting to get clogged under it. As a result, mobility of the supporting teeth appears, and the soft tissues of the oral cavity become inflamed (gingivitis).
What to do if the gums near the crown become inflamed
Inflammation of the gums near the tooth under the crown is treated based on the original cause that caused it. So, if swelling of the soft tissues appears as a result of trauma to the gums with a brush or due to the chemical components included in the rinses, it is enough to replace oral hygiene products with more suitable ones, and treat the gums themselves with antiseptics.
If swelling of the gums is caused by the development of dental pathology - gingivitis, periodontitis, etc., complex treatment is necessary - professional cleaning, curettage of periodontal pockets, application of anti-inflammatory and wound-healing ointments, injection of vitamins and sometimes antibiotics into the gums.
When flux forms, it is opened and the wound is drained.
If the flux has opened on its own and a fistulous tract has formed, endodontic treatment is carried out (if a crown covers a living tooth or not all root canals are filled) or resection of the apex of the root on which inflammation has formed. If it is presented late, it is not always possible to save the tooth under the crown and then it is removed. To the list of posts