Many people have faced this dilemma at least once in their lives. When making a decision, people base their decisions on personal experience, the opinions of friends and acquaintances, and actively search for information on the Internet. If you ask whether it is possible to treat teeth if your throat hurts badly , you get the following answers:
- yes, treat it, because the tooth hurts, and enduring pain is harmful;
- no, you will infect the doctor, and the recovery process after treatment will be delayed.
Interestingly, both sides can be equally right and wrong. Often a sore throat and toothache are related, being the root causes for each other. All that remains is to determine what started to bother you first—the throat or the teeth.
Are sore throat and dental treatment compatible?
Can a tooth cause a sore throat and why does this happen?
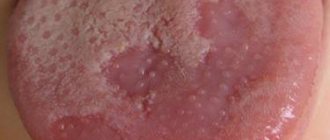
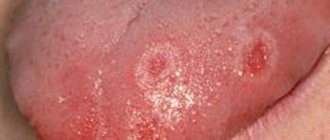
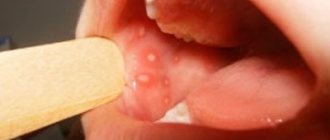
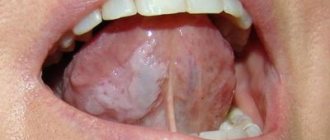
Yes, maybe it is explained by anatomical proximity. Therefore, it should be understood that we are talking about molars, and sometimes about “wisdom teeth” located close to the pharynx. If the front incisor and throat hurt at the same time, then they are unlikely to be somehow connected. And inflammation, especially purulent, of a molar can spread to the tonsils and submandibular lymph nodes, causing discomfort in the larynx and redness of the mucous membranes; Other symptoms include gingivitis and imaginary ear pain.
Accordingly, they first go to the dentist to solve the problem with a bad tooth. After treatment, doctors prescribe rinses with antiseptic solutions, which also cope with sore throats.
Non-dangerous pain
Natural post-filling pain
it is considered to be one that occurred after treatment and went away on its own after a relatively short period of time. The nature of this pain is aching and mild, which can sometimes intensify with:
- pressing (strong brushing of teeth, biting);
- alternating hot and cold dishes;
- severe stress;
- hypothermia.
The recovery period varies and depends on the type of treatment:
- if the doctor removed carious formations, the pain may persist, on average, from 3 to 5 days;
- after filling the canals, the pain disappears, as a rule, after a couple of weeks, sometimes after a month;
- after depulpation (removal of the neurovascular bundle inside the canal), a period of one to two months becomes the norm.
The general rule is: the more serious and deeper the dental intervention, the longer the rehabilitation period.
Pain under a temporary filling
is not considered dangerous if it occurs when pressure is applied to a tooth. If the sensations are very painful, you need to consult a doctor again for additional examination.
Refined diagnostics will allow you to get rid of shortcomings when replacing a temporary filling with a permanent one.
When treating a tooth, it is important to choose the correct filling size
Is it possible to treat teeth if you have a cold?
90% of specialists will answer this with a firm “no,” citing the following arguments:
- A healthy body has more strength for regeneration, which will be needed to heal inflamed gums, mucous membranes, sprout new nerve endings and stop bleeding.
- The effect of local anesthetics is reduced, because During inflammatory processes in tissues, the pH of the environment changes to the acidic side. A large dose of the same procaine is required to achieve complete pain relief. Increased doses of medications can cause allergic reactions. Considering that the manipulations are carried out near the throat, this is fraught with Quincke's edema.
- With a wet cough, sputum is actively expelled. At the most inopportune moment, you can cough in the doctor’s face, and healing also worsens. Sputum is characterized by the content of not only dead microorganisms, but also living, pathogenic ones. If it gets on inflamed gums, it can cause infection and complications including osteitis (bone inflammation) and sepsis.
COMPLICATIONS AFTER TOOTH EXTRACTION: HOW AND WHY?
After tooth extraction, your gums become inflamed, your jaw hurts, swelling appears, your cheek is swollen, your temperature rises? These are all the complications that arise after tooth extraction. Some of them go away on their own, but others require immediate medical intervention. Why do they appear, how to deal with them and when should you really worry? Tooth extraction is a difficult operation that traumatizes the tissue surrounding the tooth. Therefore, it is not surprising that unpleasant consequences occur after tooth extraction: the most common of them is swelling. Patients often complain that after tooth extraction, the gums become swollen, swelling of the cheek or a slight gumboil appears. This is caused by partial destruction of the soft tissue around the tooth. This is unpleasant, but if the tumor is small, it goes away on its own in 2-3 days. To relieve swelling after tooth extraction, ice can be applied to the cheek for about 10 minutes. If the swelling has not gone away after a day, apply heat. Keep the heating pad for 20 minutes, then take a break for 10 minutes and put the heating pad back on. Sometimes swelling can be caused by an allergy to the anesthesia. In this case, histamine, an antiallergic drug, will help. But if the swelling increases, then it may be a sign of inflammation that has arisen after tooth extraction. In this case, you should immediately consult a doctor. Temperature after tooth extraction. An increase in temperature is a normal reaction of the body to traumatic tooth extraction. It can last for 2 - 3 days, increasing in the evening. Maintain prescribed hygiene and take antipyretic medications. But if the condition does not improve, then you should visit the dentist. Pain after tooth extraction. Another common complaint is that after tooth extraction, the gums, adjacent tooth, jaw, and throat hurt. As a rule, these are common symptoms after a traumatic procedure. They are caused by damage to the periodontal tissues and nerves, which goes away on its own after a few days. For example, if a temporary aching pain appears after tooth extraction, this is normal. To relieve discomfort, you can take painkillers. But if the pain intensifies, it is still worth visiting a doctor. Uncomfortable sensations and swelling are possible after complex tooth extraction. But pain and fever are abnormal symptoms that should be reported to your doctor immediately. Often, pain and fever occur due to the fact that the patient “rinses out” a special clot that the doctor forms in the socket of the extracted tooth. The clot protects the hole and subsequently helps it heal as quickly as possible (on average, it heals completely within 6 weeks, sometimes faster, depending on the specific situation). If a clot is lost, inflammation may occur, which causes acute pain combined with fever. That is why, after tooth extraction, the doctor should always give the correct recommendations for caring for the cavity, and the patient should strictly follow them. Bleeding after tooth extraction. Immediately after a tooth is removed, there is bleeding from the socket. This is quite normal, since blood vessels rupture during surgery. In this case, the doctor will provide you with the necessary assistance. But sometimes bleeding occurs a few hours after surgery. To stop the bleeding yourself after tooth extraction, apply a small gauze swab to the hole and lightly bite it. After 15 minutes the blood stops flowing. But if the bleeding does not stop for a long time, you should consult a doctor. Pus after tooth extraction. Suppuration of the socket and periodontal tissues is caused by their infection. It can happen for several reasons. Firstly, if you did not follow the dentist's instructions regarding individual oral hygiene after surgery. Secondly, the cause may be a tooth fragment remaining in the tissues after removal. Thirdly, there is a high risk of suppuration after a complex wisdom tooth extraction, for example. If the inflammation is not treated in time, then some time after removal, suppuration, a fistula on the gum, and even a cyst may appear. If pus appears at the surgical site, consult a doctor. He will find and eliminate the cause of the inflammatory process. Dry socket after tooth extraction. A blood clot should remain in the socket after surgery. This is a very important part of the healing process. This clot protects the bone and nerve endings and serves to form bone tissue after tooth extraction. Therefore, you should not rinse your mouth for a day after the procedure and eat hot food - this will help the clot dissolve. But sometimes it does not form, and a dry socket appears. Dry socket is considered a complication. It most often occurs after complex removals accompanied by significant trauma. If there is no blood clot, then the hole after tooth extraction hurts, and sometimes it seems that the ear also hurts. Often there is an unpleasant taste in the mouth. The consequence of a dry socket after a traumatic tooth extraction can be inflammation of the gums or alveolitis. Therefore, if you experience acute pain in the socket, consult a doctor immediately. He will place a tampon with a special anti-inflammatory gel on the hole. Tampons are changed until healing begins. Paresthesia after tooth extraction. This is the name for numbness in the tongue, lips or chin after tooth extraction as a result of nerve damage. Most often it occurs after the removal of wisdom teeth, which are located next to the facial nerves. This unpleasant complication goes away within 1–2 weeks after surgery. But if the damage is severe, paresthesia may become permanent. Fortunately, this complication is quite rare. Alveolitis after tooth extraction. This is a serious complication caused by tooth extraction, which has several causes. This may be the presence of chronic inflammation of the tissues around the tooth - periodontitis, or a dry socket. In addition, alveolitis occurs if, after tooth extraction, a dental fragment remains in the tissues. All these factors cause infection of the hole and the development of its inflammation. 1–3 days after tooth extraction, pain occurs, followed by a specific smell from the mouth. Then these symptoms intensify, the hole becomes covered with a gray coating, and it becomes impossible to eat due to severe pain. In this case, only a doctor will help you, who will carry out the necessary treatment and clean the hole from infection. Do not self-medicate under any circumstances - alveolitis can develop into periostitis (inflammation of the periosteum), causing an abscess and phlegmon. Painful sensations after the removal procedure are unpleasant, but inevitable. Remember, if these sensations intensify, then in this case, complications after tooth extraction should be treated by a specialist. Do not delay your visit to the dentist, dulling the pain with analgesics. Correct and timely treatment will help you avoid more serious complications.
Why is dental treatment not recommended for sore throat?
A sore throat prevents you from opening your mouth wide, as dentists like. The patient will not sit through the entire procedure with inflamed and tense tissues of the pharynx, and the doctor will not provide the service of the required quality.
In addition, fear of the dentist, layered with fever and sore throat, will cause additional stress and completely undermine the body.
In bacterial forms of sore throat, the tongue is heavily coated with plaque containing microorganisms. This is a danger to the doctor and the patient’s health (autoinfection).
If we summarize all of the above, it turns out that it is better to reschedule the visit to the clinic. After all, with such strong-willed decisions, dentists take care of the health of both themselves and their patients. But sometimes these rules are deviated from in order to help people with sore throats.
How to relieve toothache during a cold
There are a hundred ways to relieve toothache, but only a dozen methods will be effective. Common control options include:
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) . When people have a cold, they resort to Fervex, Theraflu, Antigrippin and other drugs containing paracetamol. So why not replace the old and harmful paracetamol with a modern, soft and effective nimesulide or meloxicam? Both of the latter substances easily reduce temperature, block pain and fight inflammation;
- local anesthesia . Novocaine or lidocaine is applied to a cotton swab and applied to the diseased area. A sophisticated method suggests crushing 1 tablet of No-shpa (drotaverine) and pouring the resulting powder onto the affected area in the mouth. In both cases, the treated area becomes numb for 2-3 hours;
- traditional methods . The pulse is found on the arm on the opposite side and a clove of garlic is tied. The mechanism is not clear, but the pain subsides;
- warming up The method is effective, but dangerous: purulent inflammations cannot be heated, because this provokes the melting of surrounding tissues by pus enzymes. And only a doctor can tell about the nature of the inflammation.
The listed methods only relieve symptoms, which shortens the time of an attack of acute pain, but do not treat teeth.
And one last thing. Toothache only seems like a trifle at first - people endure it for days because of fear of dentists - but it is fraught with many dangers, just like a cold that is not cured in time. Take care of yourself and take care of your health. You are alone!
Moscow metro station Zvezdnaya, Danube Avenue, 23
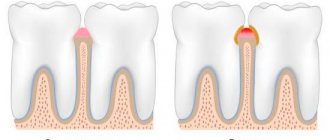
Causes of inflammation
An allergic reaction to the materials from which the prosthesis is made. This can include a plastic base (residual monomer in its composition), dyes, metal alloys, etc.
The uncomfortable base of the removable structure, resting on the mucous membrane, can rub or press unnecessarily, causing redness, pain and discomfort, especially when chewing.
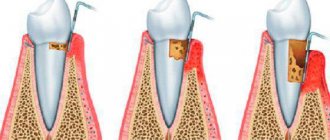
incorrectly made crown that goes deep into the periodontal sulcus will injure the gums, also causing inflammation - gingivitis. Destruction of the circular ligament leads to free penetration of microflora into the marginal periodontal area, which causes the development of periodontitis.
incorrectly made bridge , due to the supports, can have the same traumatic effect as a crown. Also, the intermediate (washing) part of the bridge resting on the mucous membrane leads to the accumulation of food debris, complicates hygiene, and sometimes causes the formation of ulcers and welts under the structure.
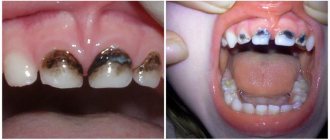
Poor hygiene and oral care leads to the accumulation of plaque, food debris, the formation of tartar and gum pockets. Which in turn is a trigger for the development of periodontal diseases, which is accompanied by inflammation, unpleasant odor, bleeding gums and the formation of pathological periodontal pockets with root exposure.
Changing the load on the prosthesis. This often happens after the loss of a side group of teeth and a long absence of their replacement. In this case, the chewing load is distributed only to the remaining supports, which leads to their overload and a corresponding periodontal reaction.
Painful sensations in the gums and inflammation of the mucous membrane may indicate the presence of pulpitis, periodontitis, periodontitis and other common diseases. The appearance of swelling, redness, and severe pain under the structure may be evidence that serious pathological changes are occurring in the jaw bone, requiring a visit to a dental clinic and the appointment of effective treatment.