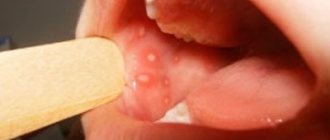
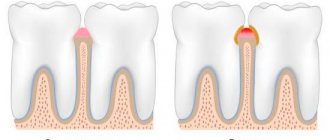
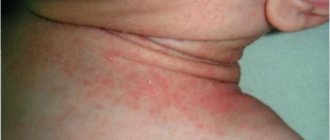
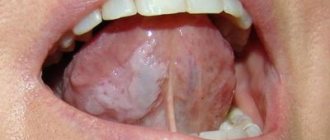
- Acute herpetic stomatitis
- Traumatic stomatitis
- Chronic aphthous stomatitis
- Candidal stomatitis
Stomatitis is an inflammation of the mucous membrane in the oral cavity. It is believed that children are most vulnerable to stomatitis. In adults, stomatitis does not occur as often. The instability of children to stomatitis is explained by the fact that they have a more delicate mucous membrane; children tend to constantly put something in their mouth and taste it, which contributes to the entry of microbes and accidental injuries. In addition, children's immunity is at the stage of formation, and therefore they are becoming acquainted with many bacteria and viruses for the first time. The first encounter with bacteria or, for example, with the herpes virus can be accompanied by a fairly violent reaction from the body.
Reasons for appearance
Opportunistic bacteria are part of the oral microflora of every person. Age doesn't matter here. Thrush appears when fungi, like yeast, become active and exceed the permissible number. Also, pathology is formed when pathogenic strains enter the patient’s body. The reason that leads to problems may be internal. Also, negative environmental factors influence deterioration of health. Often, anomalies are caused by non-compliance with hygiene rules, intestinal problems and others.
To prevent serious complications, you should consult a doctor promptly. A dental clinic that has modern equipment and uses the latest technologies will help you understand the problem and eliminate it. Advances in dentistry allow you to achieve results quickly. Having identified the true cause of the problem, the dentist will draw up a treatment plan. The problem will be solved when the provoking factor is eliminated.
Candidiasis in the oral cavity
This inflammatory disease is often diagnosed in children. It can affect a newborn. The basis of the disease is pathogenic fungi. They provoke damage to the mucous layer, and the uvula suffers. Candidiasis is suppressed by the defenses of a healthy toddler. But when fungi multiply quickly, the immune system cannot cope with them, as it weakens. The pathology progresses against the background of the following problems:
- Inflammatory processes in internal organs;
- Colds;
- Hormonal instability;
- Problems with the gastrointestinal tract;
- Long-term treatment with antibiotics;
Children's fragile immunity cannot withstand negativity. All this leads to imbalance. White palate in a baby’s mouth can appear due to severe stress, which reduces the body’s immune strength. The growth of fungi is provoked by excessive dryness of the mucous membranes and an imbalance of acid balance. The first sign of damage to the mucous membrane is itching. At risk are those guys who wear braces, are treated with hormonal drugs, and do not clean their chewing organs well. The disease develops especially quickly when unfavorable factors are combined. The baby's mucous membrane is covered with a cheesy film. Whitish crumbs are difficult to remove; ulcers form underneath them. They may bleed.
Infectious lesions
When the body's resistance decreases, the appearance of pathogenic bacteria is often associated with the appearance of one or another infection. As a result, white spots develop on the palate.
- Fungal strains are highly infectious. Pathogenic microbes quickly colonize the damaged mucosa.
- With scarlet fever, the baby's mouth turns red, a rash appears, and the temperature rises.
- With diphtheria, the film has dirty inclusions.
- With whooping cough, a putrid odor from the mouth is clearly heard.
- With dysentery, the layer is dense, and erosions appear underneath it.
Oral diseases
Oral problems cannot be ignored. Parents should immediately show the toddler to the pediatrician, who will refer the child to the dentist. Pediatric dentistry is a department where the exact cause of the disease is determined and a treatment regimen is developed. Specialists know how to work even with the smallest children. Problems in infants can develop due to dental diseases. Most of them are characterized by inflammation, swelling, the appearance of a film and ulcers. The source of infection is pathogenic bacteria. The main diseases include:
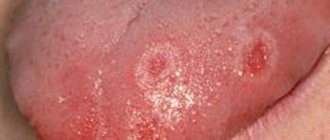
- Stomatitis, in which whitish sores with clearly defined edges appear. Children experience discomfort and refuse to eat. The disease progresses when the mucous membrane is damaged, there are not enough vitamins, allergies develop, and the body's defenses decrease.
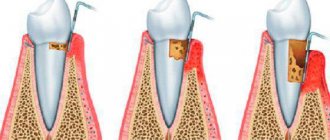
- Gingivitis, when the gums and other soft tissues of the mouth are affected.
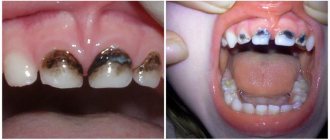
- Caries, with the active development of which white matter is diagnosed in the oral cavity in large quantities.
Stomach and intestinal problems
In pediatric practice, white spots on the palate of a child are quite common. The provoking factor is diseases of the digestive tract:
- Gastritis, which is characterized by inflammatory processes of the gastric mucosa. In addition to whitish deposits, patients experience pain, spasms, and stool disturbances.
- Dysbacteriosis, which is manifested by bloating, weight loss, problems with stool.
- Enterocolitis, in which, in addition to a film in the oral cavity, accumulation of gases and spasms of the gastrointestinal tract are diagnosed.
Symptoms of the disease
As a rule, the highest concentration of fungus is found on the surface of the inside of the cheeks, tongue, pharynx and tonsils, and palate. At an early stage of the development of the disease in children, redness of the mucous membranes is observed; they become swollen, the sensitivity of the mucous membrane increases, which is why children are often irritable, capricious, and their appetite and sleep are disturbed. The primary episode of the disease usually occurs in a more acute form; Patients may experience general symptoms: fever, headaches and dizziness, nausea or vomiting, deterioration in general health.
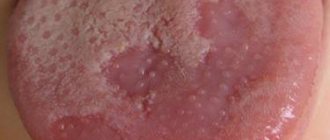
Some time after the onset of the disease, white grains begin to appear on the surface of the mucous membranes of the oral cavity, which gradually increase in size and merge together, forming plaques, and then plaque covering large areas of the mucosa. During this stage, patients suffer from severe dryness and swelling in the mouth. The mucous membranes become painful. Burning, itching and other unpleasant sensations are most often associated with the development of an allergic reaction caused by the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms and the release of toxins during their life processes. The pain intensifies when eating and swallowing food, when eating hot, sour, spicy foods and drinks. Infants often refuse to eat.
The plaque formed during candidiasis has a very characteristic appearance and resembles milk films or remains of cottage cheese. It consists of destroyed cells of the mucous membranes, food debris, bacterial mass, fibrin and keratin. Flakes, scales and plaque can also appear outside the mouth - on the edges of the lips. The spread of infection to the lips is called candidiasis. Because of this disease, the skin in the corners of the lips dries out and cracks; In some cases, the infection affects the entire surface of the lips, resulting in cracking and peeling.
In mild and moderate forms of the disease, plaque is easily scraped off, and underneath it, areas of erosion (ulceration) or maceration (softening) of the mucous membrane are found. A longer course of the disease and the lack of adequate treatment leads to deep damage to the mucous membranes, as a result of which blood appears on their surface, turning the plaque brown or brownish.
Diagnostics
If a baby has a white spot in the mouth, to make an accurate diagnosis, a number of tests are prescribed, as well as certain procedures. Usually the doctor immediately notices the problem when examining the surface of the mucous membrane. In addition, the following may be additionally prescribed:
- Scrapings or smears from the cheesy film;
- Collecting anamnesis during a conversation with parents;
- Clinical blood test;
Purpose of the study: detection and confirmation of Candida fungi. If necessary, the mother must additionally show the child to specialized doctors. This will help identify the inflammatory processes that occur in the internal organs, which will help prevent serious complications. An oral smear plays an important role in making a correct diagnosis. After drying the applied scraping onto medical glass, staining and examination under a microscope are carried out. Identification of fungal colonies allows the doctor to select the desired therapeutic regimen, taking into account the characteristics of the body and the age of the patient.
To prevent your baby from getting thrush
To prevent thrush from reaching the baby’s mucous membranes, special precautions must be taken:
- Regularly care for your child’s mucous membranes, monitor their condition when the baby is sick, and especially when he suffers from infectious diseases;
- If your child is prescribed antibacterial drugs, be sure to remember to use special means to protect the microflora;
- If candidiasis occurs during pregnancy in an expectant mother, it is necessary to urgently consult a doctor and undergo treatment. In addition, on the eve of birth, maternity hospitals carry out special prophylaxis for newborns with an increased risk of candidiasis. Thrush is especially susceptible to infants whose mothers suffer from chronic candidiasis and those who have foci of infection already in the immediate vicinity of birth. Mothers with inflammatory gynecological diseases or difficult childbirth can also transmit the risk of fungal infection to the newborn.
Treatment of white plaque on the palate of a child
The white spots will disappear if the cause of the problem is eliminated. If you regurgitate frequently, for example, you should change your feeding method and sterilize your utensils. A small area of fungal infection is treated with topical preparations. Severe forms of the disease are treated medicinally using complex drugs. Fungal diseases are dealt with:
- Clotrimazole;
- Candide;
- Pimafucin;
- Fluconazole;
- Diflucan;
A sterile gauze ball is moistened with the solution. They gently wipe the oral cavity several times a day. The duration of therapy depends on the complexity of the situation. Treatment usually lasts 7-10 days. Irrigation or lubrication is also prescribed. To boost the body’s defenses, doctors recommend vitamin complexes and probiotics for children. This will restore the natural microflora in the intestines.
Features of the oral cavity
The mucous membrane of a healthy child's mouth is bright pink due to the large number of blood vessels. As she grows older, her shade fades.
The epithelial layer is distinguished by tenderness and vulnerability, as well as some dryness due to the not very active work of the salivary glands (up to 3-4 months).
The baby's mouth is ideally suited for sucking. A wide tongue, a fold on the gums formed by the mucous membrane, pads on the inside of the lips, a “suction cup” on the upper lip - all this provides a tight grip on the bottle or nipple and facilitates the process of obtaining food.
What features or problems can be detected by looking into a baby’s mouth? Main options:
- white bumps on the palate;
- abnormal appearance or position of the tongue;
- white plaque on the inside of the mouth.
Prevention
Everyone who gives birth should know how important hygienic cleaning of the child’s oral cavity is. This procedure cannot be ignored. It can prevent many dental diseases. Therefore, do not miss visits to the dentist! Only a doctor can notice problems at an early stage. Treatment started on time will be faster and easier.
Compliance with preventive measures minimizes the risk of pathology. During the period of bearing a child, the expectant mother needs to take care of her health, pay close attention to oral hygiene procedures, and not introduce into the diet those foods that create a favorable atmosphere for the activation of fungi. Prevents problems:
- Refusal of artificial feeding, transition to breastfeeding;
- Before feeding the baby, the breasts should be treated with a solution of baking soda;
- Pacifiers, pacifiers, and bottles should be sterilized;
- After the baby has eaten, you need to give him boiled warm water to drink, which will wash away the remaining milk from the mucous membrane.
What kind of disease is candidiasis?
According to statistics, about 30% of infants experience candidiasis. The causative agent of the disease is Candida fungus. These specific microorganisms are normally present in the body of every person, even in the absence of health problems, but only in small quantities.
Oral candidiasis in children is much more common, since the immune system of children is not yet formed and is not able to resist pathogenic microorganisms and the effects of negative external factors.
With weakened immunity and the concomitant influence of provoking factors, the fungus begins to actively multiply, affecting the mucous membranes. Without therapeutic treatment, candidiasis is eliminated in exceptional cases. Much more often, if thrush is not treated, complications arise, and the infection itself spreads throughout the body.