Causes of the smell of acetone from the mouth of a child
Acetone syndrome is a condition of the body characterized by the presence of excessive amounts of ketone bodies in the blood.
This syndrome can be either a separate disease or occur in various diseases. The main signs of acetone syndrome include nausea, vomiting, lack of appetite and cramping abdominal pain. The syndrome most often occurs before the age of 12, with girls suffering from the disease much more often. Read on to learn how to treat increased acetone in children.
Pediatricians distinguish between idiopathic (primary) syndrome, which is an independent disease, and secondary, which accompanies the underlying disease. The latter include diabetes mellitus (most often a decompensated form), hemolytic anemia, thyrotoxicosis, traumatic brain injury, toxic liver damage and others. The course of secondary acetone syndrome and its prognosis largely depend on the course of the underlying disease.
Causes of acetone odor from a child’s mouth:
- lack of carbohydrates in the diet;
- disturbance of acid and water-electrolyte balance in the body;
- abuse of fatty and protein foods;
- strict diet or prolonged fasting;
- excessive physical activity;
- depletion of pancreatic reserves.
Complications and consequences
Type 1 diabetes mellitus often occurs in childhood and can be complicated by episodes of diabetic ketoacidosis, a severe state of absolute or relative insulin deficiency leading to hyperglycemia, hyperacetonemia, and systemic inflammation. Possible consequences and complications of this condition in children include disruption of acid-base homeostasis: the level of ketones also increases in the urine (which is defined as ketonuria), and along with their excretion during urination, the level of electrolytes (K and Na ions) in the plasma decreases. Cerebral edema (about 1% of cases), acute ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke, pulmonary interstitial edema and coagulopathies (due to impaired clotting factors) are also possible. In addition, as with any increase in blood acidity, the endothelium of blood vessels may suffer: oversaturation of the blood with ketone bodies increases the negative impact of free radicals on cells and leads to oxidative stress. It is believed that ketones, or rather their increased levels, are related to the occurrence of cancer pathologies. In acetonemic syndrome, there is a possibility of liver enlargement and fatty infiltration, and in severe acetonemic crises, the risk of coma and death cannot be excluded. [10], [11], [12]
Symptoms of the disease
This condition is characterized by the appearance of frequent acetonemic crises, the first of which occur at the age of two to three years. Symptoms of an acetone crisis include:
- repeated vomiting, diarrhea, temperature rises to 38°C;
- smell of acetone from the mouth;
- lack of appetite;
- primary excitement followed by drowsiness and apathy;
- arrhythmia, pale skin, unhealthy blush;
- cramping abdominal pain;
- intoxication and dehydration (dehydration).
Let us remind you that it is extremely important for parents to know what to do in case of acetonemic vomiting in a child.
Risk factors
Risk factors for the appearance of an acetone odor are noted, such as infectious diseases with a significant increase in temperature, persistent infections, helminthic infestation, and stress conditions. At a young age, a risk factor is also poor nutrition in children with a lack of the required amount of carbohydrates. Ketosis can be triggered by consuming large amounts of fat, as well as physical overload. It should be borne in mind that the trigger for the development of autoimmune diabetes mellitus in children can be the frequent use of corticosteroids (negatively affecting the adrenal cortex) and antiviral agents containing recombinant interferon alpha-2b. [5], [6], [7]
Diagnosis of the syndrome
To make a correct diagnosis, anamnesis data, patient complaints, clinical manifestations and the results of additional examination are important.
Laboratory tests include a biochemical blood test and a general urine test. Please note that the amount of acetone in children who do not suffer from this disease does not exceed 0.01 grams.
Instrumental diagnostics is echocardioscopy, with which you can see indicators of central hemodynamics. Acetone syndrome is characterized by a decrease in the diastolic volume of the left ventricle and a decrease in venous pressure. Against this background, the cardiac index is increased due to tachycardia.
Recently, you can even test your urine for acetone at home. For this purpose, special indicator test strips are used.
On our website you can familiarize yourself with the qualifications of specialists advising on this issue and learn how to check the level of acetone in children.
Acetone in the body
There is only one way for acetone to get into a child’s blood. It is considered an element of partial breakdown of fat and protein elements. For this reason, toxic substances called ketones accumulate in cells. Acetone refers specifically to their varieties.
First, ketones are oxidized almost to the point of harmless substances, after which they leave the body in urine and through the lungs. If, in comparison with the amount removed, the growth of toxic components is significantly higher, they do not have the best effect on the body’s systems, including the full functioning of the brain.
Therapeutic measures
At the first signs of the syndrome in question, the child should be reassured and given glucose. The use of a sorbent is also extremely important - it can be enterosgel or even activated carbon. To avoid dehydration, drinking plenty of fluids (mineral water) is recommended. It should be given one tablespoon at a time, but often. The use of antispasmodics is justified.
If vomiting does not stop within an hour, you must call an ambulance, which will provide qualified first aid for acetone in children.
In case of secondary acetone syndrome, treatment of the underlying disease is important.
Who is at risk
There is a category of children who have a high probability of developing acetone syndrome. Signs of such children:
- Gender Female;
- age 2-7 years;
- thin body build and slight underweight;
- increased curiosity and good learning ability;
- excellent memory;
- stubborn character;
- poor appetite;
- irritability and sleep disturbances, increased tearfulness.
Such children begin to talk early. By about 12-13 years of age, the tendency to have crises gradually disappears. Until this point, parents should always keep appropriate medications, mineral water and test strips in the house.
To minimize the possibility of acetone accumulation in the body, you need to create an environment favorable for the child’s development. He must eat right, develop mentally and physically, but not overwork and not experience constant stress. It is also important to have regular checkups with your doctor to avoid sudden deterioration in your health.
Diet with acetone in children
One of the main causes of acetone syndrome is poor nutrition. To avoid relapses, we advise parents to strictly monitor the baby’s daily diet. Carbonated drinks, chips, sweets with preservatives are strictly prohibited. Also, do not give your child fried or too fatty foods. The diet should be dominated by porridge and vegetable soups. Meat and herbs are added in small quantities. Following a diet with acetone in children is of great importance. As a rule, doctors recommend sticking to it for two to three weeks after a crisis of acetone syndrome.
Treatment of acetone odor and its causes
It’s good if parents contact a specialist as soon as their child’s breath starts to smell like acetone. In this case, the therapeutic course of treatment is aimed at two key areas:
- supplying blood cells with glucose;
- rate of ketone elimination.
If a child is vomiting, doctors recommend giving the child tea with the addition of a small amount of honey. This is necessary so that the amount of glucose has time to be replenished.
The liquid is given one teaspoon every 5 minutes to avoid the manifestation of a secondary gag reflex. The drink must be given at night. It is advisable to alternate tea with still mineral water or rice broth. In severe cases of the disease, glucose is injected into the blood intravenously through a dropper.
You cannot force a child to eat food against his wishes. If he himself asks for food, you can start with bread, cookies, baked apples, light soup or puree made from various vegetables. To avoid dehydration, adults must give the child the required amount of water.
If an increased percentage of acetone is detected, the following medications are used in therapy:
- “Atoxil” - absorb poisons and remove them from the blood;
- "Regidron" - restores the acid-base level;
- "Smecta" - like "Atoxil", makes it difficult to absorb toxic substances through the intestinal tissue.
Immediately after first aid is provided and the acute period of the illness ends, the baby is given the drug “Stimol”. It supplies the body with energy and improves overall condition. Betargin restores liver function quite well. For pancreatic dysfunction, doctors prescribe Creon. Its components improve digestion and give the child vigor.
How to reduce acetone in a child: tips for parents
As noted above, at the first signs of an emerging crisis, it is important to give glucose preparations and cleanse the intestines. For this purpose, you can do an enema with a soda solution, give a sorbent and give the baby small portions of water. Your local pediatrician will tell you in more detail how to reduce acetone in a child.
A list of easy-to-follow recommendations that will help prevent relapse:
- normalization of the daily routine;
- eliminating excessive loads;
- limiting time for watching television programs and computer games;
- proper nutrition excluding processed foods, fast food and quick snacks;
- walks in the air and moderately active games;
- adequate day and night sleep.
In addition, parents should know the dangers of increasing acetone in children and what its consequences are.
Treatment of acetone syndrome in childhood
Therapy for this condition will be very pleasant for children, because it involves eating a lot of sweets and drinking appropriately. The first thing that is recommended to do is to give your baby glucose to drink often and in small portions (newborns and under 3 years old - 1 teaspoon every 5 minutes, older children - 1 tablespoon every 10 minutes). To do this, you do not need to wait for test results and a doctor’s diagnosis.
The second way to quickly normalize a child’s condition is to give him an enema with a soda solution (1 teaspoon of dry product per 100 ml of warm water). Additionally, you need to prepare a “Regidron” solution, which will help restore the water-salt balance.
Note! All of the above methods are good until a severe symptom of the syndrome begins to appear - vomiting. Usually it is so strong that it is simply impossible to give the baby glucose to drink. Everything will immediately appear outside.
If acetone syndrome has developed sufficiently and the child has already started vomiting and diarrhea, then you need to call a doctor or an ambulance team. The patient will be given a drip with glucose solution. This is the only way to “water” the body in this state. After vomiting, the doctor may give the child antiemetics and antispasmodics.
If symptoms recur, parents should stabilize the condition and contact the pediatrician for a full examination of the patient and identification of the underlying pathology.
Forecast
If treatment is started on time, the prognosis for this condition is favorable. Timely consultation with a specialist, high-quality diagnosis and effective therapy will help avoid many serious complications. To a greater extent, this statement concerns the first (idiopathic) syndrome.
If you have any questions regarding acetone syndrome in children or need help from a specialist, we are always happy to help. The medical center is equipped with modern equipment. The appointments are conducted by doctors with many years of experience. The specialist will carry out diagnostics, tell you about the first symptoms of increased acetone in the child’s urine and about methods of prevention. Contact us - we can help you 24 hours a day.
Related services: Pediatrician consultation
Preventive measures
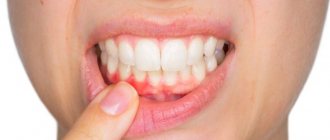
Be sure to regularly visit the dentist with your child as a preventative measure!
It is not advisable to drown out the smell of acetone with fresheners and toothpastes , otherwise in the future you will have to deal with serious diseases. It is good if the family visits the dentist once every six months, since this becomes a habit from an early age.
The first preventive measures start in early childhood in the form of high-quality teeth cleaning. Adults should teach the child to brush their teeth for a long time, and at least twice a day in the morning and evening, and after each meal, rinse their mouth well with plain water.
Habit formation should be carried out immediately after the appearance of the first teeth. Until the age of 7, the mother should be nearby and ensure that the child cleans the teeth and the space between them efficiently and for a long time.
Many fruits, berries and vegetables cope with mechanical cleansing of the oral cavity from various types of bacteria. The thing about mints and sweets is that they dry out the inside of your mouth, which is an ideal environment for pathogens to grow. To prevent dryness from appearing, during sports training and in stressful circumstances, the child should drink liquid.
If the child is still too small, teeth are cleaned using special brushes that adults put on their fingers and clean themselves.
Poor diet is a common cause of halitosis
Sometimes parents associate the occurrence of bad breath with the fact that the baby may have eaten something too odorous or stale.
Indeed, some foods can leave a not entirely pleasant smell for a long time - garlic, radishes or radishes, onions, cabbage, corn. Drinking certain juices and carbonated drinks also contributes to this. But the smell should not be very persistent - ventilation of the organs and natural cleansing of the oral cavity should quickly cope with it.
Often such a sign can occur after an excessive feast, when the baby at the festive table simply ate too much. The digestive system, in its normal mode, cannot process excess food, so it stagnates in the stomach - this is where unpleasant belching with a putrid unpleasant odor occurs. This also happens in children who are prone to overeating and obesity - for them this symptom can often be chronic. If the diet shifts towards protein foods, this stimulates constant rotting processes.
Correct introduction of the first complementary foods during breastfeeding will help avoid the appearance of excess weight in children. Very often this problem occurs among sweet lovers. Waste products released by colonies of microorganisms can cause an unpleasant odor.
Prevention measures
Parents whose child is prone to this disease should have glucose and fructose preparations in their home medicine cabinet. Also, you should always have dried apricots, raisins, and dried fruits on hand. The baby's meals should be fractional (5 times a day) and balanced. As soon as any sign of an increase in acetone appears, you should immediately give the child something sweet.
Children should not be allowed to overexert themselves, either psychologically or physically. Daily walks in nature, water procedures, normal eight-hour sleep, and hardening procedures are shown.
Between attacks, it is good to carry out preventive treatment of crises. This is best done in the off-season twice a year.
The key to fresh breath is hygiene
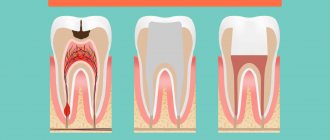
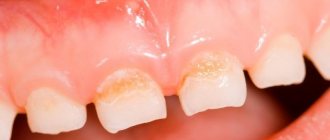
It is imperative to pay attention to the condition of the oral cavity. Maybe the child is too lazy to brush his teeth, or he does it just for show, without thoroughly cleaning the gums and interdental space. Therefore, in this case, it is possible that the baby has developed and is developing caries, and the appearance of the smell is connected precisely with this.
You need to take care of your oral cavity as soon as your baby gets his first teeth. Colonies of pathogenic microorganisms develop well in a poorly cleaned oral cavity.
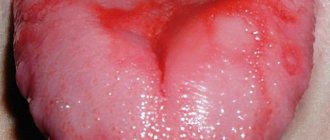
Take a good look at the condition of the oral mucosa - mothers are sometimes able to detect signs of stomatitis or other inflammations.
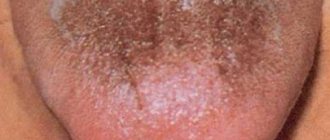
There can be a lot of food debris left on the mucous membrane of the tongue and parents should not forget about this. Very young children need to regularly clean their tongues of plaque; as they grow older, you need to teach them to do this on their own.