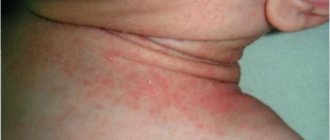
Inflammation of the vaginal cervix. Symptoms are nagging pain in the lower abdomen, purulent or mucous discharge, pain during urination and sexual intercourse. Inflammation of the cervix, or cervicitis, refers to inflammation of the narrow lower part of the organ. A healthy uterus is normally covered with epithelium that produces a mucous secretion. This substance plays a protective role and prevents infections from entering the internal cavity. When the secretory function of cells is disrupted, active growth of pathogenic microflora occurs, and symptoms of cervical inflammation develop.
According to statistics, cervicitis is diagnosed in 30% of women of childbearing age. The pathology can be in the cervical canal, then they talk about endocervicitis, or in the vaginal part of the cervix – exocervicitis. The peak incidence is recorded in the age group of 17-28 years, when a woman exhibits maximum sexual activity and rarely uses barrier contraception.
Treatment of cervical inflammation in the initial stage is carried out using conservative methods and does not require radical measures. The prognosis is favorable. But for this, a woman must undergo regular medical examinations and consult a gynecologist when the first symptoms of the disease appear.
You can get examined for signs of cervicitis in Moscow at the Alfa Health Center clinic.
Signs of cervical inflammation
Patient complaints are different for acute and chronic cervicitis.
The main symptoms of inflammation in the cervix:
- purulent or mucous discharge from the genitals;
- pain, heaviness in the uterine area;
- discomfort, burning in the genitourinary tract, aggravated by sex and urination;
- a slight rise in temperature to 37-37.2ºС.
In some cases, the inflammatory process occurs without pronounced clinical signs and is determined by the results of a gynecological smear.
Diagnosis of cervicitis at the Yauza Clinical Hospital
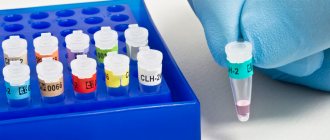
Gynecologists at the Yauza Clinical Hospital diagnose cervicitis after examination, based on medical history, colposcopy results, laboratory tests (smear microscopy, bacteriological culture for microflora and sensitivity to antibiotics, PCR, etc.). When examined for cervicitis, hyperemia (redness) of the mucous membrane, swelling, inflammatory discharge, and ectopia may be present. Colposcopy allows you to study the condition of the mucous membrane in detail and track the dynamics during the treatment process. In acute cervicitis, a cytogram of a smear from the cervical canal and a scraping from the cervix reveals a large number of leukocytes, lymphocytes, and altered epithelial cells. At the same time, it is important not to miss precancerous cell changes, especially if PCR diagnostics reveal oncogenic strains of the papilloma virus (HPV). PCR will help identify other dangerous infections (herpes virus, chlamydia, mycoplasma, etc.) based on the genetic material of their pathogens.
Causes of cervicitis
Inflammation of the cervix and appendages can be caused by the following factors:
- sexually transmitted disease: gonorrhea, trichomoniasis, chlamydia and other infections;
- microorganisms that are normally present on the vaginal mucosa;
- mechanical injuries during gynecological operations, conization, childbirth, from the use of the uterine ring, treatment with iodine, dimexide, and other means;
- hormonal disorders;
- antibiotic treatment, chemotherapy courses;
- allergy to latex or substances used in condoms;
- diseases of the female genitourinary system: colpitis, endometritis, cystitis, erosion and others.
A common cause of cervical inflammation is independent, uncontrolled use of antibiotics. Medicines inhibit the beneficial microflora of the vagina and reduce local immunity. Organisms resistant to antibiotics appear in a woman’s biota. These are the most complex cases of mixed infections that require an individual treatment plan.
Risk factors such as young age and frequent changes of sexual partners are also noted.
The most common oral diseases
Catarrhal stomatitis
Diagnosed in adults and children in most cases. Its development can be provoked by: insufficient hygiene, plaque and gum disease, oral dysbiosis, any diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (gastritis, colitis, duodenitis) and damage to the body by helminths.
It will be difficult for a person far from medicine to distinguish one disease from another. The symptoms of most of them are almost the same.
Symptoms of catarrhal stomatitis:
- Swelling of the oral mucosa;
- Whitish or yellowish coating;
- Increased sensitivity and soreness of tissues;
- Increased salivation;
- Bleeding gums;
- Bad breath.
Ulcerative stomatitis
A fairly serious disease of the oral mucosa. It can develop independently or as a complication after catarrhal stomatitis. Often this disease is diagnosed in people suffering from stomach ulcers or an acquired form of enteritis. In addition, the appearance of ulcerative stomatitis can be provoked by infectious, cardiovascular diseases, blood diseases and intestinal infections. Ulcerative stomatitis is active not only in the upper layer of the oral mucosa, but also spreads throughout its entire thickness. The symptoms are initially similar to catarrhal stomatitis, but then they intensify and are complemented by others.
Symptoms of ulcerative stomatitis:
- Increase in body temperature to 37.5 degrees;
- The appearance of ulcers on the inside of the cheek;
- Impotence;
- Headache;
- Painful enlargement of lymph nodes.
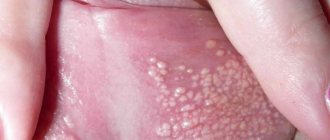
Aphthous stomatitis
It mainly develops due to weakened immunity, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and allergies. In addition, viral infections or rheumatism can trigger the occurrence of aphthous stomatitis. It is worth noting that the exact causes of this disease are unknown to medicine.
Symptoms of aphthous stomatitis:
- The appearance of small red round ulcers on the oral mucosa. Over time, the center of the ulcer becomes grayish-yellow;
- General malaise;
- Temperature increase;
- Weakness.
Glossitis
Otherwise, a tumor (inflammation) of the tongue. Can be primary or secondary. It is often a companion to stomatitis of any form. The disease is dangerous because it can be complicated by abscessation of the tongue and the development of phlegmon of the neck. The chronic form of glossitis leads to the development of papillomatous, warty and other growths on the tongue. There are different types of this disease, which are similar in their main symptoms:
- Pain and swelling of the tongue;
- Red spots on the surface of the tongue;
- Redness of the pharynx, tonsils;
- Rash and sores.
Leukoplakia
Chronic disease of the oral mucosa. It hardly bothers the patient and has a blurred clinical picture. The causes of leukoplakia are traumatic in nature. It mainly affects older men. It is located on the mucous membrane of the cheeks, in the corners of the mouth and on the lateral surfaces of the tongue. The occurrence of this disease is provoked by mechanical damage to the mucous membrane: burns from too hot or spicy food, friction with the tops of broken teeth. The seriousness of leukoplakia is that it can degenerate into cancer, so the patient needs to consult an oncologist.
Symptoms of leukoplakia:
- Pathological keratinization of the epithelium;
- Growths are white or gray;
- Mild itching and burning.
Atrophic candidiasis
The disease affects newborn children, men who smoke, women of childbearing age and the elderly. As a rule, this pathology manifests itself in an acute form. The disease is difficult for patients to tolerate and significantly reduces the quality of life. A person experiences discomfort while eating, and is bothered by a burning sensation and itching.
Symptoms of atrophic candidiasis:
- Dryness and redness of the mucous membrane;
- Whitish coating in the folds of the mouth.
Lichen
This disease can affect not only the skin, but also the oral mucosa. The acute form lasts within a month, and the moderate-acute form lasts up to six months. In cases where lichen lasts for a long time, we are talking about a chronic form of the disease. In older people, oral lichen manifests itself in the form of erosions and numerous ulcers. In addition, rashes in the form of blisters may appear on the reddened mucous membrane. This disease mainly affects people who have a history of diabetes, weakened immunity, and various diseases of the liver and gastrointestinal tract. In some cases, there is a hereditary predisposition.
Symptoms of oral lichen:
- Plaques on the surface of the mucosa;
- Discomfort while eating;
- Itching and burning.
Dysbacteriosis
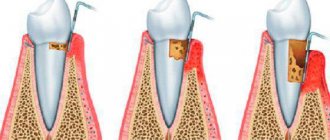
Most often, long-term antibiotic therapy leads to the formation of this pathology, which disrupts the healthy balance of microflora. If dysbiosis is not treated, it will spread further, disrupting the proper functions of the organs, completely affecting the tongue, tonsils and vocal cords. Most patients develop periodontal disease, which can lead to loosening and tooth loss.
Symptoms of dysbiosis of the oral mucosa:
- Unpleasant odor;
- Bleeding cracks in the corners of the mouth;
- Heavy plaque.
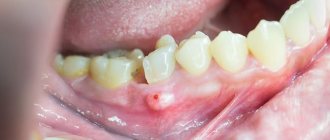
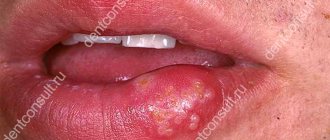
Cheilitis
The disease manifests itself not only from the inside, but also from the outside. The reasons lie in changes in hormonal balance, allergies, lack of vitamins, and the effect of fungal flora on the mucous membrane.
Symptoms of cheilitis:
- Inflammation of the lip border;
- Ulcers on the oral mucosa.
Types of cervicitis due to inflammation
- Purulent. Occurs when infected with a sexually transmitted disease. Purulent cervicitis is characterized by mucous discharge with an unpleasant odor and involvement of nearby organs and tissues in the process.
- Viral. The mucous membrane becomes inflamed when infected with cytomegalovirus, human papillomavirus or other pathogens. The disease may be accompanied by itching and the appearance of polyps.
- Bacterial. Cervicitis develops from vaginosis, when active proliferation of pathogens of the natural microflora of the vagina occurs. Infection from a sexual partner is possible.
- Atrophic. The cause of the disease is thinning of the mucous membranes. Atrophic cervicitis often occurs in women during menopause.
Diagnosis of diseases of the oral mucosa
Modern medicine has a wide range of diagnostic tests to make an accurate diagnosis.
Only a doctor can give the correct classification of the disease. For this purpose, he can use the following methods:
- Mucosal smear for microscopic examination;
- Conducting allergy tests;
- Analysis for viral infections (herpes, tonsillitis);
- General examination to identify the primary disease.
Treatment of cervicitis
To select an adequate treatment regimen for cervical disease, the duration, severity of the disease, and cause are taken into account. If cervicitis is infectious, therapy will also be required for the sexual partner.
To treat acute inflammation of the cervix, your doctor may prescribe:
- Antibiotics of the fluoroquinolone or macrolide group. At the same time, it is recommended to take antifungal drugs that will prevent the development of candidiasis;
- Means for restoring microflora. A woman is prescribed medicinal suppositories, gels with lactobacilli;
- Immunomodulators. The drugs strengthen local immunity and help beneficial microflora resist the effects of antibiotics. Immunomodulators are taken in the form of powders or tablets;
- Hormonal medications with estrogens to regenerate the thinned mucous layer;
- Physiotherapy: endocervical electrophoresis, magnetic therapy, irradiation of the cervix with ultraviolet light, laser, microwaves, low-frequency ultrasound. Treatment is primarily aimed at restoring microcirculation of blood and lymph in the affected tissues. For chronic inflammation of the cervix, physiotherapy is carried out in courses several times a year to prevent exacerbation.
In rare cases, surgery is indicated. As a rule, the operation is performed in cases of severe and extensive inflammation, when the woman did not seek diagnosis at the onset of the disease. For treatment, the method of cryodestruction, diathermocoagulation or chemical coagulation of pathological areas is used.
Particular attention is paid to the treatment of exacerbation of cervicitis in pregnant women. The doctor carefully selects medications and calculates the dosage to eliminate risks to the fetus.
general characteristics
Diseases of the oral mucosa can be infectious, inflammatory, viral or fungal. When an infection enters the oral cavity, the mucous membrane is the first to suffer. It can become inflamed, bleed, and become thinner. Conventionally, such diseases are classified as stomatitis. But besides stomatitis, there are many more problems that lead to deterioration in human health.
In almost all of the diseases described below, the symptoms will be similar: pain, rashes of various types, discoloration of the tissues of the oral cavity.
Oral diseases can be treated by a dentist, ENT specialist or therapist. When the first symptoms appear, you should consult any of these doctors for examination.
Why is cervical inflammation dangerous?
Self-medication risks complications, so only a doctor should decide how to treat a woman. If the patient does not seek help in a timely manner, acute cervicitis becomes chronic. A woman faces consequences such as erosion, miscarriage, and spread of the inflammatory process to the appendages. The risk of developing cancer increases. Chronic cervicitis leads to the formation of adhesions and infertility. Patients often experience chronic pelvic pain, menstrual irregularities and other manifestations that reduce quality of life.
Prevention
To prevent painful symptoms, experts recommend following the universal rules of oral hygiene:
- use properly selected toothbrushes, use them systematically, and also avoid bad habits, especially smoking.
- It is recommended to control your diet: in some cases, oral irritation may be caused by excessive consumption of oranges, lemons, etc.
- the habit of cleaning seeds with teeth rather than with hands can become unfavorable for the oral cavity.
Inflammation of the cervix during pregnancy
Cervicitis occurs in two out of three pregnant women at different stages of gestation. The disease is acute, not only the vaginal wall becomes inflamed, but also the labia. Women complain of burning, itching in the perineum, and discomfort. Inflammation of the cervix during pregnancy is one of the factors of miscarriage, so it is necessary to consult a doctor as soon as possible.
Cervicitis in this case is chronic. A woman may not be aware of inflammation until pregnancy, when the pathology manifests itself against the background of natural immunodeficiency.
Symptoms of gastritis development
Inflammation of the external tissues of the stomach manifests itself in various signs, which in some cases are not very pronounced. The main symptom can be considered pain in the solar plexus area, which is aggravated by eating certain foods, taking certain liquids or medications that are aggressive to the mucous membrane of the organ.
Sometimes the pain may, on the contrary, appear between meals, and become dull after eating it. Spicy foods, alcohol, and carbonated drinks lead to an exacerbation of the disease and therefore their use during gastritis is contraindicated. In addition to the sensation of pain, the patient is plagued by symptoms such as belching, vomiting and heartburn.
Doctor's recommendations
Every year, more and more women turn to us for treatment of chronic cervical inflammation. The reason is that the patient simply does not notice or ignores the first signs of cervicitis. We often detect inflammation when dealing with completely different complaints. This is dangerous for future motherhood. We recommend that couples with a history of stillbirth, frozen pregnancy, or intrauterine infection of the fetus undergo a thorough examination to identify hidden infectious agents. Only after treatment can you plan to conceive again. Miscarriages and premature births are a common consequence of cervical inflammation.
Main symptoms of stomatitis
Symptoms of stomatitis depend on its type and form, are very diverse and specific. General symptoms include redness, swelling of the mucous membrane, burning and pain in the mouth (including when eating hot, sour or spicy foods), an increase (or, conversely, a decrease) in salivation, bad breath, as well as the manifestation, in depending on the severity of the disease, specific lesions - erosions, af, ulcers.
Folk remedies for treating inflammation symptoms
Chamomile infusion will help with increased acidity.
Medicinal plants are successfully used to combat the symptoms of many serious diseases. Inflammation in the intestines was no exception.
Today, remedies to alleviate the symptoms of this disease can be found in any pharmacy. Let us list the most effective of them:
- To combat bloating and stabilize stool, mix fennel fruits, caraway seeds and chamomile flowers in equal proportions. The resulting mass is poured with boiling water. The liquid is filtered and taken after meals (maximum three times a day).
- In case of increased acidity in the stomach, prepare a tincture from pharmaceutical preparations of chamomile, elecampane, valerian, yarrow, cucumber, alder, calendula, licorice and marshmallow. The listed ingredients are mixed, poured with boiling water and placed in a water bath for 5 minutes. The finished liquid is filtered and drunk half a glass at a time before each main meal (that is, three times a day).
- For low acidity, other herbs are used. In this case, the tincture is prepared from collections of linden, marshmallow, chamomile, fennel and elecampane. The ingredients are mixed and placed in boiling water. The liquid is infused and filtered. They do not drink the drug regularly, but as a pain reliever (in other words, only during exacerbations of the disease).
- Plantain juice and honey will help reduce inflammation in the intestines. The mentioned components are mixed in a ratio of 2 to 1 and drunk three times a day (a tablespoon at least an hour before a major meal).
- Enemas based on a 3% solution of boric acid and calendula also help well with inflammation. For one session, take a tablespoon of each component. It is best to give such an enema before bedtime.