Inflammation of the salivary glands is a dangerous condition that leads to indigestion, sudden weight loss and dehydration of the body. Dogs suffering from inflammatory processes become more lethargic and apathetic, they are prone to nervous disorders and aggressiveness. For information about what causes inflammation of the salivary glands and what symptoms indicate this, see below.
Read in this article
- What is this?
- Causes of diseases
- Symptoms of inflammation of the salivary glands
- Diagnosis and treatment
- Prevention
What is this?
Saliva production is an important part of digestion. Enzymes that are released during salivation simplify the swallowing process. A healthy dog produces about 1 liter of saliva per day, depending on weight and lifestyle.
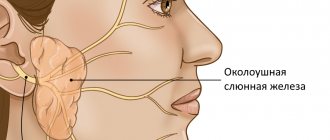
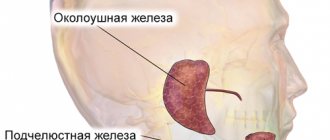
Main major salivary glands:
- Parotid. They are located in the area of the ears, and their main feature is their small size;
- Submandibular. They are located in the back of the maxillofacial apparatus between several veins;
- Sublingual. They are located under the tongue and secrete saliva, which contains a protein secretion and is rich in mucin.
The secretion secreted by the salivary glands differs in its composition and functions. Inflammation of even one pair leads to painful and unpleasant sensations, as well as problems with the digestive system.
Prevention
It is not difficult to prevent diseases of the salivary glands, excluding cases of injury. The pet should be kept comfortable. If the dog lives on the street, insulate the kennel. Provide complete and plentiful feeding, especially in winter. A well-fed dog can warm itself from the inside. To prevent food from being taken away by worms, quarterly deworming will be required. Regular vaccination in accordance with the vaccination plan will help protect against infections.
You should not feed your pet with leftovers from the owner's dinner. Food particles will stick to the gums and plaque will form, which will calcify and transform into tartar. In this case, the pet is transferred to a special food with ingredients for cleaning teeth or resort to the services of a veterinary dentist.
Causes of diseases
The most common reason that provokes the development of inflammatory processes in the salivary glands is infection. It can be of viral or bacterial origin. Remember: the sooner the cause is determined, the sooner treatment can begin.
Note! The high-risk group includes young individuals. This especially applies to several breeds: boxers, dachshunds, German shepherds and poodles.
The main causes of inflammation of the salivary glands:
- Injury
Blunt or penetrating injury to the salivary glands can lead to the development of inflammatory processes, especially if untimely or unprofessional assistance is provided.
- Penetration of foreign objects
Often, inflammation of the salivary glands is provoked by eating sharp or hard leaves, straws and other objects that can lead to blockage of the salivary ducts.
- Neoplasms
This group of causes includes tumors and cysts, but this cause is typical for adult pets. Neoplasms appear under the mucous membranes, causing inflammation.
- Past illnesses
Pathologies that can provoke inflammatory processes in the area of the salivary glands include: pharyngitis, stomatitis, severe hypothermia, etc.
Sialadenitis
Sialadenitis in dogs is usually called inflammation of the sublingual or submandibular gland. The cause of inflammation can be injuries, blockage of the salivary ducts by foreign bodies, past illnesses, etc. It manifests itself in the form of severe swelling of the affected area. If the sublingual area is damaged, the dog has difficulty moving its tongue. If the submandibular gland is damaged, the tumor can be felt in the intermaxillary space. Treatment will depend on the stage and complexity of the disease. If there is a purulent formation in the gland, the affected area must be opened and cleaned. In other cases, you can do without surgery.
Symptoms of inflammation of the salivary glands
Any inflammatory processes affecting the salivary glands are accompanied by characteristic unpleasant symptoms. They allow you to diagnose the disease in a timely manner and immediately begin treatment in a Moscow veterinary clinic to avoid complications.
Among the main symptoms:
- Excessive salivation, the pet swallowing excess saliva, and in some cases its leakage from the mouth;
- Without proper treatment, ulcers form in the area of the inflamed gland, causing saliva to acquire a pungent and unpleasant odor;
- The appearance of severe shortness of breath in the pet even when the animal is at rest;
- Difficulty in swallowing, eating food for a long time (especially dry food), severe pain;
- Increased body temperature; in later stages, the development of the disease is accompanied by mild fever.
The dog practically stops eating and drinking, causing rapid weight loss and dehydration. It is possible that the animal will develop nervous disorders and become more aggressive even towards its own owners.
Animal care
The dog needs to be provided with complete rest, surrounded with care and attention, this will speed up the healing process and lift the animal’s spirits. It is necessary to reconsider the composition of the daily menu. Swallowing food should not cause difficulty, so dry food should be completely excluded from the diet for a while. Offer your pet broth, finely chopped meat, and milk.
Very often, dog owners ignore the recommendations of specialists, and, having noticed dangerous symptoms, do not rush to see a veterinarian. In addition, it may seem that the dog has recovered on its own; this most often happens with young animals. This course of events should not be a reason for refusing to go to the doctor.
Unfortunately, you may waste time and allow the disease to progress. In most cases, cystic degeneration begins, this most often happens with the submandibular and sublingual glands. Other, no less dangerous complications may also occur.
If sialadenitis is not treated in a timely manner, necrosis or necrosis of the salivary gland tissue occurs, which can lead to irreversible consequences. This is why it is so important to seek help from a specialist in a timely manner. Remember, we are responsible for those we have tamed, so we must constantly take care of their health and safety.
Diagnosis and treatment
The first task facing a veterinarian is an accurate diagnosis of the disease. To do this, he collects anamnesis, carefully examines the animal and prescribes tests. If necessary, anesthesia is used during the examination so that the doctor can examine the pet's oral cavity.
Treatment includes medical and surgical methods. The first involves taking analgesics for pain relief, corticosteroids and sedatives. The course of conservative treatment lasts about 10-14 days and allows you to achieve lasting results.
Surgical intervention is prescribed in 15-20% of cases of inflammation, when they are provoked by neoplasms or an abnormal anatomical structure of the mouth. The operation is performed under general anesthesia, then a course of antibiotics is prescribed.
How is the treatment performed?
How to alleviate your pet's condition? Before the doctor examines him, you can try giving the dog warm water or any analgesic. Remember that you cannot self-medicate, as this can be fatal for the dog.
The doctor must examine the animal, prescribe a comprehensive examination, collect tests and perform a biopsy. If necessary, some manipulations are performed under safe anesthesia. There are two ways to solve the problem:
Drug treatment and surgery. In especially severe cases, if tumors, cysts, or stones are identified that have blocked the salivary ducts, the doctor will consider surgery appropriate. The indication for surgery is a violation of the integrity of the gland when the secretion does not come out through the duct (this may be the result of a penetrating wound).
In this case, the gland is removed, the inflammatory foci are excised with an electrocoagulator, followed by the installation of active drains and antibiotic therapy for 7-10 days. The drainage is removed on day 3-4, and the sutures are removed after 7-10 days. These dates are approximate, since much depends on the severity of the disease, the age of the animal, breed, characteristics of the body, etc.
In most cases, the doctor does not see the need for surgical intervention; antibiotic therapy gives a good result, while taking vitamins, steroids and analgesics, the treatment outcome is favorable. But the dog owner must take the task at hand seriously; the animal must take the recommended medications in a timely manner.
A pet needs care, care and attention. Walking and exposure to cold air are completely excluded. For mumps, the doctor may recommend a warming alcohol compress, physiotherapeutic procedures: UHF or heating the inflamed area with a Minin lamp. Ichthyol ointment can also be useful; it will speed up the process of abscess formation; if necessary, the doctor should open it.
Dog feeding diet
After diagnosis, it is necessary to reconsider the dog’s feeding diet. An animal with inflamed salivary glands cannot eat dry food or chew pieces of meat, so for the duration of treatment it is transferred to crushed food (broths, liquid porridges, minced meat, pasty cottage cheese, etc.).
If your pet ate dry food before illness, you can feed it canned pates from the same company. After recovery, the animal can be transferred to its usual diet.
Mumps
Mumps is the most common type of inflammation. Mumps affects the parotid glands. The cause is usually viral and bacterial infections. This type of inflammation is characterized by swelling of the glands in the parotid areas. Fortunately, mumps is a simple inflammation. In most cases, considering mumps, symptoms and treatment of this disease, we see that they are in many ways similar to inflammation of other salivary glands.
Acute and chronic forms of inflammation
The acute form of inflammation differs from the chronic course.
It can be recognized by the following symptoms:
- severe hot swelling of the tongue or head on one or both sides;
- labored breathing;
- formation of deep fistulas with purulent flow;
- fever.
ATTENTION! In a chronic course, the inflamed salivary gland increases in size, becomes dense, but not hot. With a purulent course, the formation of fistulas is possible, inside of which pus accumulates.