The appearance of an unpleasant odor from the mouth, medically called “halitosis,” is a signal of trouble in the growing organism. Kaliningrad residents can notice this symptom when communicating with a child, laughing or kissing.
In most cases, odor occurs due to poor hygiene, which disrupts the balance of microflora in the mouth and increases the number of pathogenic microorganisms. During the decomposition of bacteria, compounds of hydrogen sulfide and nitrogen are formed, which are exhaled along with the air.
In this situation, the problem can be solved with the help of hygiene and does not pose any danger to the child’s health. However, there may be other reasons for the appearance of a specific odor from the mouth. In what cases should parents be wary - we will find out further...
Risk factors affecting fresh breath
Let's start by identifying the reasons that negatively affect healthy breathing. At the same time, we note that microflora imbalance can occur even in healthy children. This happens for a number of reasons:
- failure to comply with hygiene rules, as we have already outlined;
- dry mouth due to insufficient saliva;
- insufficient water and fluid intake;
- breathing through the mouth, out of habit or due to nasal congestion;
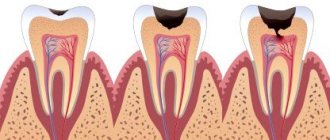
- oral infections (untreated caries, gum disease, etc.);
- consumption of foods with a pungent odor (garlic, onions) or those that provoke fermentation (legumes, grapes);
- taking medications;
- hormonal imbalance;
- smoking (relevant for teenagers).
Thus, in most cases, the cause of bad breath is problems in the oral cavity, infections and poor diet.
Causes of halitosis in children
The appearance of halitosis in children of any age can be caused by a variety of reasons, ranging from insufficient oral hygiene to the presence of a foreign body in the nose. It is important to correctly diagnose, determine the true cause of osostomy and, if possible, eliminate it.
Lack of moisture in the body
Causes increased viscosity of saliva, poor digestion, which can cause bad breath. An infant newborn receives the main liquid from mother's milk; in hot weather it is necessary to give boiled water to drink. A 4-5 year old child should drink approximately 1.5 liters of liquid per day, not limited to juices and teas. It is important to give your toddler drinking water, which helps improve digestion.
Poor oral hygiene
With the appearance of the first tooth, the baby should be accustomed to oral hygiene procedures. Children under two or three years old should have their teeth brushed by one of their parents. From the age of three, children should be taught to brush their teeth correctly on their own. Improper and insufficient cleaning of plaque contributes to the appearance of halitosis, which resolves after thorough brushing of the teeth.
Poor nutrition
If a child systematically overeats, eats fatty fried foods generously seasoned with onions and garlic, a heavy odor from the mouth will haunt him constantly. It is important to adjust the baby’s nutritional system according to his age needs, observing the drinking regime.
Stressful situation
Strong emotional shock, stress, and vivid emotions are a real test for a newborn. They cause dry mouth, which contributes to halitosis. In a stressful situation, you need to give the child a drink of water or sour juice, suck a slice of tangerine or lemon; such simple steps promote active salivation and make the child’s breathing clean and easy.
Unpleasant smell in the morning
Babies may experience bad breath after sleep. It is caused by the fact that saliva is not released at night during sleep, bacteria multiply, causing halitosis. It is enough to brush your teeth with a brush and toothpaste - and the unpleasant phenomenon disappears on its own.
Chronic nasal congestion
If your baby's mouth smells like snot, you need to pay attention to the condition of the mucous membrane of the nose. With chronic rhinitis, nasal breathing is difficult, and dry crusts form in the nasal passages. It is necessary to moisturize the surface of the mucous membrane, monitor humidity, ventilate the room well and carry out wet cleaning.
Presence of a foreign body in the nasal passages
A strong putrid odor accompanied by thick yellow discharge from the nasal passages should alert you. These symptoms are characteristic of a foreign object entering the nasal passages - beads, buttons, a piece of fruit. You should consult a doctor or emergency room as soon as possible to remove the foreign body. Otherwise, serious complications are possible, including suffocation.
Diseases of teeth and gums
Caries, stomatitis, gingivitis and other dental diseases can cause bad breath. A careful examination will reveal a carious lesion in the baby’s mouth. Even if there is no visible damage to the tooth enamel, it is necessary to consult a dentist to rule out the presence of oral diseases.
Upper respiratory tract diseases
Sore throat, tonsillitis, adenoiditis, bronchitis provoke the occurrence of halitosis in children. The pus that accumulates on the surface of the tonsils, in the lacunae, on the back wall of the throat has an unpleasant smell. The cause of the disease should be treated, rinse with an antiseptic solution, and in difficult cases, antibiotic therapy is necessary.
Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract
When a little person’s mouth smells like solvent, sour milk, vinegar, and there is an upset stomach and diarrhea, this indicates problems with the gastrointestinal tract. Consult a gastroenterologist; sometimes it is enough to adjust the baby’s diet, and the problem disappears without a trace. In more complex cases, special treatment is indicated.
Teething odor
When a baby is teething, temporary halitosis may occur, caused by inflammation of the gums and the proliferation of pathogenic bacteria. The baby's gums are red, painful and swollen. The dentist will recommend special medications that reduce the baby’s discomfort during teething.
How to distinguish a normal smell from a problematic one?
If an unpleasant symptom occurs exclusively in the morning and goes away after brushing your teeth, then we are talking about a physiological norm. If bad breath is observed after hygiene procedures and becomes protracted, then this deviation requires the closest attention from parents.
In addition, it is worth noting that the above risk factors can be eliminated. However, if hygiene is maintained, respiratory infections and specific foods are excluded, and the unpleasant symptom persists for a long time, this is a good reason to consult a doctor.
In this case, altered breathing can signal very specific diseases. Let's look at which ones further...
Treatment of unpleasant odor
In most cases, osostomy does not require special treatment. It is enough to systematically thoroughly brush your teeth and gums, review your diet, limit your consumption of sweets, give him enough liquid per day, and the unpleasant symptom will disappear on its own. If after a few days it does not disappear, you need to consult a specialist, undergo an examination and determine the cause of halitosis.
Parents should be especially concerned about the smell of acetone emanating from the baby - in this case, it is necessary to urgently call an ambulance or take the baby to the hospital to prevent the occurrence of acetone syndrome.
List of diseases that can be detected
Despite the fact that halitosis is not a disease, it is an important diagnostic symptom by which a specialist can assume the presence of a certain disease in the body. Suspected health problems may include:
- diseases of the nose and nasopharynx: sinusitis, pharyngitis, tonsillitis, adenoiditis;
- food allergies or respiratory rhinitis causing nasal congestion;
- dental diseases of teeth and gums;
- Gastrointestinal diseases: gastritis, increased stomach acidity, intestinal dysbiosis, etc.;
- endocrine disorders: diabetes, thyrotoxicosis, etc.
As can be seen from this impressive list of diseases, solving breathing problems can fall within the competence of a variety of highly specialized specialists: otolaryngologist, dentist, gastroenterologist, endocrinologist.
Psycho-emotional state disorder
Sometimes halitosis can occur in children after severe excitement.
In some cases, the cause of halitosis may be hidden in the environment that surrounds the child. The fragile psyche reacts too painfully and sensitively to stressful situations, which can be almost invisible to adults, but for a child they are a serious test.
When the nervous system is overexcited, dry mouth, acetonemic crises with all their consequences mentioned above, and digestive disorders are possible.
You need to talk to your child to try to find out the root cause of worries and fears. Maybe he has problems in the children's team (conflicts in the yard, at school or kindergarten). Older children also have more serious problems. Sometimes this syndrome can occur due to failures in studies or during exams.
Children often have problems with their home environment - they experience constant fear of possible punishment for various little things - unassembled toys, something dropped on the floor, etc. He may be afraid to once again disturb adults with a question that worries him, as he may receive an irritated answer.
Such a nervous state often results in various disturbances in the functioning of the child’s body, which can result in bad breath.
If your baby is very worried, give him a slightly acidified drink and calm him down by any available means. Once the environment is normalized and stress is relieved, halitosis should disappear.
What can a smell “tell”?
As we mentioned earlier, unhealthy breath can quite eloquently indicate a certain nature of the disease. For example:
- a sour smell indicates problems with the stomach: high acidity, reflux or dysbacteriosis;
- the smell of a rotten egg - about a stomach ulcer or a violation of bile outflow;
- putrefactive – about diseases of the esophagus and low acidity of the stomach;
- acetone – about problems with blood sugar levels (diabetes) or dehydration;
- ammonia - about kidney disease, liver dysfunction and diffuse toxic goiter;
- boiled cabbage - problems with metabolism, liver and kidney diseases.
As a rule, already at the stage of collecting anamnesis and during the clinical examination, the doctor can make an assumption about the true causes of the problem.
Specific pungent odor
Parents should be alarmed by the specific smell from the baby’s mouth, which does not go away after hygiene procedures. Limit your baby's consumption of sweets and heavy protein foods, and ensure he drinks plenty of fluids. Usually, after these events, children's halitosis goes away.
Below we will tell you which smells should cause an instant reaction from parents.
«
Acetone (acetic, solvent)
The smell of acetone or a chemical solvent emanating from a baby, especially against a background of elevated temperature, should cause maximum concern for parents. It appears in acetonemic syndrome, a dangerous condition that is quite common in children of all ages. If you suspect its occurrence, you must immediately call an ambulance, before the doctors arrive, and give the baby boiled water often and in small quantities (a teaspoon).
A slight acetone smell can be a sign of kidney disease, malfunction of the pancreas, helminthiasis (worms), dysbacteriosis, and diabetes. In any case, it is advisable to consult a doctor immediately.
Putrefactive
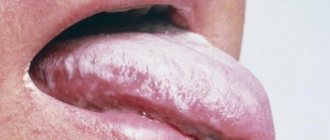
Appears with insufficient oral hygiene, the occurrence of ENT diseases (sore throat, pharyngitis, tonsillitis, in parallel, the child has a white tongue, a stuffy nose, a cough), stomatitis, caries, low acidity of the stomach (the baby often has a stomach ache), the presence of diseases of the esophagus . You should consult a dentist, ENT specialist, gastroenterologist, systematically brush your teeth with a children's toothbrush and toothpaste, and ensure drinking regime.
Purulent
A pungent purulent odor accompanies chronic inflammation and proliferation of lymphoid tissue in the baby’s nasopharynx. The tonsils become covered with purulent plaque, plugs form, emitting an unpleasant odor. The child has a high fever, a sore throat, a runny nose, and a coated tongue. Contact your pediatrician; antibiotic treatment may be necessary. After recovery, your breath will become fresh again.
Another reason for bad breath against the background of copious discharge of dense yellowish snot can be the presence of some object in the baby’s nostril. Contact your ENT specialist to examine your baby's nose.
Sourish
If your baby has a sour breath, this may indicate increased acidity and an inflammatory process in the stomach. It is necessary to contact a gastroenterologist and check the baby for the presence of gastritis. The second cause of bad breath is reflux, or the entry of gastric juice into the baby’s esophagus. In this case, the patient suffers from heartburn and pain in the hypochondrium.
Sweetish
Does the baby have a cloying sweet aroma from the mouth? There is reason to suspect liver problems. It is important to promptly visit a gastroenterologist - the symptom occurs with hepatitis or cirrhosis of the liver.
Chemical
If your toddler smells of chemicals, it is advisable to check the condition of the digestive organs, especially the gallbladder; this symptom is characteristic of biliary dyskinesia.
Chlorine
The specific smell of chlorine mixed with metallic notes appears with increased bleeding gums and periodontal disease. Contact your dentist and check the condition of your baby's teeth and gums.
Yoda
The appearance of the smell of iodine is a reason to urgently contact an endocrinologist, as it may indicate an excess of iodine that accumulates in the baby’s body. This condition can occur after a long stay at sea, after taking iodine preparations, or in the presence of thyroid pathology. In infants, an iodine tint appears when infected with Klebsiella, a bacterium that enters the child's body with unwashed fruit and affects the stomach and intestines.
Bile
If a newborn's breath smells like bile, this may indicate poor bile flow. Consult a doctor, do an ultrasound of the abdominal organs, and take general tests.
Gland
The presence of a metallic taste and iron smell from the baby's mouth may indicate the occurrence of iron deficiency anemia. You should take a blood test to determine your hemoglobin level, and if the diagnosis is confirmed, take vitamin complexes with a high iron content.
The second reason is the presence of gastritis, high acidity, dysbiosis, and diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
Urine
An ammonia smell indicates kidney pathologies, as well as diabetes. The reason for its appearance is a decrease in insulin levels and impaired carbohydrate metabolism.
Kala
It is extremely rare. It is mainly associated with poor heredity, appears with metabolic disorders, and sometimes accompanies acute intestinal dysbiosis. Diagnosed by an endocrinologist or gastroenterologist.
Rotten eggs
Belching, the smell of rotten eggs, and a white coating on the tongue are symptoms of gastritis, ulcers, liver disease, and impaired bile flow. If you find halitosis in a newborn or older child, you should contact a gastroenterologist.
Yeast
If a baby smells of yeast, this is a reason to suspect candidiasis. Often a sick stomach is also expressed by a yeasty aroma. An experienced general practitioner will be able to recognize the true cause, and he will also refer you for examination if gastrointestinal diseases are suspected.
Diagnosis and treatment
To diagnose ENT diseases, an otolaryngologist uses hardware and laboratory tests. These include:
- rhinoscopy – to examine the nasal cavity;
- radiography and computed tomography - to assess the condition of the sinuses;
- examination of nasal secretions to determine the causative agent of inflammation;
- Blood and urine tests will complement the clinical picture.
In the process of collecting anamnesis, the doctor is interested in the following questions:
- How long has the child been complaining of discomfort?
- What time of day does the smell appear and how long does it last?
- What foods did the child eat?
- how much water does he drink?
- Does the smell go away after brushing your teeth?
- What chronic diseases does he have?
- what medications does he take?
Treatment does not imply the elimination of the symptom itself, as such, but the therapy of the specific disease that provoked its appearance. If, as a result of examination and diagnostic measures, pathologies of the nose or nasopharynx were identified, the doctor will prescribe adequate drug treatment, which may include:
- antibacterial therapy (taking antibiotics);
- vasoconstrictors and antihistamines;
- special medical procedures;
- physiotherapy: inhalations, UV and UHF therapy;
If necessary, the otolaryngologist can refer a small patient to specialized specialists if the solution to this problem falls within their competence (dentist, gastroenterologist, etc.).
Bad breath can cause respiratory diseases
If there is no visible pathology in the oral cavity, visiting a pediatric dentist can also add clarity to the fact that the cause of the unpleasant odor may be respiratory diseases. And if there are no other symptoms, you should definitely go to the pediatrician.
Tonsillitis
Acute or chronic forms of tonsillitis (inflammation of the tonsils) contribute to the accumulation of pathogenic microorganisms and their reproduction, the formation of mucus and suppuration. Very often this condition is accompanied by bad breath.
The structure of the tonsils themselves is cavernous; small decomposing particles of food sometimes accumulate in their cavities.
Regular gargling should be included in the list of mandatory hygiene procedures.
Bronchitis
With bronchitis (inflammation of the respiratory tract) of various etiologies or pneumonia, often bad breath can be one of the manifestations of these diseases.
A lot of sputum accumulates in the bronchioles and bronchi, which comes out when coughing, and it is accompanied by an unpleasant odor.
Adenoids and rhinitis
One of the causes of bad breath is accumulated phlegm.
With rhinitis (runny nose) of an allergic or infectious nature, purulent masses always form abundantly, and discharge flows down the back wall of the nasopharynx. This mucus decomposes under the influence of bacteria, resulting in the release of volatile sulfur compounds with a very unpleasant odor.
When the adenoids are inflamed or overgrown, when they block the posterior nasal passages (most of their lumen), as well as a runny nose, the baby breathes through the mouth, which causes the oral cavity to dry out. This contributes to the massive proliferation of colonies of microorganisms and various unpleasant symptoms.
Why do adenoids enlarge in a child?
For small children, be sure to make sure that he does not put anything in his nostril. The baby could even forget about it and the foreign body does not bother him in any way, but this will result in irritation of the mucous membrane, secretion of mucus with an unpleasant odor and difficulty in nasal breathing.
Preventive recommendations
In conclusion of our review, I would like to draw the attention of parents to adjusting their children's diet. Our nutritional recommendations are as follows:
- Let us remember that “bad” bacteria love a sweet environment, so it makes sense to limit the consumption of industrially produced sweets and sugar.
- As a dessert, you can offer your child natural sweets made from dried fruits and nuts, as well as fresh fruit.
- Replace carbonated drinks with pure water or herbal tea made from chamomile and mint.
- To create beneficial microflora in the intestines, a child should consume more “live” fermented milk products: cottage cheese, kefir, yoghurts.
Parents need to understand that this delicate problem requires a qualified approach, since over time it can lead not only to problems at the physiological level, but also cause social isolation of the child.
Kaliningrad residents can make an appointment with a pediatric otolaryngologist by filling out an online form on our website or by calling: +7 (4012) 357-773 or +7 (4012) 973-100.
Preventive measures
To promptly prevent the appearance of halitosis in your baby, you must follow a few simple rules:
- Brush your baby's teeth thoroughly twice a day, starting when the first tooth emerges. It is necessary to teach your child how to use a brush and toothpaste correctly to remove plaque from the surface of the teeth.
- Adhere to the age-specific nutrition system, introduce vegetables, fruits, and foods rich in phosphorus and calcium into your child’s diet.
- Eliminate sugar, chocolate, and other sweets from your diet and replace them with honey.
- Give your child plenty of fluids, especially drinking water.
- Visit your dentist regularly to prevent the development of caries.
»
What to do if a small child has terrible breath during an acute respiratory viral infection
When seasonal viral diseases (including sore throat) occur, severe inflammation occurs in the baby’s nasopharynx. It can appear on the tonsils, throat, nose (with sinusitis), lungs, depending on the specific disease. As a result, the inflamed areas become covered with plaque and pus, which creates stale, unpleasant breath. But don’t worry, halitosis goes away as soon as the children recover. Doctors always prescribe regular rinsing with antiseptic solutions (furacilin, rotokan and others), they quickly get rid of stench.
Intestinal infections
In a newborn, diarrhea is a sign of dysbiosis
Intestinal infections are caused by an imbalance of opportunistic flora and damage by pathogenic bacteria. Diseases of this kind are contact diseases. Therefore, parents need to comply with all hygiene standards for themselves and their baby.
Signs of intestinal infection:
- loose, frequent stools;
- the presence of a large amount of mucus in the stool, pieces of undigested food, and in severe cases - blood;
- abdominal pain - the baby screams and pulls his legs towards his tummy;
- anxiety;
- there may be a refusal to eat, the baby does not want to breastfeed;
- increased body temperature;
- general weakness, lack of activity;
- vomit;
- drowsiness.
If such symptoms appear, the child should be immediately shown to a pediatrician. You may need to be hospitalized in the infectious diseases department of the hospital and take hydration measures.
What measures to take
Bad breath in children should not be ignored. Diseases inside the tissues of the oral cavity and internal organs can occur without significant symptoms, and such a seemingly insignificant symptom allows you to consult a doctor in a timely manner and begin the necessary treatment.
If you experience bad breath, it is recommended to contact a pediatric dental clinic. The specialist will examine the oral cavity, prescribe a diagnosis and, if the development of oral diseases is confirmed, carry out treatment. Often, to combat bad breath from a child, it is enough to start brushing your teeth properly and change your diet.
If, based on the diagnostic results, the specialist suspects the development of pathologies of internal organs or the respiratory system, the doctor will give the necessary recommendations and refer the patient to a more specialized specialist.
Changes in stool in some diseases in children
Liquid, foul-smelling stool , up to 10 times a day, in the form of pea puree, is observed with typhoid fever, sometimes containing a small amount of mucus. Stool analysis in children - medical.
With dysentery, the stool is light, mixed with mucus, streaks of blood, pus, odorless, like “rectal spitting” against the background of tenesmus. Sometimes there are no fecal masses at all.
Salmonellosis is characterized by an acute onset of the disease with high fever, vomiting, and abdominal pain. The stool is copious, watery, foul-smelling, with an admixture of greenery, like “swamp mud.” There is a small amount of mucus and, as a rule, there is no blood.
With cholera, the disease begins with moderate pain around the navel and frequent loose stools against a background of normal or low-grade fever. Dehydration develops quickly, accompanied in severe cases by vomiting and fever. The stool is copious, watery, odorless, like “rice water” (whitish liquid with flakes of mucus), and never contains blood.
In diseases caused by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli , young children experience copious, watery, colorless bowel movements with mucus flakes.
With escherichiosis caused by enteroinvasive E. coli, there is a high temperature with scanty bowel movements mixed with mucus, blood, and abdominal pain.
Diseases caused by enteropathogenic Escherichia coli are observed in children under the age of 1.5-2 years and are characterized by a gradual onset with moderate watery bowel movements, low-grade fever and an undulating course.
With adenoviral and enteroviral diarrhea , other clinical signs of these diseases are observed, the stool is fecal in nature, 3-5 times a day, and dehydration does not develop.
With rotavirus gastroenteritis (for 30-40% of all patients), an acute onset of the disease is observed with fever, vomiting (gastroenteritis variant) and (or) copious watery stools (enterocolitic variant), sometimes with an admixture of mucus, against a background of scanty respiratory symptoms (moderate hyperemia , granularity of the soft palate and arches, nasal congestion) with rumbling along the large intestine. The disease has a strict seasonality (October-March). Young children get sick.
Staphylococcal enterocolitis is more common in children under one year of age, in the presence of a characteristic epidemic history (purulent foci in the child, unfavorable premorbid background, mastitis in the mother, long-term treatment with antibiotics, etc.). There is a gradual development of intestinal dysfunction against the background of low-grade fever and moderate intoxication. The stool is liquid, fecal, mixed with mucus and sometimes streaked with blood.
For staphylococcal food toxicoinfection, a typical indication is the consumption of infected food (cakes, creams, pastries, salads with mayonnaise); The disease most often has a group nature. Characterized by rapid development of the disease with persistent, debilitating vomiting against a background of high fever and rapid normalization of the condition within 2-3 days. The stool is liquid, watery, sometimes fecal, without pathological impurities.
Campylobacteriosis is characterized by an acute onset of the disease with pain in the abdominal area, mainly around the navel, previous intestinal dysfunction, enlarged liver and involvement of the pancreas in the process, copious, “foamy”, foul-smelling stools mixed with blood.
Yersiniosis is characterized by the presence of multiple organ symptoms (skin rash, joint pain, enlarged liver and spleen) . In the intestinal form, pain is observed in the abdominal area, mainly in the right iliac region. Stool 3-6 times a day, liquid, fetid, fecal, mixed with mucus.
With amoebiasis, stools are frequent, in the form of “raspberry jelly” (mucus gives the stool a glassy, shiny surface). With giardiasis, stool 3-4 times a day, yellow-green in color, soft consistency. With massive infestation, stools become more frequent up to 20 times a day and become mucous and bloody.
With mycotic enterocolonopathies (candidiasis), there is an increase in bowel movements, abundant, liquid or pasty feces, usually without a large admixture of mucus (blood, as a rule, is absent).
With viral hepatitis, the stool is acholic - gray-clay color, without pathological impurities. Vaccination of a child against hepatitis at the Markushka children's clinic.