Candida mushrooms: from conditionally pathogenic to pathogenic
These oval or round unicellular microorganisms are present in the normal microflora of most healthy people. They are well protected from external factors and feel quite comfortable at human body temperature.
The very presence of Candida fungi in the body does not equate to a disease: the development of the pathological process begins if, under the influence of any factors, the fungi begin to actively multiply.
In most cases, this occurs due to decreased immunity.
The onset of the disease does not indicate a change in the properties of the fungus, but rather a change in the state of the body, in particular, a sharp decrease in its protective mechanisms.
to contents ^
Causes of candidiasis
Intensive reproduction of the fungus can be provoked by various factors:
- Prolonged hypothermia or, conversely, being in a climate that is too hot and humid.
- A disease, especially if antibacterial drugs are used in its treatment.
- Severe stress.
- Changes in hormonal levels (with endocrine disorders, use of hormonal drugs, during pregnancy).
- Choosing underwear that is the wrong size or made from synthetic materials.
to contents ^
What is systemic candidiasis
Systemic or visceral candidiasis is a severe form of thrush, caused by yeast fungi of the genus Candida albicans. The infection affects internal organs and systems, causes their inflammation, and leads to severe, sometimes irreversible complications.
The main cause of the pathology is congenital or acquired immunodeficiency. In both the first and second cases, the balance of microflora in the patient’s body is disturbed, in which beneficial microorganisms that control the activity and vital activity of pathogenic fungi and bacteria die, and their place is taken by a pathogenic infection. Gradually, the number of candida increases in number, they penetrate into the circulatory and lymphatic systems, from where, together with blood and lymph, they are spread throughout the body, settling and continuing to actively multiply in the tissues of target organs.
Persons who have been diagnosed with the following pathologies are at risk of contracting systemic candidiasis:
- diabetes;
- pulmonary tuberculosis;
- oncological tumors;
- HIV infection;
- extensive burn injuries;
- cirrhosis of the liver.
Also, fungal disease often develops in people who uncontrollably take antibiotics, cytostatics, immunosuppressants, and hormonal drugs. Premature newborns and children with critically low body weight are at risk. Artificial ventilation, chemotherapy, surgery on the abdominal organs, the need for constant use of intravascular and urinary catheters are manipulations that can also lead to serious complications, including systemic candidiasis.
Considering the location of the fungal infection, the following types of visceral thrush are distinguished:
- Anorectal. Manifested by the formation of ulcers and erosions in the anus.
- Bronchopulmonary. Accompanied by respiratory failure, often leading to the progression of complicated candidal pneumonia.
- Gastrointestinal. The infection affects the mucous membranes of the esophagus, stomach, and various parts of the intestines.
- Lower respiratory tract. Accompanied by symptoms similar to those of bronchitis.
- Urinary. Causes damage to the kidneys and bladder.
Types and symptoms of candidiasis
Manifestations of the disease are very diverse and depend on the specific location of development of the inflammatory process.
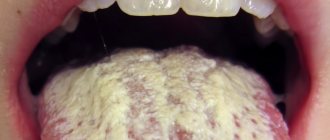
Oral candidiasis
Oral candidiasis is most common in childhood. It manifests itself as redness of the mucous membranes of the throat, gums and tongue. Swelling develops. As the disease develops, areas of white plaque with a cheesy consistency form on the oral mucosa. If treatment measures are not taken, their number increases, and erosions occur under the plaque.
When oral candidiasis becomes chronic, damage to the mucous membranes of the nose, pharynx and esophagus is possible.
to contents ^
Candidiasis of the skin
Fungal pathology can spread in the folds of the skin: in the armpits, under the mammary glands. The folds between the fingers and toes are affected. In some cases, skin lesions outside the folds are noted.
The disease manifests itself in the form of small blisters. Individual areas merge to form affected areas. Between the toes of the limbs there is peeling of the skin, cracks, and itching. Externally, the palms look like they are burned.
to contents ^
Candidiasis of the genital organs
This type of disease affects the external organs of the reproductive system: in women – the vaginal mucosa, in the stronger sex – the glans penis and foreskin. A clear sign of the disease is copious white curdled discharge accompanied by itching. There is discomfort during intimate contact and when urinating.
Candidiasis localized in the intestines
Most often it occurs as a result of previous intestinal infections and the use of antibacterial drugs. In children, this condition can be caused by poor nutrition.
Intestinal candidiasis is manifested by pain in the abdomen, flatulence, diarrhea, and the presence of white cheesy flakes in the stool.
Candidiasis in women
To a greater extent, genital candidiasis occurs among women: about 75% of them have experienced its symptoms at one point. In half of the women who became ill, the disease relapsed.
Candidiasis in women makes itself felt with the following symptoms:
- noticeable milky-white, curd-like vaginal discharge with an unpleasant odor;
- a feeling of itching, irritation, burning, most noticeable after urination and water procedures, as well as before menstruation;
- pain during and after intimate contact.
If a woman ignores such manifestations, the disease can spread to the area of the inguinal folds, affecting the vaginal mucosa and, in some cases, the vaginal area of the cervix.
to contents ^
Candidiasis and pregnancy
About 90% of pregnant women suffer from the disease. Such a high prevalence of thrush during pregnancy is due to the fact that in the female body during this period processes occur that give impetus to the active reproduction of the Candida fungus: hormonal levels change, the body’s defense mechanisms decrease, and a lack of vitamins and minerals occurs.
Despite the fact that the disease is diagnosed in the vast majority of pregnant women, a frivolous attitude towards it is unacceptable.
- There is a risk of transmission of Candida fungus to the fetus. This can happen not only during the baby’s passage through the birth canal, but also in utero.
- Infection with the fungus creates conditions for the development of intrauterine oxygen deficiency in the fetus.
- The risk of premature birth, as well as the birth of a baby with low body weight, increases.
- There is a threat of polyhydramnios formation and premature rupture of amniotic fluid.
During pregnancy, the symptoms of candidiasis do not always appear clearly. It is important to carefully monitor the condition of the body, at the slightest suspicion of infection, consult a doctor and not self-medicate.
to contents ^
Vaginal candidiasis: 7 pressing issues - MEDSI
Table of contents
- What causes candidiasis?
- How does candidiasis develop?
- How does thrush manifest?
- How does vaginal candidiasis occur?
- Why is candidiasis dangerous for pregnant women?
- How is the diagnosis made?
- How to treat candidiasis?
- Advantages of carrying out the procedure at MEDSI
Candidiasis (“thrush”) is a fungal infection of the mucous epithelium (from the Latin name of yeast-like fungi: Candida - “white”).
The causative fungus has several varieties; in our latitudes, Candida albicans predominates, which belongs to the opportunistic microflora - with normal immune function, its carriage is not a disease and does not cause discomfort. Symptoms appear when the immune status is impaired or under the influence of external factors - the fungus affects the mucous membranes (oral cavity, intestines, etc.).
In women, vaginal candidiasis is most common.
What causes candidiasis?
- HIV, immunodeficiencies
- Pregnancy
- Powerful stress
- Long-term use of estrogen
- Glucocorticoids
- Injury to the mucous membrane: conization of the cervix, abortion, childbirth, erosion
- Antibacterial therapy: by destroying pathogenic bacteria, antibiotics also remove normal flora microbes - the natural protection of mucous membranes from the introduction of fungi
- Taking cytostatics (chemo drugs that suppress tumor growth)
- Immunosuppressants (suppress the immune system)
- Radiotherapy (irradiation)
- Penetration of atypical fungi from outside – Candida tropicalis or others.
How does candidiasis develop?
Natural protection is provided not only by humoral factors (blood proteins), but also by its own normal flora: the predominance of lactobacilli in the vagina suppresses the growth of fungi. Disruption of the microflora due to injury, medication, as well as the penetration of fungi from the outside, with poor hygiene, allows candida to multiply intensively.
When fungi settle on the walls of the genital tract, they injure the epithelium and adhere tightly to the mucous membrane. Their waste products acidify the vaginal environment and irritate the sensory nerves. When these products enter the bloodstream, an immune reaction is triggered, manifested by inflammation. When the immune response is excessive, allergic reactions occur, which worsen the symptoms of the disease.
The result of infection of the genital tract by Candida fungi is a white discharge resembling curd flakes, consisting of desquamated epithelium, mucus and a mass of fungi, as well as a complex of easily recognizable symptoms.
How does thrush manifest?
The most indicative for diagnosing the disease are cheesy discharge, which can differ in volume, density, consistency, have a yellowish tint and even take the form of quite large lumps.
Almost always, the discharge is accompanied by itching, often unbearable, burning, a feeling of heaviness, distension in the vagina, swelling and redness of the visible mucous membranes. Painful urination and pain during sexual intercourse may occur.
Symptoms may intensify after thermal procedures, in hot weather, or with prolonged sitting.
With the chronic course of a fungal infection, frequent relapses, the clinical picture may be blurred, some symptoms are absent - a fungal infection is detected by chance during a smear analysis.
How does vaginal candidiasis occur?
There are 4 forms of the disease:
- Acute candidiasis - characterized by copious discharge, itching, pain, burning of the genitals. Vivid clinical manifestations persist for up to a week, then gradually subside. There are no symptoms of general intoxication, the temperature is normal
- Chronic candidiasis - the disease returns in the presence of predisposing factors, but is not so violent, often asymptomatic. It may be complicated by the addition of a secondary infection, since the mucous membrane is constantly injured by the fungus. It occurs more severely in diabetes mellitus and leukemia
- Recurrent candidiasis - alternating exacerbations (more than 4 per year) and remissions
- Carriage – fungi constantly live on the mucous membrane of the genital tract, but do not reproduce, as they are suppressed by normal flora and immune defense factors
Why is candidiasis dangerous for pregnant women?
In pregnant women, vaginal candidiasis requires treatment, despite the fact that it does not directly affect the pregnancy and the course of labor:
- The damaging effect of the fungus on the mucous membrane and severe inflammation can provoke the development of a secondary infection in conditions of reduced immunity with minor errors in hygiene, which can lead to intrauterine infection of the fetus
- When a child passes through the birth canal, contamination may occur, which will manifest itself in the newborn as stomatitis, otitis, sinusitis or gastrointestinal lesions
Treatment of vaginal candidiasis in pregnant women involves a careful choice of therapy, a balanced balance of benefits and harms.
How is the diagnosis made?
A gynecologist diagnoses and treats candidiasis. He conducts a visual examination on the chair and takes biological material (urogenital smear).
Material research can be carried out using two methods:
- Smear microscopy is the examination of smears on glass slides under a microscope. Allows you to determine the amount of fungus, assess the level of inflammation by the number of leukocytes
- Bakposev (microflora analysis) - placing the material on a nutrient medium and growing it in order to identify the pathogen. Also allows you to determine the sensitivity of the fungus to drugs
How to treat candidiasis?
Treatment for vaginal candidiasis includes:
- Taking antifungal drugs
- Antibiotics
- Antimicrobials
- Glucocorticosteroids (in complex therapy)
- Combined drugs (antifungal antibiotics of three different groups, antibiotics + antimicrobial + antifungal agent + glucocorticosteroid)
- Douching or bathing with soda solution
Most modern medications are produced not only in tablet form, but also in the form of vaginal tablets, capsules, suppositories, and creams. They are used locally and do not have a systemic effect, so they can be prescribed to pregnant and lactating women.
Advantages of carrying out the procedure at MEDSI
- Practicing obstetricians and gynecologists at MEDSI follow current global trends in treatment
- Possibility of express diagnostics
- Individual approach to each patient, selection of a treatment regimen taking into account the characteristics of the body
- Monitoring over time, correction of the treatment regimen, discount on re-appointment
To make an appointment, call 8 (495) 7-800-500 (open 24 hours a day).
Candidiasis in men
Representatives of the stronger sex are much less susceptible to candidiasis compared to women. This is due to the anatomical characteristics of the male body.
When affecting the male body, thrush manifests itself as follows:
- There is swelling and redness in the area of the glans penis and foreskin.
- There is a burning sensation and pain when urinating.
- During an erection, intimate contact and after it, pain occurs.
- A white cheesy coating with a sour odor appears.
The appearance of symptoms of candidiasis in a man signals a serious malfunction in the body’s defense system.
Lack of proper treatment in men leads to the development of candidal balanitis (damage to the glans penis) and balanoposthitis (inflammation of the foreskin).
For information about the characteristics of the disease and common myths associated with thrush, watch this video:
to contents ^
How the disease is transmitted
Yeast fungi of the genus Candida albicans belong to the opportunistic microflora that lives on the skin and mucous membranes of almost every person who does not have health problems. The activity of the infection is suppressed by the body's protective immune system.
The first acquaintance with Candida fungi occurs during the first year of a child’s life - through contact with an adult, using various household items, eating a certain type of food on the surface of which there are fungi.
A common cause of fungal infection in adults is promiscuity and unprotected sex. Persons who visit swimming pools, baths, saunas and do not observe the rules of personal hygiene are at greatest risk of becoming infected with a pathogenic microorganism.
Treatment of candidiasis
The process of getting rid of unpleasant manifestations begins with diagnosis. After examining the patient, a bacterial culture is prescribed - a method that allows one to determine the causative agent of the disease.
During the study, a scraping is taken from the mucous membrane at the site of the lesion. The material is placed in a special environment for several days, where the fungus grows, forming colonies. Based on the data obtained, a final diagnosis is made and a treatment regimen is prescribed.
to contents ^
Drug therapy for candidiasis
For any type of localization of the lesion, complex treatment is required:
Normalization of the immune system: restoration of intestinal microflora, use of immunomodulators.
Elimination of local manifestations of the disease: ointments, suppositories, creams, vaginal tablets (Clotrimazole, Pimafucin, Miconazole).
Systemic treatment: tablets or capsules taken orally (Diflucan).
It is impossible to destroy Candida fungus using antibacterial drugs. Sometimes antibiotics only accelerate the spread of fungal pathology, further disrupting the state of the intestinal microflora.
The process of getting rid of thrush during pregnancy differs from the treatment of this disease in patients of other categories. First of all, it is necessary to exclude the possibility of adverse effects of drugs on the fetus. Therefore, topical agents with low toxicity and absorption, with a minimum number of side effects, are prescribed.
to contents ^
Candidiasis and diet
Human immunity largely depends on the state of the intestinal microflora. With an existing fungal disease, it is almost always impaired. Therefore, to speed up recovery, it is important to follow a diet, which is an element of general treatment.
It is necessary to exclude from the menu foods that contain large quantities of simple carbohydrates: confectionery, sweets, honey, sweet fruits and packaged juices, alcohol.
- The consumption of pasta and starchy vegetables: potatoes, carrots, pumpkin should be limited.
- It is recommended to give preference to lean varieties of meat and fish, stewed, boiled and baked vegetables.
- To normalize the intestinal microflora, you need to include fermented milk products in your menu.
During the treatment of a fungal infection, it is recommended to drink less coffee and tea: the substances contained in them may reduce the effectiveness of antifungal drugs.
to contents ^
Traditional methods in the treatment of candidiasis
There are many popular ways to get rid of unpleasant symptoms, but it should be remembered that they are auxiliary and often minimize pathological symptoms without eliminating the cause of the disease.
- Pour 2 tablespoons of dry calendula (flowers) into 200 ml of boiling water, leave for 40 minutes to infuse. It is recommended to wash the genitals with the strained product. In addition to calendula, you can use celandine, chamomile, oak bark, and yarrow for these purposes.
- Baking soda is a common way to treat candidiasis at home. This substance has a detrimental effect on the fungal habitat. Dissolve 2 tablespoons of baking soda in a liter of boiled water. You can wash the genital area daily with this solution (it is better to do the procedure in the evening). It is important not to leave excess moisture on the genitals after it.
In women, soda procedures should be carried out with caution: this can provoke disturbances in the vaginal microflora.
Therapy with traditional methods and herbal medicine for candidiasis should be carried out in parallel with drug treatment recommended by a doctor.
to contents ^
Diagnosis and treatment of systemic thrush
Very often, systemic candidiasis is diagnosed in advanced stages, when the infection has penetrated deeply into the body and affected several organs. In this case, drug therapy will not help completely get rid of the fungus. At any period of life, the patient may again encounter a fungal disease and its consequences.
If you have suspicious symptoms, you should make an appointment with your doctor. During the initial appointment, the specialist will ask about disturbing symptoms, collect all important data, and conduct a visual examination. To clarify the diagnosis, a referral is given for a comprehensive diagnostic examination.
Laboratory diagnostic procedures play a leading role in determining and identifying the causative agent of systemic candidiasis. They allow you to identify the pathogen in the blood and other biological fluids of the body:
- sputum;
- effusion formed in the abdominal cavity;
- feces;
- exudate released from wounds on the body.
The laboratory assistant takes the necessary samples, after which in the laboratory, using special equipment, he identifies the type, quantity and extent of distribution of the microorganism.
To confirm the diagnosis, the following diagnostic measures are prescribed:
- Repeated blood donation for seeding and cultivation in a nutrient substrate.
- Biopsy of affected organs.
Additionally, instrumental research methods are prescribed that will help assess the general condition of the body and the functioning of internal organs:
- radiography;
- endoscopy;
- gastroscopy;
- magnetic resonance imaging (MRI);
- computed tomography (CT);
- ultrasonography.
Treatment of systemic candidiasis is selected individually and is aimed at solving the following problems:
- Elimination of the root causes that provoked a malfunction of the immune system and activation of the growth of a fungal infection.
- Destruction of the causative agent of visceral candidiasis.
- Stimulation of the body's immune defense, involving the use of immunomodulators, vitamin and mineral complexes.
- Normalization of the functioning of affected internal organs.
- Restoration of beneficial microflora of the body.
To destroy a fungal infection, antimycotic drugs are prescribed, the dosage and duration of use of which is determined by the doctor individually, taking into account the degree of neglect, the severity of the disease and the general health of the patient.
The following systemic antifungal drugs will help quickly and effectively destroy a fungal infection:
- "Amphocetrin B";
- "Flucytosine";
- "Fluconazole";
- "Miconazole";
- "Itraconazole"
In case of complicated course of systemic candidiasis, in addition to antifungal therapy, solutions of potassium and sodium iodide, antigastamines, and a polyvalent vaccine based on Candida cultures are prescribed.
Throughout the entire period of treatment, the patient must remain in the hospital under the constant supervision of medical staff and the attending physician. This allows you to monitor the dynamics of therapy in detail and, if necessary, adjust the therapy regimen. After the disease is defeated, the patient must follow the rules of prevention throughout his life to prevent relapses.