While expecting a child, the body of the expectant mother undergoes various changes associated with the restructuring of all organs and systems. Which must now ensure the vital functions of both the female body and the development of the unborn child. For this reason, a woman’s metabolism may change, a lack of microelements and vitamins in the body may be detected, etc. Very often this is reflected in the condition of the teeth, since a growing fetus requires a lot of calcium for its formation. Therefore, doctors strongly recommend taking care of your teeth during pregnancy to prevent their damage and loss in the future.
The more attention a wisdom tooth requires during pregnancy. Since “eights”, due to their characteristics, can cause a lot of inconvenience to any person, and when carrying a child this can become especially problematic.
Content:
- Pregnancy and wisdom teeth - how to recognize the process of active growth
- Pericoronitis - complication 2.1. Classification of pathology
- What can an expectant mother do on her own?
- Removal
- What you should never do
- Competent treatment
- Rehabilitation after surgery
It happens that wisdom teeth begin to actively grow during pregnancy .
This is due to the fact that “eights” are cut later than other units. The process of their active growth can be triggered by hormonal and metabolic changes that occur in a woman’s body during pregnancy. The process of the appearance of eighth units in itself cannot be called negative - it is a variant of the norm. But for many expectant mothers it occurs with complications. It was also not uncommon for units to stand at the wrong angle and put extreme pressure on their “neighbors.” And this is an indication for emergency removal.
What to do after tooth extraction during pregnancy
Even if the procedure was successful, without pain, complications may develop during the recovery period. It is very important that after extirpation a blood clot is formed and firmly attached. It protects the resulting cavity with exposed bone and nerve endings from infection by bacteria and food.
The natural “plug” may come off in the following cases:
- sticking to a cotton swab (placed after surgery) if held for too long;
- licking the hole with the tongue;
- using a drinking straw;
- newly opened bleeding.
If the blood clot falls out, a new surgical intervention will be required. Otherwise, an inflammatory process will occur, which can lead to complications.
It is not recommended to get tired on the day of surgery. After the procedure, you need to go home and rest. You can eat after 3 - 4 hours. Food should be at a comfortable temperature, soft or liquid. Spicy, rough foods that injure soft tissues should be excluded. You should not smoke, as nicotine constricts blood vessels and interferes with healing.
You can rinse your mouth on the second day. As an antiseptic, pharmaceutical preparations, decoctions of medicinal plants, and an aqueous solution with salt and soda are used. Medicines will prevent the development of infection and speed up wound healing. Rinsing should be gentle and not intense, otherwise the blood clot will come off.
When brushing teeth, the surgical site is bypassed. You should use a toothbrush with soft bristles.
Until the wound heals, you should not overheat the body or exert physical stress. Otherwise, bleeding may resume.
Pregnancy and wisdom teeth - how to recognize the process of active growth
The symptoms that occur in pregnant women when the bone tissue above the figure eight “gives way” often differ from the classic picture. First, the woman notes that she began to get tired faster. Her performance decreases and her body temperature rises. In this case, the condition of the gums in the first days of symptoms may not change in any way.
Only after a few days (and sometimes weeks) it becomes clear that all the ailments are associated with teething. Signs characteristic of the situation are:
- pain when feeling the inflamed gum;
- acquisition of a red-blue hue by the mucous membranes located in the eruption zone;
- involuntary cheek twitching;
- enlarged and painful lymph nodes;
- the appearance of bad breath (it is not possible to get rid of it using standard hygiene products);
- hoarseness of voice;
- discomfort or throbbing pain in the ear on the causative side;
- painful sensations when chewing food, swallowing saliva, liquids.
If the first symptoms of the eruption of “eights” appear, it is important for the pregnant woman to calm down and not panic. It is quite possible that the emergence of new units will not be associated with any problems. But if the pain becomes severe, you should definitely get a dental consultation.
My wisdom tooth hurts, what should I do?
According to statistics, it is wisdom teeth that most often cause problems.
Erupted “eights” are quickly affected by caries, and sometimes even remain in the bone tissue and in most cases cause discomfort. So what to do with a wisdom tooth when it hurts, haunting you day and night?
What is known about wisdom teeth?
They got their name because they begin to erupt between the ages of 18 and 30. Scientists consider them to be a vestigial organ that does not bear any functional load when chewing food for years. Therefore, at present, some people do not develop “eights” at all.
Their medical name is third molars. These teeth were originally designed for chewing rough food. This determines their specific structure (large root base, width) and strength.
But this is also the main root cause of painful processes during growth, because the larger the area of the upper edge, the more difficult it is to tear the soft tissues and pass through them. Moreover, the bone tissue has already been formed, so the “eights” need to literally break their way, which leads to the formation of edema, suppuration, tumors and other unpleasant consequences.
Typically, discomfort is caused by recumbent “eights”, which grow horizontally in the jaw. They don't have enough space to erupt and put pressure on neighboring teeth. As a result, the entire dentition shifts. Moreover, recumbent “eights” severely injure the gums, which leads to chronic inflammation.
Signs of wisdom teeth erupting
- Pain in the jaw, radiating to the ears and temples
- Inflammation, swelling and itching of the gums behind the last tooth
- Enlarged lymph nodes
- Temperature increase
- Painful swallowing
- Persistent runny nose
- Difficulty opening your mouth
- Halitosis, that is, bad breath.
The presence and nature of symptoms depends on the individual characteristics of the body. There are cases when a person does not experience discomfort or pain at all when teething: this means that the “eight” is growing correctly and does not interfere with neighboring teeth. But it is still necessary to visit the dentist, since the formation of pathology can occur in a hidden form.
What types of wisdom teeth are there? For “eights” that have difficulty erupting, there are special terms in dentistry - “dystopic” and “retained”.
Dystopic teeth are those that grow incorrectly due to lack of space in the jaw. Usually they are shifted towards the tongue, cheeks or located at an angle. Impacted teeth are unerupted teeth that remain completely in the bone. There may also be a state of semi-retention, when the tooth appears, but cannot fully erupt.
Why do wisdom teeth hurt and gums become inflamed?
Most often, pain occurs due to difficult eruption for several reasons.
- Dystopia. This is a situation where the figure eight grows incorrectly relative to the jaw due to lack of space. Trauma to the buccal mucosa, as well as the development of various bite deformities, can be the consequences of a dystopic tooth if it is not removed in time.
- Retention. This is a pathology in which the wisdom tooth erupts with a delay. In this case, the crown of the tooth can be partially cut through or completely hidden under the gum. Late eruption of the figure eight can negatively affect the patient’s general well-being.
- Pericoronitis. This is an inflammation of the gums that occurs when tooth eruption is difficult or incomplete. The reason for this is the development of infection under the hood of the wisdom tooth - this is the part of the mucous membrane that covers the tooth during eruption. The main symptoms of pericoronatitis are pain, swelling and redness of the gums.
- Caries and its complications (pulpitis, periodontitis). It is quite difficult to qualitatively remove plaque from the surface of a wisdom tooth, since the “figure eight” is located far away. As a result, caries occurs. Progressing over time, it can destroy the tooth quite severely and cause pain.
What to do if your wisdom tooth hurts?
The first and most important rule is to make an appointment with a doctor! Only a doctor can assess the severity of the situation. After the examination, you will be given an x-ray and given options for solving the problem.
If a tooth erupts and your gums hurt, what should you do?
If this pain is periodic and rather discomforting, then you can massage the gums, treat them locally with antiseptics and anesthetic gels (they will be mentioned below). As a rule, this is enough to relieve discomfort before visiting a doctor.
But sometimes a gum hood forms; the gums become swollen, inflamed, and the pain becomes more severe. What to do at home:
- sign up for an appointment with the doctor
- take an anti-inflammatory pain reliever - for example Nimesil or Nurofen.
- Take frequent baths with warm soda or saline solution
- rinse your mouth with a decoction of chamomile, calendula or sage
- treat with chlorhexidine 0.05% or miramistin
- Apply ointment "Cholisal", "Rapid" or "Asepta"
It is important, do not neglect hygiene; carefully use a brush and irrigator to thoroughly clean the surfaces of adjacent teeth. The more plaque accumulates (i.e. a breeding ground for microorganisms), the greater the inflammation.
Treatment for inflammation of a wisdom tooth
Between the chewing surface of the tooth and the hood, favorable conditions are created for the proliferation of pathogenic bacteria and the gums become inflamed. For minor inflammation, as first aid, you can rinse your mouth with an antiseptic and apply bandages with anti-inflammatory gel. These measures must be combined with taking anti-inflammatory and painkillers, but under the supervision of a doctor.
With significant inflammation, symptoms such as discharge of pus, severe swelling of the gums and cheeks, pain when swallowing, and fever are observed. In this case, you should immediately consult a doctor to avoid complications. Treatment is carried out by a dental surgeon. It consists of excision (incision) of the hood under local anesthesia and medicinal treatment of surrounding tissues. As a result, the suppuration goes away. Afterwards, antiseptic rinses and anti-inflammatory gels are also prescribed, and antibacterial therapy may be prescribed.
However, most often “wisdom” teeth are removed, because scientists have already determined that they are a rudiment that does not help us chew food, but much more often creates problems.
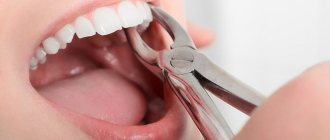
Wisdom tooth removal
This is a very common procedure.
Most often, the operation takes place on an outpatient basis under local anesthesia. It is possible to perform removal under oxygen sedation with nitrous oxide to reduce anxiety or under medicated sleep conditions.
Before the removal procedure, a thorough diagnosis is carried out, and, if necessary, antibacterial therapy is prescribed.
The removal itself is painless, as it is carried out using painkillers. But in the process, soft tissues are injured, so after the removal of the wisdom tooth and the cessation of anesthesia, the patient experiences pain. After a few days, the swelling finally subsides and the pain subsides.
This is also facilitated by the prescription of antimicrobial drugs. After removal, the doctor gives recommendations on nutrition, lifestyle and hygiene for several weeks. Compliance with all medical recommendations will help to avoid the development of complications and speed up the recovery process.
If your wisdom tooth hurts during pregnancy or while breastfeeding, what should you do?
You should contact your dentist at the first discomfort. At home, while waiting for a visit to the doctor, you can resort to safe local measures:
- Take frequent baths with warm soda or saline solution
- rinse your mouth with a decoction of chamomile, calendula or sage
The remaining medications will be prescribed by the doctor after consultation and examination.
In most cases, it is possible to solve the problem using gentle therapeutic methods and avoid urgent wisdom tooth removal during pregnancy.
If possible, the surgical procedure is postponed to a later time. Its implementation is undesirable due to possible side effects (stress, fever, painful rehabilitation).
But the dentist always focuses on the condition of the teeth in a particular case. He will try to save the tooth and delay the surgical procedure if possible. However, in case of severe inflammation, for example during a purulent inflammatory process, removal will be carried out urgently, since this contributes to the spread of infection throughout the body.
The source of infection poses risks much higher than when using medications during removal. Therefore, it is very important to solve the problem in order to avoid complications for the mother and her baby.
When breastfeeding a baby, the mother must carefully monitor her own health. If there is an infection, it can be passed on to the child, since communication with him is very close.
In addition, a bad tooth causes stress and is physically exhausting, and this can have a bad effect on the quality and quantity of milk.
If your wisdom tooth hurts during breastfeeding, the first thing you should do is visit a dentist.
As with pregnancy, the need for extraction is determined only by a doctor after a thorough diagnosis. X-ray examinations can be safely performed during breastfeeding.
If it is possible to postpone the date of the operation, then extirpation is carried out closer to the end of breastfeeding, since after the procedure you may need drugs that can penetrate into mother's milk. However, if the situation is serious and requires emergency intervention, the doctor will decide to remove it.
The procedure for a woman during lactation is no different from that performed for ordinary patients.
For local anesthesia, drugs approved for pregnancy and lactation are used. They do not contain toxic components that can cause allergies and other side effects. The issue of feeding a child should be discussed with a doctor. Local anesthetics practically do not enter the blood, and components penetrate into mother's milk in minimal quantities.
If the doctor has not prescribed other medications, then you can feed the baby within a few hours. But if antibiotic therapy is necessary after a complex removal, then breastfeeding will have to be stopped for several days.
Anesthesia is used only in extreme cases, if a complex and lengthy extraction is being performed. If general anesthesia is necessary, the child is temporarily transferred to artificial nutrition. During this period, the mother must express milk regularly to ensure milk production continues.
Prevention measures
It is virtually impossible to change the atypical arrangement of 8s. But you can prevent the pain that occurs during eruption through routine removal. In this case, unexpected pain can be avoided, and, as a rule, healing in the absence of inflammation proceeds better and faster.
Particular attention should be paid to a comprehensive examination at the stage of planning a new addition to the family.
Based on x-rays, the doctor will be able to tell how the wisdom tooth will behave during pregnancy. When unfavorable factors are identified, it is easier to remove extra eights in advance.
Since teeth decay faster during pregnancy, it is necessary to carry out proper oral hygiene and undergo a preventive examination by a dentist while carrying a child.
Doctors’ recommendations for healthy teeth are very simple and known to everyone, you just need to follow them:
- brush your teeth twice a day;
- rinse your mouth after every meal
- use dental floss;
- eat well;
- limit consumption of sugary foods
- Get regular check-ups with a dentist
The most effective way to avoid trouble is to monitor the condition of your oral cavity and follow these simple and effective recommendations. Be healthy.
Pericoronitis - a complication
Pericoronitis (pericoronitis) is a condition in which the soft tissues surrounding an erupting tooth become severely inflamed. Very often, this diagnosis is made to patients who have begun to see “figure eights” in their mouths. It is characterized by symptoms:
- sore gums;
- swelling;
- specific taste in the mouth.
For pericoronitis, surgery is most often indicated. During this procedure, the doctor excises the “hood” covering the unit to facilitate its eruption. Also, with this complication, there is sometimes a need for removal.
Classification of pathology
Pericoronitis is classified into:
- serous;
- purulent.
The disease always develops from the serous form. This is its initial stage. A large amount of serous fluid accumulates in the mucous tissues. Pain occurs when palpating the affected area.
If a woman does not go to the dentist on time, the serous form turns into a more dangerous one - purulent. Then the swelling becomes even stronger, and the body temperature periodically rises. A “hood” begins to cover the bone tissue, under which there is a large amount of pus.
The purulent form is treated exclusively surgically . After opening the “fistula,” the tissues are washed and the patient is prescribed antibiotics. Considering that such manipulations are extremely undesirable during the period of bearing a child, it is important not to start the disease and consult a doctor at the first sign of it.
When to delete
Of course, it is undesirable to remove a tooth during pregnancy, but there are a number of indications for which surgical intervention is performed even during this period. If the problematic unit is not removed, a purulent infection may develop that can harm the fetus.
Indications for removal:
- an erupting tooth causes damage to nearby units;
- constant pain that does not subside even after taking analgesics;
- cyst formation;
- spread of the inflammatory process to the facial nerve;
- inability to save a molar due to its severe destruction or advanced caries process.
In such cases, the tooth must be removed even during pregnancy. However, it is better to refrain from surgical intervention in the first two months of gestation, as well as in the last ninth month.
What can an expectant mother do on her own?
Pregnant women should not self-medicate. But, if the eruption of wisdom teeth proceeds according to the classic scenario and does not cause negative symptoms, the woman can calm down. In this case, she does not need to run to the dentist.
To eliminate the occurrence of unpleasant sensations associated with putting pressure on the inflamed gum, you must try to chew food on the “healthy side”. After eating, be sure to rinse your mouth with warm water or a decoction of herbs. It is also permissible to purchase a special pharmacy rinse for this purpose.
If the pain intensifies, medical consultation is indicated. If for some reason it is impossible to get it right now, the expectant mother can take a no-shpa tablet to reduce the pain. But this should be a one-time “action”.
What does it mean about abnormal growth of a distant molar?
The symptoms of tooth eruption are very different from the pain caused by the carious process. Teething is preceded by general malaise and weakness. The process itself may be accompanied by:
- feeling of pressure on the gums;
- pain radiating to the ear and temple;
- headache;
- sharp pain when pressing on the inflamed area;
- redness and swelling of the gums in the area of the erupting unit;
- increased body temperature;
- enlarged cervical and submandibular lymph nodes;
- increased pain when swallowing.
At the first symptoms, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Removal
As practice shows, only in 5% of cases pregnant women have to pull out the “eight”. In other situations, it is possible to do without deletion. Extraction is permissible only if there are strict indications, including:
- inability to relieve severe pain using available painkillers;
- frequent recurrence of pericoronitis;
- the formation of an abscess affecting the facial nerve;
- destruction and suppuration of bone tissue;
- the formation of a hollow tumor on the bone in the figure eight area.
In all these cases, the woman is scheduled for dental surgery. Anesthesia is selected taking into account the duration of pregnancy and existing concomitant diseases. However, earlier than in the second trimester, extraction is contraindicated.
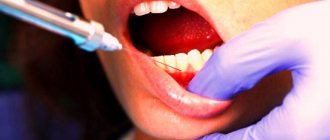
Tooth extraction during pregnancy: anesthesia and medications
Anesthesia is required for surgery. General anesthesia is not acceptable. Anesthesia with lidocaine and similar anesthetics with adrenaline is also not carried out for pregnant women. The drugs can cause cramps, muscle weakness, severe allergic reactions, and lower blood pressure.
Modern painkillers contain a minimum of adrenaline and do not contain vasoconstrictor components that cause uterine hypertonicity. When applied topically, they are practically not absorbed into the blood, therefore they are safe for the fetus.
Among the acceptable medications, the safest ones can be identified:
- Ultracaine;
- Alfacaine;
- Artifrin;
- Primacaine;
- Ubistezin.
During forced surgery, you do not have to endure pain, as happened several decades ago. Today, extraction is done absolutely painlessly.
If gum tissue is cut during surgery, antibiotic therapy is necessary. Pregnant women are usually prescribed Amoxiclav, which has an antibacterial and bactericidal effect. To reduce fever, a minimum dosage of Paracetamol may be prescribed.
Chlorhexidine, Miramistin, Romazulan - safe antiseptics - are used for mouth rinsing.
What you should never do
A pregnant woman is strictly prohibited from doing the following things, as they can lead to malformations of the fetus:
- Take analgesics without a doctor's prescription. All drugs of this pharmacological group have many side effects.
- Apply painkillers to the inflamed gum. Such advice is available on the Internet, but you cannot follow it. Such compresses increase inflammation and create conditions for the formation of ulcers. In addition, the active compounds of the medications used will be absorbed into the systemic bloodstream and negatively affect the health of the fetus.
- Warm the affected area. Heat increases local blood circulation and helps the purulent tumor grow faster.
Self-medication during pregnancy is unacceptable. This is important for all women in an “interesting” position to understand.
Where does the figure eight grow?
It is called so because of its late eruption. If a child’s first milk teeth appear at the age of one, and molars appear before the age of twelve, then at what age do wisdom teeth grow? They will appear when the jaw bone tissue is fully formed. This period occurs between 16 and 27 years of a person’s life. In 3% of people they may appear after many years, and in 8% they do not appear at all. These are four chewing eights on the jaw - third molars, which normally are no different from the rest. Every person has rudiments, but not everyone has them.
The process is not associated with pathology; rather, the problem is that the eighth painters are considered a rudiment that does not carry a functional load.
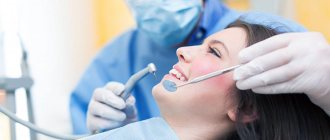
Competent treatment
Doctors can offer pregnant women only three options for eliminating inflammation during the eruption of wisdom teeth:
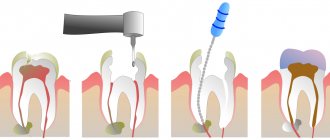
- Excision of the hood. The operation is simple and is performed under local anesthesia. The doctor makes a small incision, which reduces the likelihood of an abscess forming and speeds up the process of the “figure eight” appearance.
- Excision of the upper tissues of the mucous membrane. It is carried out if the doctor sees an abnormal bone structure in the image. The altered structures are then removed to save the tooth.
- Ripping out. It is used rarely and only if previous methods have proven ineffective. If extraction is unavoidable, it should be postponed until the threat to the health of the fetus is minimal.
Is it necessary to remove a tooth?
Only a dentist can prescribe the correct treatment. Removal is recommended in difficult situations to prevent complications. If it is possible to do without surgery, it is not planned. When selecting a treatment method, the doctor takes into account the patient’s condition. Wisdom tooth removal is justified if:
- The process of growth causes unbearable pain;
- The inflammatory process in the gum tissue progresses;
- A cyst or granuloma has formed on the top of the tooth;
- Purulent exudate is released;
The operations are performed under anesthesia. Local anesthetics approved during pregnancy are used. Please note that the source of infection in the body is much more dangerous than anesthetic drugs. Therefore, it is necessary to cure or remove the figure eight in order to prevent serious complications in the fetus and the woman in labor.
It is better to operate within 13 – 32 weeks. It is contraindicated to carry out procedures later or earlier. Anesthetics used are those that do not penetrate into the placenta, in particular, ultracaine, primacaine. The correct dosage is extremely important. It is calculated depending on the age, general condition of the woman in labor, and the duration of pregnancy.
In addition to removal, dissection of the hood is practiced, when a minimal incision of the mucous membrane is made over the bone tissue. This prevents the accumulation of pus and speeds up the advancement of the unit. If the bone tissue structure is normal, excision may be recommended, when the upper section of the mucosa covering the site where the rudiment is cut is completely removed. This allows you to do without pulling out the figure eight.
Rehabilitation after surgery
If a woman was unable to avoid surgical treatment, she needs to pay maximum attention to the rehabilitation process. Recovery will be faster if the expectant mother:
- will follow all medical prescriptions;
- will provide complete rest to the damaged area (it should not be touched with hands, tongue, or foreign objects);
- will not eat solid foods;
- will carry out high-quality oral hygiene;
- He will come for a follow-up appointment when the dental surgeon says so.
Take care of the health of your smile. If you are planning to conceive, treat any existing oral diseases in advance. If the problem arose after conception, be sure to get dental care - do not risk your health and the health of your baby.
Possible risks that may develop after teeth extraction for pregnant women
This procedure is classified as a surgical intervention; all possible complications must be taken into account:
- acute allergic reaction to anesthesia;
- fainting;
- bleeding;
- injury to the bone tissue of an adjacent tooth or gums;
- neuritis;
- alveolitis and other pathological conditions, inflammatory processes.
One of the negative consequences that obstetricians-gynecologists fear may be the occurrence of uterine hypertonicity. Simply put, these are muscle contractions, spasms, which are very similar in nature to contractions. In the early stages they can cause miscarriage, in the later stages they can cause premature birth.
Prevention methods
- Every six months it is necessary to make an appointment at the dental clinic, especially before planning to conceive.
- Balance your diet to eliminate possible deficiencies of calcium and other microelements.
- Walk in the sun more, it helps to get vitamin D, which is necessary for the absorption of calcium.
- The advice is not very relevant for pregnant women, but: get rid of bad habits. Smoking causes tooth decay.
- Clean your mouth twice a day with a brush and paste, and after each meal with a mouthwash.
In the article, we told you at what week of pregnancy you can have teeth removed, how this will affect the fetus and the health of the expectant mother. And for quality dental services, make an appointment at Dentika.
What happens if you delay removal?
Sometimes the tooth does not have to be pulled out; it is treated. Proper sanitation of the oral cavity is less painful and dangerous for both the woman and the baby. Therefore, doctors try to use all available therapeutic agents so as not to resort to extraction. Even very deep carious lesions can be cleaned and the cavity sealed in order to “hold out” until childbirth.
But, as we said, there are indications in which it is strictly forbidden to delay the operation. Because in some cases there may be a serious infection of the tissues, bacteria enter the bloodstream, and pain causes muscle spasms, including the uterus.
We recommend that you act in accordance with your dentist's opinion.