Fissure caries is a lesion of the hard tissues of the tooth, localized in the natural recesses of the chewing group of teeth. The risk group includes children with temporary dentition, people with poor hygiene, as well as those with teeth with complex fissure anatomy. Unfortunately, patients often do not notice the pathology and do not consult a doctor. This leads to an aggravation of the process and possible complications (pulpitis, periodontitis, tooth loss). It is important to identify the process in a timely manner, identify it and begin treatment immediately.
Make an appointment with a therapist by phone+7(985)532-21-01
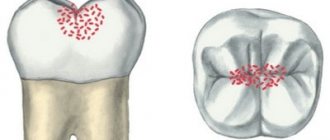
What is fissure caries?
Fissures - this professional term refers to the natural pits and grooves that exist on the surfaces of chewing teeth. In these recesses, food debris clogs and accumulates, and therefore the fissures of the chewing teeth are vulnerable to caries. Therefore, it is so important to thoroughly brush your teeth and clean the fissures of your chewing teeth from plaque and food debris.
Fissure caries is clearly visible on the surface of the tooth, but only if the tooth has open fissures, that is, those natural depressions, the bottom of which is completely visible visually. But chewing teeth also have closed fissures: the structure of this type of fissure is very similar to the structure of a bottle. In closed fissures, only the upper narrow groove is clearly visible upon examination, but in depth it expands and forms a cavity. Diagnosing caries with closed fissures is a difficult task and, of course, you won’t find such caries on your own; you will definitely need to visit a doctor’s office.
In order to prevent fissure caries and begin its treatment in a timely manner, you need to undergo regular preventive examinations at the dentist’s office. Our VENSTOM dental clinic in Moscow uses the most modern diagnostic equipment and techniques to detect and treat caries on time!
Calculate the cost of treatment by taking a short test in 20 seconds!
Do not delay your treatment, because in this matter time plays against us.
Fissurotomy
The difference between fissurotomy and the previous method is that before sealing, the condition of the fissure is diagnosed using a sharp probe, during which narrow, deep grooves and fissures are opened or widened. In order to detect caries in dental tissue, laser diagnostics and the vital staining method are also used.
In order to expose suspicious fissures, a diamond or carbide bur is used. If during the preventive removal of the fissure enamel layer no signs of caries are detected, sealing is carried out using low-viscosity composite materials or glass ionomer cements.
Why does fissure caries occur?
Fissure caries occurs for only one reason - poor dental and oral hygiene. If after eating you do not brush your teeth, do not rinse your mouth and perform dental hygiene less than 2 times a day, fissure caries will not keep you waiting, because plaque and food debris quickly accumulate in the pits and depressions on the surfaces of the chewing teeth. This environment is extremely favorable for the development of carious bacteria.
Bacteria will multiply, their vital activity will lead to weakening of the tooth enamel and when it becomes thinner to a certain extent, fissure caries will begin.
Signs of a wedge-shaped tooth defect:
- Formation in the cervical region of a characteristic V-shaped ledge with a shiny smooth surface;
- Gradual pigmentation of the resulting defect - the affected areas acquire a yellowish-brownish color;
- It is possible to develop hyperesthesia with a pain reaction to temperature and other stimuli;
- With deep defects, hygiene procedures (cleaning, rinsing the mouth) cause pain;
- The crown part of the tooth becomes brittle; with a sharp simultaneous load, there is a high risk of tooth fracture.
When diagnosing, the doctor analyzes the location of the grooves, their shape, the shade of the teeth, and the density of the enamel. The depression with a wedge-shaped defect has a hard bottom, smooth walls and smooth edges, unlike a carious cavity.
Signs of fissure caries
By what signs can you recognize the development of fissure caries? Fissure caries has the same symptoms as other forms of the disease:
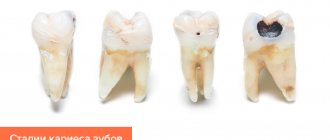
1. With fissure caries in the staining stage on the chewing surfaces of the teeth, you can see a change in the shade of the enamel - it becomes whitish. Apart from whitish spots, fissure caries does not show itself in anything at this stage of development - the tooth does not hurt.
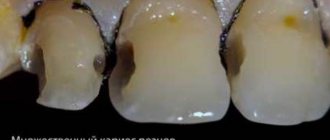
2. With superficial fissure caries, the spots become larger and darker, acquiring a distinct contour. Tooth sensitivity to hot/cold, sour/sweet foods may occur.
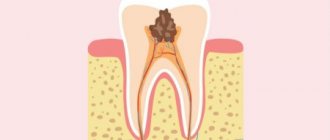
3. Average fissure caries already affects the dentin, so the destruction of the tooth will be clearly visible - a cavity will appear on the surface of the crown, which is popularly called simply “a hole in the tooth.” Unpleasant sensations may occur when eating, but usually they pass quickly - you just have to stop chewing on the affected tooth and rinse your mouth well.
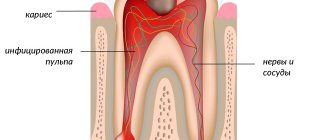
If fissure caries is not treated, it will turn from medium to deep and the destructive process will reach the pulp (nerve) of the tooth. If the infection penetrates into the pulp, the dentist will no longer have to treat fissure caries, but its complication - pulpitis.
Any person can notice rare and deep fissure caries on their teeth during dental hygiene, but the diagnosis of fissure caries in the spot stage and fissure superficial caries requires a visit to the doctor’s office. Small specks of demineralized enamel may not be noticed under plaque, which is actively accumulating in the fissures, and even more so it will be impossible to independently detect caries if the fissures are closed.
Wedge-shaped defect - what is it?
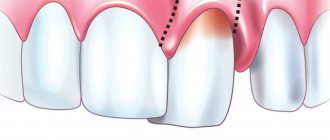
This term refers to the loss of dental tissue in the cervical region, and the defect resembles a triangle (wedge) in shape.
A wedge-shaped dental defect differs from ordinary caries not only in external signs, but also in the characteristics of its occurrence and course. A V-shaped lesion of hard tissues is detected precisely in the area of the tooth neck - the most vulnerable place from an anatomical point of view. As the wedge-shaped defect increases in the periodontium, destructive phenomena develop, against the background of which tissue atrophy and gradual lowering of the marginal gum occur.
Causes of pathology
Due to their occurrence, there are several types of wedge-shaped defects:
- Abfraction type (from the English abfraction - microdamage). Such defects arise due to local stresses in the cervical region, which are caused by improper distribution of chewing pressure. A similar problem is often found in patients with malocclusions and people with bruxism. During the contact of the upper and lower dentition, individual teeth experience an atypical load. The cutting edge, equator zone, chewing surfaces cope with excess bending stress, and the neck area, due to its smaller thickness and mineralization, begins to collapse. The enamel gradually changes its structure, becoming weaker and losing its upper layers.
- Abrasive in nature. Tissue deficiency occurs due to their accelerated abrasion under the influence of aggressive factors. Highly abrasive pastes, very hard toothbrushes, long brushing of teeth, and folk remedies for lightening enamel at home (soda, salt) have a negative impact. Abrasives not only contribute to the destruction of vulnerable areas of the teeth, but also injure the soft tissues of the oral cavity.
- Erosive type. The main role in the formation of defects here belongs to chemical agents, especially acids, which are found in carbonated drinks, fizzy candies, fruits and berries, wine and juice. Acids interact with calcium ions, without which the enamel crystal lattice loses stability. The upper layers become porous and more susceptible to external factors. As a result, hard tissues are destroyed. Defects of an erosive nature are typical for representatives of the chemical industry who are faced with the deposition of chemical compounds in the oral cavity.
Predisposing factors for wedge-shaped defects are periodontal diseases, peptic ulcers of the stomach and duodenum, increased stomach acidity, psychoneuroses, and irregular oral hygiene.
Symptoms of a wedge-shaped defect
The disease most often affects canines and premolars. Typically, wedge-shaped defects are detected on several teeth; a single lesion is rare in clinical practice.
Diagnosis of fissure caries: basic and auxiliary methods
The main diagnosis of fissure caries will consist of visual inspection and probing. If caries has affected the fissures, they will noticeably darken, the tissue in them will soften and the probe that the dentist uses during the examination will get caught on them. But if the caries is still in the staining stage or the tooth has deep and narrow fissures, additional diagnostic measures can be carried out:
- X-ray of a tooth. A fairly effective diagnostic method that allows you to detect fissure caries at the earliest stages of development, since carious lesions will be clearly visible on the pictures;
- Fissurotomy. A specific study that helps to see how deep the carious damage has gone in the tooth. Fissurotomy is carried out as follows: using a drill, the doctor opens the fissures to a small depth (up to 1 mm) and looks at how much caries has managed to destroy the tooth.
Diagnosis of fissure caries can be carried out using a laser. This is the most modern and effective method for diagnosing caries at any stage of its development: the laser is reflected differently from healthy and diseased tooth tissues. The difference in the reflections of the laser beam is noted by the device, which immediately sounds a sound signal. But laser diagnostics of fissure caries is carried out only in those clinics that have the appropriate equipment.
Symptoms of fissure caries
Fissure caries is difficult to detect at an early stage, since at first it is asymptomatic. It is usually discovered during a routine examination. Subjective symptoms that begin to bother a person appear only as the pathology progresses. Let us describe the stages of development of caries in the fissure area:
- Initial. An area of demineralization appears in the fissures, resembling a white spot in appearance. It is often localized in the center of the crown. Apart from a visual defect, which is difficult to detect on your own, no symptoms are observed.
- Superficial. The carious lesion penetrates deeper into the enamel and increases demineralization. He has not yet reached the internal hard tissues of the tooth. A painful reaction to sweet foods appears. Immediately after eliminating the irritant, the pain goes away.
- Average. A carious cavity forms, bacteria penetrate the dentin and begin to destroy it. A person complains of acute pain when chewing food, sudden temperature changes and brushing teeth. The discomfort disappears as soon as the irritating factor is eliminated.
- Deep. The last stage of caries is accompanied by acute pain from hot drinks, food, cold air, a toothbrush, etc. Aching and shooting pain is possible, especially at night. There is a risk of the caries process transferring to the soft tissues inside the tooth. Pulpitis or periodontitis may occur.
During the diagnosis, the doctor must determine the stage of caries and the extent of its spread. These data make it possible to determine how the pathology should be treated - with therapy or filling.
How will fissure caries be treated?
After diagnosing and diagnosing “fissure caries,” a method of treating it is selected. Since patients usually come to dentists with moderate fissure caries, below we will describe all stages of its treatment.
1. Pain relief. When treating medium fissure caries, the doctor will need to remove all affected and destroyed tissue with a drill. This can be unpleasant for the patient, so local anesthesia is given before treatment begins.
2. After the anesthetic has taken effect, a rubber dam, a special latex overlay, is installed on the area where fissure caries is treated. The rubber dam reliably isolates the area of treatment from saliva and moisture from the oral cavity, which may contain bacteria. In addition, careful isolation of the tooth from moisture is important for high-quality filling. If moisture gets into the cavity at the time of placing the filling, the adhesion between the filling materials and the natural tissues of the tooth will deteriorate and this can lead to the filling falling out.
3. After installing the rubber dam, the dentist will begin working on the tooth. When treating fissure caries, it is extremely important to remove all destroyed and damaged tissue. If this is not done, caries will continue to develop directly under the filling.
4. By removing tissue damaged by fissure caries, the dentist will form a cavity in the tooth for installation of a filling. This cavity is treated with a special etching solution that cleans the tissue, and then an adhesive composition is placed into it.
5. The dentist will restore >the crown of the tooth
The process of treating fissure caries is completed by grinding and polishing the installed filling.
If a tooth is severely damaged by fissure caries, then it is better to restore it not with a filling, but with a special restorative inlay, which can be made of different materials: gold, ordinary metal, ceramics.
Inlays are fixed in the tooth using special cement and differ from fillings in having a longer useful life, and in addition, in reduced risks of developing secondary fissure caries. In addition, fillings even made from the highest quality composites darken over time, but ceramic inlays retain their aesthetic appearance throughout their entire service life. Of course, restoring a tooth with an inlay after treating fissure caries will cost more, but the high cost will be justified by the durability and reliability of the restoration.
Why is cervical caries dangerous?
Develops faster. Due to the small thickness of the enamel, the affected area quickly darkens and begins to collapse. If plaque and tartar accumulate in the root part of the crowns, it is better to contact the dentist as soon as possible - caries can form in just a few weeks.
Leads to tooth loss. Without treatment, the tooth is destroyed at the base, becomes brittle, and can break even under light load. Such fractures may extend below the gum line, in which case the tooth will have to be removed.
Source of infection in the mouth. It can provoke caries on other teeth, increase the risk of problems with the gastrointestinal tract, cardiovascular, respiratory, immune systems, etc.
Gum diseases. With cervical caries, the affected area is located at the edge of the gum or goes under it. This provokes the proliferation of bacteria in the periodontal pocket, inflammation, the appearance of gingivitis and other gum diseases.
Is it possible to cure fissure caries without drilling the tooth?
Fissure caries can be cured without drilling a tooth, but to do this you need to regularly visit the dentist’s office and undergo preventive examinations. If fissure caries is detected at the spot stage, it is treated without drilling the tooth, through remineralization or Icon technology.
From here we can draw a simple conclusion - if you want to treat your teeth without pain and drilling with a drill, you need to pay close attention to the prevention of caries.
Calculate the cost of treatment by taking a short test in 20 seconds!
Do not delay your treatment, because in this matter time plays against us.
Treatment procedure
The treatment plan is determined by the stage of the lesion:
- if there is only a white spot on the enamel, removing plaque and remineralization is enough. Additionally, periodontal cleaning can be performed;
- if a dark spot has already formed, grinding is performed, the affected tissue is removed, restoration or remotherapy is performed;
- when a cavity is formed, it is processed, the affected tissue is removed, and a filling is performed;
- with a large cavity depth and inflammation, removal of the affected pulp, root canal treatment, and filling may be required.
Treatment of deep cervical caries is complicated by the location of the affected area: blood and saliva enter the treatment area. At the white spot stage, it can be removed without anesthesia. If the enamel has already darkened or begun to deteriorate, the doctor performs anesthesia before starting treatment.
How to prevent fissure caries
The best prevention of fissure caries is regular and high-quality oral hygiene, as well as periodic professional teeth cleaning in the dentist’s office.
If you have deep, closed fissures, fissure sealing can be an effective method of preventing fissure caries. This is a simple event during which the fissures are sealed with a special sealing compound. Fissure sealing is carried out in both children and adult patients and helps to significantly reduce the risk of developing fissure caries.
An excellent method of preventing fissure caries is a course of remineralizing therapy. The essence of the procedure is to treat teeth with special compounds based on fluoride and calcium, which strengthen tooth enamel.
Do you still have questions about the treatment of fissure caries? Ask them in the chat on the website of our dentistry in Moscow - VENSTOM, or even better - come for a consultation with our specialists!
Clinical researches
The active components of the complex help reduce bleeding and inflammation in the oral cavity.
- A unique complex of vitamins, microelements and plant extracts, specially selected to maintain the health of the oral cavity and the body as a whole.
- Coral calcium and coenzyme Q10 in the composition strengthen gums and tooth enamel.
- Vitamins support general immunity.
At the Department of Therapeutic Dentistry of St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I.P. Pavlova, it was proven that the joint use of Asepta dental line products makes it possible to achieve a complex effect. Taking into account the active components that make up these Asepta products, their clinical properties and the effect they have on the soft tissues of periodontium, they can be used both as independent agents in the initial stages of diseases, and in combination with medications for severe forms of chronic periodontal diseases.
Considering the therapeutic and prophylactic properties of the Asepta line, they can be used for inflammatory diseases of the oral mucosa, such as catarrhal stomatitis, glossitis and cheilitis.
Sources:
- The use of new anti-inflammatory drugs in the complex of therapeutic and preventive measures for periodontal diseases (E.D. Kuchumova, A.A. Leontyev, O.V. Kalinina, L.Yu. Orekhova, S.B. Ulitovsky) E.D. Kuchumova, Ph.D., Associate Professor, A.A. Leontyev, dentist, O.V. Kalinina, dentist, L.Yu. Orekhova, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor, Head of Department, S.B. Ulitovsky, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof. Department of Therapeutic Dentistry of St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I.P. Pavlova
- The use of drugs from the Asepta line in the complex treatment of inflammatory periodontal diseases (N.V. Berezina E.N. Silantyeva S.M. Krivonos, Kazan State Medical Academy. Kazan.) N.V. BEREZINA, E.N. SILANTIEVA, S.M. KRIVONOS Kazan State Medical Academy
- The role of anti-inflammatory rinse in the treatment of periodontal diseases (L.Yu. Orekhova, A.A. Leontyev, S.B. Ulitovsky) L.Yu. OREKHOVA, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof., Head of Department; A.A. LEONTIEV, dentist; S.B. ULITOVSKY, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof. Department of Therapeutic Dentistry of St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I. P. Pavlova
Cost of treating a wedge-shaped defect
| Superficial caries | 2 200 ₽ |
| Average caries | 3 800 ₽ |
| Deep caries | 4 600 ₽ |
| Relief of acute pain (anesthesia, medicinal treatment of canals, application of medications, temporary filling) | from 3,100 ₽ |
| Temporary filling | 300 ₽ |
| Treatment of cervical caries | 3 200 ₽ |
Make an appointment
Stages of the disease
There are several stages in the course of a wedge-shaped defect:
- Initial. The depression is almost impossible to see with the naked eye; damage to the enamel can only be diagnosed by a dentist.
- Superficial. The defect is revealed in the form of a superficial groove 2-3 mm long; the tooth can react to external stimuli.
- Average. The notch becomes deeper, its length increases to 4-4.5 mm, the walls of the defect are visually determined, which converge with each other in the form of the letter V.
- Deep. The wedge-shaped defect is clearly visible, the length of which is 5 mm or more. In depth, the lesion reaches the deep layers of dentin, in severe cases it reaches the pulp chamber.
The first two stages are usually diagnosed in young patients. Medium and deep degrees of damage are more typical for mature people who have crossed the 40-45 year mark.
It is noteworthy that during the course of the disease there are 2 phases - rapid and stable. In the fast phase, tissue loss occurs at a high speed (in 2-3 months), and tooth hypersensitivity develops. In the stabilization phase, the development of the disease slows down, hyperesthesia decreases or disappears altogether.